Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (47): 7608-7614.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.47.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparative analyses of histological and material properties of reticular dermis derived from human, swine and rats
Zhang Yong-hu, Song Guo-dong, Zuo Hai-bin, Jia Jun, Ma Yin-dong, Fan Chun-jie, Li Pei-long
- Department of Burn, Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan 250013, Shandong Province, China
-
Revised:2014-10-23Online:2014-11-19Published:2014-11-19 -
Contact:Song Guo-dong, Professor, Department of Burn, Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan 250013, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Yong-hu, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Burn, Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan 250013, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Clinical Specialist Construction Programs of China; Shandong Provincial Technology Development Projects, No. 2013GSF11870; the Medicine and Health Scientific Development Plan of Shandong Province, No. 2011HZ008; Jinan Overseas Students Pioneer Project, No. 20080405
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yong-hu, Song Guo-dong, Zuo Hai-bin, Jia Jun, Ma Yin-dong, Fan Chun-jie, Li Pei-long. Comparative analyses of histological and material properties of reticular dermis derived from human, swine and rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(47): 7608-7614.
share this article
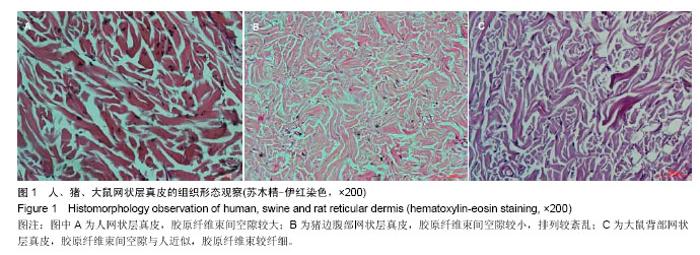
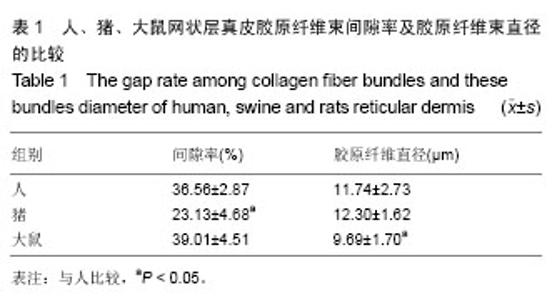
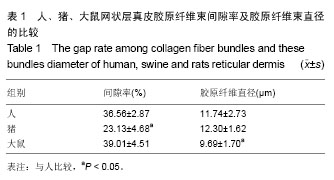
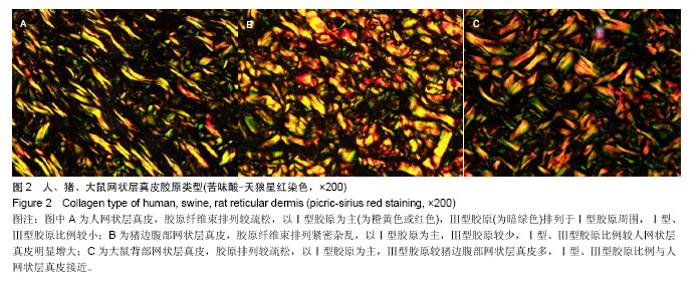
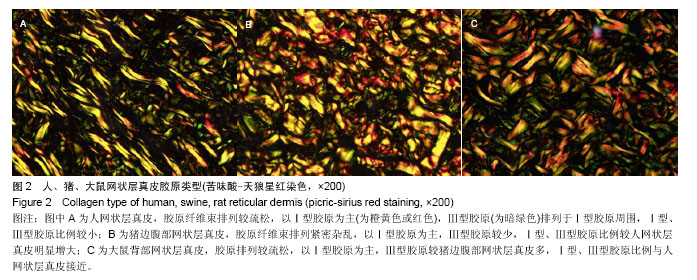
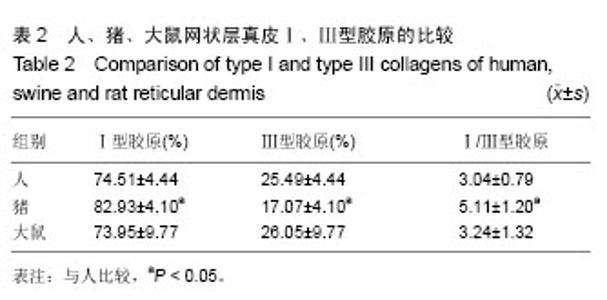
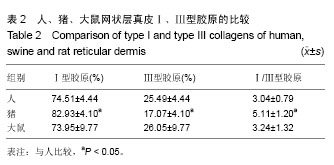
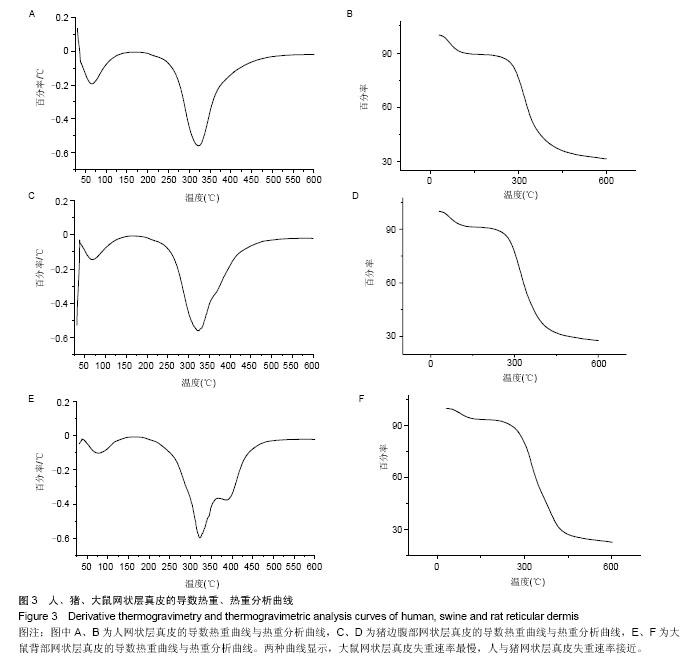
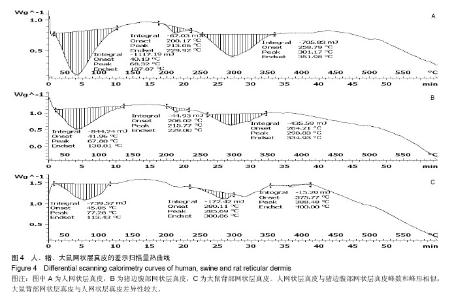
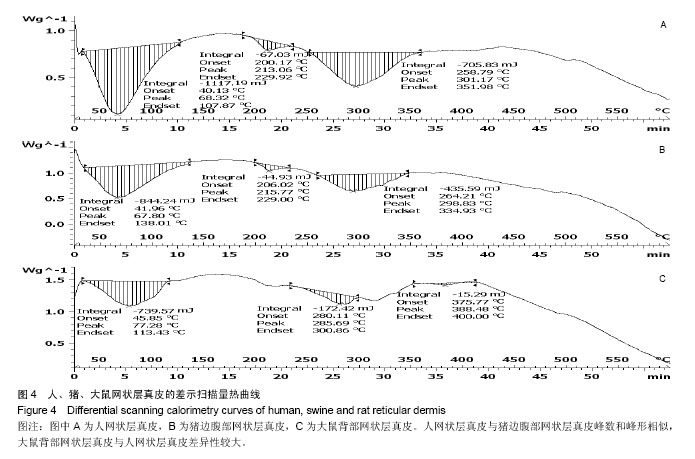
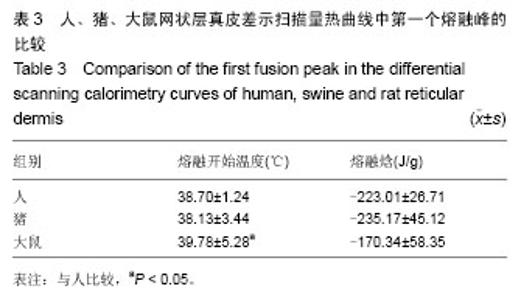
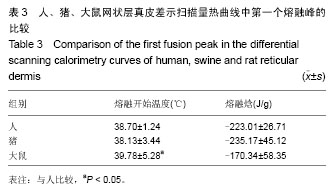
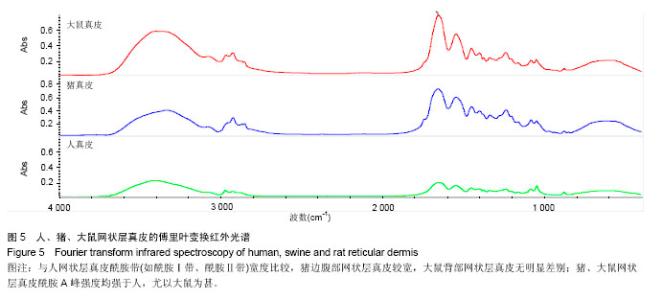
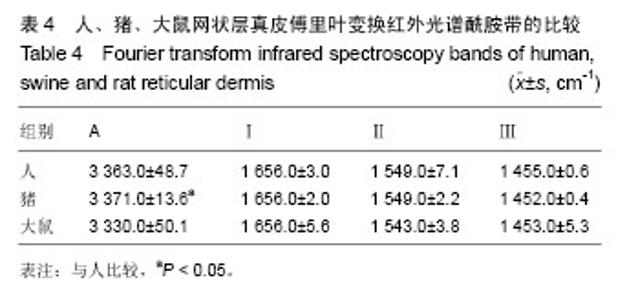
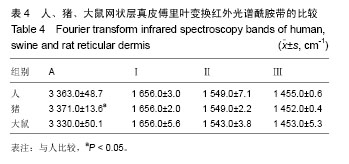
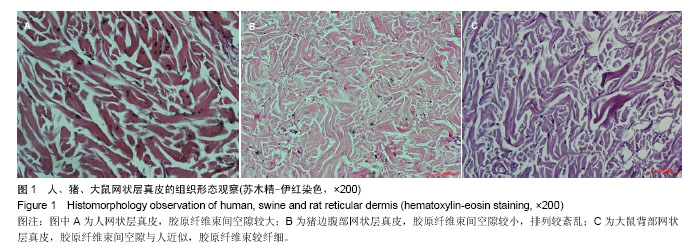
2.1 大体观察 3组标本新鲜时均为乳白色,猪边腹部真皮可见大量毛孔,且较为粗大,质地较人和大鼠稍僵硬,伸展性稍差。大鼠网状层真皮质地较为细腻、柔软,也可见较多毛孔,但较细小。人真皮质地在3组之中居中,毛孔较少,伸展性较大。 2.2 生物力学 3组样品复水效果良好,复水后组织呈乳白色,与真空干燥前质地无明显区别。力学检测结果显示:与人网状层真皮比较,猪边腹部网状层真皮的杨氏模量[(29.79±18.82),(36.58±10.79) MPa,P=0.44]、大鼠背部网状层真皮的杨氏模量[(37.99±16.55),(36.58± 10.79) MPa,P=0.36]差异均无显著性意义。 2.3 苏木精-伊红染色 光镜观察结果:猪真皮胶原纤维较为粗大,排列较紧密,毛细血管较人少见且血管直径较小;大鼠真皮胶原较纤细,排列疏松,毛细血管较猪真皮多,与人真皮近似,见图1。 测量结果:猪胶原纤维束直径与人比较差异无显著性意义[(12.30±1.62),(11.74±2.73) μm,P=0.34]。大鼠胶原纤维束直径与人比较差异有显著性意义[(9.69±1.70),(11.74±2.73) μm,P < 0.05],即大鼠真皮胶原纤维比人真皮胶原纤维细;间隙率测量结果显示,人与猪之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),而人与鼠之间差异无显著性意义,即猪真皮较人排列致密,大鼠与人近似(P=0.17),见表1。"
| [1] 陆树良,青春,刘开英,等.瘢痕形成机制的研究:真皮"模板缺损"学说[J]. 中华烧伤杂志,2007, 23(1): 6-12. [2] Levin F, Turbin RE, Langer PD. Acellular Human Dermal Matrix as a Skin Substitute for Reconstruction of Large Periocular Cutaneous Defects. Ophthal Plast Recons. 2011; 27(1): 44-47. [3] Chang M, Ahn SE, Baek S. The effect and applications of acellular dermal allograft (AlloDerm) in ophthalmic plastic surgery. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42(5): 695-699. [4] Hartzell TL, Taghinia AH, Chang J, et al. The Use of Human Acellular Dermal Matrix for the Correction of Secondary Deformities after Breast Augmentation: Results and Costs. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(5): 1711-1720. [5] Chevallay B, Herbage D.Collagen-based biomaterials as 3D scaffold for cell cultures: applications for tissue engineering and gene therapy. Med Biol Eng Comput.2000;38(2): 211-218. [6] Guo R, Teng J, Xu S, et al. Comparison studies of the in vivo treatment of full-thickness excisional wounds and burns by an artificial bilayer dermal equivalent and J-1 acellular dermal matrix. Wound Repair Regen. 2014;22(3): 390-398. [7] 成令忠,钟翠平,蔡文琴.现代组织学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2003:717-718. [8] David NH.Total Burn Care.Fourth Edition. America: Saunders.2012:497-500. [9] Pozner JN, White JB, Newman MI.Use of porcine acellular dermal matrix in revisionary cosmetic breast augmentation. Aesthet Surg J.2013;33(5): 681-690. [10] Spear SL, Sinkin JC, AL-Attar A. Porcine acellular dermal matrix (strattice) in primary and revision cosmetic breast surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131(5): 1140-1148. [11] Patel KM, Nahabedian MY, Albino F, et al. The use of porcine acellular dermal matrix in a bridge technique for complex abdominal wall reconstruction: an outcome analysis. Am J Surg.2013;205(2): 209-212. [12] 郑必祥,彭代智,左海斌,等.巴马小型猪与人真皮的组织形态学和生物力学基本特征比较研究[J].第三军医大学学报, 2010, 32(8): 754-758. [13] 邵阳,武岩,贾军,等.低免疫原性猪真皮支架制备及其细胞相容性评价[J].中华烧伤杂志,2012,28(5):329-335. [14] Zuo H, Peng D, Zheng B, et al. Regeneration of mature dermis by transplanted particulate acellular dermal matrix in a rat model of skin defect wound.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012; 23(12): 2933-2944. [15] Jimenez ML, Brown TD, Brand RA. The effects of grip proximity on perceived local in vitro tendon strain. J Biomech. 1989;22(8-9): 949-955. [16] Bottino MC, Jose MV, Thomas V, et al. Freeze-dried acellular dermal matrix graft: effects of rehydration on physical, chemical, and mechanical properties.Dent Mater. 2009;25(9): 1109-1115. [17] Chong AK, Riboh J, Smith RL, et al. Flexor tendon tissue engineering: acellularized and reseeded tendon constructs. Plast Reconstr Surg.2009;123(6): 1759-1766. [18] 孙振球,徐勇勇,颜艳,等.医学统计学[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2010:552-559. [19] Jithendra P, Rajam AM, Kalaivani T, et al. Preparation and characterization of aloe vera blended collagen-chitosan composite scaffold for tissue engineering applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2013;5(15): 7291-7298. [20] Matthias Wagner(著).热分型应用基础[M].陆立明译.上海:东华大学出版社,2011:106-127. [21] Sandor M, Xu H,Connor J, et al. Host response to implanted porcine-derived biologic materials in a primate model of abdominal wall repair. Tissue Eng A.2008;14(12): 2021-31. [22] Sionkowska A.Interaction of collagen and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) in blends. Eur Polym J.2003;39(11): 2135-2140. [23] 常建华,董绮功.波谱原理及解析[M].北京:科学出版社, 2005: 63-66,103-106. [24] 邓芹英,刘岚,邓慧敏.波谱分析教程[M].2版.北京:科学出版社, 2007:35-36. [25] Montagna W, Yun J S. The Skin Of the Domestic Pig. J Invest Dermatol. 1964; 42:11-21. [26] Riekki R, Parikka M, Jukkola A, et al. Increased expression of collagen types I and III in human skin as a consequence of radiotherapy. Arch Dermatol Res. 2002;294(4): 178-184. [27] 荣艳华,张国安,王成,等.不同年龄组人正常皮肤Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原含量的比较[J].中华烧伤杂志, 2008, 24(1):51-53. [28] Ramshaw JA, Shah NK, Brodsky B. Gly-X-Y tripeptide frequencies in collagen: a context for host-guest triple-helical peptides. J Struct Biol. 1998;122(1-2): 86-91. [29] Okuyama K. Revisiting the Molecular Structure of Collagen. Connect Tissue Res.2008;49(5): 299-310. [30] Shoulders MD, Kamer KJ, Raines RT. Origin of the stability conferred upon collagen by fluorination. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009;19(14): 3859-3862. [31] Mizuno K,Peyton DH,Hayashi T,et al.Effect of the-Gly-3(S)- hydroxyprolyl-4(R)-hydroxyprolyl- tripeptide unit on the stability of collagen model peptides. FEBS J.2008;275(23): 5830-5840. [32] Shanmugam G, Reddy SM, Natarajan V, et al. 2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol disrupts the triple helical structure and self-association of type I collagen.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013; 54:155-159. [33] Bouligand Y, Denefle JP, Lechaire JP, et al. Twisted architectures in cell-free assembled collagen gels: study of collagen substrates used for cultures. Biol Cell. 1985;54(2): 143-162. [34] Park SH, Song T, Bae TS, et al. Comparative analysis of collagens extracted from different animal sources for application of cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Precis Eng Man.2012;13(11): 2059-2066. |
| [1] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [2] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [3] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [4] | Huang Zhusong, Lin Yu, Chen Xiang, Lan Jinfu, Guan Yong, Gao Xi. Alcohol extract of Morinda officinalis improves lipid metabolism and bone metabolism in ovariectomized obese rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 205-210. |
| [5] | Chen Yutong, Li Chenchen, Liu Yang, Zheng Yaqin, Yang Xihua, An Meiwen. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model in Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 237-241. |
| [6] | Zhang Shengmin, Cao Changhong, Liu Chao. Adipose-derived stem cells integrated with concentrated growth factors prevent bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2982-2987. |
| [7] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| [8] | Jiang Tao, Wu Shuo, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Mayire·Nuermaimaiti, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB promotes the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1976-1981. |
| [9] | Zang Jing, Luan Zuo, Wang Qian, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wu Youjia, Guo Aisong. Two kinds of stem cell nasal transplantation for treating white matter injury in premature rat infants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 101-107. |
| [10] | Wang Jing, Lu Changfeng, Peng Jiang, Zhu Chen, Xu Wenjing, Cheng Xiaoqing, Fang Jie, Zhu Yaqiong, Zhao Yanxu, Jiang Wen, Xu Hongguang, Wang Yu. Establishment and evaluation of traumatic neuroma model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 716-719. |
| [11] | Cao Qingjun, Yang Fenghua, Wang Hua. Hippocampal astrocytes in juvenile rats with persistent epilepsy: the role of cannabinoid receptor type 2 in regulating MAPK pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5179-5185. |
| [12] | Cai Bozhi, Chen Xiancai, Ni Na, Lin Weishen, Yuan Yanping, Lin Changmin, Huang Keng. Wnt5a expression in the regeneration of the inferior segment of rat hair follicle at embryonic and postnatal stages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5018-5022. |
| [13] |
Li Ying, Lin Wentao, Weng Xiquan.
Effects of different exercise intensities on visfatin level and glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4196-4200. |
| [14] | Jiang Tao, Shao Min, Chen Qingzhen, Ling Cuimin, Shen Zhen, Wang Gang, Huo Shaochuan, Lin Yanping, Liu Haiquan, Wang Qinsheng, Zeng Zhenming. Inokosterone effects on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts from neonatal Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3636-3642. |
| [15] | Yuan Guoqiang, Qin Yongsheng, Peng Peng. High-intensity interval training for treating pathological cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats: effects and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3708-3715. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||