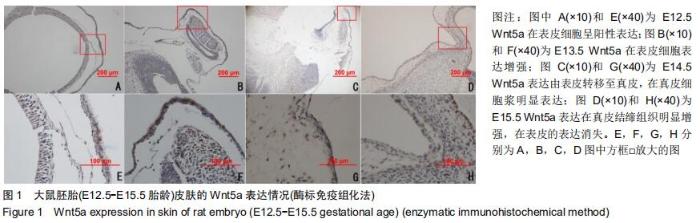
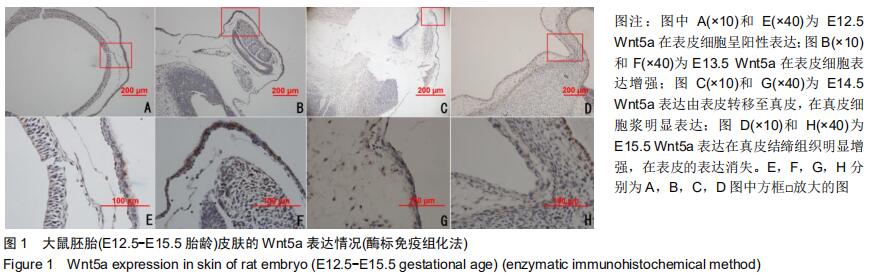
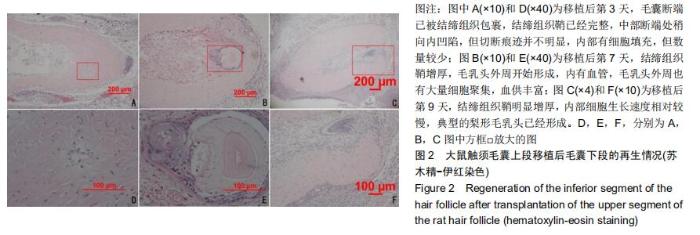
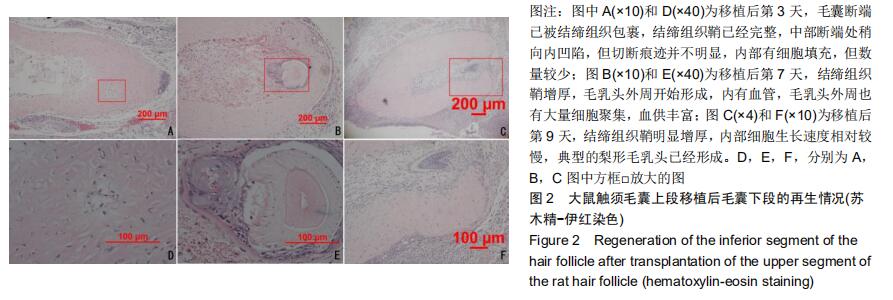
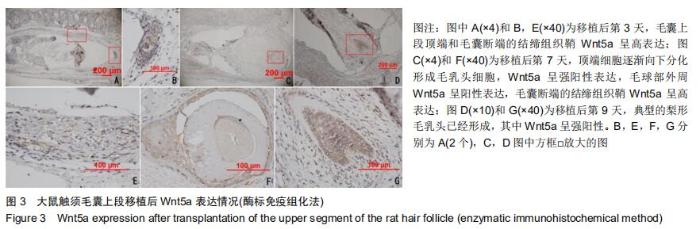
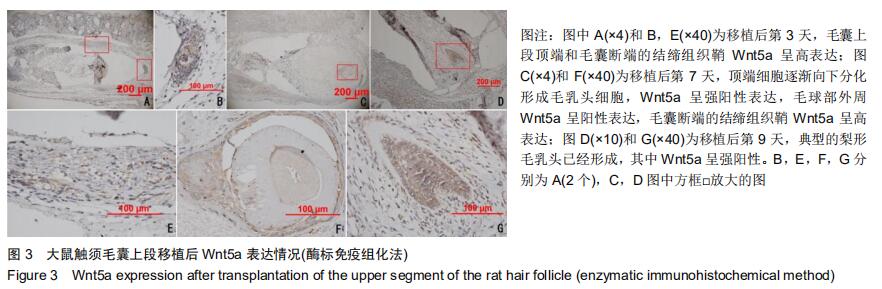
|
[1] COTSARELIS G,YANG CC. Review of hair follicle dermal cells.J Dermatol Sci. 2010;57(1):2-11.
[2] HE L, LEI M, XING Y, et al.Gsdma3 regulates hair follicle differentiation via Wnt5a-mediated non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway.Oncotarget.2017;8(59):100269-100279.
[3] LIEN WH, FUCHS E. Wnt some lose some: transcriptional governance of stem cells by Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Genes Dev. 2014;28(14):1517-1532.
[4] YANG H, ADAM RC, GE Y, et al. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Micro-niches Govern Stem Cell Lineage Choices.Cell. 2017; 169(3):483-496.e13.
[5] RISHIKAYSH P, DEV K, DIAZ D, et al. Signaling involved in hair follicle morphogenesis and development.Int J Mol Sci. 2014,15(1):1647-70.
[6] 纪影畅,李宇,鲁峰,等.大鼠胚胎皮肤毛囊形态发生与Wnt-10b/ β-catenin的表达[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2010,21(1):50-53.
[7] GUPTA K, LEVINSOHN J, LINDERMAN G, et al. Single-Cell Analysis Reveals a Hair Follicle Dermal Niche Molecular Differentiation Trajectory that Begins Prior to Morphogenesis. Dev Cell.2019;48(1):17-31.e6.
[8] JAHODA CA, HORNE KA, OLIVER RF. Induction of hair growth by implantation of cultured dermal papilla cells. Nature. 1984;311(5986):560-562.
[9] JAHODA CAB, OLIVER RF, REYNOLDS AJ, et al. Human hair follicle regeneration following amputated and grafted into nude mouse. J Invest Drmatol.1996;107(6):804-807.
[10] 韩乐,刘本,陈贤燕,等.甘草酸二铵对人毛囊生长作用及对Wnt/ β连环蛋白信号通路的影响[J].中华皮肤科杂志, 2018,51(2): 138-142.
[11] YUAN YP, HUANG K, XU YM, et al. Canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling control the regeneration of amputated rodent vibrissae follicles.J Mol Histol. 2016;47(1): 1-8.
[12] ZHAO B, CHEN Y, YANG N, et al.miR-218-5p regulates skin and hair follicle development through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting SFRP2.J Cell Physiol.2019;234(11): 20329-20341.
[13] 林常敏,蔡湘娜,蔡博治,等.人毛乳头细胞微囊诱导大鼠足垫毛囊形成模型的建立[J].中国美容整形外科杂志, 2015,26(3): 186-189.
[14] WUELLING M, SCHNEIDER S, SCHROTHER VA, et al. Wnt5a is a transcriptional target of Gli3 and Trps1 at the onset of chondrocyte hypertrophy.Dev Biol. 2020;457(1):104-118.
[15] WU X, VAN DIJK EM, NG-BLICHFELDT JP, et al. Mesenchymal WNT-5A/5B Signaling Represses Lung Alveolar Epithelial Progenitors.Cells. 2019;8(10). pii: E1147.
[16] AKOUMIANAKIS I, SANNA F, MARGARITIS M, et al. Adipose tissue-derived WNT5A regulates vascular redox signaling in obesity via USP17/RAC1-mediated activation of NADPH oxidases.Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(510). pii: eaav5055.
[17] DENG Q, LI P, CHE M, et al. Activation of hedgehog signaling in mesenchymal stem cells induces cartilage and bone tumor formation via Wnt/β-Catenin.Elife. 2019;8. pii: e50208.
|