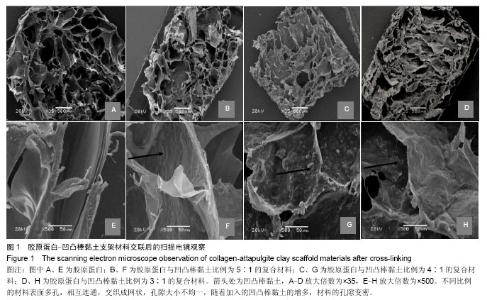
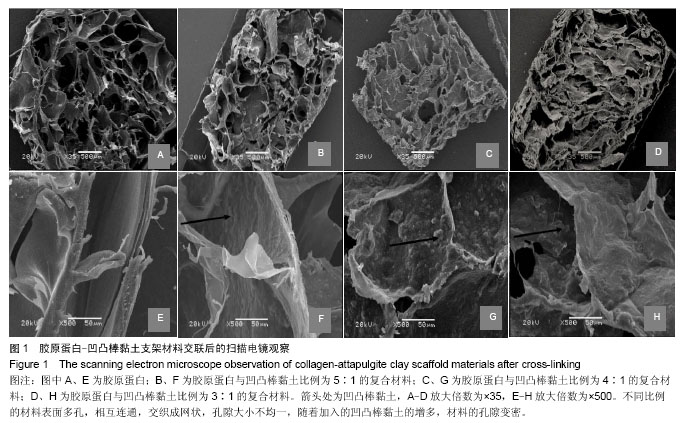
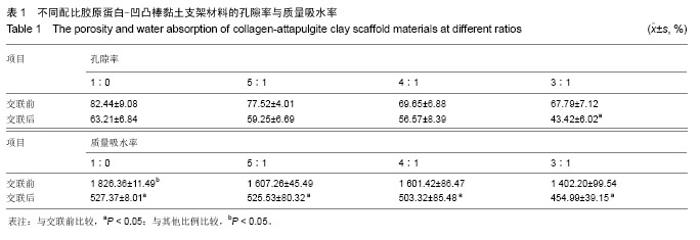
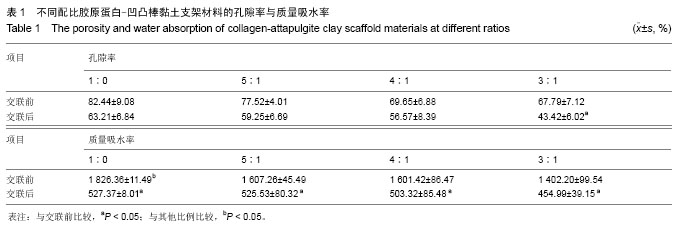
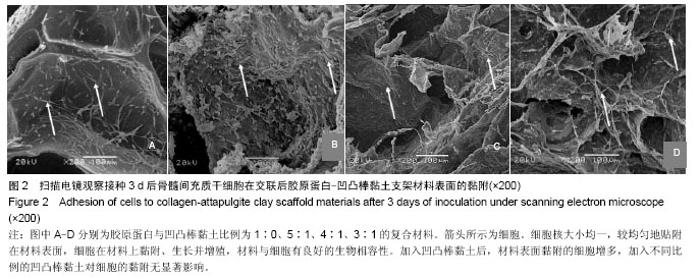
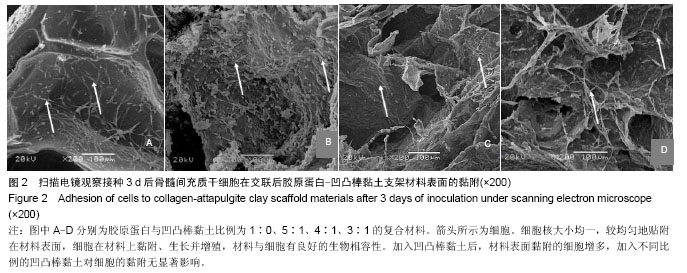
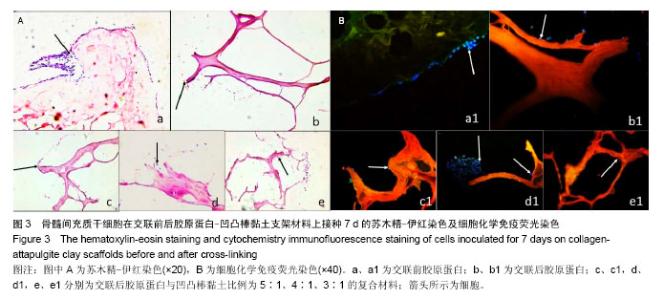
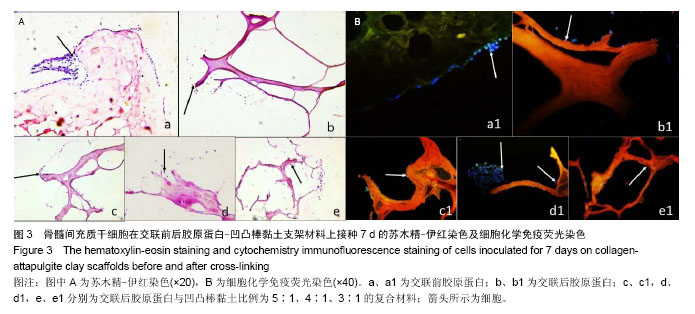
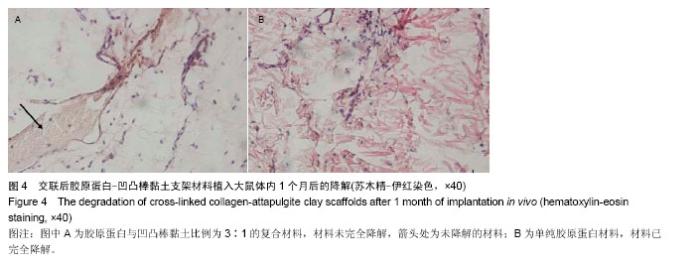
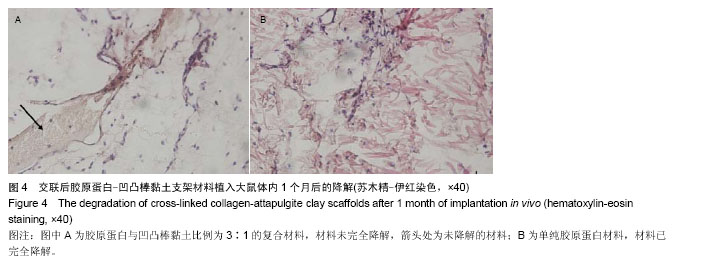
| [1] Oliveira AL,Sousa EC,Silva NA,et al.Peripheral mineralization of a 3D biodegradable tubular construct as a way to enhance guidance stabilization in spinal cord injury regeneration.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2012;23(11):2821-2830.
[2] 王身国,杨健,蔡晴,等.组织工程用生物材料及细胞支架研究进展[J].中华整形外科杂志,2000,16(6):328-330.
[3] 徐大朋,王绪凯.骨组织工程支架研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2014,7(3):177-181.
[4] 刘雷,韦庆军,肖仕辉.骨组织工程支架材料的选择及其细胞相容性[J].广东医学,2014,35(1):147-149.
[5] 马新芳,张静莹.骨组织工程支架材料的研究现状与应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(30):4895-4899.
[6] 陆兴,张永红,李二峰,等.羟基丁酸-羟基辛酸聚合物/胶原软组织工程支架的细胞亲和性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(12): 1895-1900.
[7] 周长春,樊渝江,谭言飞,等.磷酸钙与胶原双相多级仿生骨组织工程支架研究[J].成都大学学报,2014,33(2):101-105.
[8] 马立坤,叶鹏,邓江,等.丝素蛋白/壳聚糖/纳米羟基磷灰石骨组织工程支架材料的体外细胞毒性评价[J].西部医学,2014,26(8): 975-978.
[9] 蒋挺大,张春萍.胶原蛋白[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2001.
[10] Donzelli E,Salvadè A,Mimo P,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells cultured on a collagen scaffold: In vitro osteogenic differentiation.Arch Oral Biol.2007;52(1):64-73.
[11] Shen YH,Shoichet MS,Radisic M.Vascular endothelial growth factor immobilized in collagen scaffold promotes penetration and proliferation of endothelial cells.Acta Biomater. 2008;4(3): 477-489.
[12] Zhong S,Teo WE,Zhu X,et al.An aligned nanofibrous collagen scaffold by electrospinning and its effects on in vitro fibroblast culture.J Biomed Mater Res A.2006;79(3):456-463.
[13] Bosnakovski D,Mizuno M,Kim G,et al.Chondrogenic differentiation of bovine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in different hydrogels: influence of collagen type II extracellular matrix on MSC chondrogenesis. Biotechnol Bioeng.2006;93(6):1152-1163.
[14] 高桥.BMSCs复合壳聚糖-胶原蛋白修复兔大块关节软骨缺损[J].临床医学工程,2010,17(4):42-44.
[15] Yu W,Zhao W,Zhu C,et al.Sciatic nerve regeneration in rats by a promising electrospun collagen/poly(ε-caprolactone) nerve conduit with tailored degradation rate.BMC Neurosci. 2011; 12(1):68.
[16] Boland ED,Matthews JA,Pawlowski KJ,et al.Electrospinning collagen and elastin:preliminary vascular tissue engineering. Front Biosci. 2004;9:1422-1432.
[17] 姜东林,杨骏宇,姜升阳,等.京尼平交联L-赖氨酸修饰胶原蛋白支架的性能和生物相容性[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2014,31(4): 816-821.
[18] 陶玲,任珺,白天宇,等.凹凸棒粘土的产品开发与利用[J].资源开发与市场,2012(5):416-419.
[19] 詹庚申,郑茂松.美国凹凸棒石黏土开发应用浅议[J].非金属矿, 2005,28(2):36-39.
[20] 王艺洁,任珺,陶玲,等.凹凸棒粘土的结构与组成研究综述[J].矿产保护与利用,2012,32(4):44-47.
[21] Fielding G,Bose S.SiO2 and ZnO dopants in three-dimensionally printed tricalcium phosphate bone tissue engineering scaffolds enhance osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vivo.Acta Biomater.2013;9(11):9137-9148.
[22] Wang DX,He Y,Bi L,et al.Enhancing the bioactivity of Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold with a nano-hydroxyapatite coating for the treatment of segmental bone defect in a rabbit model.Int J Nanomedicine.2013;8:1855.
[23] 宁思敏,王东,孙海钰,等.大鼠成骨细胞与壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合支架降解产物的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(12):1846-1851.
[24] 刘鹏,王东,孙海钰,等.胶原-纳米羟基磷灰石复合支架的细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2012,15(42): 7831-7834.
[25] 谢浩,方晓雨.基于SiO2材料的细胞固定化研究及应用[J].广州化工,2011,39(10):16-18.
[26] 倪硕,李澎,张卫国,等.制备软骨组织工程支架的方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(3):446-451.
[27] 刘越,赵艳梅,田学忠,等.明胶纳米羟基磷灰石三维多孔骨支架的制备及其生物安全性评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(16): 1634-1640.
[28] 柴枫,赵铱民,王忠义,等.RP构建不同孔隙率骨支架材料对成骨细胞增殖的影响[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2003,4(3):137-139.
[29] 宋忠臣,束蓉,谢玉峰,等.Bio-oss 胶原与骨髓基质细胞相容性的实验研究[J].上海口腔医学,2008,17(2):161-164.
[30] 陈岩,赵宜江,周守勇,等.聚丙烯酰胺/凹凸棒粘土复合吸附材料的研究[J].高校化学工程学报,2010,24(2):274-279. |