Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (43): 6979-6984.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.43.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and performance of biologic antimicrobial materials for pelvic tissue repair
Ling You1, 2, Xu Bin1, Chen Xiao-feng2
- 1Grandhope Biotech Co., Ltd., National Engineering Laboratory for Regenerative Implantable Medical Devices, Guangzhou 510530, Guangdong Province, China; 2College of Materials Science and Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510641, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2014-08-06Online:2014-10-15Published:2014-10-15 -
About author:Ling You, M.D., Grandhope Biotech Co., Ltd., National Engineering Laboratory for Regenerative Implantable Medical Devices, Guangzhou 510530, Guangdong Province, China; College of Materials Science and Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510641, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Technology R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology, No. 2012BAI17B00; the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities, No. 2012ZP0001, 2013ZB0005; China Postdoctoral Foundation, No. 2013M531853
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ling You, Xu Bin, Chen Xiao-feng. Preparation and performance of biologic antimicrobial materials for pelvic tissue repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(43): 6979-6984.
share this article
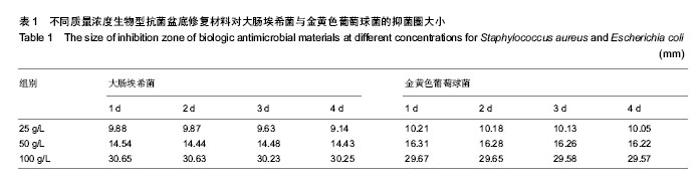
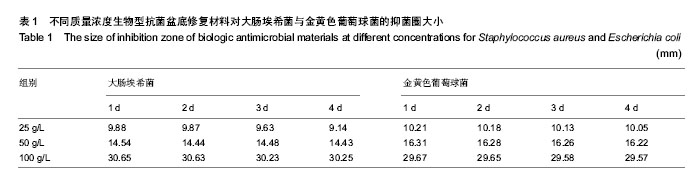
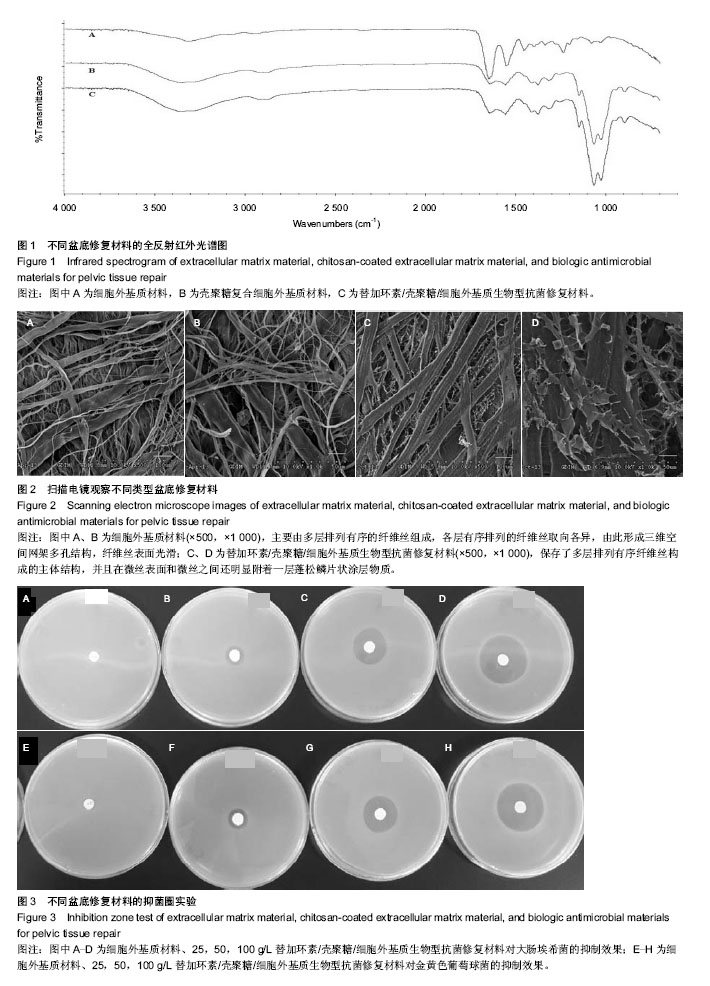
2.1 生物型抗菌盆底修复材料的红外光谱检测 红外光谱图1中A、B、C曲线分别为细胞外基质材料、壳聚糖复合细胞外基质材料及生物型抗菌修复材料。 由图可见,相对细胞外基质材料而言,复合壳聚糖后在3 359 cm-1左右峰明显增宽,归属于O-H伸缩振动吸收峰与N-H的伸缩振动吸收峰,是壳聚糖复合后分子内和分子间氢键缔合重叠而产生的多重特征吸收峰。1 647 cm-1为C=O伸缩振动吸收峰,1 559 cm-1为N-H的面内弯曲振动吸收峰,1 378 cm-1为N-H的面外弯曲振动吸收峰[23]。 1 152 cm-1为C-O-C氧桥的不对称伸缩振动峰,1 068 cm-1和1 028 cm-1为糖环骨架的伸缩振动峰,峰吸收强,是复合壳聚糖后特征吸收,而细胞外基质材料吸收谱中未见该吸收,说明壳聚糖在细胞外基质材料上复合成功[24-27]。 2.2 生物型抗菌盆底修复材料的表面形貌 图2A,B和图2C,D分别为细胞外基质材料和生物型抗菌修复材料的微观表面形貌图。 由图可见,细胞外基质材料主要由多层排列有序的纤维丝组成,各层有序排列的纤维丝取向各异,由此形成三维空间网架多孔结构(图2A),纤维丝表面光滑,无明显其他物质附着在纤维丝表面(图2B)。生物型抗菌修复材料同样保存了多层排列有序的纤维丝构成的主体结构(图2C),并且在微丝表面和微丝之间还明显附着一层蓬松鳞片状涂层物质(图2D),材料微表面三维孔洞变小,但仍维持多孔连通特性。 2.3 生物型抗菌盆底修复材料的抗菌效果 如图3所示,对大肠埃希菌和金黄色葡萄球菌培养24 h后,细胞外基质材料组平板内菌胎生长正常,无抑菌圈出现,均未表现出明显的抗菌性能。生物型抗菌盆底修复材料组在25,50,100 g/L的抗菌剂量时均出现明显抑菌圈,并且随着抗菌剂质量浓度的增大,抑菌圈直径显著增加,表现出良好的抗菌性能。 为考察生物型盆底抗菌材料持续抗菌能力,实验含菌平板继续培养至4 d,每天测量抑菌圈大小,见表1所示,尽管随着时间的延长,平板内菌胎长得很密,各抗菌剂量的生物型盆底修复材料抑菌圈直径仅有略微缩小,未见明显变化。第4天与第1天相比,同一抗菌剂量组大肠埃希菌和金黄色葡萄球菌两种受试菌株平板抑菌圈大小差异均无显著性意义。"
| [1] Sensoy N,Dogan N,Ozek B,et al.Urinary incontinence in women: prevalence rates, risk factors and impact on quality of life.Pak J Med Sci.2013;29(3):818-822. [2] Kwon BE,Kim GY,Son YJ,et al.Quality of life of women with urinary incontinence: a systematic literature review.Int Neurourol J.2010;14(3):133-138. [3] Ko Y,Lin SJ,Salmon JW,et al.The impact of urinary incontinence on quality of life of the elderly.Am J Manag Care.2005;11(4):103-111. [4] Hermieu JF,Le Guilchet T.Genital prolapse and urinary incontinence: a review. J Med Liban.2013;61(1):61-66. [5] Minassian VA,Drutz HP,Al-Badr A.Urinary incontinence as a worldwide problem. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2003;82(3): 327-338. [6] Sergent F,Gay-Crosier G,Resch B,et al.A comparative study between two procedures of TVT retropubic mid-urethral sling placement for treatment of female stress urinary incontinence. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod.2013;2315(13):215-219. [7] Fan X,Wang Y,Wang Y,et al.Comparison of polypropylene mesh and porcine-derived, cross-linked urinary bladder matrix materials implanted in the rabbit vagina and abdomen. Int Urogynecol J.2014;25(5):683-689. [8] Jensen KK,Rashid L,Pilsgaard B,et al.Pelvic floor reconstruction with a biological mesh after extralevator abdominoperineal excision leads to few perineal hernias and acceptable wound complication rates with minor movement limitations: single-centre experience including clinical examination and interview.Colorectal Dis. 2014;16(3): 192-197. [9] Rice NT,Hu Y,Slaughter JC,et al. Pelvic mesh complications in women before and after the 2011 FDA public health notification.Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2013;19(6): 333-338. [10] Rickey LM,Huang L,Rahn DD,et al.Risk factors for urgency incontinence in women undergoing stress urinary incontinence surgery.Adv Urol.2013;2013(7):1-8. [11] Wu MP,Huang KH,Long CY,et al.In vitro extracellular matrix model to evaluate stroma cell response to transvaginal mesh. Neurourol Urodyn.2013;66(3):488-492. [12] Badylak SF.The extracellular matrix as a biologic scaffold material. Biomaterials. 2007;28(25):3587-3593. [13] Badylak SF.Xenogeneic extracellular matrix as a scaffold for tissue reconstruction.Transpl Immunol.2004;12(3-4): 367-377. [14] Campoccia D,Montanaro L,Arciola CR.A review of the biomaterials technologies for infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials.2013;34(34):8533-8554. [15] Campoccia D,Montanaro L,Arciola CR.A review of the clinical implications of anti-infective biomaterials and infection- resistant surfaces.Biomaterials.2013; 34(33):8018-8029. [16] Alvarez J,Cvach K,Dwyer P.Complications in pelvic floor surgery. Minerva Ginecol. 2013;65(1):53-67. [17] Moore T,Tubman I,Levy G,et al.Age as a risk factor for perioperative complications in women undergoing pelvic reconstructive surgery. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2010;16(5):290-295. [18] 何伟,王翔,高莹,等.新型纳米银/聚氨酯胆道支架表面抗菌涂层的体外抑菌试验[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(3): 453-456. [19] Kova?evi? J, Mesak LR,Allen KJ. Occurrence and characterization of Listeria spp. in ready-to-eat retail foods from Vancouver, British Columbia. Food Microbiol.2012; 30(2):372-378. [20] 姜双应.四种抗菌产品抑菌作用的实验室观察[J].中国消毒学杂志,2008,25(3):255-257. [21] Zhang H,Tang J,Meng X,et al.Inhibition of bacterial adherence on the surface of stents and bacterial growth in bile by bismuth dimercaprol.Dig Dis Sci.2005; 50(6):1046-1051. [22] Li D,Xiao XR,Zhu Z,et al.Study the inhibitory effects of three oral actinomyces on growth of oral Candida albicans in vitro.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi.2008; 26(5):553-555. [23] Zhou B,Hu Y,Li J,et al.Chitosan/phosvitin antibacterial films fabricated via layer-by-layer deposition.Int J Biol Macromol. 2014;64:402-408. [24] 董炎明.壳聚糖衍生物的红外光谱分析[J].纤维素科学与技术, 2001,9(2):42-54. [25] Mahjub R,Dorkoosh FA,Amini M,et al.In vitro characterization and cell cytotoxicity of insulin nanoparticles composed of quaternized aromatic derivatives of chitosan.J Control Release. 2013;172(1):112-118. [26] Amaral IF,Granja PL,Barbosa MA.Chemical modification of chitosan by phosphorylation: an XPS, FT-IR and SEM study.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2005;16(12): 1575-1593. [27] 李立华,李红,罗丙红,等.壳聚糖及其衍生物在组织工程中的应用[J].功能高分子学报,2005,18(2):347-352. [28] Helström L,Nilsson B.Impact of vaginal surgery on sexuality and quality of life in women with urinary incontinence or genital descensus.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2005;84(1): 79-84. [29] Benhaim Y,de Tayrac R,Deffieux X,et al.Treatment of genital prolapse with a polypropylene mesh inserted via the vaginal route. Anatomic and functional outcome in women aged less than 50 years.J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod. 2006;35(3): 219-226. [30] Capobianco G,Donolo E,Wenger JM,et al.Efficacy and 9 years' follow-up of posterior intravaginal slingplasty for genital prolapse.J Obstet Gynaecol Res.2014;40(1):219-223. [31] Ulukent SC,Kaya B,Bat O,et al.Prolene mesh migration into the rectum after sacral colpopexy presented with frozen pelvis.Int J Surg Case Rep.2013;4(11):1004-1006. [32] Thomin A,Touboul C,Hequet D,et al.Genital prolapse repair with Avaulta Plus mesh: functional results and quality of life.Prog Urol.2013;23(4):270-275. [33] Freytes DO,Tullius RS,Badylak SF.Effect of storage upon material properties of lyophilized porcine extracellular matrix derived from the urinary bladder.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2006;78(2):327-333. [34] Turner NJ,Yates AJ Jr,Weber DJ,et al.Xenogeneic extracellular matrix as an inductive scaffold for regeneration of a functioning musculotendinous junction. Tissue Eng Part A.2010;16(11):3309-3317. [35] Liu L,Li D,Wang Y,et al.Evaluation of the biocompatibility and mechanical properties of xenogeneic (porcine) extracellular matrix (ECM) scaffold for pelvic reconstruction.Int Urogynecol J.2011;22(2):221-227. [36] Huber JE,Spievack A,Simmons-Byrd A,et al.Extracellular matrix as a scaffold for laryngeal reconstruction.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol.2003;112(5):428-333. [37] Badylak SF.The extracellular matrix as a scaffold for tissue reconstruction. Semin Cell Dev Biol.2002;13(5):377-383. [38] Badylak SF,Gilbert TW.Immune response to biologic scaffold materials. Semin Immunol.2008;20(2):109-116. [39] Khalili H,Dashti-Khavidaki S,Khaleghi S,et al.Evaluation of tigecycline activity against methicillin-resistante staphylococcus aureus isolated from Biological Samples.Iran J Pharm Res.2010;9(1):61-65. [40] Swoboda S,Ober M,Hainer C,et al.Tigecycline for the treatment of patients with severe sepsis or septic shock: a drug use evaluation in a surgical intensive care unit.J Antimicrob Chemother.2008;61(3):729-733. [41] Blot S,De Waele JJ,Vogelaers D.Essentials for selecting antimicrobial therapy for intra-abdominal infections.Drugs. 2012;72(6):17-32. |
| [1] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [2] | Li Xinping, Cui Qiuju, Zeng Shuguang, Ran Gaoying, Zhang Zhaoqiang, Liu Xianwen, Fang Wei, Xu Shuaimei. Effect of modification of β-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan hydrogel on growth and mineralization of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3493-3499. |
| [3] | Chen Song, He Yuanli, Xie Wenjia, Zhong Linna, Wang Jian. Advantages of calcium phosphate nanoparticles for drug delivery in bone tissue engineering research and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3565-3570. |
| [4] | Chen Siyu, Li Yannan, Xie Liying, Liu Siqi, Fan Yurong, Fang Changxing, Zhang Xin, Quan Jiayu, Zuo Lin. Thermosensitive chitosan-collagen composite hydrogel loaded with basic fibroblast growth factor retards ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2472-2478. |
| [5] | Liu Feng, Zhang Yu, Wang Yanli, Luo Wei, Han Chaoshan, Li Yangxin. Application of temperature-sensitive chitosan hydrogel encapsulated exosomes in ischemic diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2479-2487. |
| [6] | Li Jie, Xu Jianzhen, Hu Ping, Lei Qiqi, Zhang Wenning, Ao Ningjian . Preparation and performance evaluation of carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized glucomannan/Panax notoginseng compound sponge dressing for chronic wound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2528-2534. |
| [7] | Gan Zhoujie, Pei Xibo. Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles in tumor therapy: superiority of nanoparticles in accumulation and drug release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2562-2568. |
| [8] | Feng Xiaoxia, Hou Weiwei, Jin Xiaoting, Wang Xinhua. Construction of periodontal biomimetic membrane with electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibers and electrosprayed chitosan microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 511-516. |
| [9] | Li Li, Ma Li, Li He. Preparation and characterization of magnetic chitosan microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 577-582. |
| [10] | Li Xuan, Lu Min, Li Mingxing, Ao Meng, Tang Linmei, Zeng Zhen, Hu Jingwei, Huang Zhiqiang, Xuan Jiqing. In vitro multi-modal imaging of magnetic targeted nanoparticles and their targeting effect on hepatic stellate cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 566-571. |
| [11] | Xiang Haibin, Li Xinxia, Liang Qiuzhen, Song Xinghua. Specific bone-targeting nanoscale drug delivery system: advantages and clinical applicability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 612-618. |
| [12] | Liu Haiyan, Hu Yang, Wu Xiuping, Pan Haobo, Jing Xuan. Chitosan-based polysaccharide biomaterial for prevention and treatment of oral diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 631-636. |
| [13] | Liao Jian, Huang Xiaolin, Huo Hua, Zhou Qian, Cheng Yuting, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Yang Tongjing, Liao Yunmao, Liang Xing. Effects of calcined bone/chitosan composite materials on proliferation and adhesion in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5447-5453. |
| [14] | Fang Yulu, Yi Bingcheng, Shen Yanbing, Tang Han, Zhang Yanzhong. Potential of corn husk fibers reinforced chitosan-based hydrogels in cartilage tissue engineering scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5493-5501. |
| [15] | Liao Jian, Huang Xiaolin, Zhou Qian, Huo Hua, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Yunmao, Liang Xing. Calcined bone/chitosan composite promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4941-4947. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||