Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (42): 6763-6768.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.42.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation analysis of pathogenesis of optic neuritis with helper T cell subsets in a mouse experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model
Yao Han-yun1, Wen Fang2, Dong Xin-yu3
- 1Department of Neurology, Wuhan No.1 Hospital, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China
2Department of Neurology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China
3Affiliated Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China
-
Revised:2014-09-18Online:2014-10-08Published:2014-10-08 -
Contact:Yao Han-yun, Department of Neurology, Wuhan No.1 Hospital, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Yao Han-yun, Master, Physician, Department of Neurology, Wuhan No.1 Hospital, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yao Han-yun, Wen Fang, Dong Xin-yu. Correlation analysis of pathogenesis of optic neuritis with helper T cell subsets in a mouse experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(42): 6763-6768.
share this article
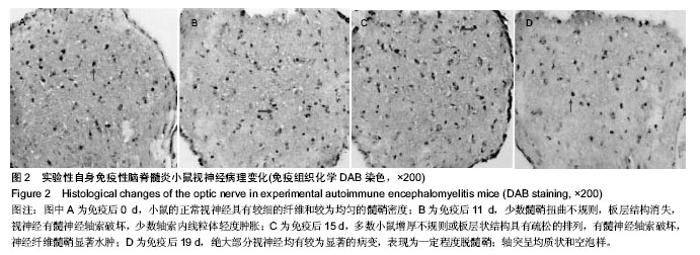
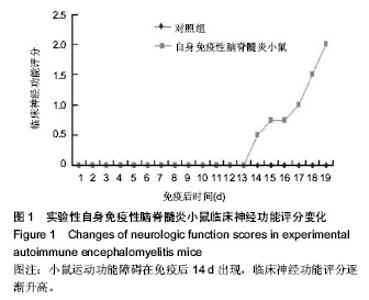
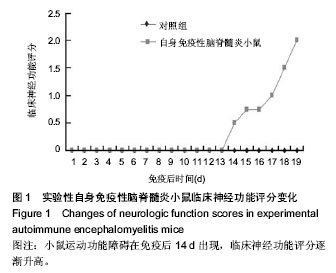
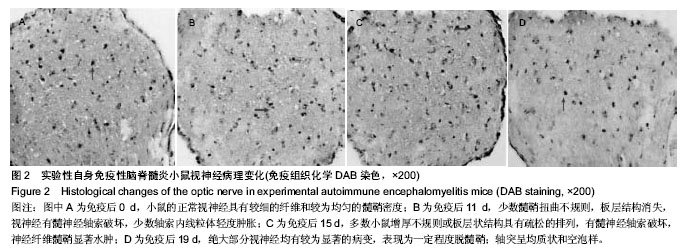
2.3 实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经病理变化 免疫后0 d,小鼠的正常视神经具有较细的纤维和较为均匀的髓鞘密度(图2A)。免疫后11 d,少数髓鞘扭曲不规则,板层结构消失;视神经有髓神经轴索破坏,少数轴索内线粒体轻度肿胀(图2B)。免疫后15 d,多数小鼠增厚不规则或板层状结构具有疏松的排列,有髓神经轴索破坏,神经纤维髓鞘显著水肿(图2C)。免疫后19 d,绝大部分视神经均有较为显著的病变,表现为一定程度脱髓鞘;轴突呈均质状和空泡样,微管消失,甚至可见髓鞘塌陷;髓鞘板层状分离、剥脱,轴突髓鞘部分向内向外突起,或板层具有日益增大的分离范围,夹杂着髓鞘半环形套叠等,有间隙形成在轴突轴膜和髓鞘间,具有较低的电子密度,细胞器消失(图2D)。"
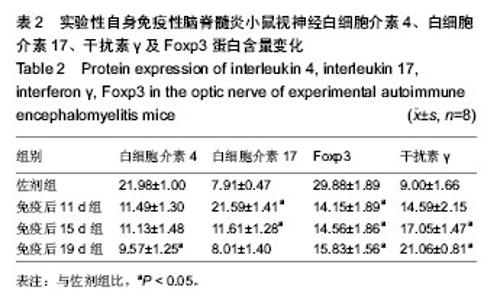
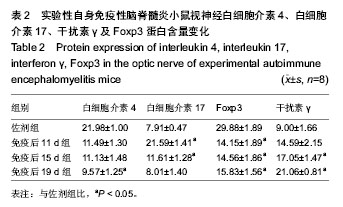
2.4 实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经白细胞介素4、白细胞介素17、干扰素γ及Foxp3蛋白含量变化 实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经白细胞介素4蛋白含量免疫后19 d组实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎明显比佐剂组低 (P < 0.05),但免疫后11 d组和免疫后15 d组之间的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经白细胞介素17蛋白含量免疫后11 d组和免疫后15 d组均明显比佐剂组高(P < 0.05),但免疫后19 d组和佐剂组之间的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经干扰素γ蛋白含量免疫后15 d组和免疫后19 d组明显比佐剂组高(P < 0.05),但免疫后11 d组和佐剂组之间的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经Foxp3蛋白含量免疫后11 d组、免疫后15 d组、免疫后19 d组均明显比佐剂组低(P < 0.05),但免疫后11 d组、免疫后 15 d组、免疫后19 d组之间的差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见表2。"
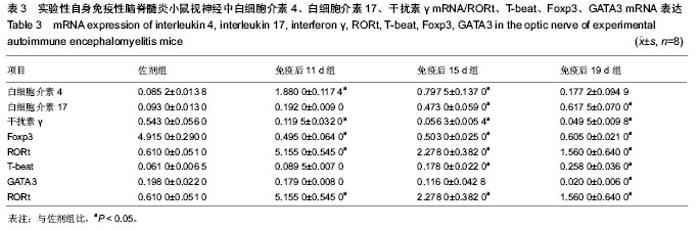
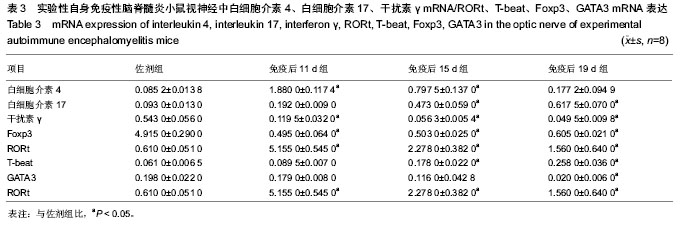
2.5 实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经中白细胞介素4、白细胞介素17、干扰素γ及Foxp3 mRNA的表达 实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经中白细胞介素4 mRNA表达免疫后11 d组、免疫后15 d组明显比佐剂组高(P < 0.05),但免疫后19 d组和佐剂组之间的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经中白细胞介素17、T-beat mRNA表达免疫后15 d组、免疫后19 d组明显比佐剂组高(P < 0.05),但免疫后11 d组和佐剂组之间的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经中干扰素γ、Foxp3 mRNA表达免疫后11 d组、免疫后15 d组、免疫后19 d组均明显比佐剂组低(P < 0.05);实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经中RORt mRNA表达免疫后11 d组、免疫后15 d组、免疫后19 d组均明显比佐剂组高(P < 0.05),同时免疫后11 d组、免疫后15 d组、免疫后19 d组之间的差异均显著(P < 0.05);实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠视神经中GATA3 mRNA表达免疫后19 d组明显比佐剂组低(P < 0.05),但免疫后11 d组、免疫后15 d组和佐剂组之间的差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见表3。"
| [1] 张荣伟.辅助性T细胞亚群在EAE小鼠早期视神经炎发病中的作用及β-榄香烯干预的实验研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2009. [2] 扈煜.Tc17、Th22、Treg/Th17细胞亚群在ITP发病中的意义及机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2013. [3] 张静.microRNA-155调节Th1/Th17细胞分化并与多发性硬化发病机制相关[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2013. [4] 邓昱.IL-12-+重组卡介苗新生期接种干预实验性哮喘模型的作用及其机制研究[D].重庆医科大学,2010. [5] 蕳雪静.小鼠弓形虫眼病模型的建立及IL-10对其炎症和免疫应答的影响[D].济南:山东大学,2012. [6] 周玉海.免疫性前列腺炎组织Th17T淋巴细胞浸润及其相关细胞因子表达研究[D].济南:山东大学,2010. [7] 解玉泉.Th17细胞/白介素-17在病毒性心脏病中的作用及机制研究[D].上海:复旦大学,2012. [8] 朱德生.FTY-720对EAE小鼠的治疗作用及其机制的实验研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2013. [9] 张荣伟,周志可,禹红梅.等.β-榄香烯对EAE小鼠视神经炎治疗作用的研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2011,27(4):342-346. [10] 陈斌华,黄勇帆,项嘉亮.肺支原体肺炎患儿血清中辅助性T细胞亚群表达细胞因子的变化及其临床意义[J].中国医药导报,2013,10(21):58-63. [11] 王志玉,史爱云.视网膜挫伤模型兔视神经细胞的凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(18):2848-2854. [12] 高洁,乔清理,解楠.基于实验数据计算机仿真大鼠视神经纤维对于胞外点电极刺激的响应与影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(9):1629-1633. [13] 张磊.Th22细胞在AS和RA中的表达及其作用机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2012. [14] 杨帆.疏肝健脾固髓方治疗多发性硬化的临床及机制的初步研究[D].中国中医科学院,2013. [15] 陆玉蕾.肝脏TCRγδ-+ CD3-+ CD4-- CD8--T 细胞在小鼠病毒性肝炎中的作用及其作用机制[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012. [16] 郭秋野.miR-146a在自身免疫性淋巴增生综合征致病机制中的作用[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2013. [17] 张晋渝.MicroRNA-155在T细胞耗竭中的作用及其机制研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2013. [18] 石云.CD24分子对调节性T细胞发育及功能的影响[D].广州:南方医科大学,2012. [19] 聂大奥.外周血T细胞亚群构成比例与冠状动脉粥样硬化关系的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013. [20] 赵殿元.DC上表达的LSECtin对辅助性T细胞亚群分化的影响及其机制研究[D].北京:中国人民解放军军事医学科学院,2013. [21] 邹敏书.Peyer小结中滤泡辅助性T细胞诱导B细胞分化成分泌IgA的浆细胞参与IgA肾病机制[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012. [22] 张玉卓.TIPE2和FOXP3 mRNA在原发性肝癌患者PBMCs及肝组织中的表达及临床意义的初步探讨[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2012. [23] 高楚淇,伍丽萍,施秉银.雄激素对BALB/c小鼠脾脏主要辅助性T细胞亚群的影响[C].中华医学会,2012. [24] 袁正洲.来氟米特对实验性变态反应性脑脊髄炎防治作用的研究[D].泸州:泸州医学院,2013. [25] 王志红.miR-30a在多发性硬化症及EAE中的作用和机制研究[D].重庆:第二军医大学,2013. [26] 孙垚.结核病人与健康成人外周血γδT细胞Vδ1-8亚群分布的差异[D].蚌埠:蚌埠医学院,2014. [27] 金学敏.莱菔硫烷对EAE小鼠脾组织CD4+CD25+Foxp3+调节型T细胞表达的影响及机制探讨[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2012. [28] 陈立.γδT细胞产生IL-17的亚群分析和诱导分化条件的探讨[D].蚌埠:蚌埠医学院,2014. [29] Fisher-Shoval Y, Barhum Y, Sadan O, et al. Transplantation of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the EAE mouse model of MS. J Mol Neurosci. 2012;48(1):176-184. [30] Robinson C, Woo S, Walsh A, et al. The antioxidants vitamins A and E and selenium do not reduce the incidence of asbestos-induced disease in a mouse model of mesothelioma. Nutr Cancer. 2012;64(2):315-322. [31] Nakajima H, Hosokawa T, Sugino M, et al. Visual field defects of optic neuritis in neuromyelitis optica compared with multiple sclerosis. BMC Neurol. 2010;10(1):45. [32] Tan YV, Abad C, Wang Y, et al. VPAC2 (vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor type 2) receptor deficient mice develop exacerbated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with increased Th1/Th17 and reduced Th2/Treg responses. Brain Behav Immun. 2014 [Epub ahead of print]. [33] Liu N, Kan QC, Zhang XJ, et al. Upregulation of immunomodulatory molecules by Matrine treatment in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Exp Mol Pathol. 2014 [Epub ahead of print]. [34] Knier B, Rothhammer V, Heink S, et al. Neutralizing IL-17 protects the optic nerve from autoimmune pathology and prevents retinal nerve fiber layer atrophy during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Autoimmun. 2014 [Epub ahead of print]. [35] Lu P, Wang M, Zheng P, et al. Th17/Treg unbalance is involved in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014;30(10):1013-1017. [36] Chen C, Li YH, Zhang Q, et al. Fasudil regulates T cell responses through polarization of BV-2 cells in mice experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 [Epub ahead of print]. [37] Zhao YF, Zhang X, Ding ZB, et al. The therapeutic potential of rho kinase inhibitor fasudil derivative fad-1 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Mol Neurosci. 2014 [Epub ahead of print]. [38] Liu X, He F, Pang R, et al. IL-17-induced MiR-873 attributes to the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by targeting A20 ubiquitin editing enzyme. J Biol Chem. 2014 [Epub ahead of print]. [39] Dias DS, Fontes LB, Crotti AE, et al. Copaiba oil suppresses inflammatory cytokines in splenocytes of C57Bl/6 mice induced with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Molecules. 2014;19(8):12814-12826. [40] Cappellano G, Woldetsadik AD, Orilieri E, et al. Subcutaneous inverse vaccination with PLGA particles loaded with a MOG peptide and IL-10 decreases the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Vaccine. 2014;32(43): 5681-5689. [41] Castelo-Branco G, Stridh P, Guerreiro-Cacais AO, et al. Acute treatment with valproic acid and l-thyroxine ameliorates clinical signs of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and prevents brain pathology in DA rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2014; 71:220-233. [42] Xie L, Chen J, McMickle A, et al. The immunomodulator AS101 suppresses production of inflammatory cytokines and ameliorates the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2014;273(1-2):31-41. [43] Djiki? J, Nacka-Aleksi? M, Pilipovi? I, et al. Age-associated changes in rat immune system: Lessons learned from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Exp Gerontol. 2014;58C:179-197. [44] Zager A, Peron JP, Mennecier G, et al. Maternal immune activation in late gestation increases neuroinflammation and aggravates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the offspring. Brain Behav Immun. 2014 [Epub ahead of print]. [45] Benveniste EN, Liu Y, McFarland BC, et al. Involvement of the janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway in multiple sclerosis and the animal model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014;34(8):577-588. [46] Fang L, Zheng Q, Yang T, et al. Bushen Yisui Capsule ameliorates axonal injury in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neural Regen Res.2013;8(35): 3306-3315. [47] Figueiredo CA, Drohomyrecky PC, McCarthy SD, et al. Optimal attenuation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by intravenous immunoglobulin requires an intact interleukin-11 receptor. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e101947. [48] Dungan LS, McGuinness NC, Boon L, et al. Innate IFN-γ promotes development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: A role for NK cells and M1 macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44(10):2903-2917. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||