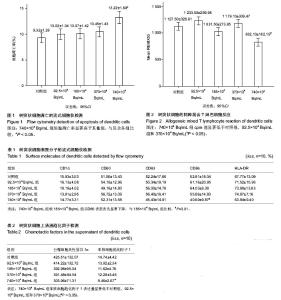
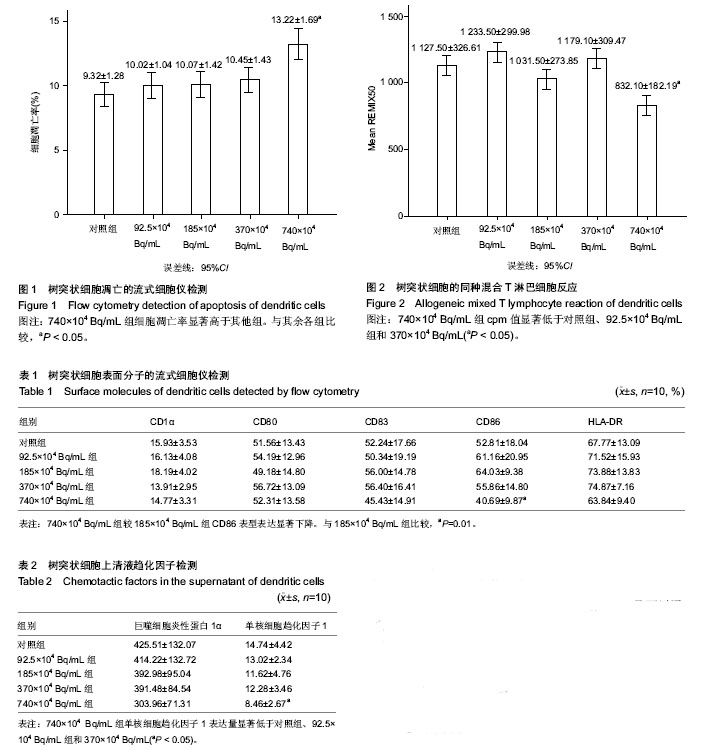
| [1] 王冰,王红梅,徐方云,等.树突状细胞与肿瘤免疫[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2013,35(11):1666-1671.
[2] Yang XH, Xia H, Chen Y, et al. Inducible expression of endomorphins in murine dendritic cells. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(35): 2811-2817.
[3] 陶新全,王明明.18-氟-脱氧葡萄糖诱导Lewis肺癌细胞凋亡的实验研究[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2009,34(10):865-867.
[4] Chun SH, Park GY, Han YK,et al.Effect of lowdose radiation on differentiation of bone marrow cells into dendritic cells. Dose Response.2013;11(3):374-384.
[5] 董娟聪,王金虎,卢良杰,等.不同剂量电离辐射对小鼠树突状细胞(DC)表型及功能的影响[J].辐射防护,2012,32(4): 199-203,209.
[6] Rao V,Saunes M,Jorstad S,et al.In vitro experiments demonstrate that monocytes and dendritic cells are rendered apoptotic by extracorporeal photochemotherapy, but exhibit unaffected surviving and maturing capacity after 30Gy gamma irradiation.Scand J Immunol.2008;68(6): 645-651.
[7] Yoshino H,Takahashi K,Monzen S,et al.Differential induction from X-irradiated human peripheral blood monocytes to dendritic cells.J Radiat Res.2008;49(3):293-303.
[8] Cummings RJ,Mitra S,Foster TH,et al.Migration of skin dendritic cells in response to ionizing radiation exposure. Radiat Res.2009;171(6):687-697.
[9] Kawase Y,Naito S,Ito M,et al.The effect of ionizing radiation on epidermal langerhans cells-a quantitative analysis of autopsy cases with radiation therapy.J Radiat Res. 1990; 31(3):246-255.
[10] Rao V,Saunes M,JØrstad S,et al.In vitro experiments demonstrate that monocytes and dendritic cells are rendered apoptotic by extracorporeal photochemotherapy,but exhibit unaffected surviving and maturing capacity after 30 Gy gama irradiation.Scand J Immunol.2008;68(6):645-651.
[11] Shigematsu A,Adachi Y,Koike-kiriyama N,et al.Effects of low-dose irradiation on enhancement of immunity by dendritic cells.J Radiat Res.2007;48(1):51-55.
[12] Salem ML,Cole DJ.Dendritic cell recovery post-lymphodepletion: a potential mechanism for anti-cancer adoptive T cell therapy and vaccination.Cancer Immunol Immunother.2010;59(3):341-353.
[13] Torihata H,Ishikawa F,Okada Y,et al.Irradiation up-regulates CD80 expression through two different mechanisms in spleen B cells,B lymphoma cells,and dendritic cells.Immunology. 2004;112(2):219-227.
[14] 吴明媛,朱一蓓,周菊英,等.X射线照射对人树突状细胞免疫功能的影响[J].辐射防护,2006,26(1):35-39.
[15] 杨彦勇,蔡建明.电离辐射对树突状细胞的影响[J].第二军医大学学报,2011,32(10):1133-1136.
[16] Jahns J,Anderegg U,Saalbach A,et al.Influence of low dose irradiation on differentiation,maturation and T-cell activation of human dendritic cells.MutatRes.2011;709-710(1-2):32-39.
[17] 闫鹏,江其生,李峰生,等.小剂量X射线照射对人树突状细胞抗原递呈及白介素-12分泌的影响[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2012, 32(3):225-229.
[18] Wang Y S,Tsang Y W,Chi C H,et al.Synergistic anti-tumor effect of combination radio- and immunotherapy by electro-gene therapy plus intra-tumor injection of dendritic cells.Cancer Lett.2008;266(2):275-285.
[19] Roses RE,Datta J,Czerniecki BJ.Radiation as immunomodulator:implications for dendrtic cell-based immunotherapy. Radiat Res.2014;182(2):211-218.
[20] 董娟聪,林承赫,王金虎,等.低剂量X射线对小鼠树突状细胞与T淋巴细胞之间免疫反应的影响[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2012,32(1):55-57.
[21] Merrick A,Errington F,Milward K,et al.Immunosuppressive effects of radiation on human dendritic cells:reduced IL-12 production on activation and impairment of naive T-cell priming. Br J Cancer.2005;92(8):1450-1458.
[22] 李晓,江其生,李峰生,等.低剂量X射线对人树突状细胞体外迁移能力的影响及其机制[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2013, 33(5): 476-479.
[23] Liu C,Lin J,Zhao L,et al.Gamma-ray irradiation impairs dendritic cell migration to CCL19 by down-regulation of CCR7 and induction of cell apoptosis.Int J Biol Sci.2011;7(2): 168-179.
[24] 周传丰,杨彦勇,刘聪,等.大剂量γ射线对树突状细胞表型及功能的影响[J].第二军医大学学报,2011,32(4): 364-367. |