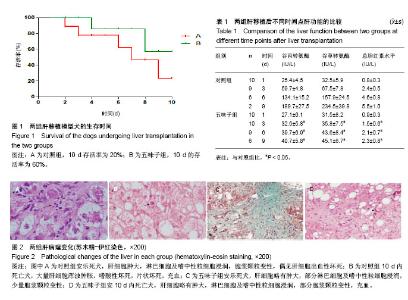
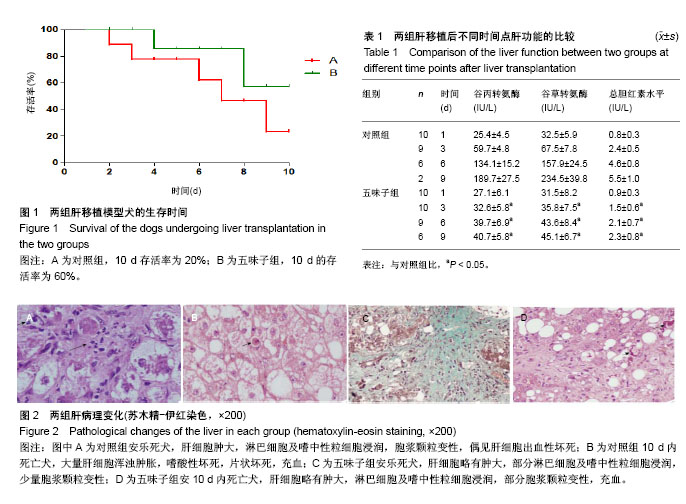
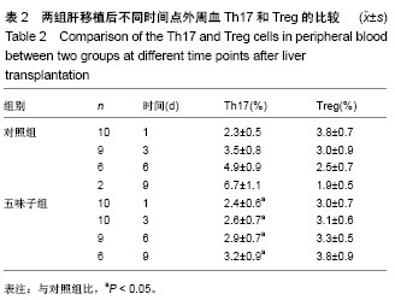
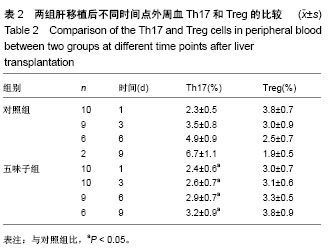
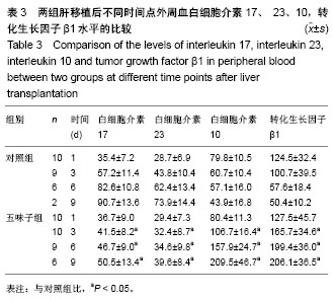
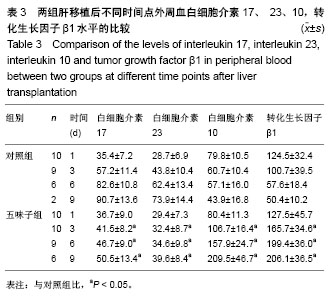
| [1] 李宜轩,陈建光,李凤,等.北五味子提取物对实验性肝纤维化大鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2014, 40(2): 285-288. [2] 俞青./北五味子不同提取物对小鼠脂质代谢的影响初探[D]. 北京中医药大学, 2013.[3] 刘宇灵,付赛,樊丽姣,等.南北五味子化学成分、药理作用等方面差异的研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2017, 23(12):228-234.[4] 蒋艳.华中五味子化学成分及生物活性的研究[D].中南民族大学,2011. [5] 陈礼治,张义,焦正,等.五味子提取物制剂对他克莫司药动学的影响[J].世界临床药物,2017,38(5):358-363.[6] 李丹. 护肝片对比格犬体内他克莫司药动学的影响及其四种有效成分同时测定[D].河北医科大学,2017.[7] 王玮,朱声挥,郭闻渊,等.LC-MS/MS测定肝移植患者体内他克莫司和五酯胶囊主要成分的方法学建立及应用[J].中国现代应用药学,2016,33(7):854-859.[8] 李冰.五味子制剂对他克莫司血药浓度的影响及对肝损伤防护作用的研究[D].福建医科大学,2013.[9] 赵德芳, 陈立坤.单纯冷藏与低温机械灌注保存肝移植前后炎症因子和凋亡因子的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(33):5322-5326.[10] 王洋,李心鑫 ,曹经琳,等.Th17细胞水平对乙型肝炎肝硬化原位肝移植术后并发症预测意义的研究[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2015, 23(8):616-621.[11] Gao Y, Zhang M, Li J, et al.Circulating FoxP3+ regulatory t and interleukin17-producing Th17 cells actively influence HBV clearance in de novo hepatitis B virus infected patients after orthotopic liver transplantation. PLoS One. 2015 ;10(9):e0137881.[12] Zhou Y, Yang X, Zhang H, et al.The roles of T helper type 17/regulatory T cells in acute rejection after liver transplantation in rats. Transplantation. 2015 ;99(6):1126-1131.[13] 陈倩,吴育晶,程能能,等.五味子提取物对大鼠肝 CYP3A 酶的双重作用[J].药学学报,2010, 45 (9): 1194−1198.[14] Wang Y, Zhang M, Liu ZW, et al.The ratio of circulating regulatory T cells (Tregs)/Th17 cells is associated with acute allograft rejection in liver transplantation. PLoS One. 2014;9(11): e112135.[15] Xu L, Gong Y, Wang B, et al.Randomized trial of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation for hepatitis B virus cirrhosis: regulation of Treg/Th17 cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 29(8):1620-1628.[16] Giles DA, Moreno-Fernandez ME, Divanovic S. IL-17 axis driven inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progression.Curr Drug Targets. 2015;16(12):1315-1323.[17] 蒋艳.华中五味子化学成分及生物活性的研究[D].中南民族大学,2011. [18] 秦小清.五味子甲素逆转肿瘤多药耐药的效应及其机制研究[D].中国人民解放军军事医学科学院,2011.[19] Li X, Sun J, Fan X, et al. Schisandrol B promotes liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018; 818 : 96-102.[20] 佟彤.四种中药多糖及两种中药油脂的免疫调节作用[D].北京协和医学院,2016.[21] Jin CY, Wang DL, Fang ZD. Effect of integrative Chinese and Western medicine in treating chronic urticaria and its impact on interleukin-10 and interleukin-8 in peripheral blood. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2008; 28(4):358-360.[22] Jiang W, Wang X, Xu X, et al. Effect of Schisandra sphenanthera extract on the concentration of tacrolimus in the blood of liver transplant patients. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010;48 (3): 224-229.[23] 王宝莲.中药五味子成分的药代动力学及代谢研究[D].中国协和医科大学,2009. [24] 张晓君,王正昕,郭闻渊,等.五酯胶囊在肝移植术后的临床应用[J].肝胆外科杂志,2010,8(02):100-102.[25] 裴彬.五味子甲素对大鼠肝细胞色素P450 3A的抑制作用[D].第二军医大学,2006.[26] 裴彬,蔡雄,缪晓辉,等.五味子甲素对大鼠肝细胞色素P4503A影响的研究[J].肝脏,2006,7 (04):261-263. [27] Li X, Fan X, Li D, et al. Schisandra sphenanthera extract facilitates liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016;44 (5): 647-652.[28] Chen Z, Guo M, Song G, et al. Schisandrin B inhibits Th1/Th17 differentiation and promotes regulatory T cell expansion in mouse lymphocytes .2016,35(6):257-264. |