Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (20): 3230-3235.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.20.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Heparanase expression in necrotic bone and peripheral blood after osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Tian Kai-xuan, Han Yong-tai
- Department of Orthopedic Diseases, Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2014-03-18Online:2014-05-14Published:2014-05-14 -
Contact:Han Yong-tai, Master, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedic Diseases, Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Tian Kai-xuan, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedic Diseases, Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Kai-xuan, Han Yong-tai. Heparanase expression in necrotic bone and peripheral blood after osteonecrosis of the femoral head[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(20): 3230-3235.
share this article
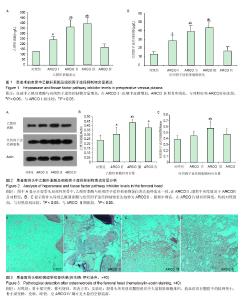
2.1 参与者数量分析 纳入患者特发性股骨头坏死患者36例,股骨颈骨折患者9例,治疗过程无脱落,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 患者术前血浆中乙酰肝素酶与组织因子途径抑制物表达 股骨头坏死患者术前血液中乙酰肝素酶与组织因子途径抑制物含量增高,在ARCOⅠ-Ⅲ期中逐渐增加,ARCO Ⅳ期有所降低。在ARCOⅡ、Ⅲ期中含量最多,两组之间差异无显著性意义,均与其他3组之间差异有显著性意义。ARCOⅠ期中含量高于对照组及ARCO Ⅳ期,差异有显著性意义。对照组及ARCO Ⅳ期比较差异无显著性意义,但ARCO Ⅳ期表达趋势较高。见图1。 2.3 两组患者患侧股骨头组织中乙酰肝素酶与组织因子途径抑制物表达 股骨头局部中乙酰肝素酶与组织因子途径抑制物表达较对照组增加(图2A),其表达趋势为ARCOⅡ、Ⅲ期中增高,在ARCO Ⅳ期有所降低,均较对照组高(图2B,C)。乙酰肝素酶的表达在ARCO Ⅱ-Ⅳ期中明显高于对照组,差异有显著性意义。ARCO Ⅲ期表达显著性高于ARCOⅡ期。组织因子途径抑制物表达中ARCO Ⅲ期高于ARCO Ⅱ期及对照组,差异有显著性意义。 2.4 两组患者股骨头组织病理学检查结果 对照组:骨小梁完整,排列规则,骨小梁中骨细胞清晰可见,空骨陷窝少见,造血细胞丰富,脂肪细胞相对较少,形态正常。实验组:股骨头坏死组织髓腔组织中脂肪细胞直径增大,大量脂肪细胞堆积,造血组织在髓腔中的比例变小,骨小梁变稀、变细,随着坏死程度加重部分骨小梁断裂,有骨碎片出现,空骨陷窝明显增多,髓腔脂肪细胞肥大,有的相互融合成泡状,至ARCO IV期骨髓腔内造血组织明显减少,骨小梁结构紊乱,广泛地骨小梁断裂、稀疏、纤细,可见大量的空骨陷窝(图3)。"

| [1] 中华医学会骨科分会显微修复学组中国修复重建外科专业委员会骨缺损及骨坏死学组.成人股骨头坏死诊疗标准专家共识(2012年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(6):606-610. [2] Sugano N, Atsumi T, Ohzono K, et al.The 2001 revised criteria for diagnosis, classification, and staging of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Sci. 2002;7(5): 601-605. [3] Sato M, Sugano N, Ohzono K, et al.Apoptosis and expression of stress protein (ORP150, HO1) during development of ischaemic osteonecrosis in the rat. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001; 3(5):751-759. [4] 李静东,赵德伟,崔大平,等.成人酒精性股骨头缺血性坏死病理与MRI影像学对坏死程度的定量分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2011,26(8):689-691. [5] Wang Y,Yin L,Lin Y,et al. Preventive effects of puerarin on alcohol-induced osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:1059-1067. [6] Markin HJ.Nontraumatic necrosis of bone(osteonecrosis). N Engl J Med.1992;326(22):1473-1479. [7] Lykissas MG, Gelalis ID, Kostas-Agnantis IP, et al.The role of hypercoagulability in the development of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2012; 4(2): e17. [8] Suehiro M, Hirano T, Mihara K, et al. Etiologic factors in femoral head osteonecrosis in growing rats. J Orthop Sci. 2000;5(1):52-56. [9] Wang Y,Li Y,Mao K,et al.Alcohol-induced adipogenesis in bone and marrow: a possible mechanism for osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003;(410):213-24. [10] Takahashi S, Fukushima W, Kubo T, et al.Pronounced risk of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head among cigarette smokers who have never used oral corticosteroids: A multicenter case-control study in japan. J Orthop Sci. 2012;17(6):730-736. [11] Zhang Y, Wang R, Li S, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 predict susceptibility to steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in chinese population. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:169. [12] 王玉峰,常楚,范广宇,等. 特发性股骨头缺血坏死动脉病变与发病机制探讨[J].中华实验外科杂志,2003,20(3):271-272. [13] Jones JP.Fat embolism and osteonecrosis.Orthop Clin North Am. 1985;16:595-633. [14] Jones JP. Fat embolism intravascular coagulation and osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop.1993;292:294-308. [15] Vlodavsky I, Friedmann Y, Elkin M, et al.Mammalian heparanase: gene cloning expression and function in tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med.1999; 5(7):793-802. [16] Glueck CJ, Freiberg RA, Sieve L, et al. Enoxaparin Prevents Progression of Stages I and II Osteonecrosis of the Hip. Clin Orthop.2005;435: 164-170. [17] Norman D, Miller Y, Sabo E, et al.The effects of enoxaparin on the reparative processes in experimental osteonecrosis of the femoral head of the rat. APMIS. 2002; 110:221-228. [18] Parish CR, Freeman C, Hulett MD. Heparanase: a key enzyme involved in cell invasion. Biochim Biophys Acta 2001; 1471:M99-108. [19] Vlodavsky I, Friedmann Y. Molecular properties and involvement of heparanase in cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2001;108:341-347. [20] Shafat I, Ben-Arush M, Issakov J, et al. Pre-clinical and clinical significance of heparanase in ewing's sarcoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(9):1857-1864. [21] Wang X, Wen W, Wu H, et al. Heparanase expression correlates with poor survival in oral mucosal melanoma. Medi Oncol. 2013;30(3):1-6. [22] Vlodavsky I, Abboud-Jarrous G, Elkin M, et al. The impact of heparanase and heparin on cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 2006;35: 116-127. [23] Nadir Y, Brenner B, Fux L, et al. Heparanase enhances the generation of activated factor X in the presence of tissue factor andactivated factor VII. Haematologica. 2010; 95: 1927-1934. [24] Nadir Y,Brenner B,Zetser A,et al. Heparanase induces tissue factor expression in vascular endothelial and cancer cells.J Thromb Haemost.2006;4:2443-2451. [25] Nadir Y,Brenner B,Gingis-Velitski S,et al.Heparanase induces tissue factor pathway inhibitor expression and extracellular accumulation in endothelial and tumor cells. Thromb Haemost. 2008;99:133-141. [26] Cenni E, Fotia C, Rustemi E, et al.Idiopathic and secondary osteonecrosis of the femoral head show different thrombophilic changes and normal or higher levels of platelet growth factors. Acta Orthop.2011;82:42-49. [27] Omeroglu H, Inan U.Inherited thrombophilia may be a causative factor for osteonecrosis of femoral head in male patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip: a case series. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2012;132:1281-1285. [28] Korompilias AV, Ortel TL, Urbaniak JR.Coagulation abnormalities in patients with hip osteonecrosis. Orthop Clin North Am 2004;35:265-271. [29] Gagala J, Buraczynska M, Mazurkiewicz T, et al.Prevalence of genetic risk factors related with thrombophilia and hypofibrinolysis in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head in poland. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2013; 14(1): 264. [30] 郭志义,冷希岗. 组织因子途径抑制物因子及其医学应用前景[J].国外医学生物医学工程分册,2002,25(5):213-219. [31] Peleda E, Davisb M,Axelmanc E,et al.Heapranase role in the treatment of avascular necrosis of femur head. Thromb Res. 2013;131(1):94-98. [32] Meirovitz A, Goldberg R, Binder A, et al.Heparanase in inflammation and inflammation-associated cancer. FEBS Journal. 2013;280(10):2307-2319. [33] Nadir Y, Brenner B.Heparanase procoagulant activity.Thromb Res. 2012;129 Suppl 1:S76-79. [34] Peled E, Rovitsky A, Axelman E, et al.Increased heparanase level and procoagulant activity in orthopedic surgery patients receiving prophylactic dose of enoxaparin. Thromb Res. 2012; 130(1):129-134. [35] Nadir Y, Kenig Y, Drugan A,et al.An assay to evaluate heparanase procoagulant activity.Thromb Res.2011; 128(4): e3-8. [36] Nadir Y, Brenner B.Heparanase procoagulant effects and inhibition by heparins.Thromb Res. 2010;125 Suppl 2:S72-76. [37] Nadir Y, Brenner B.Heparanase coagulation and cancer progression.Best Pract Res Clin Haematol.2009;22(1):85-92. [38] Katz BZ, Muhl L, Zwang E,et al.Heparanase modulates heparinoids anticoagulant activities via non-enzymatic mechanisms.Thromb Haemost. 2007;98(6):1193-1199. [39] Vlodavsky I, Ilan N, Nadir Y, et al.Heparanase, heparin and the coagulation system in cancer progression.Thromb Res. 2007;120 Suppl 2:S112-120. [40] Nasser NJ, Sarig G, Brenner B,et al.Heparanase neutralizes the anticoagulation properties of heparin and low-molecular- weight heparin.J Thromb Haemost.2006;4(3): 560-565. [41] Ihrcke NS, Parker W, Reissner KJ,et al.Regulation of platelet heparanase during inflammation: role of pH and proteinases.Platt JL.J Cell Physiol.1998;175(3):255-267. [42] Parish CR, Coombe DR, Jakobsen KB,et al.Evidence that sulphated polysaccharides inhibit tumour metastasis by blocking tumour-cell-derived heparanases.Int J Cancer. 1987;40(4):511-518. |
| [1] | Han Jie1, Chen Yueping1, Mo Jian1, Wang Dawei1, Su Bo1, Li Shuzhen1, Xia Tian2, Wang Shixin2. Ultrastructural evaluation of a rabbit model of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head after treatment with panax notoginseng saponins [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1035-1039. |
| [2] | Zhai Pei, Li Pengfei, Liang Zhenghui, Zeng Jianchun, Cai Guoxiong, Zeng Yirong, Fan Yueguang. Differential expression of miR-672-5p in rat osteoblasts after intervention by long-acting, intermediate-acting and short-acting hormones [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 809-814. |
| [3] | Yin Hao, Zhou Enchang, Pan Zhengjun, Chen Guang, Jiang Hua. Finite element analysis of the four and three cannulated screws combined with buttress plate fixation for the treatment of Pauwels III femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5133-5137. |
| [4] | Hu Liang1, Wang Junhai1, Wang Zhilie1, Xie Jinyuan1, Chen Deng1, Ding Fan2. Vascular endothelial growth factor combined with mutant hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha promotes angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 378-383. |
| [5] | Su Lianbin, Feng Eryou, Zhang Yiyuan, Zhuo Youguang, Xiao Lili, Wang Wulian, Lin Feitai. Whether direct anterior approach for total hip arthroplasty is a risk factor of eccentric reaming to the anterior column of the acetabulum? [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(20): 3117-3123. |
| [6] | Sun Liang1, Liu Wanlin1, Na Risong2, Zhao Zhenqun1. 3-Methyladenine regulating autophagy gene Beclin1 can alleviate the occurrence and development of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2391-2396. |
| [7] | Peng Chenjian, Du Bin, Sun Guangquan, Liu Xin, Xue Peng, Cao Liangquan. Three-dimensional printing beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold loaded with icariin particles for repairing osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2162-2168. |
| [8] | Zhao Jun, Zhang Xiaofeng, Xu Xilin, Wang Zhengchun, Fang Xiangchun, He Xuefeng, Xie Xinsheng, Zhang Cheng. Treating femoral head necrosis by directed differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: application and evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2127-2132. |
| [9] | Li Yunlong, Zhao Zhenqun, Liu Wanlin. Regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway on autophagy in steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(12): 1921-1929. |
| [10] | Zhang Tian-yi, Dong Wei, Mi Pan-pan, Kong Fan-lin, Zhu Jun, Wu Jian-wei, Qiao Jin-huan, Fan Guo-feng, Tian Feng-de. Three-dimensional finite element analysis on stress distribution after greater trochanter bone flap for treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(7): 1090-1095. |
| [11] | Yang Li-feng, Xiao Dong-min, Peng Chun-lei, Li Kang-hua, Yang Bin-hui, Liu Feng-hu, Wei Yong-kun, Zhang Bo, Li Wu-jian, Zheng Jin-zhe, Wang Wei-gang. Finite element analysis for self-made femoral head brace device in the treatment of early femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(7): 1096-1101. |
| [12] | Zeng Ping1, Lai Chongrong2, Li Jinyi1, Du Mindong1, He Kaiyi1, Sun Bin1, Huang Xiaohua1, Qin Gang1 . Core decompression, autologous iliac bone graft, allogeneic fibular fixation combined with traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of peri-collapse stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5746-5752. |
| [13] | Zhou Xin, Yang Yanfei, Niu Wenjie, Wei Xiaochun, Duan Wangping. Relationship between internal fixation removal and femoral head necrosis after femoral neck fracture in young and middle-aged patients: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(35): 5724-5729. |
| [14] | Fan Siqi, Zeng Ping, Lai Chongrong, Liu Xiong. Association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism with femoral head necrosis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(35): 5730-5734. |
| [15] | Tong Peng1, Wang Yang2, Liang Ying3. Establishment and comprehensive evaluation of animal models of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(32): 5169-5174. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||