Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (12): 1921-1929.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1130
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway on autophagy in steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head
Li Yunlong1, Zhao Zhenqun2, Liu Wanlin2
- 1Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2019-04-28Published:2019-04-28 -
Contact:Zhao Zhenqun, Chief physician, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Liu Wanlin, Professor, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Li Yunlong, Master candidate, Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760391 (to ZZQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yunlong, Zhao Zhenqun, Liu Wanlin. Regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway on autophagy in steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(12): 1921-1929.
share this article
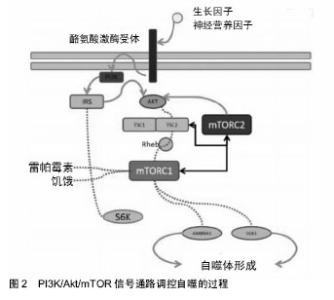
2.1 自噬的概念与过程 自噬由比利时科学家 Christian de Duve在1963年溶酶体国际会议上首先提出,2016年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖授予名誉教授Yoshinori Ohsumi,表彰他发现了自噬的机制[6]。根据细胞内底物进入溶酶体的途径不同,广义的自噬可分为3类:巨自噬、微自噬和分子伴侣介导的自噬,其中巨自噬最为普遍,多数文章所涉及的自噬为巨自噬。 自噬是一个动态的过程,可分为起始、成核、延伸、成熟和降解等阶段。自噬的过程由一系列自噬相关蛋白(ATG蛋白)所介导,超过30种蛋白质参与到自噬途径 中[7-8],相应的ATG蛋白被顺序激活,以调节自噬的不同阶段。这些蛋白可根据其功能分为不同的复合物:ULK1激酶复合物、ATG9-ATG2-WIPI1/Atg18复合物、PIK3C3/ Vps34-BECN1-PIK3R4/p150/Vps15复合物和2种泛素样连接体系(包括ATG12-ATG5和LC3/GABARAP蛋白)[9-10]。 微管相关蛋白1轻链3(LC3)是哺乳动物细胞中酵母ATG8(Aut7/Apg8)基因的同源基因,是自噬体膜上的标记蛋白,在自噬体形成的后期发挥作用,即前自噬体结构的延伸。微管相关蛋白1轻链3在哺乳动物细胞中有3种亚型,即微管相关蛋白1轻链3A、微管相关蛋白1轻链3B和微管相关蛋白1轻链3C,每个亚型可分为Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型,其中只有微管相关蛋白1轻链3B与自噬相关。前体微管相关蛋白1轻链3不在细胞中处理,而是由Atg4裂解形成胞质微管相关蛋白1轻链3Ⅰ。经裂解和泛素化后,微管相关蛋白1轻链3Ⅰ在细胞质中均匀分布,与自噬体囊泡膜上的磷脂酰乙醇胺结合形成微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ,微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ具有膜结合能力,位于自噬体膜和前自噬体膜上,当自噬被激活时,微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ随着细胞内自噬体的增加而增加。因为微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ始终稳定地位于自噬体膜上,直到和溶酶体融合,所以微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ的数量与自噬体的数量成正比,可作为自噬体的标记,微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ表达的增加可用于指示自噬的激活[11-12]。在哺乳动物细胞中,自噬刺激条件下,ULK1复合物(主要由ULK1, ATG13, ATG101和RB1CC1/FIP200组成)通过一系列磷酸化-去磷酸化过程被激活,自噬开始发生。其中对自噬诱导起最直接、最重要作用的是ULK1。在起始阶段之后,逐渐形成一个杯状的双层膜结构的吞噬泡[13]。在酵母细胞中,吞噬泡膜的成核发生在吞噬泡组装位点(PAS)。自噬的起始步骤是ULK1和PIK3C3复合物向成核位点的募集[14-15],PIK3C3复合物在成核位点产生磷脂酰肌醇3-磷酸(PtdIns3P),从而形成一个磷脂酰肌醇3-磷酸丰富的环境,增强ULK1复合物和其他ATG蛋白在生长膜上的定位[13],并触发磷脂酰肌醇3-磷酸结合效应蛋白的组装,这对于随后吞噬泡的延伸和自噬体的成熟是至关重要的[16]。 ATG12泛素样连接体系介导ATG12与ATG5的结合,然后与ATG16L1相结合[13-14],ATG16L1位于延长膜上,有利于微管相关蛋白1轻链3随后修饰为磷脂酰乙醇胺偶连形式。据推测这可能与自噬底物的选择性靶向有关[17]。在吞噬泡延伸期间,ATG9-ATG2-WIPI1复合物可能存在向正在生长的吞噬泡募集脂类的现象[18]。最后,磷脂酰肌醇3-磷酸结合蛋白、PIK3C3复合物和其相互作用的配体、以及RAB蛋白促进了自噬体与溶酶体的运输和融合[19]。 2.2 PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路 随着分子生物学的发展及检测技术的进步,自噬分子调控机制研究逐渐深入。PI3K/Akt/mTOR是调控细胞自噬的重要信号通路。大量研究表明,PI3K/Akt/mTOR 通路是经典的自噬信号通路之一,而且该通路是自噬调控过程中目前已知的唯一抑制性通路,活化后可以抑制自噬,保护细胞免受凋亡,相反,抑制该通路可以诱导自噬和凋亡[20],见图2,在细胞自噬、凋亡、细胞周期、细胞的增殖、生长、存活、运动和新陈代谢中发挥重要作用,并且与蛋白质的合成和细胞分化密切相关[21-26]。"
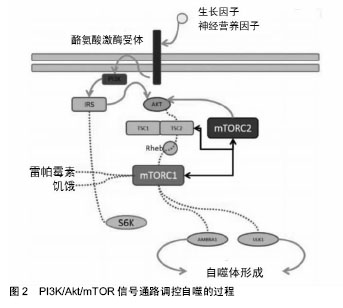

2.2.1 PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路组成 (1)PI3K:PI3K(PI-3-Kinase)的实质是脂质激酶,参与胞内增殖、分化、转移、代谢等多种过程。最初证明PI3K与自噬有关的证据是1982年发现的Ⅲ类PI3K分子的抑制剂3-甲基腺嘌呤(3-MA)能够抑制自噬,是调控自噬的重要分子。PI3K是一类相关的、协同作用的分子,可以转导下游信号。在结构上大致分为3个不同的类 别[27],Ⅰ类PI3K是由调节亚基(P85)和催化亚基(P110)组成的异二聚体,又分为2个子类别,ⅠA类和ⅠB类。ⅠA类PI3K有α,β和δ形式,由3个调节亚基p85α,p85β,或p55γ之一和3个催化亚基p110α,p110β或p110δ之一组成。唯一的ⅠB类PI3K由调节亚基p101和催化亚基p110γ组成。目前研究最多的是Ⅰ类PI3K,通常由其催化亚基指代。 受体酪氨酸激酶或G蛋白偶联受体通过磷酸化的酪氨酸残基与共有基序YXXM结合后激活调节亚基[22-24],调节亚基被激活后,催化亚基进行磷脂酰肌醇(3,4)-二磷酸(PIP2)向磷脂酰肌醇(3,4,5)-三磷酸(PIP3)的转化[24,28-29]。同源性磷酸酶-张力蛋白(PTEN)是通路中的一种抑制因子,能够抑制PIP3磷酸化,通过将PIP3去磷酸化为PIP2来抑制PI3K/Akt/mTOR途径,逆转Akt活化并阻止下游信号的传导,因此,PIP3的细胞水平由PI3K和PTEN的竞争活性决定[30]。关于Ⅱ类PI3K目前尚缺乏研究[29,31],Ⅲ类PI3K属于空泡蛋白质分拣蛋白34(VPS34:PIK3C3),是自噬的关键调节因子[32]。Ⅱ类和Ⅲ类PI3K被各种刺激所激活(可能不与磷酸酪氨酸YXXM基序结合),在细胞内发挥不同功能,其机制和结果目前正在研究中。 PI3K以其各种形式在体内发挥多种作用,包括记忆的储存和提取、代谢、胰岛素信号传导和免疫力等方面。PI3K的重要性在于其在自噬中的作用,以及其作为信号转导的第2信使,这可能是未来通过自噬及该信号通路来研究激素性股骨头坏死的一个重要方向。PI3K作为PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路的起始因子,可被多种生长因子所激活,促使Akt活化,Akt后可激活下游的靶蛋白mTOR,在自噬调控中发挥非常重要的作用。 (2)Akt:Akt又称蛋白激酶B,是PI3K活动下游的一个直接效应分子,也是一种原癌基因,可以调节多个下游效应物和信号通路,促进细胞增殖、分化、凋亡、血管生成和新陈代谢等[33]。Akt的3种主要亚型为Akt1、Akt2和Akt3。研究表明,Akt已被证实与多种人类癌症有关,Akt1在人类原发性胃腺癌中高表达,Akt2在卵巢癌、胃癌、乳腺癌和胰腺癌中高表达,Akt3在原发性黑色素瘤、卵巢肿瘤和前列腺癌中高表达[34]。在没有PTEN的抑制作用的情况下,Akt被磷酸化,并导致哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)的激活,随即调节RNA翻译、蛋白质合成、细胞生长和自噬。 Akt被磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶-1(PDPK1)和mTOR复合体2(mTORC2)磷酸化,磷酸化后的Akt具有活性,然后磷酸化mTORC1和其他下游效应物,最终影响细胞周期的进程、蛋白质合成和增殖、细胞凋亡,自噬和新陈代谢等。通过各种下游蛋白(例如mTORC1)和转录因子(例如叉头转录因子(FOXO)或翼状螺旋转录因子)来传递信号,PI3K/Akt活动在自噬的信号转导和下游通路的增殖、分化和存活中起着关键性的作用。Akt与PI3K的紧密结合以及其对自噬调控的作用可以启发今后通过研究该通路从而对自噬与激素性股骨头缺血性坏死关系做进一步研究。 (3)mTOR:mTOR是Akt的一个重要底物,是一种广泛表达的相对分子质量为289 000的丝氨酸/苏氨酸激 酶[35],是PI3K相关激酶家族的成员,进化上相对保守。在真核生物中感知并响应各种信号,来调节细胞生长、存活和其他多种生物过程[36]。mTOR包括2种功能不同的蛋白质复合体,mTOR复合体1(mTORC1)和mTORC2[30],它们的组成、活化方式和对雷帕霉素的敏感性不同[37-38],并且位于复杂的信号通路的中心,在响应多种应激条件和生长因子信号后被激活,并可以调节多种细胞功能,包括蛋白质合成(转录和翻译)、细胞生长和增殖、核糖体和线粒体合成、细胞骨架的组构、免疫应答以及自噬,是自噬的主要调节因子[39]。激活mTOR可以抑制自噬,相反,抑制mTOR可以诱导自噬发生[40]。 mTORC1和mTORC2最初是基于它们对雷帕霉素抑制作用的敏感性不同而确定的,mTORC1对雷帕霉素敏感,而mTORC2对雷帕霉素不敏感,但是,高剂量雷帕霉素的长期治疗也能抑制mTORC2的活性。雷帕霉素不损害mTOR本身的激酶活性,其机制是破坏mTOR蛋白复合物的组装。下面着重介绍一下mTOR细胞通路。 2.2.2 mTORC1的上游调控通路 mTORC1由5种蛋白组成,包括mTOR、Deptor(含有DEP结构域的mTOR反应蛋白)、mLst8(mammalian lethal with Sec13 protein 8,又称G蛋白β亚基样蛋白,GβL)、PRAS40(富含脯氨酸的Akt底物)和Raptor(mTOR调节相关蛋白[22]。mTORC1感知并整合许多细胞内外信号,例如,其可以传达营养物质可用的信号(即氨基酸)、能量水平(ATP)、生长因子(如胰岛素样生长因子1和表皮生长因子)和应激条件(缺氧或DNA损伤)[41]。生长因子和营养物质可以激活mTORC1信号,从而促进蛋白质合成、细胞生长和增殖、细胞代谢等。相反,营养缺乏、低能量水平或细胞应激会抑制mTORC1,导致生物合成率降低、分解代谢过程活化、细胞增殖减慢,以在次优条件下维持细胞活力。mTORC1的其他功能还包括转录的调节、脂质的生成、自噬诱导和线粒体活性等。在自噬诱导方面,mTORC1通过磷酸化蛋白(例如ULK1和ATG13)来阻止自噬的发生。 mTORC1上游的信号整合主要发生在结节性硬化症基因TSC1-TSC2复合物的水平上,TSC1-TSC2复合物的激活会导致mTORC1信号的整体抑制。信号整合也可以发生在溶酶体水平上:为了响应氨基酸,mTORC1被募集到细胞内靠近外围的溶酶体的表面,并被激活。在营养物质缺乏的情况下,溶酶体会聚集在核周区,这会阻碍mTORC1的激活。mTORC1的亚细胞定位在溶酶体膜上,因此它有能力整合营养和生长因子信号,并为mTORC1介导的自噬调节提供了物质基础。 2.2.3 mTORC1下游的底物和作用 mTORC1一旦激活,便会驱动一系列下游底物的磷酸化,其中最具特征的是2个下游信号分子,真核细胞翻译起始因子4E(eIF4E)-结合蛋白1(4E-BP1)和S6激酶1 [42],在哺乳动物中,S6激酶1是自噬的正向调节因子,其促进自噬的机制可能与自噬体形成和成熟过程中蛋白质的合成有关,或者直接对自噬的途径进行调节[43]。Bahrami等[41]发现,4E-BP1和S6激酶1的活化会导致蛋白质翻译的增强,进一步导致细胞的生长、分化、增殖、血管生成,以及细胞的代谢、凋亡和存活。当4E-BP1未被mTORC1磷酸化时,会抑制mRNA翻译。相反,当4E-BP1被mTORC1磷酸化时,4E-BP1从eIF4E分离,允许eIF4E将翻译起始因子eIF4G募集到大多数mRNA的5’端,从而引发帽依赖性翻译。因此,4E-BP1对蛋白质翻译的影响不仅局限于“开启”或者“关闭”蛋白质的合成,还可以通过调节帽依赖性翻译和非帽依赖性翻译之间的转换来改变新生蛋白质的范围。事实上,在特定的应激条件下,如营养物质耗尽、缺氧或代谢应激,细胞可以降低mTORC1的活性,这会导致帽依赖性翻译的停止,同时会促进必需促生存因子的非帽依赖性翻译。被mTORC1磷酸化后的S6激酶1通过磷酸化或与多个蛋白质结合从而促进mRNA的翻译。 mTORC1还可以刺激脂质合成和线粒体增殖,所有这些都会导致mTORC1介导的细胞生长和增殖,并促进能量储备,以备日后营养物质缺乏的情况。营养物质充足时,mTOR的激活可以促进细胞的合成代谢过程,营养物质缺乏时,mTOR受抑制,促进了自噬的发生。同时,有研究表明,当营养物质缺乏时,雷帕霉素对mTORC1的药理抑制作用会强烈诱导自噬。 2.2.4 mTORC2调控通路 与mTORC1所不同,目前关于mTORC2的上游调控知之甚少。mTORC2的组成是mTOR、Deptor、mLst8、雷帕霉素不敏感Rictor、mSin1(哺乳动物应激激活的蛋白激酶反应蛋白1)和Proctor(和Rictor同时观察到的蛋白)。现有研究表明,mTORC2可能通过生长因子刺激细胞而被激活[44],但其对营养物质和能量应激不敏感。最近,Liu等[38]确定了PI3K生长因子刺激与mTORC2激活之间的联系。他们发现mSin1的pH结构域是mTORC2的一个组成部分,可以干扰mTOR的激酶结构域以抑制其活性。激活的PI3K会产生PIP3,与mSin1的pH结构域相互作用,抑制其对mTOR的抑制活性,导致mTORC2的活化。 另有报道称TSC1-TSC2复合物能够激活mTORC2,而TSC1-TSC2复合物对mTORC1却是抑制作用。mTORC2通过直接与核糖体结合而被激活,激活后mTORC2促进Akt信号传导,从而刺激细胞的存活、增殖和迁移,并调节各种代谢过程。这些效应可以直接通过Akt介导的特异性底物(例如叉头框蛋白O1(FOXO1)和叉头框蛋白O3(FOXO3),其磷酸化作用会阻止其促凋亡功能)的磷酸化作用而实现,或者间接通过mTORC1对Akt的依赖性而激活。迄今为止已知的mTORC2的下游效应物主要是AGC激酶家族的成员,包括Akt、蛋白激酶C和血清糖皮质激素调节激酶[44],可以调节细胞骨架的组构、细胞存活、脂质平衡和新陈代谢[45]。 2.3 PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路在自噬调控中的作用 自噬可通过mTOR依赖途径和非mTOR 依赖途径而激活。mTOR依赖性途径,即PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路及其相关因子可以调控细胞自噬[46]。目前,有大量关于PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路与自噬关系的研究,证实了其在调控自噬中起到的重要作用[47]。而且,在已知的自噬通路中,对于以mTOR为核心的经典自噬通路的研究最为普遍[48]。 mTOR是PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路的重要效应蛋白,通过抑制ULK复合物的形成,阻断内质网膜脱落形成自噬体膜,可负调控细胞自噬[49-50]。mTORC1抑制自噬,是自噬的主要负向调控因子,PI3K/Akt通路是mTORC1主要的上游调节剂,参与不同类型细胞凋亡的存活和抑制。 Akt的活化可以通过在丝氨酸残基136上磷酸化BAD(Bcl-2相关细胞死亡激动剂)来抑制细胞凋亡[51],减少半胱氨酸肽酶Caspase9的活性,在细胞凋亡的起始步骤中起作用,并抑制叉头家族转录因子FKHRL1对细胞核的影响,这与细胞死亡诱导蛋白(如Fas配体)的转录有关,从而促进细胞存活。Akt还可以通过抑制TSC的抑制作用,通过在丝氨酸残基939上磷酸化TSC2,并结合到14-3-3蛋白上,从而促进mTOR的活化。接着,TSC2的磷酸化会促进Rheb(脑组织中丰富表达的Ras同源类似物)的活化并刺激mTOR,使其具有活性。mTOR的激活会导致许多靶蛋白的磷酸化,这些靶蛋白与翻译、核糖体合成和细胞生长相关,如S6激酶和4EBP。 饥饿或应激可以抑制mTOR的活性,从而导致AMBRA1(自噬/beclin-1调节蛋白1)的去磷酸化,激活ULK1复合物。此外,雷帕霉素通过抑制mTOR可以诱导自噬的发生[12]。雷帕霉素主要作用于对雷帕霉素高度敏感的mTORC1,而对雷帕霉素相对不敏感的mTORC2则参与Akt丝氨酸473的磷酸化过程。雷帕霉素对mTORC1的抑制还可以阻断S6K的磷酸化和IRS1(胰岛素受体底物)在几个抑制位点上的磷酸化,然后增强Akt的磷酸化,这是PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号转导通路负反馈机制的一部分,通过增加Akt的活性来诱导细胞存活并抗凋亡。 在激素性股骨头缺血性坏死中可能存在自噬过度活化的现象,过度自噬会导致骨坏死的发生,因此,通过调节PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路可以实现以下有益的结果:一方面,诱导PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路可以促进细胞存活并阻止过度自噬,从而可能有助于减少激素性股骨头缺血性坏死。mTOR调节过度自噬的一个下游靶点是死亡相关蛋白1。在氨基酸缺乏时,mTOR介导的死亡相关蛋白1磷酸化减少,死亡相关蛋白1的抗自噬功能得以恢复。因此,在mTOR缺乏的情况下,死亡相关蛋白1再度活化,防止在营养物质缺乏时过度自噬的发生[43]。同时,一项研究表明,mTOR信号通路在自噬启动过程中被抑制,但在长时间饥饿后会被重新激活。重新激活的mTOR会减弱自噬,并从自噬溶酶体中排出原溶酶体小管和囊泡,从而恢复溶酶体稳态[52]。这种负反馈机制可确保在营养补充后自噬的逆转,从而防止过多的细胞质空泡化,过多的细胞质空泡化会导致自噬型细胞死亡。另一方面,抑制mTORC1可以刺激受损或有毒蛋白质的自噬,激活mTORC2可以上调细胞存活,通过Akt间接负向地调节自噬。 2.4 自噬与激素性股骨头缺血性坏死 2.4.1 激素性股骨头缺血性坏死中存在自噬的现象 目前国内外研究对于自噬与激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的具体关系仍无定论,激素可引起组织缺血缺氧,是自噬的重要诱因[53-54],同时激素可引起股骨头缺血坏死[55]。 激素诱导的股骨头缺血性坏死与骨细胞和成骨细胞凋亡有关。赵振群等[56]通过实验发现,骨髓造血细胞DNA氧化损伤和骨细胞凋亡参与了激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的早期病理过程,并且前者先于后者发生。同时,其证明了在激素性股骨头缺血性坏死早期,激素抑制了低氧诱导因子1α的表达,并促进骨细胞凋亡的发生[57]。Jia等[58]研究发现,激素可诱导骨细胞发生凋亡和自噬,并且与其剂量有关,较低剂量的激素可以激活自噬,而较高剂量的激素会导致细胞凋亡。同时,有研究表明,地塞米松和其他糖皮质激素增加了caspase蛋白家族的表达,尤其是caspase-3,这与成骨细胞和其他细胞凋亡有关[59-60]。Feng等[61]研究发现,地塞米松诱导的成骨细胞凋亡与剂量和时间有关。最近,Liu等[62]研究发现,地塞米松可以通过增加Beclin1和微管相关蛋白1轻链3BⅡ的水平并降低P62的表达引起自噬。 目前有大量研究可以证明细胞自噬与细胞凋亡密切相关,例如,上述Liu等[62]的研究结果表明,地塞米松促进活性氧的产生,其通过激活MC3T3-E1细胞中的自噬和内质网应激来增强细胞凋亡。相反,Han等[63]却在研究中发现,地塞米松诱导的自噬可以保护细胞免于凋亡,自噬通过与Bax/Bcl-2的相互作用而成为成骨细胞凋亡的重要调节因子,表明自噬是激素诱导细胞中的一种存活机制,可以降低细胞凋亡的发生率并促进细胞存活。此外,Yang等[64]发现,血清剥夺条件下的成骨细胞存在自噬,雌二醇通过ER-ERK-mTOR途径增加自噬水平以挽救成骨细胞凋亡。但是,Wang等[65]却在研究中发现,抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路会导致成骨细胞损伤。 另外,Tong等[66]在其研究中证明了破骨细胞与激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的发生有关,破骨细胞活性及数量增加所引起的软骨下骨的骨质丢失是引起股骨头塌陷的直接原因,如果可以抑制破骨细胞的活性和数量,则能够预防激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的发生。同时,Chen等[67]在研究中发现,类固醇可以抑制骨再生并促进破骨细胞的分化,活骨Ⅰ方可通过调节股骨头破骨细胞的骨形态发生蛋白2、转化生长因子β1、Smads和OPG/ RANKL的表达,有效促进股骨头坏死的修复,对于激素性股骨头缺血性坏死也具有预防作用。另有证据表明,自噬可以调节破骨细胞分化。Kim等[68]在研究中证实,山奈酚能抑制自噬和破骨细胞生成。Liu等[69]发现,天然黄酮异甘草素可以降低微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ和Beclin 1的积累,抑制自噬并发挥抗破骨细胞生成作用。同时,雷帕霉素可以通过激活自噬来逆转天然黄酮异甘草素的抗破骨细胞生成作用,增加破骨细胞并上调破骨细胞相关基因的表达。 以上大量研究表明,自噬影响激素性股骨头缺血性坏死中成骨细胞和破骨细胞的相互作用[70]。激素性股骨头缺血性坏死发病机制与骨细胞和成骨细胞凋亡相关,细胞自噬与细胞凋亡亦密切相关,例如细胞自噬可以增加或减少细胞凋亡、改变骨量等[71]。同时,破骨细胞与激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的发生有关,自噬与破骨细胞和破骨细胞相关疾病亦有关,如骨关节炎、骨质疏松症和根尖周病变等[72-73]。综合上述研究以及此课题组先前的相关研究[74],作者认为,激素性股骨头缺血性坏死和自噬相关,激素性股骨头缺血性坏死中存在细胞自噬的现象,细胞凋亡和自噬可能共同调节激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的病理过程。 2.4.2 自噬在激素性股骨头缺血性坏死中的双向作用自噬在细胞存活中具有双重调节作用,适应性自噬可以在能量缺乏或饥饿条件下保护细胞,而过度激活的自噬则可以诱导细胞凋亡和破坏细胞成分,导致骨坏死和其他许多疾病,包括癌症、衰老和退行性疾病等。在正常细胞中,自噬通常被认为是细胞的保护机制。然而,研究者对于激素性股骨头缺血性坏死中自噬的机制却知之甚少,这也是此次研究的目的,即综述激素性股骨头缺血性坏死中PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路对自噬调控的研究进展。自噬在激素性股骨头缺血性坏死中的作用存在争议。目前主要有2种说法,一种是自噬对激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的有益作用,例如,Liao等[75]在研究中发现,普伐他汀通过激活内皮祖细胞自噬从而可能有助于改善地塞米松诱导的股骨头缺血性坏死,降低股骨头坏死的风险,相反,抑制自噬,细胞则迅速发展为坏死,并观察到普伐他汀是通过上调微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ/ Beclin-1和自噬体形成来增强内皮祖细胞中的自噬活性的。同时,Zhu等[76]发现,自噬的激活可能是地塞米松诱导细胞凋亡的一种保护机制,甲状旁腺激素可通过增强自噬来对激素诱导的股骨头缺血坏死产生保护作用。而且,Hu等[77]在研究中首次证明了球状脂联素可以通过AMPK/mTOR信号通路激活自噬,保护软骨细胞,免受H2O2诱导的细胞凋亡,从而达到减少或预防骨关节炎的作用。同时,近期的一系列研究表明,AMPK激活后可以保护成骨细胞免受H2O2诱导的细胞凋亡,自噬激活对于成骨细胞具有保护作用[78-81]。这可以启发将自噬与激素性股骨头缺血性坏死相联系,自噬对激素性股骨头缺血性坏死中股骨头软骨细胞及成骨细胞是否也有类似的作用,值得深入研究。还有研究说明了自噬对于骨转移的积极作用,例如氟伐他汀通过诱导p53表达,激活裸鼠肺腺癌细胞中AMPK-mTOR依赖的自噬,从而增加了抗骨转移作用,减少了骨坏死的发生。 虽然目前有众多关于自噬的积极作用,但是仍有研究表明了自噬对激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的不利作用,例如,Li等[82]通过实验发现,在地塞米松诱导的体外成骨细胞损伤中,自噬被过度激活,而抑制自噬可以减弱地塞米松诱导的细胞损伤,从而有助于减少骨坏死。因此,过度活化的自噬可能是导致激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的重要因素。 通过上述研究结果可以发现,目前对于自噬与激素性股骨头缺血性坏死发病机制关系的研究才刚刚开始,因此,究竟是抑制自噬还是激活自噬有助于改善激素性股骨头缺血性坏死,抑制或激活自噬的程度如何,以及PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路如何通过调控自噬来影响激素性股骨头缺血性坏死等问题有待进一步研究。"

| [1] Okazaki S, Nagoya S, Matsumoto H, et al. Development of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head requires toll-like receptor 7 and 9 stimulations and is boosted by repression on nuclear factor kappa B in rats. Lab Invest. 2015;95(1): 92-99.[2] Ao W, Ming R, Jincheng W. The pathogenesis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic review of the literature. Gene. 2018;671:103-109. [3] Lian JB, Stein GS, Wijnen AJV, et al. MicroRNA control of bone formation and homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012; 8(4): 212-227. [4] Li M, Gao P, Zhang J. Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis: potential and emerging therapeutic targets for cardiac diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(3): 332.[5] Xue X, Feng Z, Li Z, et al. Salidroside inhibits steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway: In vitro and in vivo studies. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 17(3): 3751-3757.[6] Van Noorden R, Ledford H. Medicine Nobel for research on how cells 'eat themselves'. Nature. 2016;538(7623): 18-19.[7] Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Bravo-San Pedro J, et al. Autophagy in malignant transformation and cancer progression. Embo J. 2015; 34(7): 856-880.[8] Rebecca VW, Amaravadi RK. Emerging strategies to effectively target autophagy in cancer. Oncogene. 2016; 35(1): 1-11.[9] Tanida I. Autophagosome formation and molecular mechanism of autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14(11): 2201-2214.[10] Shibutani S, Yoshimori T. A current perspective of autophagosome biogenesis. Cell Res. 2014;24(1): 58-68.[11] Zhang Z, Singh R, Aschner M. Methods for the Detection of Autophagy in Mammalian Cells. Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2016; 69:20.12.1-20.12.26.[12] Klionsky D, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 2016;12(1): 1-222.[13] Carlsson S, Simonsen A. Membrane dynamics in autophagosome biogenesis. J Cell Sci. 2015;128(2): 193-205.[14] Russell R, Yuan H, Guan K. Autophagy regulation by nutrient signaling. Cell Res. 2014;24(1): 42-57.[15] Koyama-Honda I, Itakura E, Fujiwara TK, et al.Temporal analysis of recruitment of mammalian ATG proteins to the autophagosome formation site. Autophagy. 2013;9(10): 1491-1499.[16] Dall'Armi C1, Devereaux KA, Di Paolo G. The role of lipids in the control of autophagy. Curr. Biol. 2013;23: R33-45.[17] Johansen T, Lamark T. Selective autophagy mediated by autophagic adapter proteins. Autophagy. 2011;7(3): 279-296.[18] Suzuki K, Akioka M, Kondo-Kakuta C, et al. Fine mapping of autophagy-related proteins during autophagosome formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(Pt 11): 2534-2544.[19] Shen H, Mizushima N. At the end of the autophagic road: an emerging understanding of lysosomal functions in autophagy . Trends Biochem Sci. 2014;39(2): 61-71.[20] David HS, P rez-Rojas JM, Jacqueline HD, et al. The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Cellular Signalling. 2014;26(12): 2694-2701.[21] Bahrami A, Hassanian S, Shahidsales S, et al. Targeting RAS signaling pathway as a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(3): 2058-2066.[22] Dibble C, Cantley L. Regulation of mTORC1 by PI3K signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25(9): 545-555.[23] Fruman D, Rommel C. PI3K and cancer: lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014; 13(2): 140-156.[24] Thorpe L, Yuzugullu H, Zhao J. PI3K in cancer: divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and therapeutic targeting . Nat Rev Cancer. 2015; 15(1): 7-24.[25] Duzgun Z, Eroglu Z, Biray Avci C. Role of mTOR in glioblastoma. Gene. 2016;575(2 Pt 1): 187-190.[26] Xia P, Xu X. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in cancer stem cells: from basic research to clinical application. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(5): 1602-1609.[27] Vanhaesebroeck B, Stephens L, Hawkins P. PI3K signalling: the path to discovery and understanding. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(3): 195-203.[28] Zou H, Li L, Garcia Carcedo I, et al. Synergistic inhibition of colon cancer cell growth with nanoemulsion-loaded paclitaxel and PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor BEZ235 through apoptosis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:1947-1958.[29] Vanhaesebroeck B, Guillermet-Guibert J, Graupera M, et al. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(5): 329-341.[30] Avan A, Narayan R, Giovannetti E, et al. Role of Akt signaling in resistance to DNA-targeted therapy. World J Clin Oncol. 2016;7(5): 352-369.[31] Gao Y, Yuan C, Yuan W. Will targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling work in hematopoietic malignancies? Stem Cell Investig. 2016;3:31.[32] Jaber N, Dou Z, Chen J, et al. Class III PI3K Vps34 plays an essential role in autophagy and in heart and liver function . Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012; 109(6): 2003-2008.[33] Yu J, Cui W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development. 2016; 143(17): 3050-3060.[34] Lin H, Lin C, Huo C, et al. AKT3 promotes prostate cancer proliferation cells through regulation of Akt, B-Raf, and TSC1/TSC2. Oncotarget. 2015; 6(29): 27097-27112.[35] Maiese K. Targeting molecules to medicine with mTOR, autophagy and neurodegenerative disorders. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;82(5): 1245-1266.[36] Coffey R, Shi Y, Long M, et al. Ubiquilin-mediated Small Molecule Inhibition of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 (mTORC1) Signaling. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(10): 5221-5233.[37] Yang H, Rudge D, Koos J, et al. mTOR kinase structure, mechanism and regulation. Nature. 2013; 497(7448): 217-223.[38] Liu P, Gan W, Chin Y, et al. PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-Dependent Activation of the mTORC2 Kinase Complex. Cancer Discov. 2015; 5(11): 1194-209.[39] Heras-Sandoval D , Pérez-Rojas, Jazmin M, et al. The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Cell Signal. 2014;26(12): 2694-2701.[40] Wang K, Yang H, Jiang W, et al. Puquitinib mesylate (XC-302) induces autophagy via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal cancer cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015; 36(6): 1556-1562.[41] Bahrami A, Khazaei M, Hasanzadeh M, et al. Therapeutic potential of targeting pi3k/akt pathway in treatment of colorectal cancer: rational and progress. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(3): 2460-2469.[42] Walker N, Belloli E, Stuckey L, et al. Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTORC2 as Key Signaling Intermediates in Mesenchymal Cell Activation. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(12): 6262-6271.[43] Hu Z, Yang B, Mo X, et al. Mechanism and Regulation of Autophagy and Its Role in Neuronal Diseases . Mol Neurobiol. 2015; 52(3): 1190-209.[44] Oh W, Jacinto E. mTOR complex 2 signaling and functions. Cell Cycle. 2011;10(14): 2305-2316.[45] Laplante M, Sabatini D. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012;149(2): 274-293.[46] Wang Z, Wang Y, Huang Y, et al. bFGF regulates autophagy and ubiquitinated protein accumulation induced by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion via the activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:9287.[47] Cao Z, Yang Y, Yu S, et al. Pogostone induces autophagy and apoptosis involving PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in human colorectal carcinoma HCT116 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;202:20-27.[48] Sun X, Du F, Liu S. Modulation of autophagy in exJSRV-env- transfected cells through the Akt/mTOR and MAPK signaling pathway . Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;485(3): 672-678.[49] Su R, Jin X, Zhang W, et al. Particulate matter exposure induces the autophagy of macrophages via oxidative stress-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Chemosphere. 2017;167:444-453.[50] Li Y, Liu Y, Shi F, et al. Knockdown of Rap1b Enhances Apoptosis and Autophagy in Gastric Cancer Cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Oncol Res. 2016;24(5): 287-293.[51] Meng Y, Lin Z, Ge N, et al. Ursolic Acid Induces Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway . Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(7): 1471-1486.[52] Yu L, Mcphee C, Zheng L, et al. Termination of autophagy and reformation of lysosomes regulated by mTOR. Nature. 2010;465(7300): 942-946.[53] Zhao Z, Bai R, Liu W, et al. Roles of oxidative DNA damage of bone marrow hematopoietic cells in steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(1). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15017706.[54] Bai R, Na Y, Liu W, et al. Quantitative assessment of ABCB1 polymorphisms and non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femur head risk. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2016;9(11): 21542-21548.[55] 冯卫,刘万林,苏秀兰,等. 激素性股骨头缺血坏死与血管壁中主要促血管生长因子生理活性关系的实验研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2008, 10(10): 960-964.[56] 赵振群,刘万林,龚瑜林,等. 骨髓造血细胞DNA氧化损伤与骨细胞凋亡在早期激素性股骨头坏死中的表现[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(11): 1652-1657.[57] 赵振群,张志峰,刘万林,等. 激素性股骨头坏死过程中低氧诱导因子1α与骨细胞凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(51): 8201-8207.[58] Jia J, Yao W, Guan M, et al. Glucocorticoid dose determines osteocyte cell fate. FASEB J. 2011;25(10): 3366-3376.[59] Dai W, Wang L, Jin G, et al. Beta-ecdysone protects mouse osteoblasts from glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in vitro. Planta Med. 2017;83(11): 888-894.[60] Ryu J, Ko J, Kim M, et al. Prednisolone induces apoptosis in corneal epithelial cells through the intrinsic pathway. Sci Rep, 2017; 7(1): 4135.[61] Feng Z, Zheng W, Tang Q, et al. Fludarabine inhibits STAT1-mediated up-regulation of caspase-3 expression in dexamethasone-induced osteoblasts apoptosis and slows the progression of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head in rats. Apoptosis. 2017;22(8): 1001-1012.[62] Liu W, Zhao Z, Na Y, et al. Dexamethasone-induced production of reactive oxygen species promotes apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in MC3T3-E1 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2018; 41(4): 2028-2036.[63] Han Y, Zhang L, Xing Y, et al. Autophagy relieves the function inhibition and apoptosis?promoting effects on osteoblast induced by glucocorticoid . Int J Mol Med. 2018; 41(2): 800-808.[64] Yang Y, Chen K, Li B, et al. Estradiol inhibits osteoblast apoptosis via promotion of autophagy through the ER-ERK-mTOR pathway. Apoptosis. 2013; 18(11): 1363-1375.[65] Wang J, Ma X, Feng Y, et al. Magnesium ions promote the biological behaviour of rat calvarial osteoblasts by activating the pi3k/akt signalling pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017; 179(2): 284-293.[66] Tong P, Xiao L, Ji W, et al. Research on the role of metabolism of fatty substance and osteoclast activity during the development of steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009;22(2): 110-113.[67] Chen W, Kong X, Wan R, et al. Effects of huogu I formula (I) on correlated factors of bone regeneration in chickens with steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head. Chin J Integr Med. 2012;18(5): 378-384.[68] Kim CJ, Shin SH, Kim BJ, et al. The effects of kaempferol- inhibited autophagy on osteoclast formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(1): E125.[69] Liu S, Zhu L, Zhang J, et al. Anti-osteoclastogenic activity of isoliquiritigenin via inhibition of NF-κB-dependent autophagic pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;106:82-93.[70] Luo P, Gao F, Han J, et al. The role of autophagy in steroid necrosis of the femoral head: a comprehensive research review. Int Orthop. 2018;42(7): 1747-1753.[71] 孟晨阳,刘万林,白锐,等. 激素性股骨头缺血性坏死发病机制中的细胞自噬[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(8): 1280-1287.[72] Hocking L, Whitehouse C, Helfrich M. Autophagy: a new player in skeletal maintenance? J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27(7): 1439-1447.[73] Manolagas S, Parfitt A. For whom the bell tolls: distress signals from long-lived osteocytes and the pathogenesis of metabolic bone diseases. Bone. 2013; 54(2): 272-278.[74] 王文选,赵振群,刘万林,等. Beclin 1和MAP1-LC3在家兔激素性股骨头缺血坏死中表达的实验研究[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2017, 23(9): 811-815.[75] Liao Y, Zhang P, Yuan B, et al. Pravastatin protects against avascular necrosis of femoral head via autophagy. Front Physiol. 2018;9:307.[76] Zhu L, Chen J, Zhang J, et al. Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Induces Autophagy to Protect Osteocyte Cell Survival from Dexamethasone Damage. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23: 4034-4040.[77] Hu J, Cui W, Ding W, et al. Globular Adiponectin Attenuated H2O2-Induced Apoptosis in Rat Chondrocytes by Inducing Autophagy Through the AMPK/ mTOR Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(1): 367-382.[78] Zhu Y, Zhou J, Ao R, et al. A-769662 protects osteoblasts from hydrogen dioxide-induced apoptosis through activating of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Int J Mol Sci. 2014; 15(6): 11190-1203.[79] She C, Zhu LQ, Zhen YF, et al. Activation of AMPK protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced osteoblast apoptosis through autophagy induction and NADPH maintenance: New implications for osteonecrosis treatment? Cell Signal. 2014; 26(1): 1-8.[80] Kim JH, Kang HM, Yu SB, et al. Cytoprotective Effect of Flavonoid-Induced Autophagy on Bisphosphonate Mediated Cell Death in Osteoblast. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119: 5571-5580.[81] Liu W, Mao L, Ji F, et al. Targeted activation of AMPK by GSK621 ameliorates H2O2-induced damages in osteoblasts. Oncotarget. 2017;8: 10543-10552. [82] Li X, Li Y, Li L, et al. Overactivated autophagy contributes to steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(1): 367-372.[83] Yu X, Long Y, Shen H. Differential regulatory functions of three classes of phosphatidylinositol and phosphoinositide 3-kinases in autophagy. Autophagy. 2015;11(10): 1711-1128. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [4] | Xie Yang, Zhang Shujiang, Liu Menglan, Luo Ying, Yang Yang, Li Zuoxiao. Mechanism by which rapamycin protects spinal cord neurons in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 695-700. |
| [5] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [6] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||