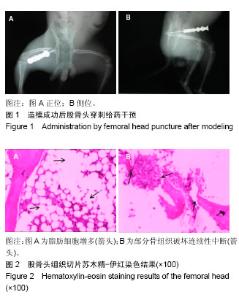
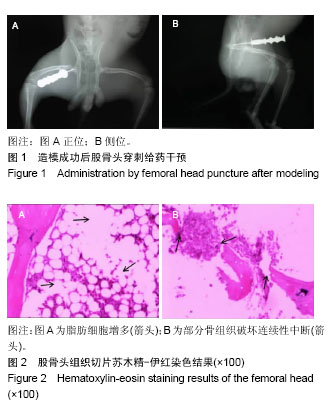
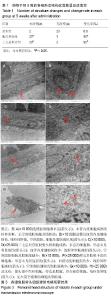
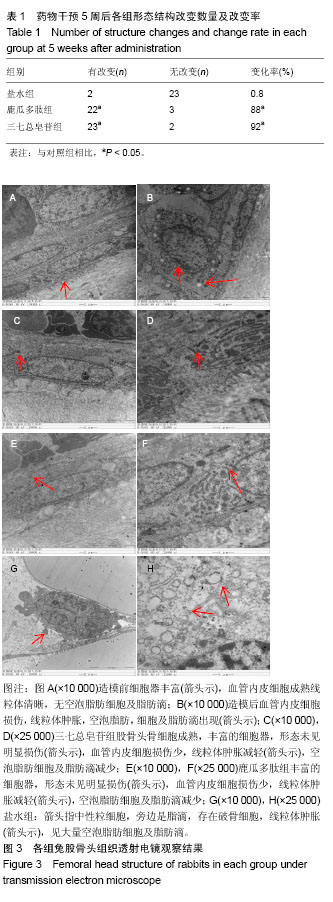
| [1] Fukushima W, Fujioka M, Kubo T, et al.Nationwide epidemiologic survey of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010,468(10):2715-24. [2] 王大伟,史宝明,李小峰,等.三七总皂苷干预股骨头缺血性坏死兔成骨细胞护骨素基因的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(20):3728-3732.[3] 强辉,冯敏,刘慧通,等.三七皂苷对激素性股骨头坏死早期细胞凋亡的影响及其机制[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2018, 39(1): 111-115[4] 王大伟,潘华,李红波,等.三七总皂苷对酒精诱导骨髓基质干细胞分化影响的实验研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(8):1410-1413. [5] 韩杰,王世鑫,莫坚,等.三七总皂苷对激素性股骨头缺血性坏死模型兔骨组织血管内皮生长因子和骨形态形成蛋白-2 mRNA表达的影响[J]. 广西医学, 2016, 38(5):611-614.[6] 王伟,刘利英,王坤正,等. 激素性股骨头坏死模型的建立及其发病机理的探讨[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2007, 28(5): 544-547.[7] 魏伟,吴希美,李元建.药理实验方法学[M]. 4版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2010: 1243-1245.[8] Deckers MM, van Bezooijen RL, van der Horst G, et al.Bone morphogeneficp proteins stimulate angiogenesis through osteoblast-derived vascular endothelial growth factor.Endocrinology.2002;143:1545-1553 [9] 费腾,阎作勤.激素性股骨头坏死发病机制的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2011,5(4):504-508. [10] 周正新.袁浩教授论治股骨头缺血性坏死的学术特点[J].中医正骨,2003,15(6):56.[11] 陈卫衡.股骨头坏死“痰瘀同治”的理论基础[J].江苏中医药, 2008,40(5):3-4.[12] 冯伟,傅文彧,魏义勇,等.单味中药对成骨相关基因表达的影响[J].中医正骨,2004,16(3):6-8. [13] 仲兆富,安建原,刘诗荣,等.化痰逐瘀法治疗Ⅱ期酒精性股骨头缺血性坏死的疗效观察[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志2003,11(6): 41-43. [14] 滕居赞,林宝举,苏波,等. 三七总皂苷对激素性股骨头坏死家兔血液流变学影响[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2013,15(007): 31-33. [15] Leva E, Huscher C, Rode H, et al. Management of traumatic complete pancreatic fracture in a child: case report and review of literature. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2008; 18(2):321-323.[16] 韩涛,谢雁鸣,黎元元,等. 应用鹿瓜多肽注射液治疗的颈椎病患者的临床特征与联合用药研究[J].中国全科医学, 2018(4): 480-485.[17] 段峰,温克寒,王心彧,等. 成骨细胞增殖分化中的地塞米松和鹿瓜多肽:抑制还是促增殖分化?[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(15):2314-2319.[18] 申利彬.鹿瓜多肽治疗激素性股骨头坏死组织学分析[J]. 临床医学, 2011, 31(4):103-104.[19] 刘万林.激素性股骨头缺血坏死发病机理及其研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2000, 7(2):169-172.[20] Jones JP. Epidemiological risk factors for non-traumatic osteonecrosis. Der Orthopäde.2000;29(5):370.[21] Kawai K, Tamaki A, Hirohata K. Steroid-induced accumulation of lipid in the osteocytes of the rabbit femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67(5):755-763. [22] Jones JP Jr . lntravascular cosgulation and osteonecrosis . Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; (277) : 41-53 .[23] 曾荣香,徐志毅,雷凯君,等.补阳还五汤对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠血液流变学、凝血及纤溶的影响[J].中华中医药学刊, 2012,30 (8):1852-1854 .[24] 陈晓波,陈雷雷,洪郭驹,等.桃红四物汤对激素性股骨头坏死兔股骨头微结构的影响及其机制[J],山东医药,2017,57(32):5-9.[25] 吴惠斌,史宝明.三七总皂苷对兔酒精性股骨头坏死模型组织形态学的影响[J].甘肃中医学院学报,2012,29(6):4-7. |