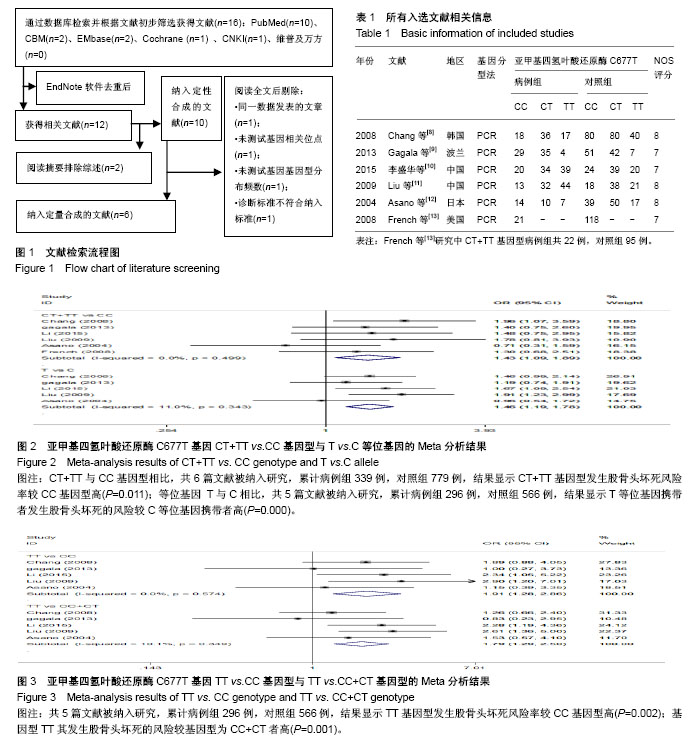
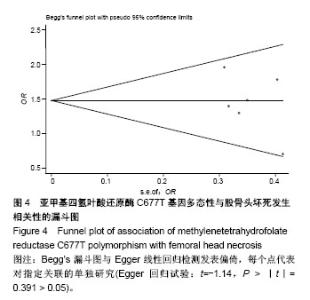
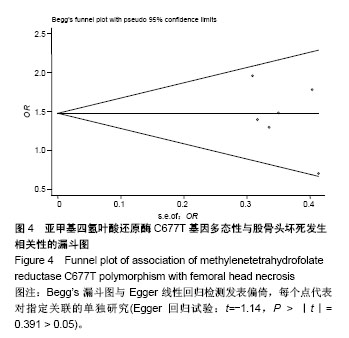
| [1] 中华医学会骨科分会显微修复学组.成人股骨头坏死诊疗标准专家共识(2012年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(6):51-56.[2] 赵海燕,夏亚一,康鹏德.股骨头坏死病因与发病机制研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(8):604-607.[3] Zalavras CG, Vartholomatos G, Dokou E, et al. Genetic background of osteonecrosis: associated with thrombophilic mutations? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;422(422):251. [4] Giusti B, Porciani MC, Brunelli T, et al. Phenotypic variability of cardiovascular manifestations in Marfan Syndrome Possible role of hyperhomocysteinemia and C677T MTHFR gene polymorphism. Eur Heart J. 2003;24(22):2038. [5] 方理刚,朱文玲,朱广瑾,等. 亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶基因多态性及血中同型半胱氨酸和叶酸水平与冠心病的关系[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2002, 30(9):515-519.[6] 黄一宁,赵宇岚,李舜伟. 同型半胱氨酸和MTHFR基因多态性与缺血性脑血管病的关系[J]. 中华医学杂志,2002,82(2):119-122.[7] 张颖冬,朱志刚,刘阳. 血浆Hcy水平及MTHFR基因多态性与脑梗死的关系[J]. 中风与神经疾病,2001,18(4):198-200.[8] Chang JD, Hur M, Lee SS, et al. Genetic background of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in the korean population. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(5):1041-1046. [9] Gagala J, Butraczynska M, Mazurkiewicz T, et al. Prevalence of genetic risk factors related with thrombophilia and hypofibrinolysis in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Poland. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2013;14(1):1-7. [10] 李盛华,周明旺,郭铁峰,等. 非创伤性股骨头坏死中医体质类型与亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶C677T位点多态性的相关性研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2015,30(6):2194-2198.[11] Liu B, Li Z, Sun W, et al. Relationship between alcohol induced osteonecrosis of femoral head and single nucleotide polymorphisms of methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase 677 C/T. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;23(9):1079. [12] Asano T, Takahashi KA, Fujioka M, et al. Relationship between postrenal transplant osteonecrosis of the femoral head and gene polymorphisms related to the coagulation and fibrinolytic systems in Japanese subjects. Transplantation. 2004;77(2):220. [13] French D, Hamilton LH, Mattano LA Jr, et al. A PAI-1 (SERPINE1) polymorphism predicts osteonecrosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. Blood. 2008;111(9):4496-4499. [14] Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603-605. [15] Garcia FL, Júnior EL, Picado CH. Coagulation disorders in patients with femoral head osteonecrosis. Acta Ortopedica Brasileira. 2013; 21(1):43-45. [16] 梁长流,蒋善群,彭少杰,等. MTHFR C677T基因多态性与高同型半胱氨酸型高血压关联性研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2011,15(6):480-484.[17] 付龙,孙溢晗,张月兰. MTHFR基因C677T多态性与H型高血压合并冠心病患者HCY、冠状动脉病变的关系[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2015,44(4): 351-356.[18] Weisberg I, Tran P, Christensen B, et al. A second genetic polymorphism in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) associated with decreased enzyme activity. Mol Genet Metab. 1998;64(3):169-172. [19] Lentz SR, Piegors DJ, Fernández JA, et al. Effect of hyperhomocysteinemia on protein C activation and activity. Blood. 2002;100(6):2108-2112. [20] Au-Yeung KK, Woo CW, Sung FL, et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia activates nuclear factor-kappaB in endothelial cells via oxidative stress. Circ Res. 2004;94(1):28-36. [21] Bernbeck B, Mauzkörholz C, Zotz RB, et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism and glucocorticoid intake in children with ALL and aseptic osteonecrosis. Klinische Pädiatrie. 2003;215(6):327. [22] Glueck CJ, Freiberg RA, Fontaine RN, et al. Hypofibrinolysis, thrombophilia, osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;386(386): 19-33. [23] Zulli A, Buxton BF, Black MJ, et al. The immunoquantification of caveolin-1 and enos in human and rabbit diseased blood vessels. J Histochem Cytochem. 2006;4(2):151-159. [24] Lentz SR. Mechanisms of homocysteine-induced atherothrombosis. J Thromb Haemostasis, 2005;3(8):1646-1654. [25] Juo SH, Liao YC, Kuo CL, et al. The MTHFR 677 C/T polymorphism influences plasma levels of adhesion molecules and nitric oxide. Thromb Res. 2008;121(4):549-554. [26] Ueland PM, Hustad S, Schneede J, et al. Biological and clinical implications of the MTHFR C677T polymorphism. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22(4):195-201. |