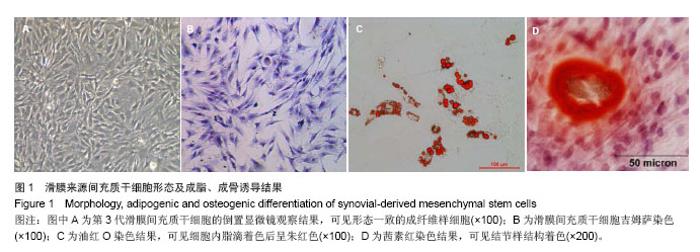
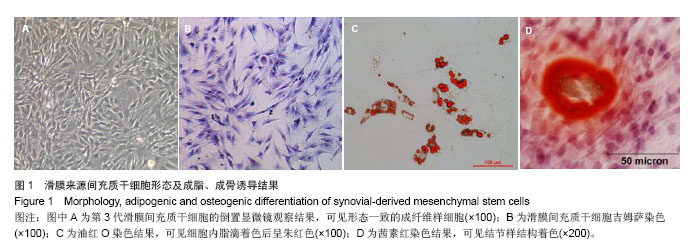
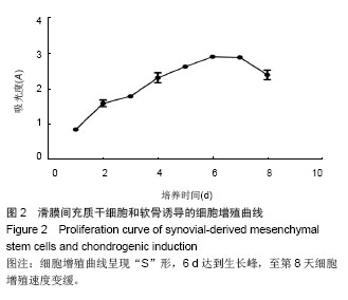
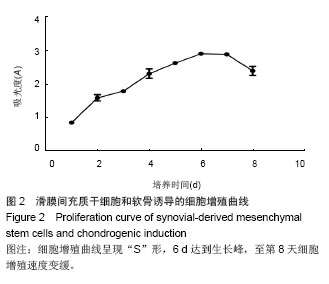
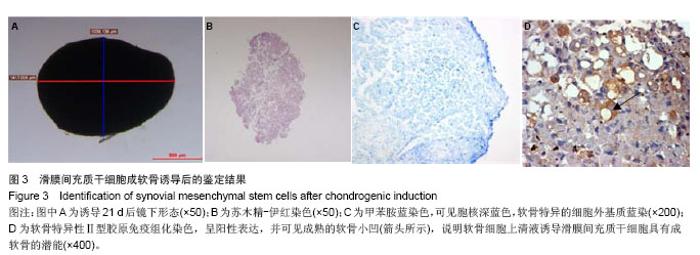
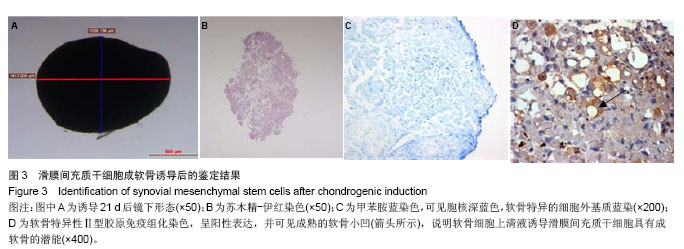
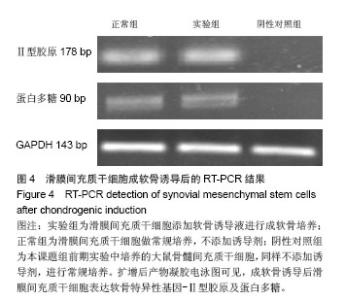
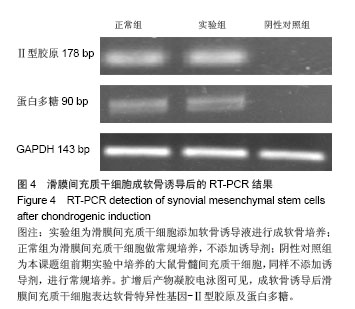
| [1]De Bari C, Dell'Accio F, Tylzanowski P,et al.Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from adult human synovial membrane.Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(8):1928-1942.
[2]Sakaguchi Y, Sekiya I, Yagishita K,et al.Comparison of human stem cells derived from various mesenchymal tissues: superiority of synovium as a cell source.Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(8):2521-2529.
[3]Yoshimura H, Muneta T, Nimura A, et al. Comparison of rat mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, synovium, periosteum, adipose tissue, and muscle. Cell Tissue Res. 2007; 327: 449-462.
[4]Brown TD, Johnston RC, Saltzman CL, et al. Posttraumatic osteoarthritis: a first estimate of incidence, prevalence, and burden of disease. J Orthop Trauma.2006;20:739-744.
[5]Simon TM, Jackson DW. Articular cartilage: injury pathways and treatment options. Sports Med Arthrosc.2006;14:146.
[6]Buckwalter JA. Articular cartilage injuries. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;402:21-37.
[7]Vats A, Bielby RC, Tolley NS, et al. Stem Cells. Lancet. 2005; 366:592-602.
[8]Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284:143-147.
[9]Jung Y, Bauer G, Nolta JA. Concise review: Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells: progress toward safe clinical products. Stem Cells. 2012; 30:42-47.
[10]Archer CW, Morrison H, Pitsillides AA. Cellular aspects of the development of diarthrodial joints and articular cartilage. J Anat.1994;184:447.
[11]Merida-Velasco JA, Sanchez-Montesinos I, Espin-Ferra J, et al. Development of the human knee joint. Anat Rec. 1997; 248(2):269-278.
[12]Edwards J. The nature and origins of synovium: experimental approaches to the study of synoviocyte differentiation. J Anat. 1994;184:493-501.
[13]Kurth T, Dell’Accio F, Crouch V, et al. Functional mesenchymal stem cell niches in adult mouse knee joint synoviumin vivo. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:1289-1300.
[14]Vandenabeele F, De Bari C, Moreels M, et al. Morphological and immunocytochemical characterization of cultured fibroblast-like cells derived from adult human synovial membrane. Arch Histol Cytol.2003;66:145-153.
[15]Pei M, He F, Vunjack-Novakovic G. Synovium derived stem cell-based chondrogenesis. Differentiation. 2008;76:1044.
[16]Jung H1, Park JS, Yeom J, et al.3D Tissue Engineered Supramolecular Hydrogels for Controlled Chondrogenesis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Biomacromolecules. 2014; 15(3):707-714.
[17]Klein T, Malada J, Sah R, et al Tissue engineering of articular cartilage with biomimetric zones.Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15: 143.
[18]Schumacher BL, Hughes CE, Kuettner KE, et al. Immunodetection and partial cDNA sequence of the proteoglycan, superficial zone protein, synthesized by cells lining synovial joints. J Orthop Res.1999;17:110.
[19]Pei M, He F, Kish V, et al. Engineering of functional cartilage tissue using stem cells from synovial lining: a preliminary study. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2008;466:1880.
[20]Pacifici M, Koyama E, Iwamoto M, et al. Development of articular cartilage: what do we know about it and how may it occur? Connect Tissue Res.2000;41:175.
[21]Archer CW, Dowthwaite GP, Francis-West P. Development of synovial joints. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2003; 69: 144.
[22]Bandara G, Georgescu HI, Lin CW, et al. Synovial activation of chondrocytes: evidence for complex cytokine interactions. Agents Actions.1991;34:285.
[23]Trippel SB.Growth factor actions on articular cartilage. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1995;43:129-132.
[24]Hatakeyama Y, Tuan RS, Shum L.Distinct functions of BMP4 and GDF5 in the regulation of chondrogenesis.J Cell Biochem. 2004;91(6):1204-1217.
[25]Blaney Davidson EN, van der Kraan PM, van den Berg WB.TGF-beta and osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(6):597-604.
[26]史新立,胡堃,孟祥提. 关节软骨修复与相关细胞因子的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(11):2047-2050.
[27]An C, Cheng Y, Yuan Q,et al.IGF-1 and BMP-2 induces differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes-like cells.Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38(4): 1647-1654.
[28]Schmidt MB, Chen EH, Lynch SE.A review of the effects of insulin-like growth factor and platelet derived growth factor on in vivo cartilage healing and repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14(5):403-412.
[29]Mishina Y.Function of bone morphogenetic protein signaling during mouse development. Front Biosci. 2003; 8:855-869
[30]Danisovic L, Lesny P, Havlas V, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Appl Biomed. 2007;5:139-150.
[31]Thorpe SD, Buckley CT, Vinardell T, et al. The response of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to dynamic compression following TGF-beta3 induced chondrogenic differentiation. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38:2896-2909.
[32]Lutz M, Knaus P. Integration of the TGF-b pathway into the cellular signalling network. Cell Signal. 2002;14:977-988.
[33]Schmierer B, Hill CS. TGFb-SMAD signal transduction: Molecular specificity and functional flexibility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:970-982.
[34]Fischer L, Boland G, Tuan RS. Wnt signaling during BMP-2 stimulation of mesenchymal chondrogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2002;84:8160-831.
[35]贺明,付勤,王广斌,等. 转化生长因子β1转染骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(19): 3685-3689.
[36]张清林,吕惠成,吴一民. 转化生长因子β1联合骨形态发生蛋白2诱导骨髓间充质干细胞体外向软骨细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(24): 4371-4375.
[37]赵基栋,苗宗宁,钱寒光,等. 转化生长因子β3诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为软骨细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(40): 7497-7500.
[38]李放,文天用. 转化生长因子β1/胰岛素样生长因子1与髓核细胞诱导脂肪间充质干细胞向髓核样软骨细胞分化的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(23): 4217-4221.
[39]王万宗. 体外三维培养条件下转化生长因子β1基因转染的兔骨髓间充质干细胞促成软骨细胞分化的实验研究[D]. 第二军医大学,2006.
[40]彭吾训,王蕾,邓进,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在含转化生长因子β1诱导培养基及二维培养条件下向软骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(29):5759-5762.
[41]向川,杜靖远,翁习生,等. 转化生长因子-β1基因和胰岛素样生长因子1基因联合转染治疗兔膝骨性关节炎的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005,22(12):1540-1542.
[42]常献, 陈斌, 李长青. 转化生长因子-β在骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞定向分化过程中的作用[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013,
21(15):1538-1540.
[43]赵庆华,贾连顺,王川,等. 转化生长因子β对人颈椎关节突关节软骨细胞基质金属蛋白酶13基因表达的调节作用及意义[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2007,22(3):204-206.
[44]郭常安,阎作勤,姚振均,等. 脂质体介导转化生长因子-β1基因修饰骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化[J]. 复旦学报:医学版,2004, 31(4):343-346.
[45]Bentley G, Biant LC, Carrington RW, et al. A prospective, randomised comparison of autologous chondrocyte implantation versus mosaicplasty for osteochondral defects in the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(2):223-230.
[46]Taipaleenmäki H, Harkness L, Chen L, et al. The Crosstalk Between Transforming Growth Factor-b1 and Delta Like-1 Mediates Early Chondrogenesis During Embryonic Endochondral Ossification. Stem Cells. 2012;30:304-313. |