Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (10): 1521-1531.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.10.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Large-scale expansion of clinical-grade human adipose-derived stem cells using the extracellular matrix
Su Yue-han1, Wei Chao2, Lv Pin-lei2, Cao Yun1, Qiu Yun2, Zheng Qing2, Xiao Shu-dong2, Wang Zheng 1, 2
- 1 Stem Cell Laboratory, Translational Medicine Base for Biological Cell Engineering Technology, Nanjing Military Region, the 455 Hospital of PLA, Shanghai 200052, China; 2 Department of Digestion, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200001, China
-
Online:2014-03-05Published:2014-03-05 -
Contact:Wang Zheng, M.D., Associate investigator, Department of Digestion, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200001, China; Stem Cell Laboratory, Translational Medicine Base for Biological Cell Engineering Technology, Nanjing Military Region, the 455 Hospital of PLA, Shanghai 200052, China -
About author:Su Yue-han, Master, Stem Cell Laboratory, Translational Medicine Base for Biological Cell Engineering Technology, Nanjing Military Region, the 455 Hospital of PLA, Shanghai 200052, China -
Supported by:Pujiang Talent Plan of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, No. 09PJ1407300; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30971468
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Su Yue-han, Wei Chao, Lv Pin-lei, Cao Yun, Qiu Yun, Zheng Qing, Xiao Shu-dong, Wang Zheng . Large-scale expansion of clinical-grade human adipose-derived stem cells using the extracellular matrix[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(10): 1521-1531.
share this article

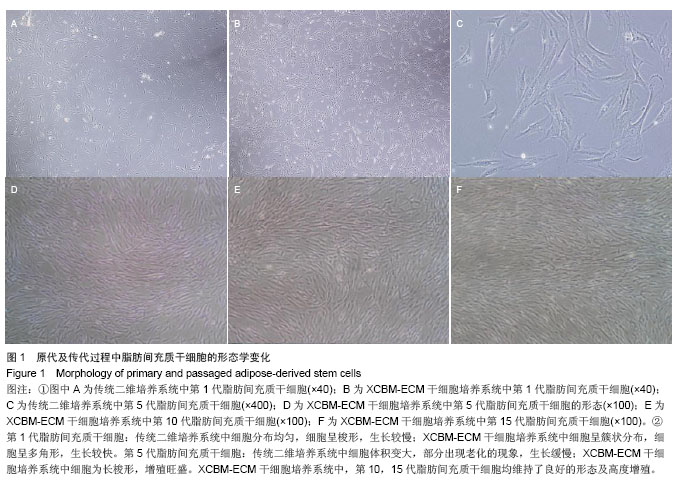
2.1 脂肪间充质干细胞的形态学观察 原代脂肪间充质干细胞在接种后24 h内贴壁,细胞的形态为短梭形、三角形。在普通二维培养系统下,脂肪间充质干细胞均匀分布,生长速度较慢;而在XCBM-ECM干细胞培养系统内,脂肪间充质干细胞呈现克隆样生长,且7 d内细胞克隆数迅速增多。 传代后,在XCBM-ECM干细胞培养系统中,仍可见脂肪间充质干细胞呈现克隆样迅速生长直至第3代,之后细胞才呈现均匀分布生长的状态。 在普通二维培养系统中,脂肪间充质干细胞传至第5代时出现生长缓慢及部分老化的现象,细胞的形态发生变化,细胞的体积变大,胞浆内出现黑色颗粒。传至第10代时,二维培养系统中的细胞大部分已基本老化,细胞数量急剧下降。 脂肪间充质干细胞在XCBM-ECM干细胞培养系统中生长状态活跃,在15代体外扩增的过程中,增殖速率基本稳定,细胞形态为长梭形,生长过程中基本保持不变,第15代脂肪间充质干细胞仍具有旺盛的增殖能力(图1)。"
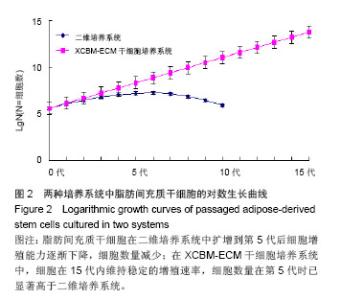
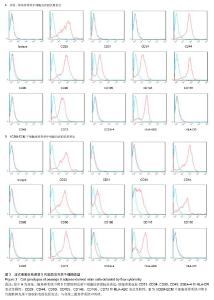
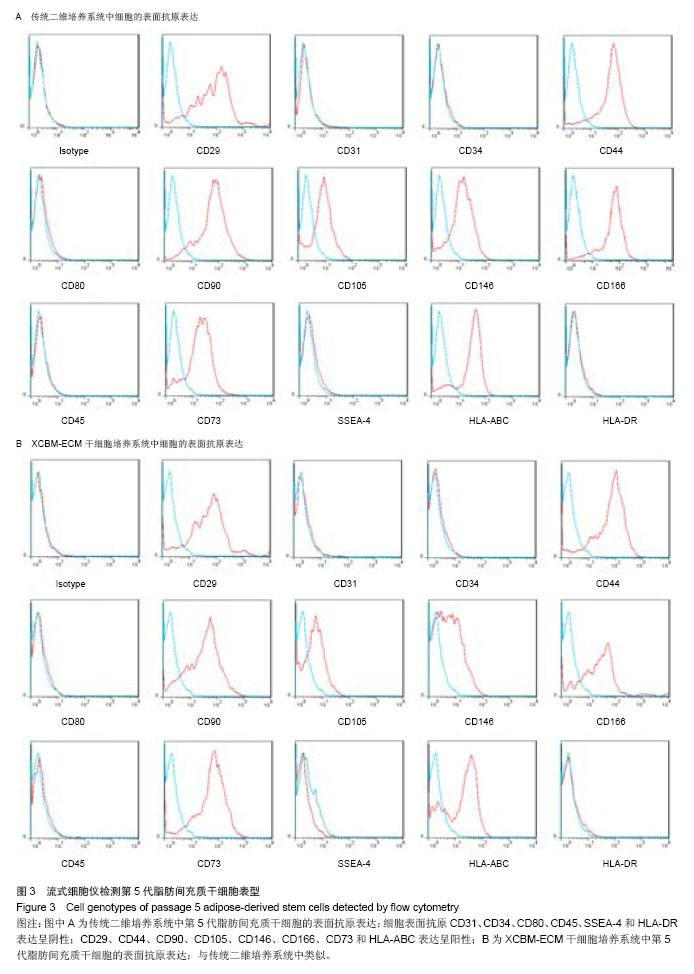
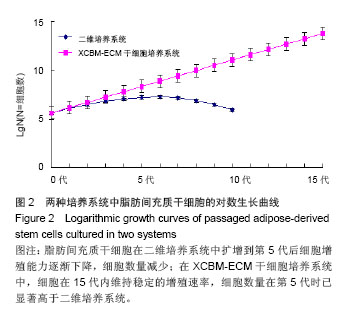
2.2 脂肪间充质干细胞的传代及增殖能力 在脂肪间充质干细胞的传代过程中取样,进行细胞计数,根据细胞总数的变化分析脂肪间充质干细胞的增殖能力。结果显示,二维培养系统中的细胞在整个培养过程中,细胞生长速率逐渐下降,第5代后细胞增殖能力明显减弱,细胞总数呈下降趋势。 XCBM-ECM干细胞培养系统中的脂肪间充质干细胞随着代数上升,细胞总数呈线性增长,细胞的增殖速率基本保持不变。传代至15代时,细胞仍具备旺盛的增殖能力。在第5代时,XCBM-ECM干细胞培养系统中的脂肪间充质干细胞总数已经是是二维培养系统中细胞的10倍以上,两者差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。实验结果表明,使用XCBM-ECM干细胞培养系统,取材于10 g脂肪的脂肪间充质干细胞经过4周左右的体外扩增,总数已可达到1×108以上(图2)。"
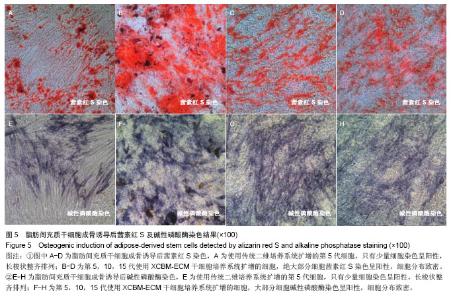
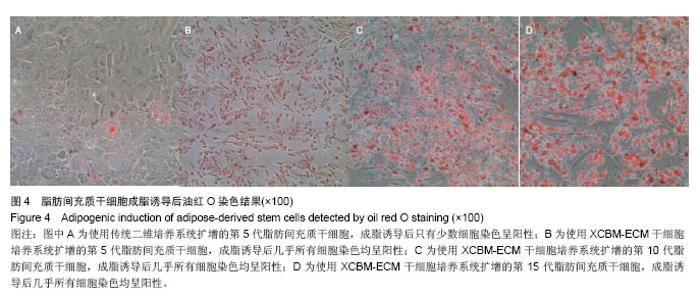
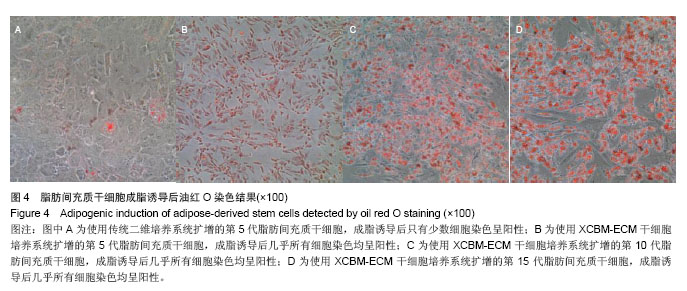
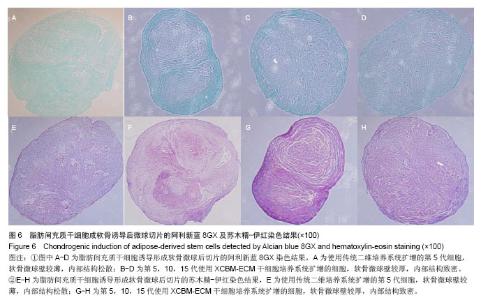
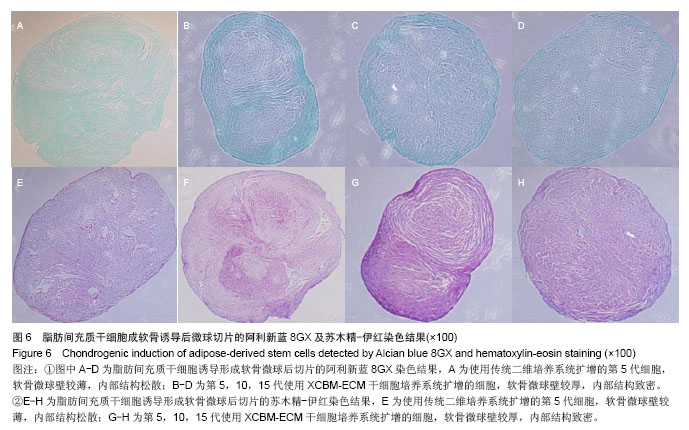
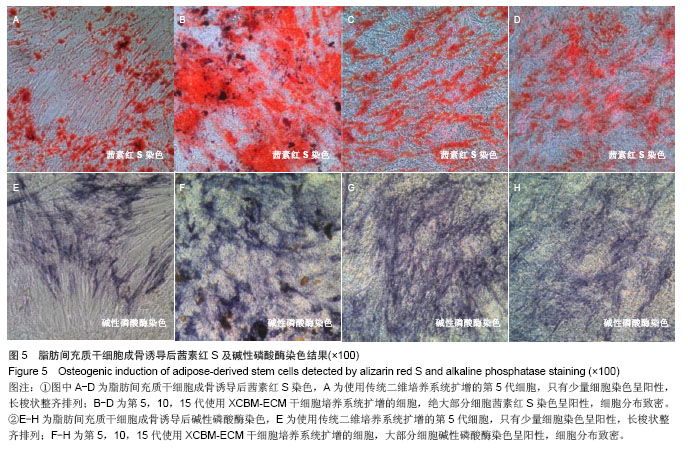
2.5 脂肪间充质干细胞的成骨诱导结果 脂肪间充质干细胞成骨诱导启动后,细胞的增殖速度减缓,细胞体积逐渐变大,形态发生改变,长梭形细胞逐渐拉长,且整齐地排列分布。成骨诱导7 d左右,细胞开始呈簇状生长,细胞形态逐渐向多角形转变。14 d时细胞分布密集,显微镜下可见钙化结节。 茜素红S染色后,成骨细胞呈橙红色(图5A-D);碱性磷酸酶染色后,成骨细胞呈蓝紫色(图5E-H)。 结果显示,使用二维培养系统扩增的第5代脂肪间充质干细胞成骨诱导后,细胞形态呈长条状,维持簇状生长,且只有少部分细胞染色呈阳性。使用XCBM-ECM培养系统扩增的第5,10和15代脂肪间充质干细胞经诱导后,出现大量钙化结节,细胞生长密集,染色后阳性率远高于二维培养系统。"
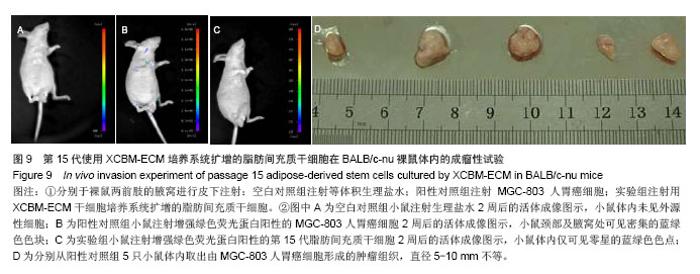
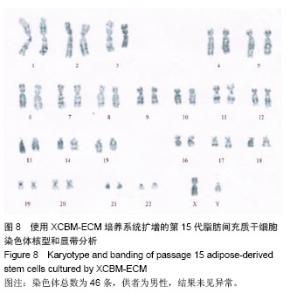
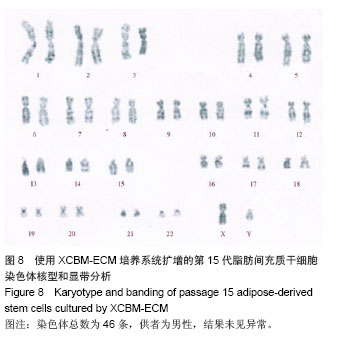
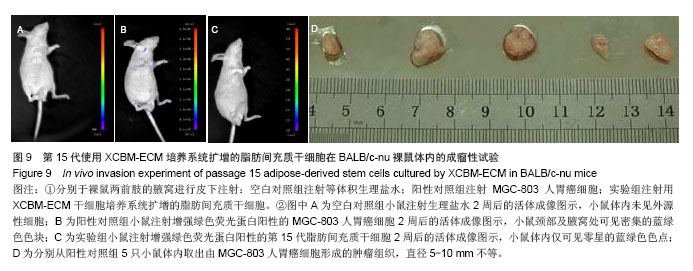
2.9 脂肪间充质干细胞的体内成瘤性试验结果 为进一步保证脂肪间充质干细胞在大规模扩增后的临床安全性,用XCBM-ECM培养系统将脂肪间充质干细胞扩增到第15代时,收集细胞荧光标记并皮下注射到BALB/c-nu裸鼠的前肢腋窝,检测脂肪间充质干细胞多次传代后是否存在体内成瘤性(图9)。被增强绿色荧光蛋白标记的细胞在活体成像系统中呈蓝绿色。结果显示,输注了MGC-803人胃癌细胞的裸鼠在腋窝及颈部出现了外源性细胞聚集(图9B)。将阳性对照组裸鼠处死后,切开其腋窝及颈部皮肤,可取出实体肿瘤组织(图9D)。将XCBM-ECM培养系统扩增的第15代脂肪间充质干细胞注射入裸鼠皮下后,小鼠体内只出现了零的外源性细胞(图9C)。将小鼠处死后,也未在其体内找到任何肿瘤组织。由此可见,使用XCBM-ECM培养系统扩增的脂肪间充质干细胞在15代内应不具备体内成瘤性。"
| [1]Guilak F, Lott KE, Awad HA, et al. Clonal analysis of the differentiation potential of human adipose-derived adult stem cells. J Cell. Physiol. 2006;206(1): 229-237.[2]Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12): 4279-4295.[3]Rodriguez AM, Elabd C, Amri EZ, et al. The human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Biochimie. 2005; 87(1):125-128.[4]Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2): 211-228. [5]Dragoo JL, Carlson G, McCornick F, et al. Healing full-thickness cartilage defects using adipose-derived stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(7): 1615-1621.[6]Safford KM, Rice HE. Stem cell therapy for neurologic disorders: therapeutic potential of adipose-derived stem cells. Current Drug Targets. 2005;6(1): 57-62.[7]Banas A, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y, et al. Rapid hepatic fate specification of adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential for liver failure. J Gastroenterol and Hepatol. 2009;24(1): 70-77.[8]Mizuno H. Adipose-derived stem cells for tissue repair and regeneration: ten years of research and a literature review. J Nippon Med Sch. 2009;76(2): 56-66.[9]Park IS, Rhie JW, Kim SH. A novel three-dimensional adipose-derived stem cell cluster for vascular regeneration in ischemic tissue. Cytotherapy. 2013;S1465-3249(13): 00681-00686. [10]Wang YL, Li G, Zou XF, et al. Effect of autologous adipose-derived stem cells in renal cold ischemia and reperfusion injury. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(9): 3198-3202.[11]Lee HJ, Jung J, Cho KJ, et al. Comparison of in vitro hepatogenic differentiation potential between various placenta-derived stem cells and other adult stem cells as an alternative source of functional hepatocytes. Differentiation. 2012;84(3): 223-231.[12]Bunnell BA, Flaat M, Gagliardi C, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells - isolation, expansion and differentiation. Methods. 2008; 45(2): 115-120.[13]Cheng NC, Chen SY, Li JR, et al. Short-term spheroid formation enhances the regenerative capacity of adipose- derived stem cells by promoting stemness, angiogenesis, and chemotaxis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(8): 584-594. [14]Murphy MB, Moncivais K, Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells: environmentally responsive therapeutics for regenerative medicine. Exp Mol Med. 2013;45: e54. [15]Fernández Vallone VB, Romaniuk MA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and their use in therapy: what has been achieved? Differentiation. 2013;85(1-2): 1-10.[16]Doorn J, Moll G, Le Blanc K, et al. Therapeutic applications of mesenchymal stromal cells: paracrine effects and potential improvements. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012;18(2): 101-115. [17]Mark P, Kleinsorge M, Gaebel R, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells display reduced expression of CD105 after culture in serum-free medium. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013: 698076. [18]Tsang WP, Shu Y, Kwok PL, et al. CD146(+) human umbilical cord perivascular cells maintain stemness under hypoxia and as a cell source for skeletal regeneration. PLoS One. 2013; 8(10): e76153. [19]Zhang D, Kilian KA. The effect of mesenchymal stem cell shape on the maintenance of multipotency. Biomaterials. 2013;34(16): 3962-3969.[20]Scadden DT. The stem-cell niche as an entity of action. Nature. 2006;441(7097): 1075-1079.[21]Sharma MB, Limaye LS, Kale VP. Mimicking the functional hematopoietic stem cell niche in vitro: recapitulation of marrow physiology by hydrogel-based three-dimensional cultures of mesenchymal stromal cells. Haematologica. 2012; 97(5): 651-660.[22]Frantz C, Stewart KM, Weaver VM. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2010;123: 4195-4200.[23]Brizzi MF, Tarone G, Defilippi P. Extracellular matrix, integrins, and growth factors as tailors of the stem cell niche. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24(5): 645-651. [24]Kazanis I, ffrench-Constant C. Extracellular matrix and the neural stem cell niche. Dev Neurobiol. 2011;71(11): 1006- 1017.[25]Watt FM, Huck WT. Role of the extracellular matrix in regulating stem cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(8): 467-473.[26]Taylor-Weiner H, Schwarzbauer JE, Engler AJ. Defined extracellular matrix components are necessary for definitive endoderm induction. Stem Cells. 2013;31(10): 2084-2094.[27]Kurtz A, Oh SJ. Age related changes of the extracellular matrix and stem cell maintenance. Prev Med. 2012;54(Suppl): S50-56.[28]Chen XD. Extracellular matrix provides an optimal niche for the maintenance and propagation of mesenchymal stem cells. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2010;90(1): 45-54.[29]Young DA, Choi YS, Engler AJ, et al. Stimulation of adipogenesis of adult adipose-derived stem cells using substrates that mimic the stiffness of adipose tissue. Biomaterials. 2013;34(34): 8581-8588. [30]Peterbauer-Scherb A, Danzer M, Gabriel C, et al. In vitro adipogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells in 3D fibrin matrix of low component concentration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(6): 434-442. [31]Schubert T, Xhema D, Vériter S, et al. The enhanced performance of bone allografts using osteogenic- differentiated adipose-derived mesenchymalstem cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32(34): 8880-8891. [32]Hicok KC, Du Laney TV, Zhou YS, et al. Human adipose-derived adult stem cells produce osteoid in vivo. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(3-4):371-380.[33]Huang JI, Zuk PA, Jones NF, et al. Chondrogenic potential of multipotential cells from human adipose tissue. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;113(2): 585-594. [34]Hamid AA, Idrus RB, Saim AB, et al. Characterization of human adipose-derived stem cells and expression of chondrogenic genes during induction ofcartilage differentiation. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2012;67(2): 99-106.[35]Mizuno H, Hyakusoku H. Mesengenic potential and future clinical perspective of human processed lipoaspirate cells. J Nippon Med Sch. 2003;70(4): 300-306.[36]Gronthos S, Franklin DM, Leddy HA, et al. Surface protein characterization of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 2001;189(1): 54-63. [37]Mitchell JB, McIntosh K, Zvonic S, et al. Immunophenotype of human adipose-derived cells: temporal changes in stromal-associated and stem cell-associated markers. Stem Cells. 2006;24(2): 376-385.[38]Jiang S, Zu Y, Fu Y, et al. Activation of the mitochondria-driven pathway of apoptosis in human PC-3 prostate cancer cells by a novel hydrophilic paclitaxel derivative, 7-xylosyl-10-deacetylpaclitaxel. Int J Oncol. 2008; 33(1): 103-111. [39]Tao Q, Lv B, Qiao B, et al. Immortalization of ameloblastoma cells via reactivation of telomerase function: Phenotypic and molecular characteristics. Oral Oncol. 2009;45(12): 239-244. [40]Lai Y, Sun Y, Skinner CM, et al. Reconstitution of marrow-derived extracellular matrix ex vivo: a robust culture system for expanding large-scale highly functional human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(7): 1095-1107. [41]Bendall SC, Stewart MH, Menendez P, et al. IGF and FGF cooperatively establish the regulatory stem cell niche of pluripotent human cells in vitro. Nature. 2007;448(7157): 1015-1021.[42]Stewart MH, Bendall SC, Bhatia M. Deconstructing human embryonic stem cell cultures: niche regulation of self-renewal and pluripotency. J Mol Med (Berl). 2008;86(8): 875-886.[43]Bendall SC, Stewart MH, Bhatia M. Human embryonic stem cells: lessons from stem cell niches in vivo. Regen Med. 2008; 3(3): 365-376. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||