Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (7): 1109-1114.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.07.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cytoskeleton and mechanical signal transduction
Yao Yi-cun, Liang Wei-guo, Ye Dong-ping
- Department of Orthopedics, Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou Red-Cross Hospital, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2013-12-12Online:2014-02-12Published:2014-02-12 -
Contact:Liang Wei-guo, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou Red-Cross Hospital, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Yao Yi-cun, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou Red-Cross Hospital, Guangzhou 510220, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 10151022001000005; the Major Medicine and Health Scientific Program of Guangzhou City, No. 2009-ZDi-04, 2008-ZDi-15
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yao Yi-cun, Liang Wei-guo, Ye Dong-ping. Cytoskeleton and mechanical signal transduction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(7): 1109-1114.
share this article
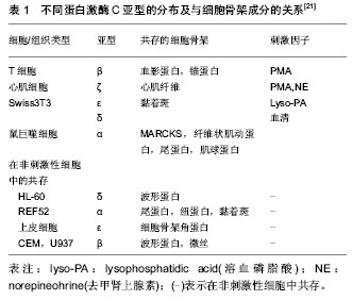
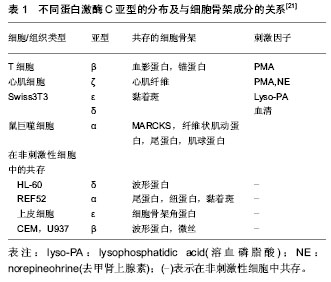
2.1 细胞骨架 2.1.1 细胞骨架的组成 细胞骨架(cytoskeleton,CSK)是位于细胞膜内侧面的蛋白质纤维网架系统。广义的细胞骨架包括细胞外基质、细胞膜骨架、细胞质骨架和细胞核骨架,它们在结构上相互连接,形成贯穿于细胞的网架体系。人们通常所说的细胞骨架主要是指细胞质骨架,主要由微管、微丝和粗细介于两者之间中间丝组成。其中,微管主要是由微管蛋白(tubulin)组装而成的直径约为24 nm的细长中空圆管状结构;微丝,又称肌动蛋白纤维,主要由肌动蛋白组装而成的直径为7 nm的丝状结构;中间丝是粗细介于微管和微丝之间的绳索状结构,其成分复杂,类型多样。除此之外,细胞骨架还包含一些与其分布和功能发挥相关的细胞骨架结合蛋白,如微管相关蛋白(MAPs)、马达蛋白(motor protein)等。 2.1.2 细胞骨架的功能 细胞骨架的3种成分在形态上、功能上虽有差异,但3者在空间上相互联系,功能上相互配合,构成了贯穿整个细胞的复杂骨架系统,决定了细胞的形态和功能。其主要功能可归结为以下几点:①结构支持作用。维持细胞的形态以及各种细胞器的定位。②参与细胞内各种细胞器、生物大分子的运输和信号传导。③作为细胞的动力装置参与保持细胞分裂、细胞迁移等在内的各种细胞运动。 2.2 细胞骨架相关力学信号通路 对于生物力学信号在细胞内传递的化学途径,目前国内外学者主要认为有Rho家族、蛋白激酶C、整合素、丝裂霉素激活的蛋白激酶( MAPK)、Ca2+通道、细胞因子、一氧化氮(NO)途径等。 2.2.1 Rho家族 Rho蛋白家族是Ras超家族成员[1],为一类小分子G蛋白( Small G protein,又称GTP ase,即GTP酶) 。到目前为止,已发现包括Rho、Rac 和Cdc42在内的三个亚家族共十余种。Rho蛋白具有GTP酶活性,是细胞内信号传导的重要枢纽,能快速转换于GTP结合的活化状态和GDP结合的非活化状态之间,将细胞外信号传至细胞内,发挥着“分子信号开关”作用。 Rho:研究表明,Rho在细胞应力纤维装配和黏附斑信号传导过程中处于中心地位[2-5]。其中最为关键的两个下游效应蛋白分子为Rho相关激酶ROCK及形成素相关蛋白mDia[6]。 ROCK是以一种GTP依赖的方式与Rho蛋白相互作用的激酶,结合Rho-GTP后其活性会增加,当其在细胞中过表达时,可以不依赖于Rho蛋白而诱导应力纤维的产生。ROCK激活会在细胞中央产生典型星状的粗大应力纤维,在应力纤维的组装中起主要作用。 ROCK可通过抑制肌球蛋白轻链(myosin light chain,MLC)磷酸酶活性,提高MLC磷酸化水平,激活肌球蛋白。还可以不依赖于钙调蛋白直接磷酸化MLC,激活肌球蛋白[7-9]。另外,cofilin是一种肌动蛋白结合蛋白,可以促进F-actin解聚,活化的ROCK可通过磷酸化LIM激酶抑制cofilin作用,维持肌动蛋白的聚合状态[10-11]。 mDia可以促进非肌球蛋白Ⅱ驱使下的肌动蛋白的收缩,mDia还可参与调节微管的组装和动态平衡[12-13],表达高活性mDia的细胞,其微管的正负两端均处于稳固状态,产生平行的纤细应力纤维,且正极与黏附斑的锚定得以加强,该过程可能导致黏附斑的下调。 以上均提示活化的Rho是通过肌球蛋白的收缩驱使应力纤维及黏附斑的形成。 Rac:Rac主要参与片状伪足的形成[14]。RacSH3区与波形蛋白WAVE结合后,能激活actin相关蛋白——Arp2/3复合体,Rac使质膜的肌动蛋白丝脱帽(uncapping),从而促进肌动蛋白聚合[15];另外,Rac还可通过下游靶分子PAK激活LIMK,进而磷酸化并失活cofilin,抑制肌动蛋白丝的解聚。 Cdc42:Cdc42称为细胞分裂周期蛋白42(cell division cycle 42),对丝状伪足的产生有重要的调控作用。Cdc42蛋白激活肌动蛋白结合蛋白p56PAK蛋白激酶,使与其结合的肌动蛋白发生重排[16]。Cdc42通过激活WASP蛋白(Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein)激活Arp2/3复合物,促进肌动蛋白聚合[17]。另外,与Ras相似,Cdc42还能通过其下游靶蛋白PAK激活LIMK,从而使cofilin失活,维持肌动蛋白的聚合[18]。 综上所述,Rho GTP ases在生物力学刺激下可通过多种途径调节细胞骨架结构和功能,在生物力学的信号传导中起重要作用。借此,Rho对细胞骨架的成分进行调节、对细胞-基质黏附及基质重塑产生影响,在细胞迁移、基因转录、细胞周期调控、膜泡运输中起重要作用,对椎间盘退变、胃黏膜的保护、肿瘤细胞转移等方面有着重要的影响。 2.2.2 蛋白激酶C(PKC) 蛋白激酶C属于肌醇磷脂依赖性丝/苏氨酸激酶家族,作为一种重要的蛋白激酶和细胞内信号分子,可作用于多种底物蛋白。目前已发现蛋白激酶C有12种亚型,根据分子结构将其分为经典型蛋白激酶C(conventional PKCs,cPKCs)、新型蛋白激酶C(novel PKCs,nPKCs)和非典型蛋白激酶C(atypical PKCs,aPKCs)。表1为蛋白激酶C的不同亚型及其在细胞内的不同定位。与蛋白激酶C共存的细胞骨架蛋白往往就是蛋白激酶C的靶底物,蛋白激酶C的激活可以直接引起该骨架蛋白的磷酸化,进而调节该细胞骨架蛋白的功能,蛋白激酶C组织特异性决定其在细胞骨架调节中的不同作用[19-20]。"
| [1] Piekny A, Werner M, Glotzer M.Cytokinesis: welcome to the Rho zone.Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15(12):651-658.[2] Williams MJ.Rho GTPases central regulators of cell migration. Small GTPases. 2012;3(1):1.[3] Raftopoulou M, Hall A. Cell migration: Rho GTPases lead the way.Dev Biol. 2004;265(1):23-32.[4] Fukata M, Nakagawa M, Kaibuchi K. Roles of Rho-family GTPases in cell polarisation and directional migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15(5):590-597.[5] Ridley AJ.Rho GTPases and cell migration.J Cell Sci. 2001; 114(Pt 15):2713-2722.[6] Nakano K, Takaishi K, Kodama A,et al. Distinct actions and cooperative roles of ROCK and mDia in Rho small G protein-induced reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.Mol Biol Cell. 1999;10(8): 2481-2491.[7] Kaunas R, Nguyen P, Usami S,et al. Cooperative effects of Rho and mechanical stretch on stress fiber organization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(44):15895-1900. [8] Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K,et al. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase).J Biol Chem. 1996;271(34):20246-20249.[9] Kimura K, Ito M, Amano M,et al. Regulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase).Science. 1996;273(5272):245-248.[10] Maekawa M, Ishizaki T, Boku S,et al.Signaling from Rho to the actin cytoskeleton through protein kinases ROCK and LIM-kinase.Science. 1999;285(5429):895-898.[11] Oude Weernink PA, Schulte P, Guo Y,et al. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase by Rho-kinase.J Biol Chem. 2000;275(14):10168-10174.[12] Narumiya S, Ishizaki T, Watanabe N. Rho effectors and reorganization of actin cytoskeleton.FEBS Lett. 1997;410(1): 68-72.[13] Vicente-Manzanares M, Rey M, Pérez-Martínez M,et al. The RhoA effector mDia is induced during T cell activation and regulates actin polymerization and cell migration in T lymphocytes.J Immunol. 2003;171(2):1023-1034.[14] Riento K, Ridley AJ. Rocks: multifunctional kinases in cell behaviour. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(6):446-456.[15] Tolias KF, Hartwig JH, Ishihara H,et al.Type Ialpha phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase mediates Rac-dependent actin assembly.Curr Biol. 2000;10(3): 153-156.[16] Edwards DC, Sanders LC, Bokoch GM,et al.Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat Cell Biol.1999;1(5):253-259.[17] Kim AS, Kakalis LT, Abdul-Manan N, et al.Autoinhibition and activation mechanisms of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein. Nature. 2000;404(6774):151-158.[18] Ren XD, Kiosses WB, Schwartz MA.Regulation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho by cell adhesion and the cytoskeleton. EMBO J. 1999;18(3):578-585.[19] Prekeris R, Mayhew MW, Cooper JB, et al.Identification and localization of an actin-binding motif that is unique to the epsilon isoform of protein kinase C and participates in the regulation of synaptic function.J Cell Biol. 1996;132(1-2): 77-90.[20] Brandt D, Gimona M, Hillmann M,et al. Protein kinase C induces actin reorganization via a Src- and Rho-dependent pathway.J Biol Chem. 2002;277(23):20903-20910. [21] 宋力,黄巧冰,赵克森.蛋白激酶C与内皮细胞骨架蛋白和血管通透性研究进展[J].中国微循环,2003,7(3):184-186,190.[22] Barry ST, Critchley DR.The RhoA-dependent assembly of focal adhesions in Swiss 3T3 cells is associated with increased tyrosine phosphorylation and the recruitment of both pp125FAK and protein kinase C-delta to focal adhesions. J Cell Sci. 1994;107( Pt 7):2033-2045.[23] Price LS, Langeslag M, ten Klooster JP,et al.Calcium signaling regulates translocation and activation of Rac.J Biol Chem. 2003;278(41):39413-39421. [24] Holinstat M, Mehta D, Kozasa T,et al. Protein kinase Calpha-induced p115RhoGEF phosphorylation signals endothelial cytoskeletal rearrangement.J Biol Chem. 2003; 278(31):28793-28798.[25] Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E.Integrin signaling.Science. 1999; 285(5430):1028-1032.[26] Duncan RL, Turner CH. Mechanotransduction and the functional response of bone to mechanical strain. Calcif Tissue Int. 1995;57(5):344-358.[27] Brakebusch C, Fässler R.The integrin-actin connection, an eternal love affair.EMBO J. 2003;22(10):2324-2333.[28] Yeung T, Georges PC, Flanagan LA, et al. Effects of substrate stiffness on cell morphology, cytoskeletal structure, and adhesion.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2005;60(1):24-34.[29] Marek L, Levresse V, Amura C,et al. Multiple signaling conduits regulate global differentiation-specific gene expression in PC12 cells.J Cell Physiol. 2004;201(3): 459-469.[30] Sieg DJ, Hauck CR, Schlaepfer DD.Required role of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) for integrin-stimulated cell migration.J Cell Sci. 1999;112 ( Pt 16):2677-2691.[31] Sun Y, Meng GM, Guo ZL,et al.Regulation of heat shock protein 27 phosphorylation during microcystin-LR-induced cytoskeletal reorganization in a human liver cell line.Toxicol Lett. 2011;207(3):270-277.[32] Chang L, Jones Y, Ellisman MH,et al. JNK1 is required for maintenance of neuronal microtubules and controls phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins.Dev Cell. 2003;4(4):521-533.[33] Vogl T, Ludwig S, Goebeler M,et al. MRP8 and MRP14 control microtubule reorganization during transendothelial migration of phagocytes.Blood. 2004;104(13):4260-4268.[34] Hunger-Glaser I, Salazar EP, Sinnett-Smith J,et al. Bombesin, lysophosphatidic acid, and epidermal growth factor rapidly stimulate focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation at Ser-910: requirement for ERK activation.J Biol Chem. 2003;278(25): 22631-22643.[35] Glading A, Bodnar RJ, Reynolds IJ,et al. Epidermal growth factor activates m-calpain (calpain II), at least in part, by extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated phosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(6):2499-2512.[36] Adachi T, Stafford S, Kayaba H,et al.Myosin light chain kinase mediates eosinophil chemotaxis in a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent manner.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111(1):113-116.[37] Galaria II, Fegley AJ, Nicholl SM,et al. Differential regulation of ERK1/2 and p38(MAPK) by components of the Rho signaling pathway during sphingosine-1-phosphate-induced smooth muscle cell migration.J Surg Res. 2004;122(2): 173-179.[38] Malchinkhuu E, Sato K, Horiuchi Y,et al. Role of p38 mitogen-activated kinase and c-Jun terminal kinase in migration response to lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine-1-phosphate in glioma cells.Oncogene. 2005; 24(44):6676-6688.[39] Launay N, Goudeau B, Kato K,et al.Cell signaling pathways to alphaB-crystallin following stresses of the cytoskeleton.Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(18):3570-3584.[40] Huang C, Jacobson K, Schaller MD. MAP kinases and cell migration.J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 20):4619-4628.[41] Goode BL, Drubin DG, Barnes G. Functional cooperation between the microtubule and actin cytoskeletons.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000;12(1):63-71.[42] Pollard TD, Cooper JA.Actin, a central player in cell shape and movement.Science. 2009;326(5957):1208-1212.[43] 富尔顿著, 袁菊等译.细胞骨架(生物学研究概说)[M].北京:科学出版社, 1991. [44] Takiguchi K, Matsumura F. Role of the basic C-terminal half of caldesmon in its regulation of F-actin: comparison between caldesmon and calponin.J Biochem. 2005;138(6):805-813.[45] Kordowska J, Hetrick T, Adam LP,et al. Phosphorylated l-caldesmon is involved in disassembly of actin stress fibers and postmitotic spreading.Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(2):95-110. [46] Babakov VN, Petukhova OA, Turoverova LV,et al. RelA/NF-kappaB transcription factor associates with alpha-actinin-4.Exp Cell Res. 2008;314(5):1030-1038. [47] Rosette C, Karin M.Cytoskeletal control of gene expression: depolymerization of microtubules activates NF-kappa B.J Cell Biol. 1995;128(6):1111-1119.[48] Hunter T, Karin M.The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992;70(3):375-387. |
| [1] | Li Jing, Xie Jianshan, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong. Expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and protein kinase C beta II in mouse back skin with different coat colors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1196-1200. |
| [2] | Wang Huili, Chen Zhijiang, Wu Bingyi. Glia maturation factor-gamma inhibits the proliferation of human colorectal cancer LoVo cells and affects the cytoskeletal motion of human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2055-2059. |
| [3] |
Peng Xu, Yang Jibin, You Qi, Jin Ying, Zhang Jun, Ge Zhen, Zou Gang, Jiang Kongjun, Liu Yi.
Effect of Psammosilene gavage on the expression of
apoptosis-related proteins in chondrocytes of a rabbit osteoarthritis model |
| [4] | Fei Jing, Zheng Hongdi, Yu Liya, Li Leiji. Involvement of GDNF/PI3K/AKT pathway in promoting facial nerve regeneration using electroacupuncture in a rabbit model of facial nerve crush injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1094-1100. |
| [5] | Yuan Guoqiang, Qin Yongsheng, Peng Peng. High-intensity interval training for treating pathological cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats: effects and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3708-3715. |
| [6] | Liu Jing, Sun Zhilu, Zhou Jun, Liao Yuan, Sun Guanghua, Wu Qi, Zhou Guijuan, Zhong Peirui, Cheng Guo, Xiao Hao, Li Lan, Liao Ying. Effect of ibandronate on mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in rat models of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 181-186. |
| [7] | Xu Limeng, Luo Wenyu, Zhang Shuwei, Wang Li. Mechanical properties and cytoskeletal protein changes after ANLN deficiency [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 87-92. |
| [8] | Zhou Yanxing1, Peng Xinsheng2, Hou Gan1, Li Jiangbin1, Zhang Hua1, Zhou Zhikun2, Zhou Yanfang3 . Inhibitory effect of capsaicin on fibroblast proliferation and its molecular mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1018-1022. |
| [9] | Liu Junyin, Feng Wei, Xie Yingchun, Li Yuwan, Zeng Jitao, Liu Ziming, Tu Xiaolin. Bone morphologic protein signaling pathway in bone regeneration and repair: accurate regulation and treatment targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 606-612. |
| [10] | Hu Guang, Zhang Kaiwei, Xu Yuankun. Lysophosphatidic acid affects the expression of connective tissue growth factor in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 2959-2964. |
| [11] | Chen Deping1, Liu Shengze1, Chen Shi1, Cong Changchun2, Liu Shuyi3, Xiao Ying4 . Effect of nerve growth factor-beta on proliferation of intraspinal schwannomas [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2373-2379. |
| [12] | Ao Xiaojing, Miao Mao, Tan Yaqin, Hao Hua. Changes of cartilage extracellular matrix and Wnt singling pathway in rabbit models of osteoarthritis after treatment by fire-needle moxibustion at Dubi and Neixiyan [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(11): 1662-1668. |
| [13] | Zheng Chunyu1, Yu Xuefeng2, Chen Shuilin2, Xu Yier3, Han Zhongli4, Sun Guicai2. Effects of aqueous extract of Sigesbeckia orientalis on JNK signaling pathway in rats with gouty arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5816-5820. |
| [14] | Hu Ruo-wen, Chen Xiao-fang. The roles of integrins and E-cadherin in the reprogramming and stemness maintenance of induced pluripotent stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4698-4705. |
| [15] | Zhong Yuan-ming1, Liang Zi-yang2, He Jia2, Xu Wei2, Mo Ri-yang2. Notch signaling pathway and the nucleus pulposus cells in degenerative intervertebral disc: roles in the repair and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(20): 3256-3262. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||