Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 1188-1194.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of Psammosilene gavage on the expression of
apoptosis-related proteins in chondrocytes of a rabbit osteoarthritis model
Peng Xu1, Yang Jibin2, You Qi2, Jin Ying2, Zhang Jun2, Ge Zhen2, Zou Gang2, Jiang Kongjun2, Liu Yi2
- 1Department of Joint Surgery, Suining Central Hospital, Suining 629000, Sichuan Province, China; 2First Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2019-05-07Revised:2019-05-21Accepted:2019-06-27Online:2020-03-18Published:2020-01-20 -
Contact:Liu Yi, Professor, Master’s supervisor, First Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Peng Xu, Master, Department of Joint Surgery, Suining Central Hospital, Suining 629000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Combined Project of Science and Technology Department of Guizhou Province, No. [2017]7015; a grant from the Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guizhou Province, No. QYZZ-2016-029
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Peng Xu, Yang Jibin, You Qi, Jin Ying, Zhang Jun, Ge Zhen, Zou Gang, Jiang Kongjun, Liu Yi.
Effect of Psammosilene gavage on the expression of
apoptosis-related proteins in chondrocytes of a rabbit osteoarthritis model
share this article
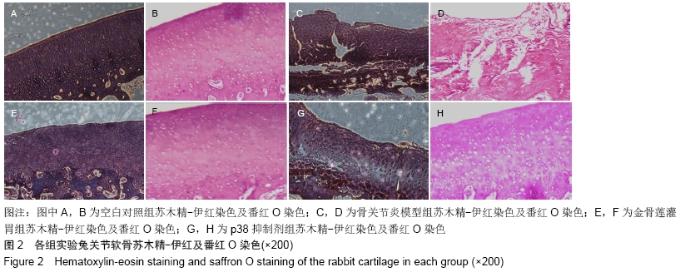
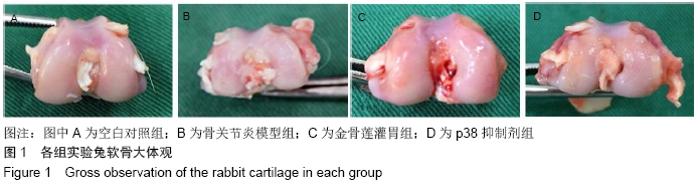
空白对照组:兔精神状态良好,食欲正常,活动自如,右侧后膝关节无肿胀、畸形,毛发光亮,体质量无减轻。股骨髁及胫骨平台软骨面色泽正常,表面光整,无骨赘。 骨关节炎模型组:兔精神状态、食欲差,造模后随时间推移活动逐渐受限,右膝关节出现肿胀,跛行,毛发稀疏暗淡,体质量减轻。关节软骨色泽灰暗,表面溃疡形成,可见大量骨赘形成,部分关节面软骨缺失,软骨下骨裸露。 金骨莲灌胃组:兔精神状态较好,食欲较正常,关节活动无明显受限,膝关节无明显肿胀,毛发较光亮,体质量无减轻。关节软骨色泽稍变暗,关节面粗糙,未见骨赘及软骨下骨裸露。 p38抑制剂组:兔精神状态、食欲较差,关节轻度肿胀。关节面粗糙伴糜烂,可见少量骨赘形成,未见明显软骨下骨裸露。 2.1.2 各组软骨组织学检查结果 关节软骨行病理切片苏木精-伊红及番红O染色观察,见图2。 "
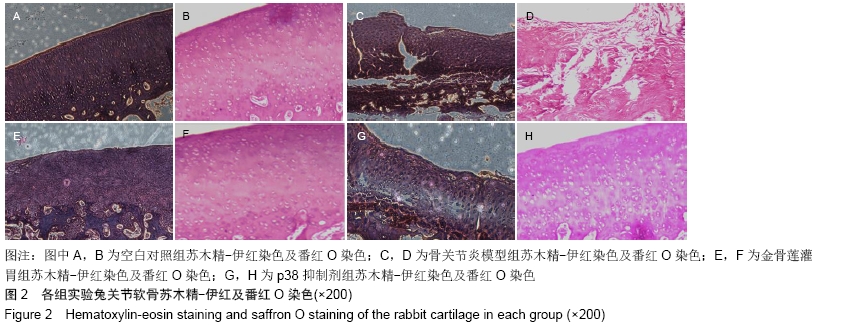
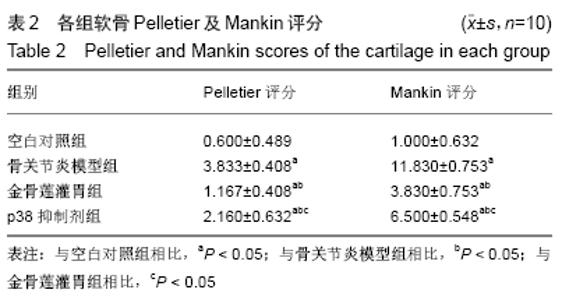
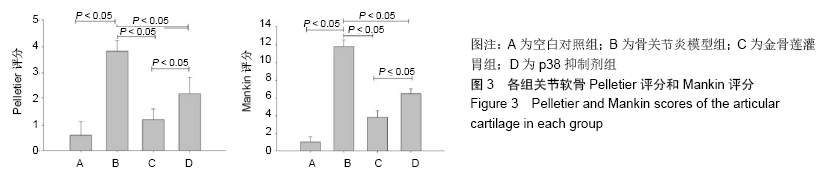
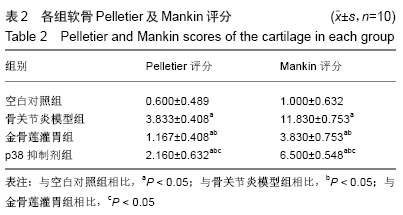
空白对照组:软骨结构完整,软骨细胞排列整齐,在钙化层及辐射层之间可见到完整的细胞潮线。番红O染色观察到细胞基质正常染色。 骨关节炎模型组:软骨变薄,软骨4层结构不完整,结构紊乱,裂隙深,可见放射带,软骨细胞明显减少,潮线破坏。番红O染色观察到细胞基质失染。 金骨莲灌胃组:软骨浅表层不规则,软骨细胞弥漫性增生,细胞潮线可见。番红O染色观察到细胞基质轻度失染。 p38抑制剂组:软骨变薄,软骨细胞局部增生,细胞潮线欠完整,番红O染色观察到细胞基质中度失染。 2.2 各组软骨Pelletier及Mankin评分 骨关节炎模型组Pelletier及Mankin评分较金骨莲灌胃组及p38抑制剂组明显升高(P < 0.05),金骨莲灌胃组Pelletier及Mankin评分较p38抑制剂组明显降低(P < 0.05),见表2,图3。 "
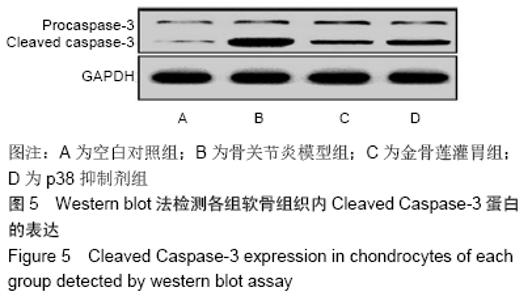
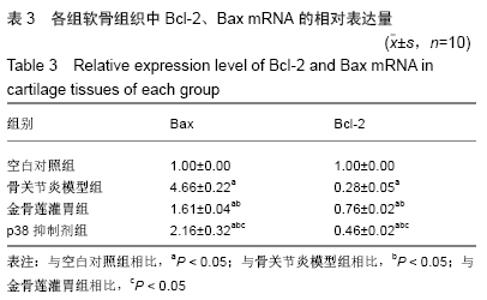
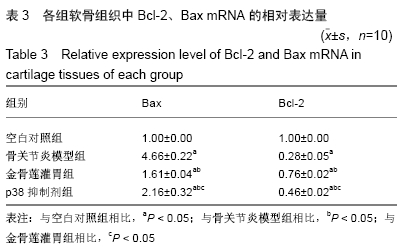
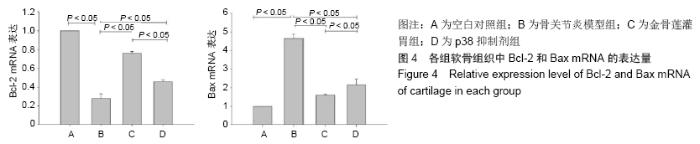
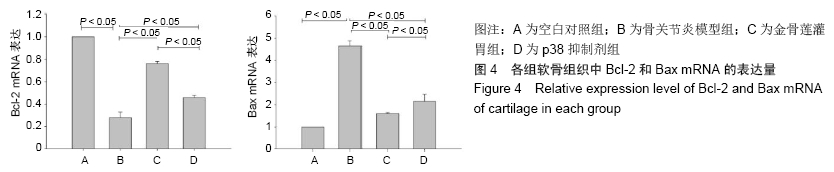
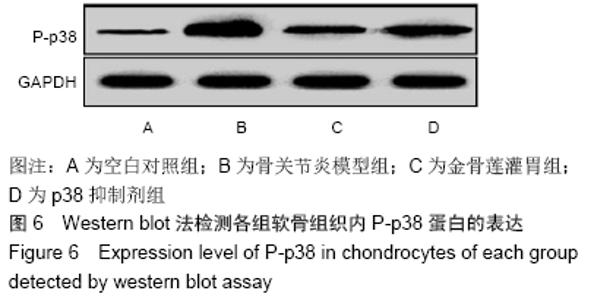
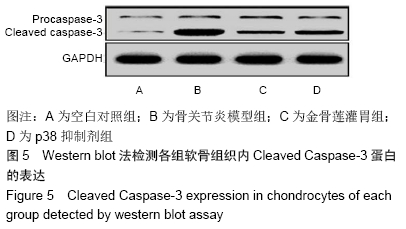
2.3.2 各组软骨组织中Bax mRNA的相对表达量 药物干预8周后,金骨莲灌胃组软骨组织中Bax mRNA的相对表达量较骨关节炎模型组及p38抑制剂组均明显降低(P < 0.05);与骨关节炎模型组相比,p38抑制剂组Bax mRNA的相对表达量明显降低(P < 0.05),见表3和图4。 2.3.3 各组软骨组织中Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白的表达量 药物干预8周后,金骨莲灌胃组Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白的表达量较骨关节炎模型组及p38抑制剂组均明显降低(P < 0.05);与骨关节炎模型组相比,p38抑制剂组Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白的表达量明显降低(P < 0.05),见图5。 "
| [1] MAN GS, MOLOGHIANU G. Osteoarthritis pathogenesis - a complex process that involves the entire joint. J Med Life. 2014;7(1):37-41. [2] KEEN HI, HENSOR EM, WAKEFIELD RJ, et al. Ultrasound assessment of response to intra-articular therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(8):1385-1391. [3] DIEPPE P. Developments in osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;50(2):245-247. [4] ZHANG Y, XU L, NEVITT MC, et al. Comparison of the prevalence of knee osteoarthritis between the elderly Chinese population in Beijing and whites in the United States: The Beijing Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(9):2065-2071. [5] NHO SJ, KYMES SM, CALLAGHAN JJ, et al. The burden of hip osteoarthritis in the United States: epidemiologic and economic considerations. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21 Suppl 1:S1-6. [6] GROGAN SP, D'LIMA DD. Joint aging and chondrocyte cell death. Int J Clin Rheumtol. 2010;5(2):199-214. [7] XING D, XU Y, LIU Q, et al. Osteoarthritis and all-cause mortality in worldwide populations: grading the evidence from a meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24393. [8] MCALINDON TE, BANNURU RR, SULLIVAN MC, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(3):363-388. [9] ONDRÉSIK M, AZEVEDO MAIA FR, da Silva Morais A, et al. Management of knee osteoarthritis. Current status and future trends. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2017;114(4):717-739. [10] LOESER RF, ERICKSON EA, LONG DL. Mitogen-activated protein kinases as therapeutic targets in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2008;20(5):581-586. [11] 高世超,殷海波,刘宏潇,等.MAPK信号通路在骨关节炎发病机制中的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(5):441-444. [12] NARANTSOGT G, MIN A, NAM YH, et al. Activation of MAPK Is Required for ROS Generation and Exocytosis in HMC-1 Cells Induced by Trichomonas vaginalis-Derived Secretory Products. Korean J Parasitol. 2015;53(5):597-603. [13] 陈蔚东,蒋青,陈东阳,等. p38蛋白激酶抑制剂对大鼠膝骨关节炎的软骨保护作用[J].山东医药,2007,47(10):21-22 [14] BIJLSMA JW, BERENBAUM F, LAFEBER FP. Osteoarthritis: an update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet. 2011;377(9783):2115-2126. [15] HENROTIN Y, MARTY M, MOBASHERI A.What is the current status of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Maturitas. 2014;78(3):184-187. [16] 王胜民,刘毅,刘波,等.金骨莲胶囊对兔膝骨关节炎软骨保护作用的研究[J].重庆医学,2016,45(26):3611-3615. [17] 王胜民,刘毅,熊华章,等.金铁锁灌胃对兔膝骨关节炎的治疗作用及其机制探讨[J].山东医药,2017,57(31):36-40. [18] LIN MN, LIU XX, WANG SL, et al. Effect of OA kneepad on apoptosis genes Bcl-2 and p53 expression in articular cartilage cells of experimental knee osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009;22(9): 688-691. [19] ROMAN-BLAS JA, MEDIERO A, TARDÍO L, et al. The combined therapy with chondroitin sulfate plus glucosamine sulfate or chondroitin sulfate plus glucosamine hydrochloride does not improve joint damage in an experimental model of knee osteoarthritis in rabbits. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;794:8-14. [20] BELLIDO M, LUGO L, ROMAN-BLAS JA, et al. Subchondral bone microstructural damage by increased remodelling aggravates experimental osteoarthritis preceded by osteoporosis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):R152. [21] PELLETIER JP, JOVANOVIC D, FERNANDES JC, et al. Reduced progression of experimental osteoarthritis in vivo by selective inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(7): 1275-1286. [22] CALVO E, PALACIOS I, DELGADO E, et al. Histopathological correlation of cartilage swelling detected by magnetic resonance imaging in early experimental osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(11): 878-886. [23] MURPHY JM, FINK DJ, HUNZIKER EB, et al. Stem cell therapy in a caprine model of osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(12): 3464-3474. [24] HAYAMI T, PICKARSKI M, ZHUO Y, et al. Characterization of articular cartilage and subchondral bone changes in the rat anterior cruciate ligament transection and meniscectomized models of osteoarthritis. Bone. 2006;38(2):234-243. [25] 许怀来,徐凡平,黄明华,等.中医外治法治疗膝骨关节炎的研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(11):85-88. [26] 曾乐,刘毅,熊华章,等.金骨莲胶囊对兔膝关节骨关节炎保护作用的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2016,24(7):7-11. [27] 王胜民,刘毅,刘晓丽,等.金铁锁对膝关节骨性关节炎兔关节软骨的保护作用及其机制[J].山东医药,2016,56(16):27-29,111. [28] MUSUMECI G, CASTROGIOVANNI P, TROVATO FM, et al. Biomarkers of Chondrocyte Apoptosis and Autophagy in Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(9):20560-20575. [29] KARSENTI E, VERNOS I. The mitotic spindle: a self-made machine. Science. 2001;294(5542):543-547. [30] SHINOURA N, MURAMATSU Y, YOSHIDA Y, et al. Adenovirus- mediated transfer of caspase-3 with Fas ligand induces drastic apoptosis in U-373MG glioma cells. Exp Cell Res. 2000;256(2):423-433. [31] SHARIF M, WHITEHOUSE A, SHARMAN P, et al. Increased apoptosis in human osteoarthritic cartilage corresponds to reduced cell density and expression of caspase-3. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(2):507-515. [32] 陈喜德,魏波,杨柳菁,等.不同病期骨关节炎大鼠关节软骨中caspase-3与细胞凋亡的相关性[J].广东医学, 2018,39(2):181-186. [33] 马钢,任明姬.骨性关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的研究[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2012,21(2):196-200. [34] 刘恒,刘超,曹永平.软骨细胞线粒体功能异常在关节软骨早期退变中的作用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(8):652-654. [35] KOURTIS A, ADAMOPOULOS PG, PAPALOIS A, et al. Quantitative analysis and study of the mRNA expression levels of apoptotic genes BCL2, BAX and BCL2L12 in the articular cartilage of an animal model of osteoarthritis. Ann Transl Med. 2018;6(12):243. [36] BROWN KK, HEITMEYER SA, HOOKFIN EB, et al. P38 MAP kinase inhibitors as potential therapeutics for the treatment of joint degeneration and pain associated with osteoarthritis. J Inflamm (Lond). 2008;5:22. [37] KÜHN K, SHIKHMAN AR, LOTZ M. Role of nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species, and p38 MAP kinase in the regulation of human chondrocyte apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 2003;197(3):379-387. [38] HAN J, SUN P. The pathways to tumor suppression via route p38. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32(8):364-371. [39] FAN Z, SÖDER S, OEHLER S, et al. Activation of interleukin-1 signaling cascades in normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage. Am J Pathol. 2007;171(3):938-946. [40] SHI J, ZHANG C, YI Z, et al. Explore the variation of MMP3, JNK, p38 MAPKs, and autophagy at the early stage of osteoarthritis. IUBMB Life. 2016;68(4):293-302. [41] RASHEED Z, AKHTAR N, HAQQI TM. Pomegranate extract inhibits the interleukin-1β-induced activation of MKK-3, p38α-MAPK and transcription factor RUNX-2 in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(5):R195. [42] MOREL C, IBARZ G, OIRY C, et al. Cross-interactions of two p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase inhibitors and two cholecystokinin (CCK) receptor antagonists with the CCK1 receptor and p38 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(22):21384-21393. |
| [1] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [2] | Zuo Zhenkui, Han Jiarui, Ji Shuling, He Lulu. Pretreatment with ginkgo biloba extract 50 alleviates radiation-induced acute intestinal injury in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3666-3671. |
| [3] | Yan Xiurui, Tao Jin, Liang Xueyun. Mechanism by which exosomes from human fetal placental mesenchymal stem cells protect lung epithelial cells against oxidative stress injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2994-2999. |
| [4] | Huang Yongming, Huang Qiming, Liu Yanjie, Wang Jun, Cao Zhenwu, Tian Zhenjiang, Chen Bojian, Mai Xiujun, Feng Enhui. Proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes co-cultured with TDP43 lentivirus transfected-human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1016-1022. |
| [5] | Zhou Wenming, Lin Yifeng, Zhang Zhen, Chi Liye. Effect of Bushen Zhuangdu Fang serum on mitochondrial apoptotic pathway of nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3643-3648. |
| [6] | Liu Jing, Sun Zhilu, Zhou Jun, Liao Yuan, Sun Guanghua, Wu Qi, Zhou Guijuan, Zhong Peirui, Cheng Guo, Xiao Hao, Li Lan, Liao Ying. Effect of ibandronate on mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in rat models of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 181-186. |
| [7] | Min Dongyu, Li Hongyan, Guan Le, Chang Jiang, Zhang Haining, Cui Xinyue, Wang Peng, Cao Yonggang. Protective mechanism of Naoxinqing Capsule in rat models of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 215-222. |
| [8] | Yu Heng, Zhou Tao. Effects of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on recovery of nerve function and telomerase reverse transcriptase expression in brain tissue of cerebral infarction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 2972-2977. |
| [9] | Li Hong, Wu Shaohua, Qiu Mingxing, Deng Qingfu, Lei Guolin, Li Qinglong. Mechanism underlying basic fibroblast growth factor and insulin-like growth factor-1 effects on proliferation and apoptosis of spermatogonial stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3017-3022. |
| [10] | Zhong Ping, Cui Xing. Mechanism of angelica polysaccharide regulating mitochondrial apoptosis for improving bone marrow failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2074-2079. |
| [11] | Xiong Fei1, Wei Yishan2. Reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip in rabbits: expression levels of Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in acetabular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4974-4978. |
| [12] | Huang Chao1, Huang Qinghua2, You Di3, Guo Wenlai1, Qu Wenrui1, Zhu Zhe1, Li Rui1 . Molecular mechanism of quercetin in the treatment of traumatic brain injury: its feasibility of clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3760-3766. |
| [13] | Yang Yukun, Zhu Xiangqing, Ruan Guangping, Wang Yanying, Kan Xiaoli, Zhang Xuejuan, Yu Qianqian, Wang Mao, He Huanyu,Pan Xinghua. Association of aging with pulmonary fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and treatment with mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2746-2752. |
| [14] | Xu Wu-ji, Yang Kang, Liu Si-hua. Effect of Liuwei Dihuang Pills on the extracellular matrix components of intervertebral disc degeneration models in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(16): 2495-2501. |
| [15] | Xu Wu-ji1, Liu Si-hua2, Yang Kang3. Liuwei Dihuang Pill inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade of nucleus pulposus cells in a model of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(12): 1861-1866. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||