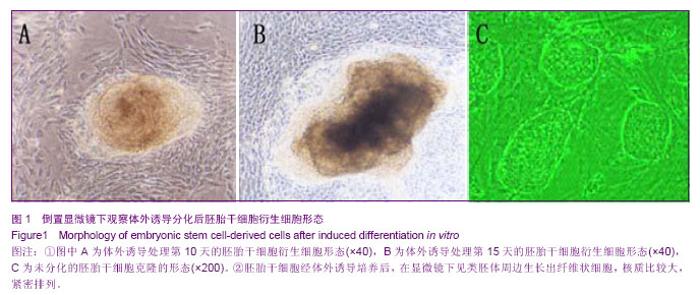
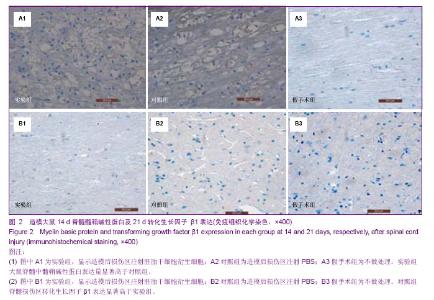
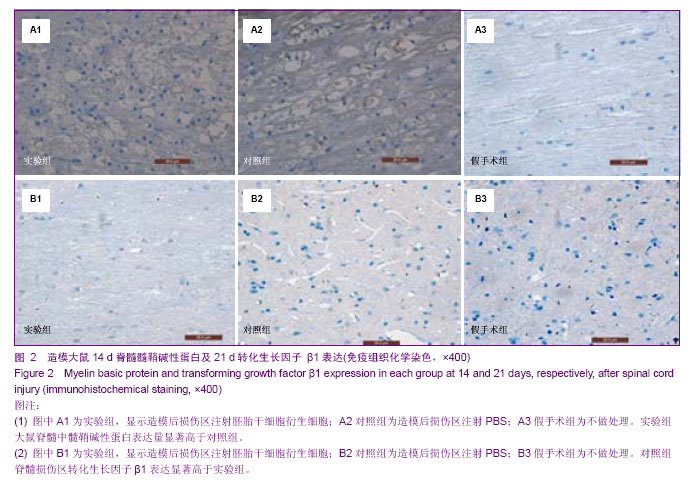
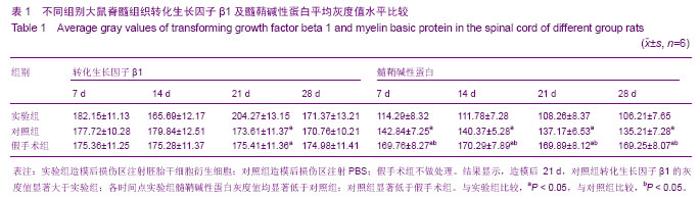
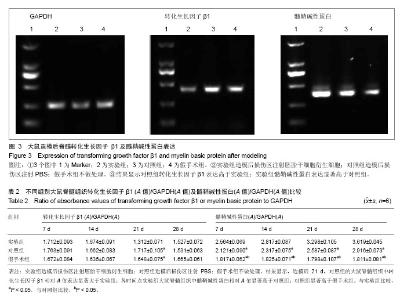
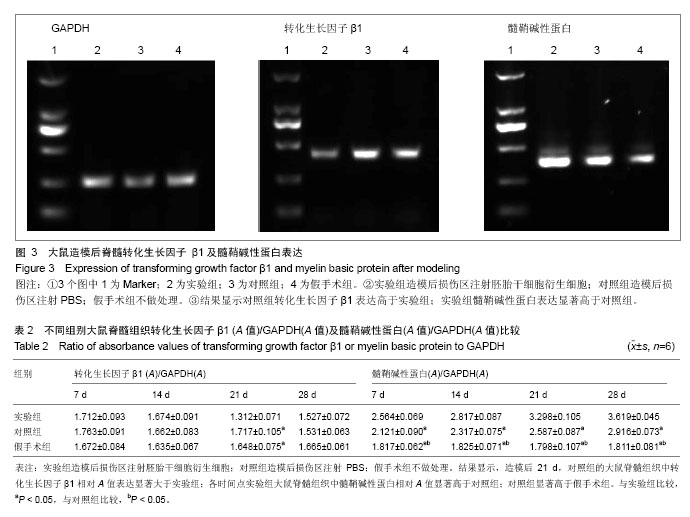
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (1): 112-118.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.01.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Embryonic stem cells transplantation effects on expression of transforming growth factor beta 1 and myelin basic protein
Yang Jian-hua, Zhang Fu-yun, Re Ji-pu, Shen Fu-guo, Qiao Jian-min
- First Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154003, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Revised:2013-11-27Online:2014-01-01Published:2014-01-01 -
Contact:Qiao Jian-min, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154003, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Yang Jian-hua, Master, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154003, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, No. D201160; the Educational Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, No. 12511539; the grant from Heilongjiang Health Bureau, No. 2010-521; the grant from Jiamusi University
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Jian-hua, Zhang Fu-yun, Re Ji-pu, Shen Fu-guo, Qiao Jian-min . Embryonic stem cells transplantation effects on expression of transforming growth factor beta 1 and myelin basic protein[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(1): 112-118.
share this article
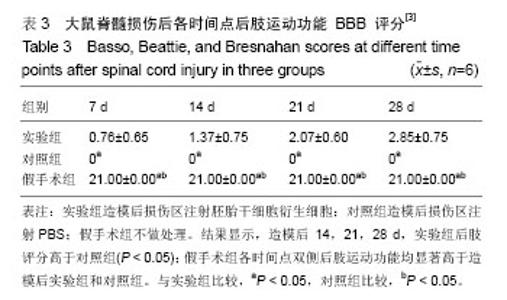
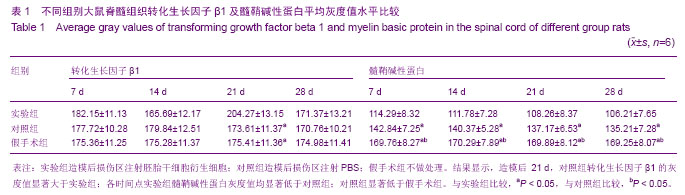
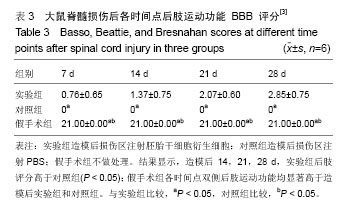
2.5 后肢运动功能评分 造模前所有的大鼠进行BBB评分均为21分。大鼠在造模6 h之后全部完全清醒,所有脊髓全横断鼠都出现了典型的截瘫综合征;伴有腹胀、尿潴留、排便困难等症状。造模后各时间点所有大鼠BBB 评分全部小于造模前,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);造模后14,21,28 d各时间点间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。对照组大鼠在检测时间内下肢功能完全丧失,肌力零级,后肢运动功能均为0分。造模后 7 d,实验组大鼠后肢功能开始恢复,造模后 14,21,28 d,实验组后肢评分高于对照组(P < 0.05)。假手术组各时间点双侧后肢运动功能均为21分,高于造模后实验组、对照组(P < 0.05) (表3)。"
| [1] 徐乐勤,丁道芳,李晓锋,等.胚胎干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2011,17(1):51-53.[2] Vadivelu S, Platik MM, Choi L,et al. Multi-germ layer lineage central nervous system repair: nerve and vascular cell generation by embryonic stem cells transplanted in the injured brain. J Neurosurg.2005;103(1):124-135.[3] Basso DM,Beattie MS,Bresnahan JC.A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats.J Neurotrauma.1995;12(1):1-21.[4] 巴迎春,范艳,王金德,等.TGF-β1和CNTF在大鼠移植神经干细胞后的损伤脊髓中的表达[J].昆明医学院学报,2012,33(3):1-7.[5] 王小莲,曾文泓,王婷,等.微囊化异种坐骨神经组织细胞移植脊髓损伤大鼠核因子κB的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(25):4619-4622.[6] 雷德强,赵洪洋,张方成,等.白介素-10对脊髓损伤后炎症影响的研究[J].山东医药,2008,48(4):6-7. [7] 廖维宏,张光铂. 进一步加强脊髓损伤修复研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2003,13(9):517-519. [8] Suzuki H, Taguchi T, Kato Y, et al.Transplantation of neurospheres derived from bone marrow stromal cells promotes neurological recovery in rats with spinal cord injury.Med Mol Morphol.2011;44(3):131-138.[9] Penkala K,Kawa M,Baumert B,et al.Functional improvement of injured retina following the adjuvant stem cellbased therapy.Preliminary report.Klin Oczna.2011;113(46):117-121.[10] Keski-Oja J, Koli K, Melchner H. TGF-beta activation by traction? Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14(12): 657-659.[11] 李云,彭春,王廷华.嗅鞘细胞移植脊髓全横断损伤大鼠大脑皮质运动区转化生长因子β表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(19):3534-3537.[12] 贾赤宇,陈璧.TGFβ1对瘢痕形成的影响[J].中华整形烧伤外科杂志,1999;15(1):72-73.[13] 周健,张富国,潘寒松,等. TGF-β蛋白在急性脊髓损伤大鼠中的研究[J].医学研究杂志,2008,37(8):31-33.[14] Lane MA, Truettner JS, Brunschwig JP, et al.Age-related differences in the local cellular and molecular responses to injuryin developing spinal cord of the opossum, Monodelphis domestica.Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25(6):1725-1742.[15] Martinou JC,Le Van Thai A,Valette A,et al.Transforming growth factor beta 1 is a potent survival factor for rat embryo motoneurons in culture. Brain Res Dev Brain Bes. 1990;52 (1-2): 175-181.[16] O'Brien MF, Lenke LG, Lou J, et al. Astrocyte response and transforming growth factor-beta localization in acute spinal cord injury. Spine. 1994;19(20):2321-2329.[17] Kim JH, Min KJ, Seol W, et al. Astrocytes in injury states rapidly produce anti-inflammatory factors and attenuate microglial inflammatory responses.J Neurochem. 2010; 115(5):1161-1171. [18] Pineau I, Sun L, Bastien D,et al. Astrocytes initiate inflammation in the injured mouse spinal cord by promoting the entry of neutrophils and inflammatory monocytes in an IL-1 receptor/MyD88-dependent fashion. Brain Behav Immun. 2010; 24(4):540-553. [19] Kreutzberg GW.Microglia,the first line of denfence in brain pathologies. Arzneimittelforschung. 1995;45(3A):357-360. [20] Flanders KC,Ren RF,Lippa CF.Transforming growth factor-betas in neurodegenerative disease. Prog Neurobiol. 1998;54(1):71-85. [21] Wang X, Chen W, Liu W, et al. The role of thrombospondin-1 and transforming growth factor-beta after spinal cord injury in the rat. J Clin Neurosci. 2009; 16(6):818-821.[22] Hamada Y, Ikata T, Katoh S, et al. Effects of exogenous transforming growth factor-beta 1 on spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1996;203(2):97-100. [23] Kohta M, Kohmura E, Yamashita T. Inhibition of TGF-beta1 promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Res.2009;65(4):393-401.[24] Harauz G, Ishiyama N, Hill CM, et al. Myelin basic protein-diverse conformational states of an intrinsically unstructured protein and its roles in myelin assembly and multiple sclerosis. Micron.2004; 35(7):503-542.[25] 吴波,孙磊,任先军.少突胶质前体细胞移植治疗对大鼠脊髓损伤轴突髓鞘化的影响[J].中华创伤杂志,2010,26(11):1035-1039.[26] 张涛,沈忆新,芦磊磊,等.硫酸软骨素酶ABC对大鼠脊髓损伤后轴突髓鞘化和胶质瘢痕的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013, 27(2):145-150.[27] Atkinson S, Li YQ, Wong CS. Changes in oligodendrocytes and myelin gene expression after radiation in the rodent spinal cord. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.2003;57(4): 1093-1100.[28] Fukuda A, Fukuda H, Swanpalmer J, et al. Age-dependent sensitivity of the developing brain to irradiation is correlated with the number and Vulnerability of progenitor cells. J Neurochem.2005; 92(3): 569-584.[29] Kotter MR, Li WW, Zhao C, et al. Myelin impairs CNS remyelination by inhibiting oligoden- drocyte precursor cell diferentiation. J Neuro-sci. 2006;26(1): 328-332. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||