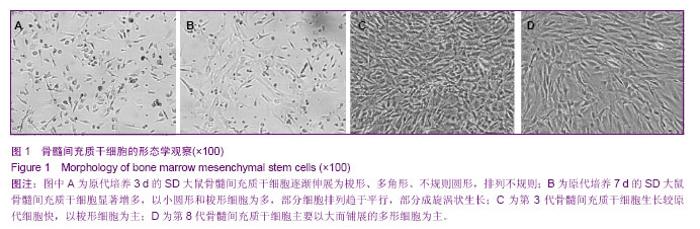
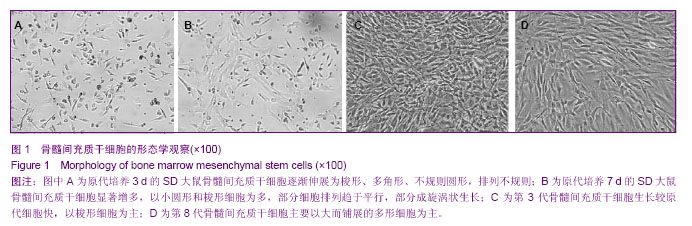
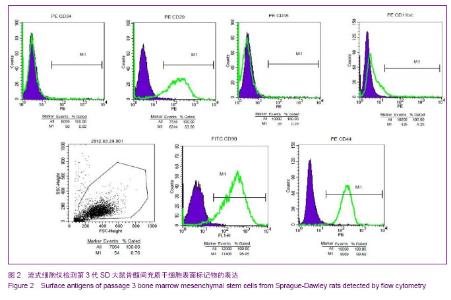
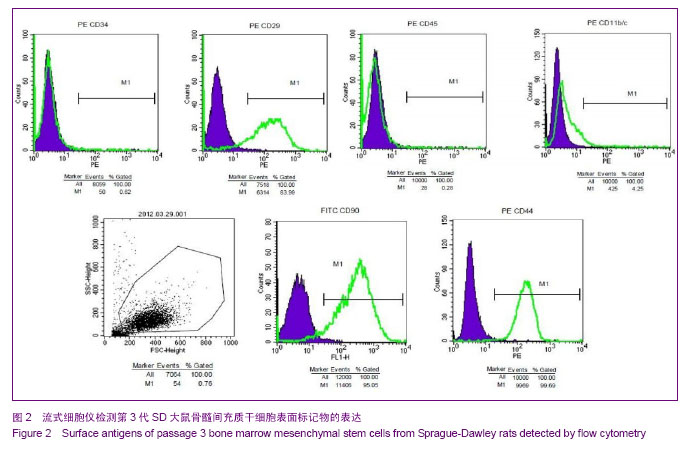
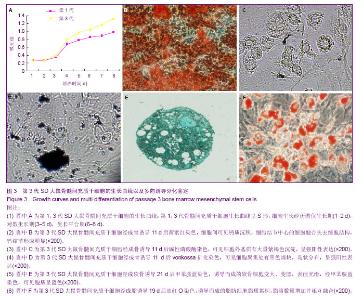
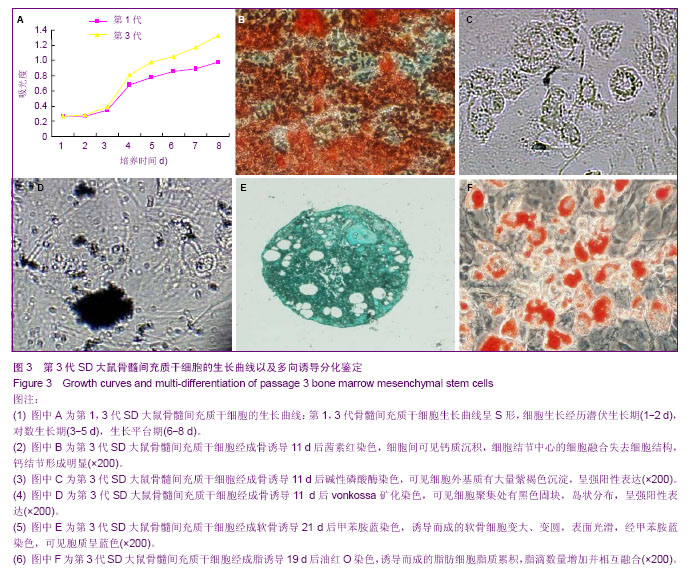
| [1] Fisher M, Hyzy S, Guldberg RE,et al. Regeneration of bone marrow after tibial ablation in immunocompromised rats is age dependent. Bone. 2010;46(2):396-401. [2] Quintavalla J, Uziel-Fusi S, Yin J,et al. Fluorescently labeled mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) maintain multilineage potential and can be detected following implantation into articular cartilage defects. Biomaterials. 2002;23(1):109-119.[3] Yamaguchi S, Kuroda S, Kobayashi H,et al. The effects of neuronal induction on gene expression profile in bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC)--a preliminary study using microarray analysis. Brain Res. 2006;1087(1):15-27. [4] Lee KD, Kuo TK, Whang-Peng J,et al. In vitro hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1275-1284.[5] Van Damme A, Vanden Driessche T, Collen D,et al. Bone marrow stromal cells as targets for gene therapy.Curr Gene Ther. 2002;2(2):195-209. [6] Charbord P. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: historical overview and concepts. Hum Gene Ther. 2010 ;21(9): 1045- 1056. [7] Wilson NH, Key B. Neogenin: one receptor, many functions. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(5):874-878.[8] Vinatier C, Mrugala D, Jorgensen C,et al. Cartilage engineering: a crucial combination of cells, biomaterials and biofactors.Trends Biotechnol. 2009;27(5):307-314.[9] Freimark D, Czermak P. Cell-based regeneration of intervertebral disc defects: review and concepts. Int J Artif Organs. 2009;32(4):197-203.[10] Liu G, Beggs H, Jürgensen C, et al. Netrin requires focal adhesion kinase and Src family kinases for axon outgrowth and attraction.Nat Neurosci. 2004;7(11):1222-1232.[11] Shahdadfar A, Frønsdal K, Haug T,et al. In vitro expansion of human mesenchymal stem cells: choice of serum is a determinant of cell proliferation, differentiation, gene expression, and transcriptome stability. Stem Cells. 2005; 23(9):1357-1366.[12] Rossignol J, Boyer C, Lévèque X,et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation and DMEM administration in a 3NP rat model of Huntington's disease: morphological and behavioral outcomes. Behav Brain Res. 2011;217(2):369-378.[13] Delcroix GJ, Garbayo E, Sindji L,et al. The therapeutic potential of human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells combined with pharmacologically active microcarriers transplanted in hemi-parkinsonian rats. Biomaterials. 2011; 32(6):1560-1573. [14] Song H, Hwang HJ, Chang W,et al. Cardiomyocytes from phorbol myristate acetate-activated mesenchymal stem cells restore electromechanical function in infarcted rat hearts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(1):296-301. [15] Oh JS, Kim KN, An SS,et al. Cotransplantation of mouse neural stem cells (mNSCs) with adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves mNSC survival in a rat spinal cord injury model. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(6):837-849.[16] Jackson WM, Nesti LJ, Tuan RS. Potential therapeutic applications of muscle-derived mesenchymal stem and progenitor cells. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10(4):505-517.[17] de Mattos Carvalho A, Alves AL,et al. Isolation and immunophenotypic characterization of mesenchymal stem cells derived from equine species adipose tissue.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009;132(2-4):303-306. [18] Kode JA, Mukherjee S, Joglekar MV,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: immunobiology and role in immunomodulation and tissue regeneration. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(4):377-391. [19] Lei Z, Yongda L, Jun M,et al. Culture and neural differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Cell Biol Int. 2007;31(9):916-923. [20] Beyer Nardi N, da Silva Meirelles L. Mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, in vitro expansion and characterization. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;(174):249-282.[21] Morikawa S, Mabuchi Y, Kubota Y,et al. Prospective identification, isolation, and systemic transplantation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells in murine bone marrow. J Exp Med. 2009;206(11):2483-2496. [22] Wang X, Hisha H, Mizokami T,et al. Mouse mesenchymal stem cells can support human hematopoiesis both in vitro and in vivo: the crucial role of neural cell adhesion molecule. Haematologica. 2010;95(6):884-891. [23] Jones EA, English A, Kinsey SE,et al. Optimization of a flow cytometry-based protocol for detection and phenotypic characterization of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells from human bone marrow. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2006; 70(6):391-399.[24] Shu XC, Zhu DH, Liu JJ,et al. In vitro studies on the growth and proliferation characteristics of rat bone mesenchymal stem cells. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;44(10): 923-927.[25] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL,et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49. [26] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ,et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.[27] Hofstetter CP, Schwarz EJ, Hess D,et al. Marrow stromal cells form guiding strands in the injured spinal cord and promote recovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(4):2199-2204. |