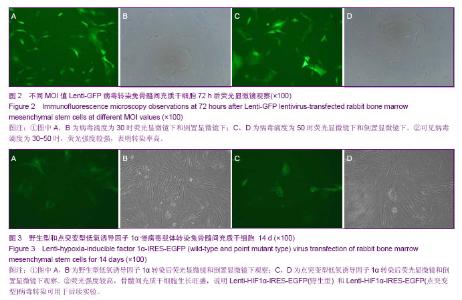
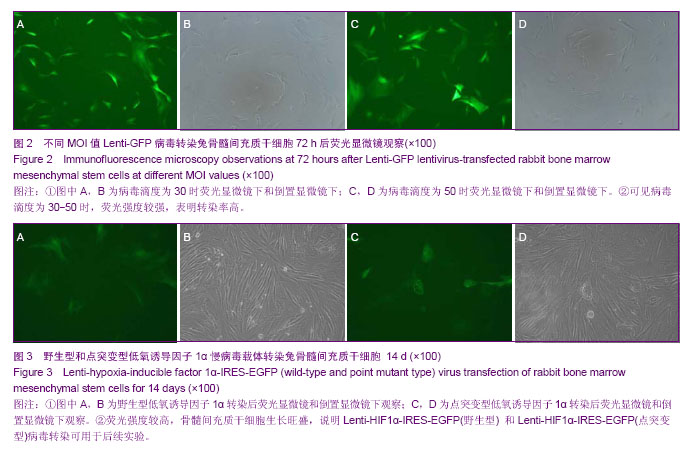
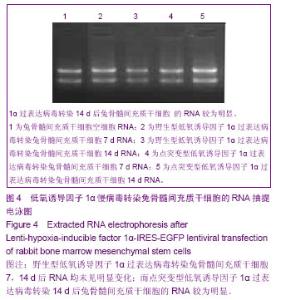
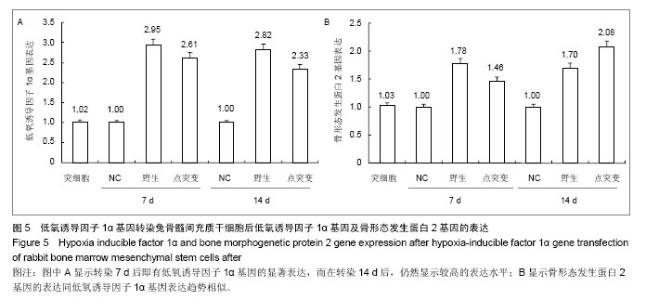
| [1] Hayden RE, Mullin DP, Patel AK. Reconstruction of the segmental mandibular defect: current state of the art. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;20(4):231-236. [2] Chanowski EJ, Sacco AG, Fung K, et al. Revascularized tissue transplant and internal transport disk distraction osteogenesis for the reconstruction of complex composite mandibular defects. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 40(4):330-336.[3] Lauren S, Caren E, Edward A, et al. Engineering vascularized tissues using natural and synthetic small molecules. J Organogenesis. 2008;4(4):215-227.[4] Semenza GL, Wang GL. A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. J Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12(12): 5447-5454. [5] 杨峰,汤欣.低氧诱导因子-1α诱导鼠胚成骨细胞血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)表达的实验研究[J].中国伤残医学,2011,19(8):1-3.[6] 邹多宏. 低氧诱导因子-1α的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2010,37(3):320-324.[7] 陆蕴松,高忠礼,刘光耀,等.低氧诱导因子-1对血管内皮生长因子的调控[J].中国老年学杂志,2009,29(7):905-907.[8] Farré-Pagés N,Augé-Castro ML, Alaejos-Algarra F, et al. A novel trephine design for sinus lift lateral approach. Case report.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal.2011;16(1):e79-82.[9] Wan C, Gilbert SR, Wang Y, et al. Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathway accelerates bone regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(2): 686-691. [10] 刘晓东,邓廉夫,王君,等.低氧诱导因子-1α对成骨细胞功能的调控作用[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2007,27(3):298-302. [11] Lee JH, Kim JH, Oh SH, et al. Tissue-engineered bone formation using periosteal-derived cells and polydioxanone/pluronic F127 scaffold with pre-seeded adipose tissue-derived CD146 positive endothelial-like cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32(22):5033-5045.[12] Li J, Li Y, Ma S, et al. Enhancement of bone formation by BMP-7 transduced MSCs on biomimetic nano- hydroxyapatite/ polyamide composite scaffolds in repair of mandibular defects. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95(4): 973-981.[13] Jiang X, Zhao J, Wang S, et al. Mandibular repair in rats with premineralized silk scaffolds and BMP-2-modified BMSCs. J Biomaterials. 2009;30(6):4522-4532.[14] Nagata M, Hoshina H, Li M, et al. A clinical study of alveolar bone tissue engineering with cultured autogenous periosteal cells: coordinated activation of bone formation and resorption. Bone. 2012;50(5):1123-1129.[15] Kohgo T, Yamada Y, Ito K, et al. Bone regeneration with self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds in tissue engineering for osseointegration of dental implants. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2011;31(4):9-16.[16] Henslee AM, Spicer PP, Yoon DM, et al. Biodegradable composite scaffolds incorporating an intramedullary rod and delivering bone morphogenetic protein-2 for stabilization and bone regeneration in segmental long bone defects. Acta Biomater. 2011; 7(10):3627-3637.[17] Ryan C. Riddle RK, Ernestina S, et al. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in angiogenic-osteogenic coupling. J Mol Med, 2009, 87(6):583-590.[18] Bartholomeusz G, Cherukuri P, Kingston J, et al. In Vivo Therapeutic Silencing of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha (HIF-1α) Using Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Noncovalently Coated with siRNA. Nano Res. 2009;2(4):279-291.[19] Fraga CA, Oliveira MV, Alves LR, et al. Immunohistochemical profile of HIF-1α, VEGF-A, VEGFR2 and MMP9 proteins in tegumentary leishmaniasis. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87(5): 709-813. [20] Liang W, Jun L, Li F, et al. Construction of recombinant adenovirus vector containing a modified gene that codes for human HIF-1α without oxygen-dependent degradation domain. J Plasmid.2010;63(1):20-26. |