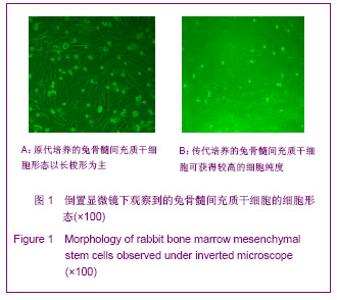
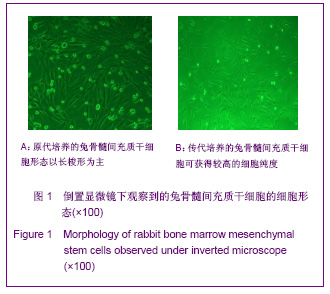
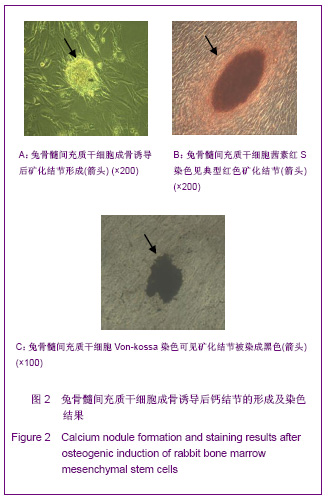
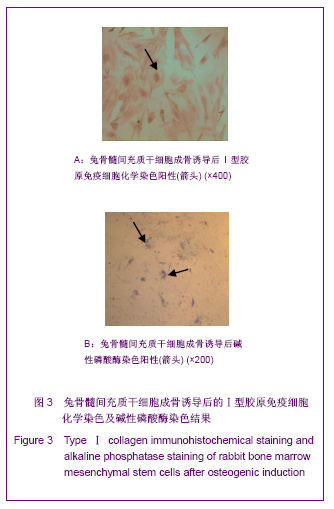
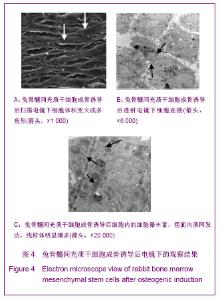
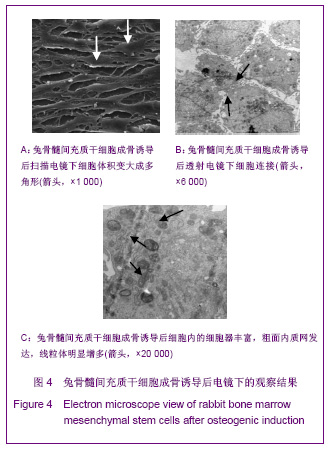
| [1] Lee HS, Huang GT, Chiang H ,et al.Multipotential mesenchymal stem cells from femoral bone marrow near the site of osteonecrosis.Stem Cells.2003;21(2):190-199.[2] Fisher M, Hyzy S, Guldberg RE, et al. Regeneration of bone marrow after tibial ablation in immunocompromised rats is agedependent. Bone. 2010;46(2):396-401.[3] Yamaguchi S, Kuroda S, Kobayashi H ,et al.The effects of neuronal induction on gene expression profile in bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) - a preliminary study using microarray analysis.Brain Res.2006;1087(1):15-27. [4] Butnariu-Ephrat M, Robinson D, Mendes DG ,et al. Resurfacing of goat articular cartilage by chondrocytes derived from bone marrow.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1996; 330):234-243.[5] Wakitani S, Goto T, Pineda SJ ,et al.Mesenchymal cell-based repair of large, full-thickness defects of articular cartilage.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1994;76(4):579-592.[6] Li XF,ZhaoJM,Su W,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(10):1721-1725. 李晓峰,赵劲民,苏伟,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(10):1721-1725.[7] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance suggestion of caring laboratory animals.2006-09-30. 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[8] Abdallah BM,Kassem M.The Use of Mesenchymal (Skeletal) Stem Cells for Treatment of Degenerative Diseases: Current Status and Future Perspectives.J Cellular Physiology. 2009; 218(1):9-12.[9] Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhjan RK,Lalykina KS.The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells.Cell Tissue Kinet. 1970;3(4):393-403.[10] Owen M.Marrow stromal stem cells.J Cell Sci Suppl.1988; 10:63-76.[11] Tse WT, Pendleton JD, Beyer WM ,et al.Suppression of allogeneic T-cell proliferation by human marrow stromal cells:implications in transplantation.Transplantation.2003;75 (3):389-397.[12] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC ,et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[13] Jiang Y,Jahagirdar B N,Reinhardt R L,et al.pulripotency of mesenchymal stem cell derived from adult marrow.Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49.[14] Zheng YH, He T, Kuang SJ, et al. Guoji Yiyao Weisheng Daobao.2010;16(02):129-134. 郑有华,何滔,匡世军,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外分离培养及其生物学特性[J].国际医药卫生导报,2010,16(02):129-134.[15] Dvorakova J, Hruba A, Velebny V,et al. Isolation andcharacterization of mesenchymal stem cell population entrappedin bone marrow collection sets. Cell Biol Int.2008; 32(9): 1116-1125.[16] Jiang H,Xiao ZM.Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu.2006;10(45): 118-120. 江华,肖增明.骨髓间充质干细胞在骨科疾病修复中的应用[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(45):118-120.[17] Huang T,Meng ZB,Jia BS,et al.Guangdong Yixue.2010;31(9): 1089-1091. 黄涛,孟志斌,贾丙申,等.全骨髓贴壁法分离培养rBMSCs及成骨诱导探讨[J].广东医学,2010,31(9):1089-1091.[18] Huang Y,Li YH.Zhongguo Shengwu Gongcheng Zazhi.2006; 26(5):85-88. 黄艳,李莹辉.影响骨髓间质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的调控因素[J].中国生物工程杂志,2006,26(5):85-88[19] Hu Z, Peel SA, Ho SK ,et al.Role of bovine bone morphogenetic proteins in bone matrix protein and osteoblast-related gene expression during rat bone marrow stromal cell differe-ntiation.J Craniofac Surg.2005;16(6): 1006-1014. [20] Morales O,Samuelsson MK,Lindgren U,et al.Effects of 1alpha,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 and growth hormone on apoptosis and proliferation in UMR 106 osteoblast-like cells.Endoc inology.2004;145(1):87-94.[21] van Leeuwen JP, van Driel M, van den Bemd GJ ,et al.Vitamin D control of osteoblast function and bone extracellular matrix mineralization.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr.2011;11(1-3): 199-226.[22] Jaiswal N,Haynesworth SE,Caplan AI,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of purified,culture -expanded human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.J Cell Biochem.1997; 64(2):295-312.[23] Marie PJ,Fromigue O.Osteogenic differentiation of human marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Regen Med.2006; 1(4):539-548.[24] Coelho MJ,Fernandes MH.Human bone cell cultures in biocompatibility testing. Part II: effect of ascorbic acid, beta-glycerophosphate and dexamethasone on osteoblastic different- iation.Biomaterials.2000;21(11):1095-1102.[25] Maniatopoulos C,Sodek J,Melcher AH.Bone formation in vitro by stromal cells Obtained from bone marrow of young adult rats.Cell Tissue Res.1988;254(2):317-330.[26] Wang ZS,Wang JY,Wang BZ, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi GongchengYanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2009;13(1):11-16. 王志顺,王江泳,王保芝,等.骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞诱导分化的超微结构改变[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(1):11-16.[27] Pan SC,Tang YJ,Xie KG,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi GongchengYanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(32): 5918-5922. 潘生才,唐毓金,谢克恭,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨诱导分化的超微结构变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(32):5918-5922. |