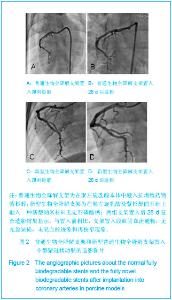
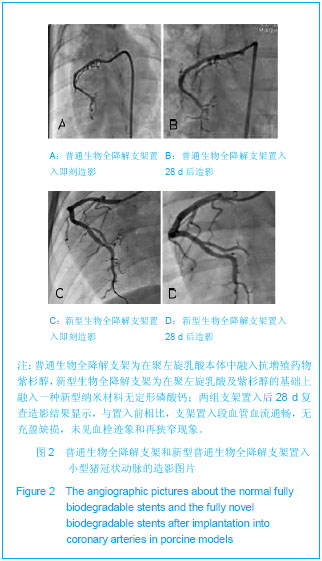
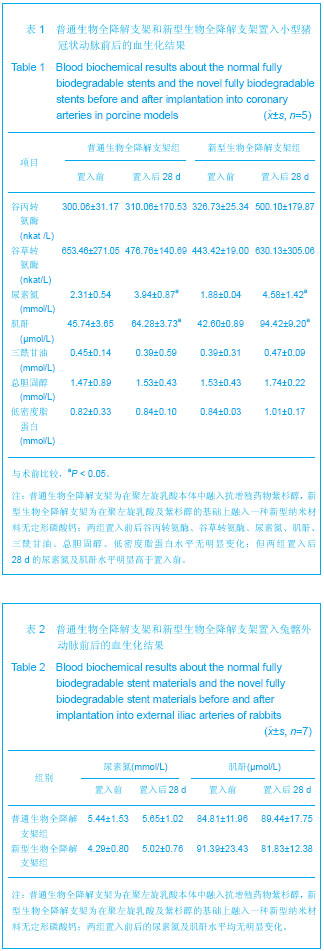
| [1] |
Xie Xiufeng, Zhang Yue, Qu Ze.
Clinical outcomes of drug-eluting balloons and drug-eluting
stents for the treatment of in-stent restenosis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 555-560.
|
| [2] |
Yuan Bo, Wang Zhiwei, Tang Yifan, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun.
Construction of polycaprolactone-tricalcium phosphate with different mixture ratios using three-dimensional printing technology and its osteoinductivity in vitro
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 821-826.
|
| [3] |
Wang Xuefeng, Shang Xifu .
Curative effects of three filling materials in the treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 863-869.
|
| [4] |
Liu Dan, Min Changqin, Lu Shuai, Chen Yue, Sun Yong.
Osseointegration induced by beta-tricalcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet-rich fibrin
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 888-893.
|
| [5] |
Cheng Jian, Zhang Jun, Guan Jie, Zeng Junkai, Zhao Xin, Xie Youzhuan.
Silver nanoparticle-doped tricalcium phosphate: in vitro and in vivo toxicity in rabbits
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 917-923.
|
| [6] |
Wei Wei, Liu Yanfei, Zhang Ling, Xiong Na .
Self-assembling peptide hydrogel: hemostatic effect and mechanism
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 310-316.
|
| [7] |
Cui Tingting, Qiu Zewen, Gui Lin, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu.
Effect of gelatin sponge/beta-tricalcium phosphate composite with different doses of basic fibroblast growth factor on bone regeneration
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 190-195.
|
| [8] |
Gao Shan, Zhou Fang, Lü Yang, Yuan Liang, Li Ailing, Qiu Dong.
Preparation and characterization of novel porous polymethyl methacrylate bone cements
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 204-210.
|
| [9] |
Peng Chenjian, Du Bin, Sun Guangquan, Liu Xin, Xue Peng, Cao Liangquan.
Three-dimensional printing beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold loaded with icariin particles for repairing osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rabbits
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2162-2168.
|
| [10] |
Li Haoliang, Wang Xibin, Zuo Ruiting.
Calcium phosphate cement/fibrin glue composite loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 promotes osteoporotic fracture healing
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2156-2161.
|
| [11] |
Zhang Minbo, Peng Qifeng, Ma Yaping, Kong Weijun, Liao Wenbo.
Physical properties and biocompatibility of 3D printed bone microparticle/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2215-2222.
|
| [12] |
Li Zhi, Tan Chunhua, Cai Xianhua, Wang Huasong, Ding Xiaoming, Zhao Yanhong.
Fabrication and biocompatibility assessment of the scaffold with biomimetic interconnected macropore structure
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2223-2227.
|
| [13] |
Bai Yulong, Gao Yufeng, Zhong Hongbin, Zhao Yantao, Guo Ruizhou, Li Li.
Allogeneic and xenogeneic tissue repair materials: how to choose a suitable virus inactivation process
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2261-2268.
|
| [14] |
Zhang Xiaodong, Liu Ying.
Patent analysis for calcium phosphate bone cements
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2269-2278.
|
| [15] |
Luo Kai, Yang Yafeng, Ma Teng, Xia Bing, Huang Liangliang, Huang Jinghui, Luo Zhuojing.
Effects of perfluorotributylamine/alginate/bioglass biomaterials on viability and osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 1995-2001.
|