Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3242-3249.doi: 10.12307/2026.058
Previous Articles Next Articles
Chemokine receptor 7-bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with porcine small intestinal submucosa promote skin repair in rats
Fan Meirong, Li Guangqi, Song Xumei, Yan Xin, Sui Ruizhi
- Medical Experimental Center, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-03-06Revised:2025-05-07Accepted:2025-05-29Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-24 -
Contact:Fan Meirong, MS, Chief technician, Medical Experimental Center, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Fan Meirong, MS, Medical Experimental Center, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. 2023AAC03616 (to FMR); Open Research Fund of Ningxia Key Laboratory of Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine, No. KF202409 (to FMR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fan Meirong, Li Guangqi, Song Xumei, Yan Xin, Sui Ruizhi. Chemokine receptor 7-bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with porcine small intestinal submucosa promote skin repair in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3242-3249.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
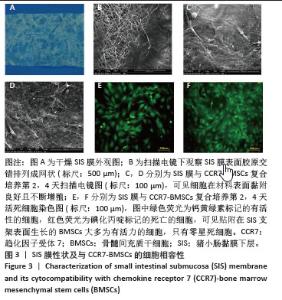
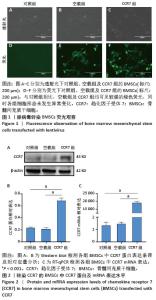
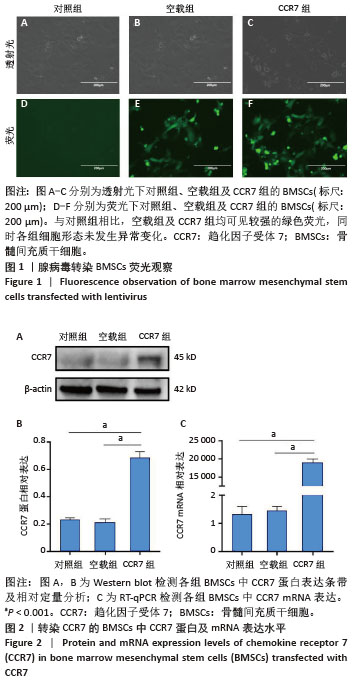
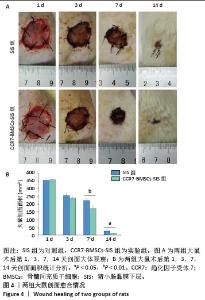
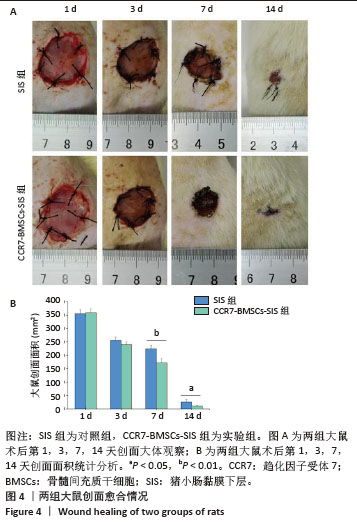
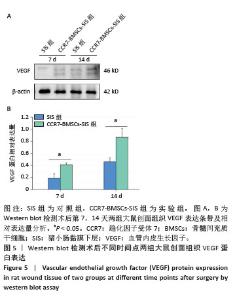
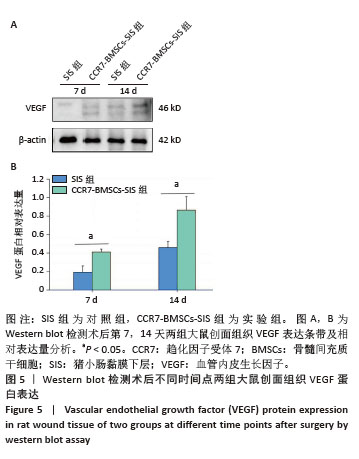
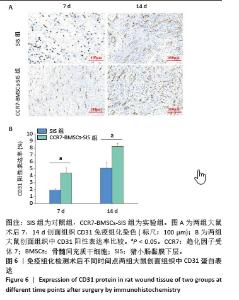
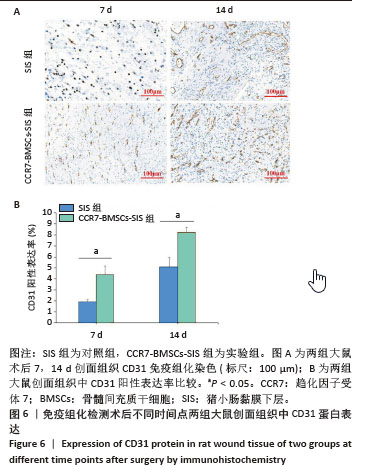
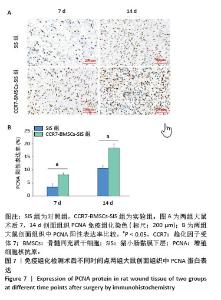
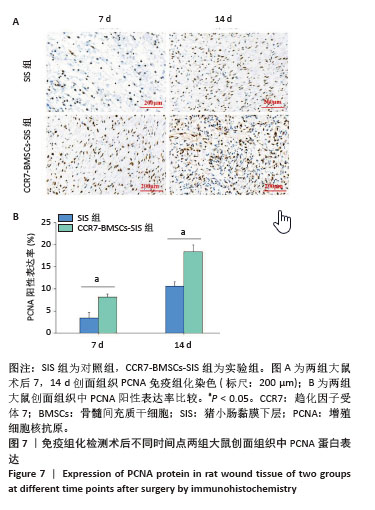
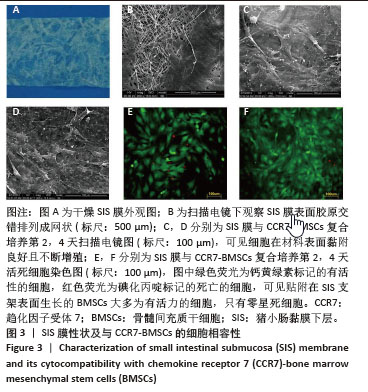
2.2 SIS膜性状及与CCR7-BMSCs的细胞相容性 干燥SIS膜呈不均匀白色片状,通过扫描电镜观察SIS膜表面胶原交错排列成三维多孔结构,孔隙结构利于细胞黏附、增殖,表面部分覆盖白色膜状胶原物质(图3A,B)。CCR7-BMSCs与SIS膜复合培养2 d后,扫描电镜观察可见SIS膜表面附着的BMSCs生长状况良好,细胞呈典型长梭形、纺锤形或多角形;细胞数量随着培养时间的延长而逐渐增多,培养4 d时可见细胞排列紧密,相互交联成片状(图3C,D)。活死细胞染色结果显示CCR7-BMSCs与SIS膜复合培养2,4 d后,BMSCs在SIS膜表面生长状态良好,细胞伸出突起呈典型长梭形或不规则形状,随着培养时间延长细胞排列为放射状或束状。贴附在SIS膜表面生长的BMSCs大多为有活力的细胞,只有零星死细胞。图中绿色荧光为钙黄绿素标记的有活性的细胞,红色荧光为碘化丙啶标记的死亡的细胞(图3E,F)。"
| [1] HOLL J, KOWALEWSKI C, ZIMEK Z, et al. Chronic Diabetic Wounds and Their Treatment with Skin Substitutes. Cells. 2021;10(3):655. [2] SHI CR, FERREIRA AL, KAUR M, et al. Cutaneous Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease: Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Management, and Supportive Care. Transplant Cell Ther. 2024;30(9S):S513-S533. [3] OZHATHIL DK, TAY MW, WOLF SE, et al. A Narrative Review of the History of Skin Grafting in Burn Care. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(4):380. [4] KHAN AA, KHAN IM, NGUYEN PP, et al. Skin Graft Techniques. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2020;37(4):821-835. [5] COSTELLO L, DICOLANDREA T, TASSEFF R, et al. Tissue engineering strategies to bioengineer the ageing skin phenotype in vitro. Aging Cell. 2022;21(2):e13550. [6] CHEN J, FAN Y, DONG G, et al. Designing biomimetic scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Biomater Sci. 2023;11(9):3051-3076. [7] ZHAO Y, PENG H, SUN L, et al. The application of small intestinal submucosa in tissue regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2024;26:101032. [8] FUJII M, TANAKA R. Porcine Small Intestinal Submucosa Alters the Biochemical Properties of Wound Healing: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines. 2022;10(9):2213. [9] JELODARI S, SADRODDINY E. Decellularization of Small Intestinal Submucosa. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1345:71-84. [10] SUHANDI C, MOHAMMED AFA, WILAR G, et al. Effectiveness of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome on Wound Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023;20(7):1053-1062. [11] SUKMANA BI, MARGIANA R, ALMAJIDI YQ, et al. Supporting wound healing by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) therapy in combination with scaffold, hydrogel, and matrix; State of the art. Pathol Res Pract. 2023;248:154575. [12] POLTAVETS V, FAULKNER JW, DHATRAK D, et al. CXCR4-CCR7 Heterodimerization Is a Driver of Breast Cancer Progression. Life (Basel). 2021;11(10):1049. [13] VAHEDI L, SHEIDAEI S, GHASEMI M, et al. Cytoplasmic CCR7 (CCR7c) Immunoexpression Is Associated with Tumor Invasion in Gastric Cancer. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2023;17(4):267-274. [14] RIZEQ B, MALKI MI. The Role of CCL21/CCR7 Chemokine Axis in Breast Cancer Progression. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(4):1036. [15] HE J, ZHANG X, XIA X, et al. Organoid technology for tissue engineering. J Mol Cell Biol. 2020;12(8):569-579. [16] SPEED OE, BAREISS A, PATEL VA, et al. Otologic use of porcine small intestinal submucosal graft (biodesign): A MAUDE database review. Am J Otolaryngol. 2023;44(5):103961. [17] ZANG C, XIAN H, ZHANG H, et al. Clinical outcomes of a novel porcine small intestinal submucosa patch for full-thickness hand skin defects: a retrospective investigation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):50. [18] JEFFERY S. Clinical benefits of small intestinal submucosa extracellular matrix and review of the evidence. J Wound Care. 2023;32(Sup2):S11-S19. [19] GUO X, XIA B, LU XB, et al. Grafting of mesenchymal stem cell-seeded small intestinal submucosa to repair the deep partial-thickness burns. Connect Tissue Res. 2016;57(5):388-397. [20] LEE C, SHIM S, JANG H, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and small intestinal submucosa hydrogel composite promotes combined radiation-wound healing of mice. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(9):1048-1059. [21] FAN MR, GONG M, DA LC, et al. Tissue engineered esophagus scaffold constructed with porcine small intestinal submucosa and synthetic polymers. Biomed Mater. 2014;9(1):015012. [22] ROSHANGAR L, SOLEIMANI RAD J, KHEIRJOU R, et al. Skin Burns: Review of Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Wounds. 2019; 31(12):308-315. [23] PEÑA OA, MARTIN P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(8):599-616. [24] LIU L, ZHENG CX, ZHAO N, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Aggregation-Released Extracellular Vesicles Induce CD31+ EMCN+ Vessels in Skin Regeneration and Improve Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(20):e2300019. [25] WEI Q, WANG Y, MA K, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Facilitate Diabetic Wound Healing Through MiR-17-5p-mediated Enhancement of Angiogenesis. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(3):1025-1040. [26] HONG W, YANG B, HE Q, et al. New Insights of CCR7 Signaling in Dendritic Cell Migration and Inflammatory Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 841687. [27] GERALDO LH, GARCIA C, XU Y, et al. CCL21-CCR7 signaling promotes microglia/macrophage recruitment and chemotherapy resistance in glioblastoma. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023;80(7):179. [28] CAI QY, LIANG GY, ZHENG YF, et al. CCR7 enhances the angiogenic capacity of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells in vitro via activation of the NF-κB/VEGF signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(7):3282-3292. [29] YUAN LH, CHEN XL, DI Y, et al. CCR7/p-ERK1/2/VEGF signaling promotes retinal neovascularization in a mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Int J Ophthalmol. 2017;10(6):862-869. [30] NAITO H, IBA T, TAKAKURA N. Mechanisms of new blood-vessel formation and proliferative heterogeneity of endothelial cells. Int Immunol. 2020; 32(5):295-305. [31] AHMAD A, NAWAZ MI. Molecular mechanism of VEGF and its role in pathological angiogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2022;123(12):1938-1965. [32] QUEISSER A, SERONT E, BOON LM, et al. Genetic Basis and Therapies for Vascular Anomalies. Circ Res. 2021;129(1):155-173. [33] DI BENEDETTO P, RUSCITTI P, BERARDICURTI O, et al. Blocking Jak/STAT signalling using tofacitinib inhibits angiogenesis in experimental arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):213. [34] VIMALRAJ S. A concise review of VEGF, PDGF, FGF, Notch, angiopoietin, and HGF signalling in tumor angiogenesis with a focus on alternative approaches and future directions. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;221:1428-1438. [35] FU T, SULLIVAN DP, GONZALEZ AM, et al. Mechanotransduction via endothelial adhesion molecule CD31 initiates transmigration and reveals a role for VEGFR2 in diapedesis. Immunity. 2023;56(10):2311-2324.e6. [36] ZENG Z, CHEN H, CAI J, et al. IL-10 regulates the malignancy of hemangioma-derived endothelial cells via regulation of PCNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;688:108404. |
| [1] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [2] | Han Teng, Ma Hong, Yang Ruoyi, Luo Yi, Li Chao. Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived exosomal delivery of angiopoietin-2 is involved in tumor angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1755-1767. |
| [3] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| [4] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [5] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [6] | Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Xu Lin, Li Haojie, Xie Tongliang, Yang Zhihang, Deng Jiang. Transverse tibial bone transfer accelerates healing of foot ulcers in a rabbit model of type 2 diabetes mellitus: involvement and regulation of circular RNA [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5639-5649. |
| [7] | Lin Kejian, Chai Yinghong, Zou Jie, Huang Ruixin, Fang Yongchao, Huang Jing, Yang Qin, Luo Xia, Zhang Hong. Preparation of Cu2+-containing microarc oxidation functional coating on medical magnesium alloy and its anti-tumor and angiogenesis-promoting effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5103-5114. |
| [8] | Yao Jinfeng, Deng Mengzhao, Xie Tian, Chen Kan, Wang Haixia. Reduced graphene oxide improves endothelial differentiation efficiency and angiogenesis ability of adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3270-3279. |
| [9] | Shi Yuxin, Kaiwusail · Tursun, Liu Jia. Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor-loaded composite bioscaffold on angiogenesis of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3343-3349. |
| [10] | Wu Jiazhou, Qian Tao, Liu Zexian, Wu Yanbin, He Ying, Li Yazhou, Peng Jiang. Three-dimensional culture of stromal vascular fraction self-assembles into complex vascularized osteogenic organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2681-2690. |
| [11] | Liu Nian, Dong Xinyue, Wang Songpeng, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming. Stem cell exosomes and biomaterial-assisted exosomes in bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 175-183. |
| [12] | Zuo Na, Tang Qi, Yu Meng, Tao Kai. Effect of miR-196b-5p in adipose-derived stem cell exosomes on burn wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 43-49. |
| [13] | Li Zikai, Zhang Chengcheng, Xiong Jiaying, Yang Xirui, Yang Jing, Shi Haishan. Potential effects of ornidazole on intracanal vascularization in endodontic regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [14] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [15] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||