Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1196-1206.doi: 10.12307/2026.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury
Yu Huifen1, Mo Licun1, Cheng Leping1, 2, 3
- 1Collaborative Innovation Centre of Regenerative Medicine and Medical BioResource Development and Application Co-constructed by the Province and Ministry, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Institute of Neuroscience and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Brain Science, Guangxi Health Commission Key Laboratory of Basic Research on Brain Function and Disease, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Key Laboratory of Longevity and Aging-related Diseases of Chinese Ministry of Education, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-11-18Accepted:2025-01-17Online:2026-02-18Published:2025-06-25 -
Contact:Cheng Leping, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Doctoral supervisor, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Regenerative Medicine and Medical BioResource Development and Application Co-constructed by the Province and Ministry, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Institute of Neuroscience and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Brain Science, Guangxi Health Commission Key Laboratory of Basic Research on Brain Function and Disease, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Key Laboratory of Longevity and Aging-related Diseases of Chinese Ministry of Education, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yu Huifen, MS, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Regenerative Medicine and Medical BioResource Development and Application Co-constructed by the Province and Ministry, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 32070976 (to CLP); Guangxi Science and Technology Base and Talent Special Project, No. AD21075052 (to CLP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
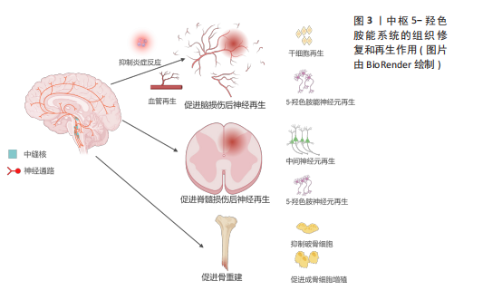
2.1 5-HT能神经元在中枢的再生作用 与其他类型神经元的轴突相比,5-HT能神经元的轴突在神经系统损伤后具有再生或者发芽的潜力,这可能与5-HT能神经元轴突能分泌某些生长因子以及特殊的突触连接方式有关[17]。另外,5-HT也可直接或者间接地促进中枢损伤附近的血管或者神经再生来帮助修复损伤[15-16],见图3。 2.1.1 5-HT能神经元促进脑部损伤神经再生 获得性脑损伤包含创伤性脑损伤和非创伤性脑损伤(脑卒中等),其中创伤性脑损伤的发病率在神经系统疾病中位居前列,通常伴随神经元死亡[18-19]。研究显示,相较于皮质神经元,5-HT能神经元在损伤后展现出更强的再生能力,且能穿透胶质瘢痕[20]。 JIN等[17]通过双光子成像技术发现,5-HT能神经元轴突在创伤性脑损伤后12周内恢复至正常水平,再生轴突与受损前形态高度一致,且在6个月后依然能分泌5-HT。同样地,小鼠大脑经历皮质损伤后,受损区域的5-HT能神经元轴突密度在1个月内恢复接近正常水平[21]。5-HT能神经元的再生能力可能归因于缓慢扩散的容积传递方式以及高表达的促轴突生长因子,如生长相关蛋白43和β1整合素[17,20]。 脑卒中是大脑的一种急性脑损伤,通常因出血或缺血导致神经元死亡,造成患者认知、语言和运动功能障碍,甚至可能导致不可逆的残疾或死亡[22]。近年来,关于5-HT能系统调节神经可塑性的研究日益增多。选择性5-HT再摄取抑制剂(如氟西汀、艾司西酞普兰)已被证明能通过改善缺血区域神经元存活、促进神经干细胞增殖和血管再生来加速脑卒中后的功能恢复[16,23-24]。5-HT再摄取抑制剂在脑卒中后的神经保护机制:一是通过抗炎、抗细胞凋亡及促进神经可塑性等作用,帮助脑卒中后神经功能的恢复。同时5-HT再摄取抑制剂还能够调节下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺轴来降低皮质醇的分泌,保护神经细胞[25]。二是通过促进神经干细胞的增殖,推动新生神经元向损伤部位迁移并参与神经网络的重建。在成人大脑的脑室下区和齿状回的颗粒下区中存在神经干细胞,这些干细胞分化产生的新生神经元向损伤部位迁移,它们最终分化成熟为具有正常功能的神经元,并融入成熟的神经网络中[23,26-27]。脑卒中后应用5-HT再摄取抑制剂能显著增加脑室下区、齿状回中的神经元增殖能力及齿状回神经元轴突的长度和数量,同时也增加5-HT和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的表达水平来抑制神经元凋亡并促进新生神经元和血管的形成[26]。三是促进血管再生。氟西汀主要通过提高低氧条件下调控血管生成的关键转录因子低氧诱导因子1α的表达水平,进而上调血管生成因子Netrin-1和血管内皮生长因子的表达诱导血管生成,同时提供了神经保护作用[28]。另外,由于脑卒中导致5-HT能神经元和中间神经元之间的连接中断,5-HT再摄取抑制剂治疗会刺激碱性成纤维细胞生长因子表达增加,重建5-HT能神经元和中间神经元的联系,这可能是通过恢复γ-氨基丁酸能神经元和5-HT能神经元之间的神经传递,为行为恢复作出了贡献[24,29]。"
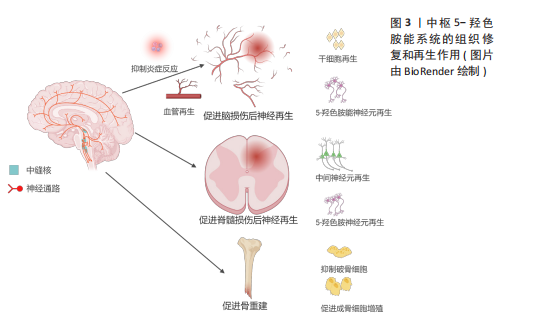
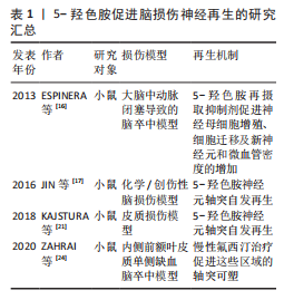
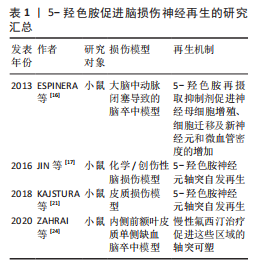
尽管大量研究表明5-HT再摄取抑制剂(如氟西汀)对中枢神经系统中的5-HT能系统有积极作用,但也有研究发现,氟西汀和舍曲林在某些脑损伤模型中未能促进5-HT神经元轴突再生[30],这种差异可能与损伤类型及测量区域的不同有关,提示5-HT再摄取抑制剂的再生效果可能因损伤类型而异,类似于5-HT在胰腺损伤中的不同再生作用[31]。此外,该研究没有探究5-HT再摄取抑制剂对脑损伤后其他属性的影响,如对神经干细胞、血管以及其他中间神经元的影响,也可能因为5-HTR的固有活性变化,通过5-HT再摄取抑制剂增加突触间隙的5-HT浓度反而对5-HT能神经元轴突再生没有影响[32]。 未来的研究应该进一步揭示5-HT能系统在各种脑损伤修复中的作用机制。尽管已有许多证据表明5-HT再摄取抑制剂在中枢神经系统可塑性中的积极作用,但是还需要继续深入探讨5-HT神经元轴突再生的机制及其与其他神经元的交互关系,尤其是在不同类型的脑损伤中。此外,结合双光子成像技术等现代神经影像学技术与分子生物学等方法,继续探讨5-HT能神经元轴突再生的分子机制,还应关注如何将这些机制与神经干细胞增殖、血管再生等多维修复手段相结合,形成一个多层次、多通路的神经修复网络。 5-羟色胺促进脑损伤神经再生的研究汇总,见表1。"
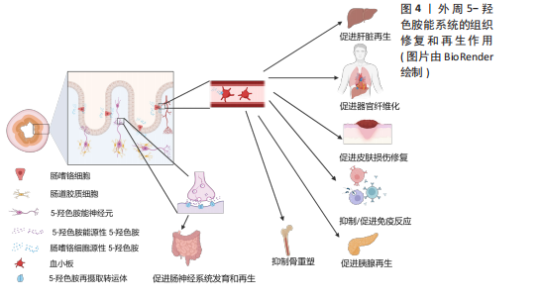
2.1.2 5-HT能神经元促进脊髓损伤后神经再生 脊髓损伤严重破坏中枢神经通路,导致运动、感觉和自主功能障碍,甚至引发瘫痪或死亡[33]。5-HT能神经元在调节脊髓运动、感觉和自主神经方面起重要作用,同时也调控疼痛传递[34]。因此,脊髓损伤后5-HT能系统的修复至关重要。 ALILAIN等[35]发现,硫酸软骨素酶ABC联合自体周围神经移植物能显著促进5-HT能轴突再生并恢复呼吸功能,移植物与脊髓损伤接合处出现广泛的轴突再生并重建连接。同样地,研究表明5-HTR在慢性脊髓损伤后通过多种亚型调控脊髓运动神经元的可塑性,有助于恢复膈肌运动和整体运动功能,其中5-HTR2A、5-HTR2B和5-HTR7在其中发挥重要作用[36]。5-HT能神经元轴突的再生机制包括增强对膈肌的支配及脊髓内神经通路的重连[35]。内源性5-HT能直接介导不同物种的轴突再生。例如,在秀丽隐杆线虫中,缺乏5-HT导致轴突再生缺陷,在外源性添加5-HT后能恢复轴突的再生能力,其中5-HT能神经元受体SER-7以细胞自主的方式介导轴突再生[37]。 在小鼠脊髓损伤模型中发现诱导NG2胶质细胞重编程后也能促进5-HT能神经元轴突的再生,主要机制可能是减少胶质瘢痕的产生从而改善损伤微环境[38]。LEIBINGER等[39]通过腺相关病毒递送人白细胞介素6诱导5-HT能神经元轴突再生,显著促进了脊髓损伤后下肢运动功能的恢复。这些再生的5-HT能神经元轴突不仅促进了脊髓和大脑之间的神经通路重新连接,还对自主神经功能的恢复发挥了重要作用。 除了5-HT能神经元轴突的直接修复作用,斑马鱼脊髓损伤模型还揭示了5-HT神经元的间接修复作用。损伤后特化的5-HT能神经元通过表达shh、nkx2.2、ascl1、fev与 lmx1b等关键基因并分泌5-HT,促进兴奋性中间神经元轴突再生及脊髓中枢模式发生器重新建立,进而恢复运动功能[15]。值得注意的是,尽管5-HT在脊髓损伤修复中的作用显著,但仅通过增加5-HT浓度并不能有效促进轴突再生或功能恢复。研究表明,5-HT再摄取抑制剂药物无法有效诱导5-HT能神经元轴突再生,这可能与5-HT受体的代偿性激活有关,导致运动神经元过度兴奋[30,40-41]。 未来的研究应进一步关注5-HT受体信号传导的精细调控,以及与其他神经修复机制的协同作用。例如,通过结合5-HT受体激动剂与基因疗法、周围神经移植物等多种干预手段,探索如何精确地引导神经轴突再生和功能恢复。同时,随着生物材料和再生医学技术的发展,如何利用微环境修饰或细胞重编程技术,最大化5-HT能系统的再生能力,也是未来的一个重要研究方向。此外,脑损伤和脊髓损伤等中枢性疾病患者通过鞘内注射直接进入到脑脊液中补充5-HT,这样不仅能绕过血脑屏障提高药物利用率、降低药物剂量,还能避免因全身给药而带来的骨质疏松等不良反应。 2.1.3 5-HT能系统在骨重塑中的作用 除了5-HT能神经元及受体在中枢神经系统中的直接作用外,中枢来源的5-HT也能通过调控神经传递,间接促进骨重塑。研究表明,骨重塑是由破骨细胞和成骨细胞协同完成,前者负责骨基质的吸收,后者负责新骨的形成[42]。中枢来源的5-HT被证实能促进骨重塑,而外周来源的5-HT则抑制骨质形成[43-44]。 研究显示,色氨酸羟化酶2缺乏小鼠椎骨和长骨的骨密度显著降低,成骨细胞数量减少,同时伴随食欲下降和能量消耗增加[44]。中枢来源的5-HT通过靶向5-HTR2C降低下丘脑腹内侧核中的交感神经元活性,从而减少蓝斑核去甲肾上腺素能神经元的活化,进而抑制破骨细胞的活性并促进成骨细胞增殖分化[45-47]。中枢5-HT能神经元通过2条主要信号途径降低交感神经活性:一是触发钙调蛋白激酶(Calmodulin kinase,CaMK)依赖的信号级联反应,通过5-HT/5-HTR2C/CaMKKβ/CaMKIV通路促进骨量增加;二是通过CREB的磷酸化,抑制下丘脑腹内侧核中的儿茶酚胺能神经元活性,从而增强骨重塑[44,47-48]。除了5-HT的这些作用,5-HTR2B在骨重塑中也高表达,它通过旁分泌途径激活5-HTR2B-前列腺素/PPAR-?/δ通路,促进成骨细胞增殖和骨质矿物质沉积。缺乏5-HTR2B的小鼠表现出成骨细胞增殖能力显著下降[49]。 尽管脑源性5-HT促进骨重建作用明确,但是肠源性5-HT对骨重建的影响仍存在争议。肠源性5-HT可能通过迷走神经作用于中枢神经系统,未来的研究应关注中枢和外周5-HT之间的相互影响[50]。探索如何单独调控外周5-HT水平以研究中枢神经系统对骨重塑的反馈机制,揭示新的治疗干预点。此外,进一步研究5-HT通过旁分泌机制调控骨微环境中细胞间的相互作用,开发高选择性的5-HT受体激动剂和拮抗剂,或许也能揭示新的骨重塑调控机制。 2.2 外周5-HT系统的再生作用 外周5-HT大部分是由肠道黏膜上皮中的内皮细胞合成、储存和释放,另外部分5-HT在肌间神经丛胞体中发现[51]。肠黏膜上皮的嗜铬细胞受到机械和化学刺激释放5-HT,5-HT被表达5-羟色胺再摄取转运体(serotonin reuptake transporter,SERT)的肠上皮细胞摄取和转运,部分未被肠道上皮细胞吸收的5-HT会经过固有层致密毛细血管床进入血液循环并被表达SERT的血小板所吸收[52]。肠源性5-HT能介导肠上皮生长、肠神经元发生。在肠外组织中,5-HT经由血小板运输到全身的各个器官并能与多种细胞类型结合,诱导细胞增殖和有丝分裂,并促进许多组织或者器官细胞再生,包括肝脏再生、组织纤维化、胰腺腺泡细胞再生等[13],见图4。5-HT被视为胃肠道健康信号的关键因素,在胃肠道运动和炎症中发挥至关重要的作用。 2.2.1 5-HT系统促进肝脏再生 在脊椎动物中,肝脏由70%-80%的实质细胞(肝细胞)和其他非实质细胞(胆管上皮细胞、窦状内皮细胞、kupffer细胞和星状细胞等)组成,成年后的肝细胞群依旧具有显著的与造血干细胞相媲美的再生能力[53]。在啮齿动物中的研究表明,肝部分切除术后3周内肝脏几乎完全恢复[54]。扩大肝切除术切除接近90% 的肝组"
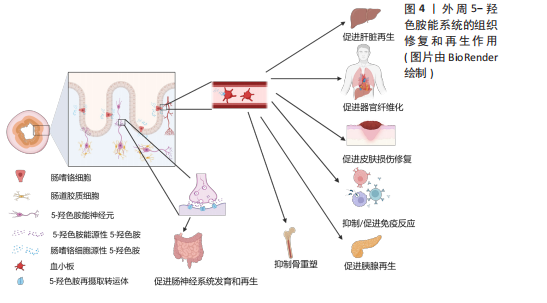

织,小鼠肝脏也可以在短时间内再生[55]。临床研究进一步验证了血小板中5-HT对肝再生的重要性。60例肝切除患者的数据显示,术前血小板中5-HT水平较低的患者术后肝再生延迟,且更易出现肝功能障碍和并发症[56]。色氨酸羟化酶1特异性敲除小鼠的实验也支持了这一点,缺乏5-HT的小鼠在肝缺血再灌注损伤后表现出肝细胞再生和修复能力减弱[57]。同样地,色氨酸羟化酶1–/–小鼠肝部分切除后肝功能明显受损,肝脏增殖细胞数目显著减少,但是在补充5-HT前体5-羟基色氨酸后肝细胞再生能力恢复[58]。上述证据都表明外周源性5-HT在肝脏再生中的关键作用。 5-HT通过多种受体介导肝再生。研究表明,肝部分切除术后,5-HTR2A和5-HTR2B的表达增加,应用拮抗剂可显著抑制肝再生,这表明血小板5-HT通过与这两种受体结合,作为生长因子促进肝细胞增殖和DNA合成[58]。TZIROGIANNIS等[59]发现,5-HTR7也在肝脏再生中发挥作用,5-HTR7阻滞剂能减缓肝细胞在G1/S期的进程,抑制肝再生。此外,5-HTR激动剂在肝小体积综合征患者中表现出显著疗效,能够减轻缺血/再灌注损伤并促进肝细胞再生[60]。 在肝星状细胞再生过程中,5-HT也发挥重要作用。星状细胞表达多种5-HT受体,包括5-HTR1B、5-HTR1F、5-HTR2A、5-HTR2B和5-HTR7,星状细胞激活时5-HTR1B、5-HTR2A及5-HTR2B的表达进一步上升[61]。5-HT通过5-HTR2A/2B促进星状细胞增殖,并诱导星状细胞分泌结缔组织生长因子,保护星状细胞免受损伤。此外,星状细胞上的SERT还能自主吸收5-HT,以促进肝脏损伤修复[62]。值得注意的是,肝脏胆管细胞可以从头合成5-HT,胆管细胞自分泌5-HT及肌成纤维细胞旁分泌转化生长因子β1,抑制胆管的5-HT产生后将刺激导管细胞、肝脏肌成纤维细胞及肝母细胞的增殖[58,63]。胆管细胞不仅表达5-HTR2A、5-HTR2B与5-HTR2C,还能通过自分泌和旁分泌途径调节胆道系统再生,并在肝脏稳态和免疫调节中起重要作用[64]。 5-HT通过多个信号通路促进肝再生。上调的pERK信号诱导YAP入核,激活结缔组织生长因子,促进肝细胞增殖[65]。GRIJALVA等[66]的研究同样显示,在肝部分切除后,Hippo通路的抑制信号减弱,YAP被激活并进入细胞核,促使肝脏恢复到正常大小。5-HT通过调节Cyclin E/CDK2复合物促进肝细胞从G1期向S期过渡,而YAP缺乏则导致p21和p27表达增加,阻碍细胞周期进程[65]。此外,5-HT还通过5-HTR2B和PLC/Ca2+/TGF-α通路激活PI3K、ERK2、mTOR和p70S6K等分子,促进肝细胞早期增殖[67],并且5-HT在肝部分切除术后能激活5-HTR2A/p70S6K通路,促进肝细胞增殖,降低发生小体积综合征的风险[68]。 在肝硬化患者中,血小板和5-HT水平显著下降,这可能限制肝再生并促进纤维化[62]。研究表明,通过脾切除术提高血小板5-HT水平能促进肝再生,但也伴随着肝纤维化的加剧[69]。目前的研究表明了5-HT系统调节的复杂性,因此亟需深入研究5-HT与肝细胞周期调控的分子机制,特别是特定5-HTR信号通路在肝细胞增殖与纤维化过程中的调控作用。开发高选择性5-HTR激动剂可能为肝硬化早期干预提供新的治疗策略。 2.2.2 5-HT系统促进器官纤维化 研究发现,胆管细胞和肝细胞表达色氨酸羟化酶1 并分泌5-HT,活化的星状细胞表达SERT和5-HT2R,这些细胞通过自分泌和旁分泌途径响应、摄取和释放5-HT,从而在纤维化过程中发挥作用[70]。EBRAHIMKHANI等[71]发现,5-HT通过5-HTR2B/ERK-JunD/转化生长因子β1通路促进肝纤维化,使用5-HTR2B 拮抗剂能够显著减轻纤维化并改善肝功能。此外,5-HTR7激动剂在四氯化碳引起的肝纤维化模型中也表现出抗纤维化效果,减少了氧化应激、炎症反应和纤维化[72]。在肺组织中5-HTR2A和5-HTR2B的表达显著上调,特别是在纤维化病灶中。应用5-HTR2拮抗剂能够通过抑制转化生长因子β1、结缔组织生长因子和纤维蛋白溶酶原激活物抑制因子1的表达,有效缓解肺纤维化[73]。类似地,抑制5-HTR2C和5-HTR7也能够通过抑制转化生长因子β1的释放,减轻博来霉素诱导的肺纤维化[74-75]。研究表明,血小板来源5-HT通过刺激心肌细胞和成纤维细胞上的5-HTR2A和5-HTR2B,诱导心室肥大和心脏瓣膜纤维化[76-79]。这些结果表明,5-HT不仅在肝纤维化中起重要作用,还参与了多种器官的纤维化病理过程。 在系统性纤维化疾病的多个小鼠模型中,5-HT水平升高,并且伴随着胶原蛋白mRNA表达增加;使用抗凝剂氯吡格雷(Clopidogrel)后,小鼠的胶原含量和肌成纤维细胞数量显著下降,纤维化症状得到明显改善;此外,色氨酸羟化酶1敲除小鼠的纤维化程度也显著降低[80-82]。临床研究进一步证实,系统性纤维化疾病和皮肤性硬皮病患者血清中5-HT水平升高,表明5-HT在这些疾病的发病机制中发挥重要作用[82-83]。 5-HT诱发纤维化与5-HT增强这些非增殖细胞的特异性增殖和诱导细胞有丝分裂有关[13]。利用5-HTR2、5-HTR7拮抗剂改善肺纤维化,利用5-HTR2拮抗剂抑制肝纤维化和心脏瓣膜纤维化[71,74-75,84]。未来的研究应集中在系统解析不同5-HTR在不同纤维化模型中的作用机制,并进一步探讨各个受体在不同纤维化阶段的功能。此外,针对血小板源性5-HT的释放也将是一个新的研究靶点。同时也可考虑将5-HTR抑制剂和目前的抗凝剂(如氯吡格雷和阿司匹林)联合治疗以开发更有效的纤维化治疗方案。 2.2.3 5-HT促进皮肤损伤修复 皮肤作为人体的第一道防线,在防御外界损伤和保持内部稳态中扮演着关键角色[85]。当皮肤结构受到破坏后,伤口愈合成为一个高度协调且动态的过程,通常包括炎症期、增生期(再上皮化和胶原沉积)及细胞外基质重塑期[86]。若愈合过程延迟,伤口则面临形成慢性溃疡或过度瘢痕的风险[87-88]。研究表明,皮肤烧伤后,受损组织中的5-HT水平显著升高,提示5-HT在血管生成和细胞增殖方面可能发挥重要作用[89]。5-HT通过与5-HT1A和5-HT2A结合,促进角质形成细胞和成纤维细胞的增殖与迁移,从而支持烧伤后皮肤的修复[90-91]。此外,5-HT在血小板聚集和血管生成中同样至关重要,它们进一步加速了愈合进程[90]。值得注意的是,5-HT再摄取抑制剂通过抑制5-HT转运体SERT的活性,减少血小板内5-HT的储备,这一机制可能会影响皮肤的愈合速度,延缓损伤修复[91]。因此,5-HT及其受体在皮肤愈合中的作用具有重要的临床意义,尤其是在创伤和烧伤治疗中,针对5-HT通路的调控有望成为有效的治疗策略。 2.2.4 5-HT在炎症中的作用 炎症是机体的一种主要防御机制,特点是在浸润或损伤部位招募免疫细胞。越来越多的证据表明,外周5-HT在免疫细胞招募和肠道炎症发生方面有重要作用[92]。在外周免疫系统中,血小板、肥大细胞和抗原递呈细胞能够评估机体的健康状况,释放炎症细胞因子并激活T细胞,从而协调适应性免疫反应。值得注意的是,这些免疫细胞具有合成、运输、储存和/或响应5-HT的能力,使5-HT在免疫调节中发挥作用[93]。更为复杂的是,几乎所有5-HT受体及亚型都在不同类型的免疫细胞中表达,构成了一个复杂且多功能的5-HT受体网络[94]。 在炎症性肠病患者和实验性结肠炎模型中,观察到肠嗜铬细胞数量和5-HT水平的变化[94]。在正常情况下,大部分5-HT通过SERT转运到肠道细胞降解或在血小板中储存,但在肠道炎症中,过量的5-HT会通过HTR激活局部免疫细胞(如T细胞、树突状细胞及巨噬细胞),触发促炎通路的激活和促炎细胞因子的分泌。与此同时,5-HT还可作为一种趋化诱导剂,将白细胞吸引到炎症部位[94]。在调节免疫平衡方面,5-HT通过激活5-HTR2A和5-HTR2B抑制辅助性T细胞17(T helper cell 17,Th17)的分化与白细胞介素17的产生,同时促进调节性T细胞(regulatory T cells,Tregs)的增殖,平衡Th17/Tregs比例,维持免疫稳态[95]。最近的研究表明,在新生小鼠的肠道中,5-HT可以直接促进Tregs的分化,从而增强免疫耐受性,且这种促进作用仅限于早期发育阶段[96]。在类风湿性疾病等多种自身免疫性疾病中,5-HT既促进炎症反应又对免疫耐受产生深远影响[95-96]。 在急性炎症期间,5-HT可促进先天性免疫细胞(如未成熟树突状细胞、单核细胞、肥大细胞和嗜酸性粒细胞)在炎症部位的招募,并与其他血小板衍生因子协同作用,将中性粒细胞导向小鼠急性炎症区域[97]。研究表明,5-HT调节结肠上皮细胞的先天性免疫反应,增加炎性细胞因子和黏附分子的表达,同时减少黏附连接蛋白(如E-钙黏蛋白)的表达,从而削弱上皮屏障的功能完整性[97]。此外,5-HT以多种方式参与炎症的加剧:增加氧化应激、激活氧化还原敏感转录因子、诱导促炎细胞因子生成。据报道,类风湿性关节炎、系统性硬化症和系统性红斑狼疮等类风湿性疾病、1型糖尿病和原发性胆汁性胆管炎以及炎症性肠病和肠易激综合征等各种胃肠道疾病中均观察到5-HT水平的改变[92]。 研究表明,5-HT能调节肠道微生物群的组成,增强结肠炎的发生风险,并增加结肠炎的易感性和严重程度[98]。此外,黏膜5-HT增多可影响自噬过程并改变肠道微生物群,从而增强对实验性结肠炎和克罗恩病(炎症性肠病的一种主要类型)的易感性。阻断5-HT信号有助于通过促进自噬改善肠道炎症,这为未来设计针对特定5-HTR和转运体的药物或抑制5-HT外周合成的疗法提供了潜在思路[92,99]。 对 SERT 基因敲除的研究表明,SERT不仅调节5-HT的摄取,还在炎症反应中起着重要作用。在炎症初期,SERT上调有助于减少5-HT的促炎作用,而在晚期炎症中,SERT表达减少加剧炎症进程[100]。鉴于SERT在炎症中的双重作用,建议在已有或可能发生肠炎的患者中谨慎使用抑制SERT的药物。 2.2.5 5-HT促进胰腺再生 胰腺细胞有显著的可塑性,在胰腺损伤之后,它们能相互转化身份,促进损伤修复[101-102]。腺泡细胞是外分泌腺的主要细胞类型,在胰腺损伤后,腺泡细胞可以通过去分化形成导管样细胞,这一过程称为腺泡-导管化生,还可通过自我复制或分裂进行修复[103-106]。 5-HT介导胰腺炎后胰腺外分泌腺再生,主要机制是通过促进腺泡细胞去分化为祖细胞启动复制程序,并激活腺泡细胞增殖来修复组织[31,107]。在色氨酸羟化酶1–/–小鼠中,胰腺祖细胞增殖显著减少,这与5-HT通过激活 Hes1-Ptf1a 轴的调控机制有关,Hes1是胰腺发育和干细胞增殖的关键因子,而Ptf1a 则调控腺泡细胞分化[31,108]。5-HT通过刺激促炎因子释放,或通过与受体结合激活蛋白激酶A和 Ras/MAPK/ERK1/2 通路来促进细胞增殖,但该作用主要局限于炎症性损伤,这可能是因为不同的损伤类型触发的细胞再生机制不同[31]。 此外,也有研究表明在怀孕期间,由于泌乳素的增加导致5-HT的合成和分泌增加(是对照组的420倍),5-HT通过5-HTR2B传导信号促进β细胞增殖[109]。类似地,5-HT也能在围产期通过5-HTR2B 调控β细胞增殖,在色氨酸羟化酶1–/–小鼠中β细胞减少了约75%,并且在成年后β细胞同样比对照组减少了约40%[109]。 上述研究确认了5-HT在胰腺损伤后再生过程中展现出广泛的潜力和重要性。未来研究应集中于评估5-HT 在腺泡细胞去分化、祖细胞增殖和腺泡-导管化生形成中的作用机制,特别是探讨泌乳素如何通过5-HT信号影响 β 细胞增殖,这将为胰腺炎和糖尿病的治疗提供新的见解。 2.2.6 5-HT促进肠神经系统再生 肠道神经元系统常被称为“第二大脑”,由肠道神经元和胶质细胞组成的神经丛构成,分为黏膜下神经丛和肌间神经丛,贯穿整个肠壁,几乎对所有的肠道功能都有影响,同时也对中枢神经系统产生一定的影响[110],进一步研究表明,5-HTR4激动剂能够有效促进肠道神经元再生。在野生型小鼠与5-HTR4敲除小鼠的对比实验中,尽管出生时两组小鼠的肠道神经元数量相似,但在出生后4个月,野生型小鼠的肠道神经元数量显著增加,而5-HTR4敲除小鼠却未见此变化,这表明5-HTR4促进出生后肠道神经元存活和神经发生[111]。此外,另一项研究将豚鼠直肠切断并行吻合手术,建立神经环路损伤模型,结果发现局部应用5-HTR4激动剂能够促进受损肌层神经丛的神经环路再生,并恢复远端肠道的排便反射,新生神经元同时表达神经干细胞标志物,提示再生神经元可能来源于肠道神经干细胞,而5-HTR4则通过促进这些干细胞的分化来实现神经元再生[112]。BELKIND-GERSON等[113]研究表明,5-HTR4激动剂不仅促进肠道神经元增殖,还能在体内诱导胶质细胞转分化为神经元。在结肠炎小鼠模型中,使用5-HTR4拮抗剂后,肠道神经元和胶质细胞的增殖受到抑制,同时,转基因小鼠中HuC/D、Sox2及Nestin的共标现象表明新增神经元来源于胶质细胞的转分化。 肠道神经系统的再生和修复是复杂的生理过程,5-HTR4作为调控肠道神经元再生的核心受体,在肠道疾病的治疗中展现了巨大的潜力[112-114]。基于上述研究,开发针对 5-HTR4 的特异性激动剂或拮抗剂可能为治疗肠道相关疾病(如肠易激综合征和炎症性肠病)提供新的治疗策略。肠道炎症、先天性巨结肠病等都存在肠道神经元缺失的现象,未来开发精准治疗可通过肠镜局部注射5-HTR激动剂直接作用于损伤部位,最大限度地减少不良反应并提高疗效。 2.2.7 外周5-HT抑制骨重塑 外周来源5-HT与中枢5-HT不同,具有抑制骨重塑的作用,但作用机制仍有争议。YADAV等[115-116]发现,肠源性5-HT通过Lrp5依赖性途径抑制成骨细胞,减少骨形成,并通过抑制色氨酸羟化酶1表达来防止卵巢切除术后的骨质流失。 然而,CUI等[117]研究表明,Lrp5基因的杂合错义突变引起显性遗传性高骨量症状与肠道5-HT无关,而是通过经典的Wnt信号通路。LIMA等[118]研究也支持这一观点,他们使用色氨酸羟化酶1抑制剂LP-533401治疗牙周炎未能改善骨质流失。在色氨酸羟化酶1–/–小鼠的研究中,尽管6周龄时色氨酸羟化酶1–/–小鼠表现出更高的骨体积和骨密度,但这一差异在16周龄时消失,这可能与破骨细胞分化缺陷有关;补充外源性5-HT后,色氨酸羟化酶1–/–小鼠的破骨细胞活性未恢复至野生型水平[43]。 目前的研究已经解释5-HT在骨重塑中的复杂性和多面性,未来的研究需进一步探讨 5-HT 如何通过调节 Lrp5 依赖性途径来抑制骨形成的作用机制,特别是肠源性5-HT对破骨细胞发育和功能的调节作用。不同年龄阶段或疾病状态下,5-HT如何影响骨代谢的变化尚未明确,这为研究5-HT在发育期、绝经期或骨质疏松等状态中的潜在作用提供了新视角。此外,评估色氨酸羟化酶1抑制剂与现有抗骨质流失药物联合使用的疗效,将有助于开发更精准的骨疾病干预策略。"

| [1] ROSEN CJ. Serotonin rising--the bone, brain, bowel connection. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360(10):957-959. [2] OKATY BW, COMMONS KG, DYMECKI SM. Embracing diversity in the 5-HT neuronal system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019;20(7):397-424. [3] XUE C, LI G, ZHENG Q, et al. Tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab. 2023;35(8):1304-1326. [4] BARNES NM, AHERN GP, BECAMEL C, et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CX. Classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine; pharmacology and function. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73(1):310-520. [5] DODDS KN, TRAVIS L, KYLOH MA, et al. The gut-brain axis: spatial relationship between spinal afferent nerves and 5-HT-containing enterochromaffin cells in mucosa of mouse colon. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022;322(5):G523-G533. [6] MARGOLIS KG, CRYAN JF, MAYER EA. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: From Motility to Mood. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(5):1486-1501. [7] ZHAO S, KHOO S, NG SC, et al. Brain functional network and amino acid metabolism association in females with subclinical depression. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(6):3321. [8] CAI X, LIU H, FENG B, et al. A D2 to D1 shift in dopaminergic inputs to midbrain 5-HT neurons causes anorexia in mice. Nat Neurosci. 2022;25(5):646-658. [9] DE DEURWAERDERE P, DI GIOVANNI G. 5-HT interaction with other neurotransmitters: An overview. Prog Brain Res. 2021;259:1-5. [10] BERGER M, GRAY JA, ROTH BL. The expanded biology of serotonin. Annu Rev Med. 2009;60:355-366. [11] GERSHON MD. The shaggy dog story of enteric signaling: serotonin, a molecular megillah. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1383: 307-318. [12] NEUMANN J, HOFMANN B, DHEIN S, et al. Cardiac roles of serotonin (5-HT) and 5-HT-receptors in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(5):4765. [13] SHAH PA, PARK CJ, SHAUGHNESSY MP, et al. Serotonin as a mitogen in the gastrointestinal tract: revisiting a familiar molecule in a new role. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;12(3):1093-1104. [14] NAJJAR SA, HUNG LY, MARGOLIS KG. Serotonergic Control of Gastrointestinal Development, Motility, and Inflammation. Compr Physiol. 2023;13(3):4851-4868. [15] HUANG CX, ZHAO Y, MAO J, et al. An injury-induced serotonergic neuron subpopulation contributes to axon regrowth and function restoration after spinal cord injury in zebrafish. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):7093. [16] ESPINERA AR, OGLE ME, GU X, et al. Citalopram enhances neurovascular regeneration and sensorimotor functional recovery after ischemic stroke in mice. Neuroscience. 2013;247:1-11. [17] JIN Y, DOUGHERTY SE, WOOD K, et al. Regrowth of serotonin axons in the adult mouse brain following injury. Neuron. 2016;91(4):748-762. [18] GOLDMAN L, SIDDIQUI EM, KHAN A, et al. Understanding acquired brain injury: a review. Biomedicines. 2022;10(9):2167. [19] MAAS AIR, MENON DK, MANLEY GT, et al. Traumatic brain injury: progress and challenges in prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21(11):1004-1060. [20] HAWTHORNE AL, HU H, KUNDU B, et al. The unusual response of serotonergic neurons after CNS Injury: lack of axonal dieback and enhanced sprouting within the inhibitory environment of the glial scar. J Neurosci. 2011;31(15):5605-5616. [21] KAJSTURA TJ, DOUGHERTY SE, LINDEN DJ. Serotonin axons in the neocortex of the adult female mouse regrow after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Res. 2018;96(4):512-526. [22] FEIGIN VL, BRAININ M, NORRVING B, et al. World Stroke Organization (WSO): global stroke fact sheet 2022. Int J Stroke. 2022;17(1):18-29. [23] DILLEN Y, KEMPS H, GERVOIS P, et al. Adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone and its regulation after ischemic stroke: implications for therapeutic approaches. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11(1):60-79. [24] ZAHRAI A, VAHID-ANSARI F, DAIGLE M, et al. Fluoxetine-induced recovery of serotonin and norepinephrine projections in a mouse model of post-stroke depression. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):334. [25] VILLA RF, FERRARI F, MORETTI A. Post-stroke depression: Mechanisms and pharmacological treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;184:131-144. [26] KOT M, NEGLUR PK, PIETRASZEWSKA A, et al. Boosting neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus using antidepressants and mesenchymal stem cells. Cells. 2022;11(20): 3234. [27] CAMPERO-ROMERO AN, REAL FH, SANTANA-MARTíNEZ RA, et al. Extracellular vesicles from neural progenitor cells promote functional recovery after stroke in mice with pharmacological inhibition of neurogenesis. Cell Death Discov. 2023; 9(1):272. [28] DONG P, LI Q, HAN H. HIF‑1alpha in cerebral ischemia (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2022;25(2): 41. [29] SCHNEIDER CL, MAJEWSKA AK, BUSZA A, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for functional recovery after stroke: similarities with the critical period and the role of experience-dependent plasticity. J Neurol. 2021;268(4):1203-1209. [30] JANOWITZ HN, LINDEN DJ. Chronic Treatment with Serotonin Selective Reuptake Inhibitors Does Not Affect Regrowth of Serotonin Axons Following Amphetamine Injury in the Mouse Forebrain. eNeuro. 2024;11(2):ENEURO.0444-22.2023. [31] SAPONARA E, GRABLIAUSKAITE K, BOMBARDO M, et al. Serotonin promotes acinar dedifferentiation following pancreatitis-induced regeneration in the adult pancreas. J Pathol. 2015;237(4):495-507. [32] FOUAD K, RANK MM, VAVREK R, et al. Locomotion after spinal cord injury depends on constitutive activity in serotonin receptors. J Neurophysiol. 2010; 104(6):2975-2984. [33] ZHENG B, TUSZYNSKI MH. Regulation of axonal regeneration after mammalian spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24(6):396-413. [34] BERNATONIENE J, SCIUPOKAS A, KOPUSTINSKIENE DM, et al. Novel Drug Targets and Emerging Pharmacotherapies in Neuropathic Pain. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(7):1799. [35] ALILAIN WJ, HORN KP, HU H, et al. Functional regeneration of respiratory pathways after spinal cord injury. Nature. 2011;475(7355):196-200. [36] GONZALEZ-ROTHI EJ, ALLEN LL, SEVEN YB, et al. Prolonged intermittent hypoxia differentially regulates phrenic motor neuron serotonin receptor expression in rats following chronic cervical spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2024;378:114808. [37] ALAM T, MARUYAMA H, LI C, et al. Axotomy-induced HIF-serotonin signalling axis promotes axon regeneration in C. elegans. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10388. [38] TAI W, DU X, CHEN C, et al. NG2 glia reprogramming induces robust axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury. iScience. 2024;27(2):108895. [39] LEIBINGER M, ZEITLER C, GOBRECHT P, et al. Transneuronal delivery of hyper-interleukin-6 enables functional recovery after severe spinal cord injury in mice. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1): 391. [40] FAUSS GNK, HUDSON KE, GRAU JW. Role of Descending Serotonergic Fibers in the Development of Pathophysiology after Spinal Cord Injury (SCI): Contribution to Chronic Pain, Spasticity, and Autonomic Dysreflexia. Biology (Basel). 2022;11(2): 234. [41] RYU Y, OGATA T, NAGAO M, et al. Early escitalopram administration as a preemptive treatment strategy against spasticity after contusive spinal cord injury in rats. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):7120. [42] DAPONTE V, HENKE K, DRISSI H. Current perspectives on the multiple roles of osteoclasts: Mechanisms of osteoclast-osteoblast communication and potential clinical implications. Elife. 2024;13:e95083. [43] CHABBI-ACHENGLI Y, COUDERT AE, CALLEBERT J, et al. Decreased osteoclastogenesis in serotonin-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(7):2567-2572. [44] YADAV VK, OURY F, SUDA N, et al. A serotonin-dependent mechanism explains the leptin regulation of bone mass, appetite, and energy expenditure. Cell. 2009;138(5): 976-989. [45] TAKEDA S, ELEFTERIOU F, LEVASSEUR R, et al. Leptin regulates bone formation via the sympathetic nervous system. Cell. 2002; 111(3):305-317. [46] ELEFTERIOU F, AHN JD, TAKEDA S, et al. Leptin regulation of bone resorption by the sympathetic nervous system and CART. Nature. 2005;434(7032):514-520. [47] OURY F, YADAV VK, WANG Y, et al. CREB mediates brain serotonin regulation of bone mass through its expression in ventromedial hypothalamic neurons. Genes Dev. 2010; 24(20):2330-2342. [48] SHI H, CHEN M. The brain-bone axis: unraveling the complex interplay between the central nervous system and skeletal metabolism. Eur J Med Res. 2024;29(1):317. [49] COLLET C, COUDERT AE. Bone and Serotonin Receptor Type 2B[M]//Maroteaux L, Monassier L. 5-HT2B receptors: from molecular biology to clinical applications. Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2021:133-142. [50] LIU Y, WEI JA, LUO Z, et al. A gut-brain axis mediates sodium appetite via gastrointestinal peptide regulation on a medulla-hypothalamic circuit. Sci Adv. 2023;9(7):eadd5330. [51] SPENCER NJ, KEATING DJ. Role of 5-HT in the enteric nervous system and enteroendocrine cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2025;182(3):471-483. [52] LIU N, SUN S, WANG P, et al. The mechanism of secretion and metabolism of gut-derived 5-hydroxytryptamine. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(15):7931. [53] ZARET KS, GROMPE M. Generation and regeneration of cells of the liver and pancreas. Science. 2008;322(5907):1490-1494. [54] MICHALOPOULOS GK, BHUSHAN B. Liver regeneration: biological and pathological mechanisms and implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(1):40-55. [55] KOPASZ AG, PUSZTAI DZ, KARKAS R, et al. A versatile transposon-based technology to generate loss- and gain-of-function phenotypes in the mouse liver. BMC Biol. 2022;20(1):74. [56] STARLINGER P, ASSINGER A, HAEGELE S, et al. Evidence for serotonin as a relevant inducer of liver regeneration after liver resection in humans. Hepatology. 2014; 60(1):257-266. [57] NOCITO A, GEORGIEV P, DAHM F, et al. Platelets and platelet-derived serotonin promote tissue repair after normothermic hepatic ischemia in mice. Hepatology. 2007; 45(2):369-376. [58] LESURTEL M, GRAF R, ALEIL B, et al. Platelet-derived serotonin mediates liver regeneration. Science. 2006;312(5770):104-107. [59] TZIROGIANNIS KN, KOURENTZI KT, ZYGA S, et al. Effect of 5-HT7 receptor blockade on liver regeneration after 60-70% partial hepatectomy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014;14:201. [60] TIAN Y, GRAF R, EL-BADRY AM, et al. Activation of serotonin receptor-2B rescues small-for-size liver graft failure in mice. Hepatology. 2011; 53(1):253-262. [61] TSUCHIDA T, FRIEDMAN SL. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14(7):397-411. [62] RUDDELL RG, MANN DA, RAMM GA. The function of serotonin within the liver. J Hepatol. 2008;48(4):666-675. [63] OMENETTI A, YANG L, GAINETDINOV RR, et al. Paracrine modulation of cholangiocyte serotonin synthesis orchestrates biliary remodeling in adults. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;300(2):G303-G315. [64] KYRITSI K, CHEN L, O’BRIEN A, et al. Modulation of the tryptophan hydroxylase 1/monoamine oxidase‐a/5‐Hydroxytryptamine/5‐Hydroxytry‐ ptamine receptor 2A/2B/2C Axis regulates biliary proliferation and liver fibrosis during cholestasis. Hepatology. 2020;71(3): 990-1008. [65] FANG Y, LIU C, SHU B, et al. Axis of serotonin -pERK-YAP in liver regeneration. Life Sci. 2018;209:490-497. [66] GRIJALVA JL, HUIZENGA M, MUELLER K, et al. Dynamic alterations in Hippo signaling pathway and YAP activation during liver regeneration. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014;307(2):G196-G204. [67] NAITO K, MOTEKI H, KIMURA M, et al. Role of serotonin in liver regeneration. Curr Top Pharmacol. 2019;23:39-44. [68] WEN Y, EMONTZPOHL C, XU L, et al. Interleukin‐33 facilitates liver regeneration through serotonin‐involved gut‐liver axis. Hepatology. 2023;77(5): 1580-1592. [69] NAGAO Y, AKAHOSHI T, KAMORI M, et al. Liver regeneration is promoted by increasing serotonin content in rat liver with secondary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatol Res. 2011;41(8):784-794. [70] RUDDELL RG, OAKLEY F, HUSSAIN Z, et al. A role for serotonin (5-HT) in hepatic stellate cell function and liver fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 2006;169(3):861-876. [71] EBRAHIMKHANI MR, OAKLEY F, MURPHY LB, et al. Stimulating healthy tissue regeneration by targeting the 5-HT(2)B receptor in chronic liver disease. Nat Med. 2011;17(12):1668-1673. [72] POLAT B, HALICI Z, CADIRCI E, et al. Liver 5-HT7 receptors: A novel regulator target of fibrosis and inflammation-induced chronic liver injury in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;43:227-235. [73] FABRE A, MARCHAL-SOMME J, MARCHAND-ADAM S, et al. Modulation of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis by serotonin receptor antagonists in mice. Eur Respir J. 2008;32(2):426-436. [74] ELAIDY SM, ESSAWY SS. The antifibrotic effects of alveolar macrophages 5-HT2C receptors blockade on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Pharmacol Rep. 2016;68(6):1244-1253. [75] TAWFIK MK, MAKARY S. 5-HT7 receptor antagonism (SB-269970) attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats via downregulating oxidative burden and inflammatory cascades and ameliorating collagen deposition: Comparison to terguride. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;814:114-123. [76] DHALLA NS, MOTA KO, ELIMBAN V, et al. Role of vasoactive hormone-induced signal transduction in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Cells. 2024;13(10):856. [77] SHIMIZU K, SUNAGAWA Y, FUNAMOTO M, et al. The selective serotonin 2A receptor antagonist sarpogrelate prevents cardiac hypertrophy and systolic dysfunction via inhibition of the ERK1/2-GATA4 signaling pathway. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021; 14(12):1268. [78] TARBIT E, SINGH I, PEART JN, et al. Increased release of serotonin from rat primary isolated adult cardiac myofibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2021; 11(1):20376. [79] WALDUM H, WAHBA A. Serotonin-A Driver of Progressive Heart Valve Disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:774573. [80] PANG Q, JIN H, WANG Y, et al. Depletion of serotonin relieves concanavalin A-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress, and TGF-beta1/Smads signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett. 2021;340:123-132. [81] PYTLIAK M, VARGOVÁ V, MECHÍROVÁ V, et al. Serotonin receptors - from molecular biology to clinical applications. Physiol Res. 2011;60(1):15-25. [82] SAGONAS I, DAOUSSIS D. Serotonin and systemic sclerosis. An emerging player in pathogenesis. Joint Bone Spine. 2022;89(3): 105309. [83] ZHAO M, WU J, WU H, et al. Clinical Treatment Options in Scleroderma: Recommendations and Comprehensive Review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2022; 62(2):273-291. [84] BAHR FS, RICKE-HOCH M, PONIMASKIN E, et al. Serotonin receptors in myocardial infarction: friend or foe? ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024;15(8):1619-1634. [85] MARTINS AM, ASCENSO A, RIBEIRO HM, et al. The Brain–skin connection and the pathogenesis of psoriasis: a review with a focus on the serotonergic system. Cells. 2020;9(4):796. [86] JOHNSON BZ, STEVENSON AW, PRÊLE CM, et al. The role of IL-6 in skin fibrosis and cutaneous wound healing. Biomedicines. 2020;8(5):101. [87] GUPTA D, KAUSHIK D, MOHAN V. Role of neurotransmitters in the regulation of cutaneous wound healing. Exp Brain Res. 2022;240(6):1649-1659. [88] XU H, ZHANG J, JIANG Y, et al. Fractal analysis of rat dermal tissue in the different injury states. Int Wound J. 2022;19(5): 1016-1022. [89] SAMUELSSON A, ABDIU A, WACKENFORS A, et al. Serotonin kinetics in patients with burn injuries: a comparison between the local and systemic responses measured by microdialysis—a pilot study. Burns. 2008; 34(5):617-622. [90] SADIQ A, MENCHETTI I, SHAH A, et al. 5-HT1A receptor function makes wound healing a happier process. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1406. [91] SADIQ A, SHAH A, JESCHKE MG, et al. The role of serotonin during skin healing in post-thermal injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(4):1034. [92] BANSKOTA S, KHAN WI. Gut-derived serotonin and its emerging roles in immune function, inflammation, metabolism and the gut-brain axis. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2022;29(2):177-182. [93] WU H, DENNA TH, STORKERSEN JN, et al. Beyond a neurotransmitter: The role of serotonin in inflammation and immunity. Pharmacol Res. 2019; 140:100-114. [94] KOOPMAN N, KATSAVELIS D, HOVE AST, et al. The multifaceted role of serotonin in intestinal homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9487. [95] WAN M, DING L, WANG D, et al. Serotonin: a potent immune cell modulator in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2020;11:186. [96] SANIDAD KZ, RAGER SL, CARROW HC, et al. Gut bacteria–derived serotonin promotes immune tolerance in early life. Sci Immunol. 2024;9(93):eadj4775. [97] BANSKOTA S, GHIA JEKHAN WI. Serotonin in the gut: blessing or a curse. Biochimie. 2019;161:56-64. [98] GRONDIN JA, KHAN WI. Emerging Roles of Gut Serotonin in Regulation of Immune Response, Microbiota Composition and Intestinal Inflammation. J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2023;7(1):88-96. [99] HAQ S, WANG H, GRONDIN J, et al. Disruption of autophagy by increased 5-HT alters gut microbiota and enhances susceptibility to experimental colitis and Crohn’s disease. Sci. Adv. 2021;7(45): eabi6442. [100] HATAMNEJAD MR, BARADARAN GHAVAMI S, SHIRVANI M, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and inflammatory bowel disease; Beneficial or malpractice. Front Immunol. 2022;13:980189. [101] BREUNIG M, MERKLE J, WAGNER M, et al. Modeling plasticity and dysplasia of pancreatic ductal organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28(6):1105-1124. [102] PURI S, FOLIAS AE, HEBROK M. Plasticity and dedifferentiation within the pancreas: development, homeostasis, and disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(1):18-31. [103] GRIMONT A, LEACH SD, CHANDWANI R. Uncertain Beginnings: Acinar and Ductal Cell Plasticity in the Development of Pancreatic Cancer. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022; 13(2):369-382. [104] MEANS AL, MESZOELY IM, SUZUKI K, et al. Pancreatic epithelial plasticity mediated by acinar cell transdifferentiation and generation of nestin-positive intermediates. Development. 2005;132(16):3767-3776. [105] JENSEN JN, CAMERON E, GARAY MV, et al. Recapitulation of elements of embryonic development in adult mouse pancreatic regeneration. Gastroenterology. 2005;128(3):728-741. [106] FALCOMATÀ C, SAUR D. Self-renewal equality in pancreas homeostasis, regeneration, and cancer. Cell Rep. 2021; 37(11):110135. [107] STANGER BZ, HEBROK M. Control of cell identity in pancreas development and regeneration. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144(6): 1170-1179. [108] MANTOVANI MC, SILVA IBB, LOJUDICE FH, et al. Pancreatic stem cells and regenerative medicine of endocrine pancreas//DOS SANTOS GOLDENBERG RC, DE CARVALHO AC. Resident Stem Cells and Regenerative Therapy: Sources and Clinical Applications. Elsevier Inc. 2024:75-103. [109] MOON JH, KIM YG, KIM K, et al. Serotonin regulates adult beta-cell mass by stimulating perinatal beta-cell proliferation. Diabetes. 2020;69(2):205-214. [110] SHARKEY KA, MAWE GM. The enteric nervous system. Physiol Rev. 2023;103(2): 1487-1564. [111] LIU MT, KUAN YH, WANG J, et al. 5-HT4 receptor-mediated neuroprotection and neurogenesis in the enteric nervous system of adult mice. J Neurosci. 2009;29(31):9683-9699. [112] MATSUYOSHI H, KUNIYASU H, OKUMURA M, et al. A 5-HT(4)-receptor activation-induced neural plasticity enhances in vivo reconstructs of enteric nerve circuit insult. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010;22(7):806-813. [113] BELKIND-GERSON J, HOTTA R, NAGY N, et al. Colitis induces enteric neurogenesis through a 5-HT4-dependent mechanism. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21(4):870-878. [114] LI Z, CHALAZONITIS A, HUANG YY, et al. Essential roles of enteric neuronal serotonin in gastrointestinal motility and the development/survival of enteric dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci. 2011; 31(24):8998-9009. [115] YADAV VK, BALAJI S, SURESH PS, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of gut-derived serotonin synthesis is a potential bone anabolic treatment for osteoporosis. Nat Med. 2010;16(3):308-312. [116] YADAV VK, RYU JH, SUDA N, et al. Lrp5 controls bone formation by inhibiting serotonin synthesis in the duodenum. Cell. 2008;135(5):825-837. [117] CUI Y, NIZIOLEK PJ, MACDONALD BT, et al. Lrp5 functions in bone to regulate bone mass. Nat Med. 2011;17(6):684-691. [118] LIMA GM, CORAZZA BJ, MORAES RM, et al. The effect of an inhibitor of gut serotonin (LP533401) during the induction of periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 2016;51(5):661-668. |
| [1] | Zhang Di, Zhao Jun, Ma Guangyue, Sun Hui, Jiang Rong. Mechanism of depression-like behavior in chronic social defeat stress mice based on high-throughput sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1139-1146. |
| [2] | Sun Yajie, Zhao Xinchen, Bo Shuangling. Spatiotemporal expression of bone morphologic protein 7 in mouse kidney development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1156-1161. |
| [3] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [4] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [5] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [6] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [7] | Wen Fan, Xiang Yang, Zhu Huan, Tuo Yanfang, Li Feng. Exercise improves microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| [8] | Fu Zhenyi, Li Junhao, Zhang Yating, He Yunkai, Liu Junyu, Wei Yunhao, Liu Jiaxin. Schwann cells promote peripheral nerve regeneration: retrospect and prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1236-1246. |
| [9] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [10] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [11] | Wen Xiaolong, Weng Xiquan, Feng Yao, Cao Wenyan, Liu Yuqian, Wang Haitao. Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| [12] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [13] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [14] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [15] | Zhang Jiuxuan, Zhang Jinnan, Sui Xiaofan, Pei Xiaxia, Wei Jianhong, Su Qiang, Li Tian. Effects of ammonia poisoning on cognitive behavior and hippocampal synaptic damage in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1122-1128. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||