Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1320-1330.doi: 10.12307/2026.033
Previous Articles Next Articles
A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective
Yang Zeyu1, Zhi Liang1, Wang Jia1, Zhang Jingyi1, Zhang Qingfang2, Wang Yulong3, Long Jianjun3
- 1School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, Dapeng Hospital, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518100, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Rehabilitation, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518035, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-18Accepted:2025-02-15Online:2026-02-18Published:2025-06-28 -
Contact:Long Jianjun, Senior technologist, Master’s supervisor, Department of Rehabilitation, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518035, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Yang Zeyu, Master candidate, School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Medical Innovation Technology Transformation Center of Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, No. HTHZQSWS-KCCYB-2023060 (to LJJ); Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen, No. SZSM202111010 (to WYL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
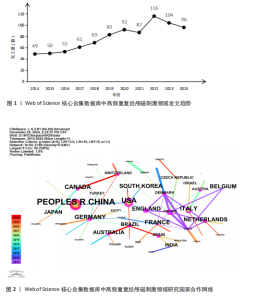
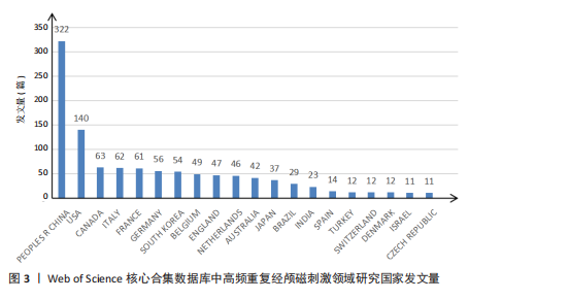
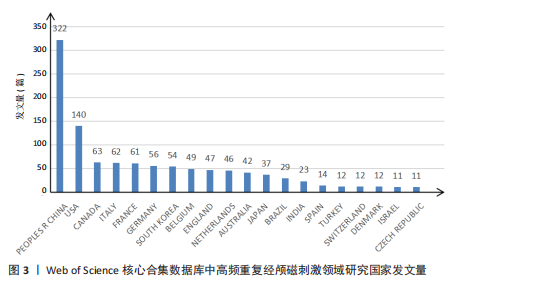
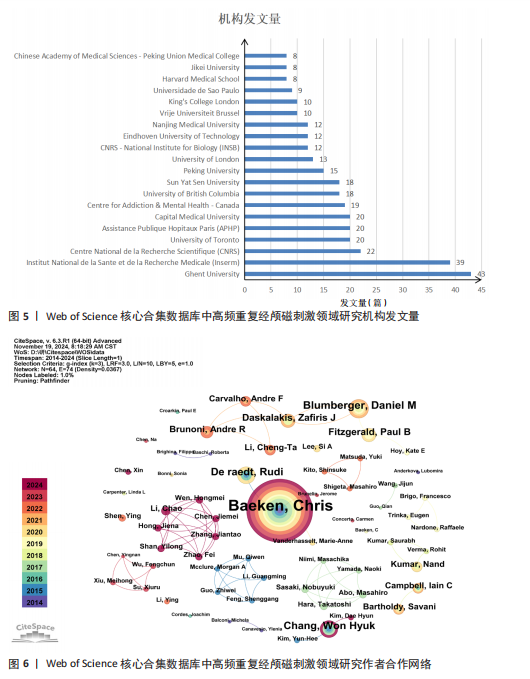
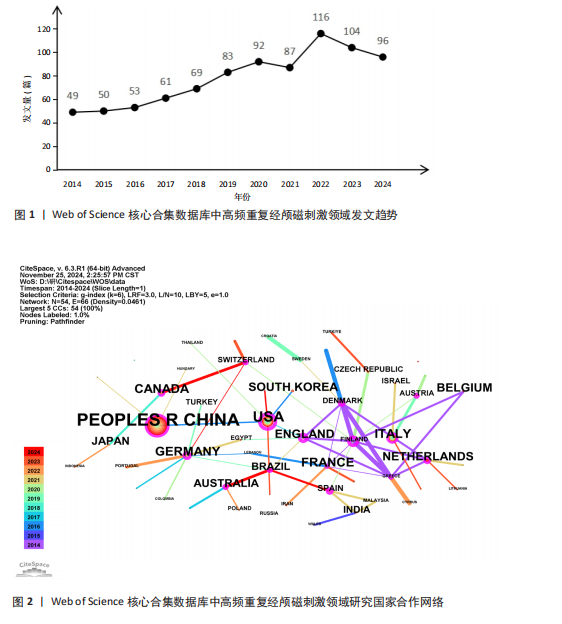
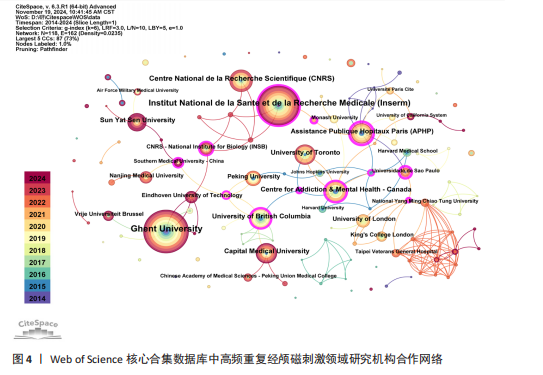
2.1 高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究发文量趋势 发文量能反映某个领域的研究热点和发展状况[17]。从2014-01-01/2024-11-15,符合检索条件的文章共有860篇。如图1所示,在全球范围内,高频重复经颅磁刺激领域的发文量呈正增长趋势,从2014年的49篇增加到2024年的96篇,增加了95.92%,表明高频重复经颅磁刺激研究是一个具有被持续挖掘潜力的领域。近5年来,高频重复经颅磁刺激领域的年发文量均在80篇以上,这在一定程度上反映出该领域正逐渐成为一个研究热点,具有广阔的发展前景。但与2022年相比,2023年的发文量略有下降。 2.2 高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究国家/地区发文量及合作分析 以“国家”为节点,阈值选择g-index(k=6)、Top N=50,得到节点数54、连线数66的国家合作网络图谱(图2)。此次检索共纳入54个国家/地区。发文量前20的国家如图3所示,其中发文量最多的是中国(322篇),远远领先于其他国家;其次是美国(140篇),接下来是加拿大(63篇)、意大利(62篇)和法国(61篇)。发文量前5的国家占总发文量的54.55%。在中心性方面,排名前3的国家分别是芬兰、英国和美国,说明它们与更多的国家展开了交流。图2中节点圆圈出现外圈颜色代表其短期内被大量引用或者中心性大于0.1,节点之间的线条紧密相连,但大节点之间或通过大节点的线条通常较细,相比之下,小节点之间的线条相对较粗。由此可以推断,尽管国际间交流密切,但发文量高的国家并没有与世界各地表现出紧密的合作关系,例如中国、美国和加拿大与其他国家的合作关系较浅;而发文量较低国家之间的交流更为密切,例如丹麦、芬兰和希腊之间的连线更粗,这可能是由于它们之间的地理位置较近,促进了合作和知识交流。 2.3 高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究机构发文量及合作分析 以“机构”为节点,阈值选择g-index(k=6)、Top N=50,得到节点数118、连线数162的机构合作网络图谱(图4),总共有118个机构为高频重复经颅磁刺激领域做出了贡献。发文量前20的机构如图5所示,根特大学(Ghent University)的发文量最高,共发表了43篇文章,其次是法国国家健康与医学研究院[Institut National de la Sante et de la "

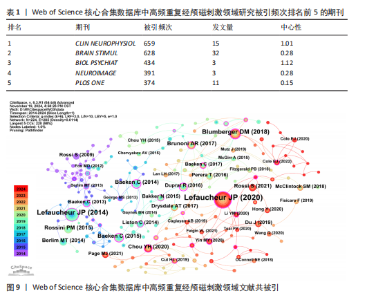
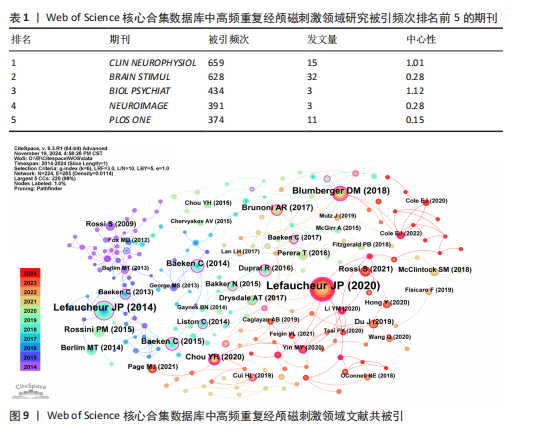
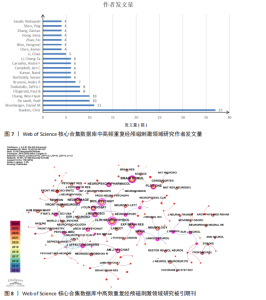
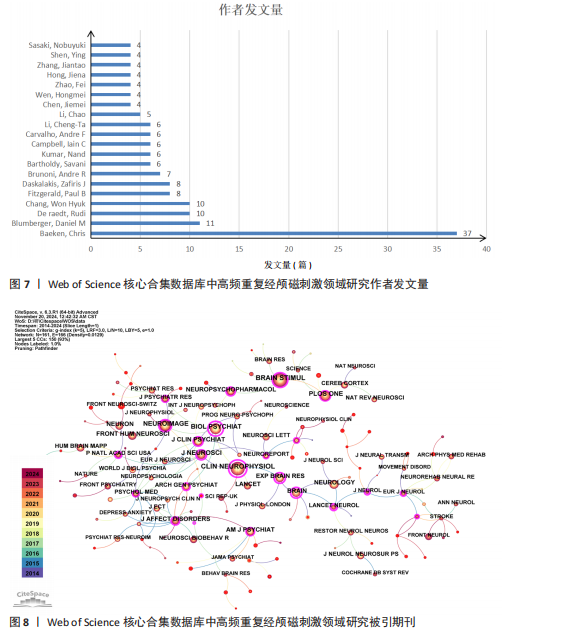
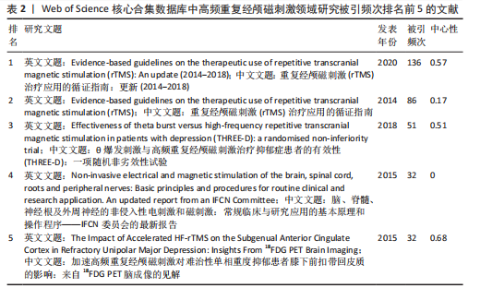
Recherche Medicale(Inserm)](39篇)和法国国家科学研究中心[Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS)](22篇);首都医科大学(Capital Medical University)是中国发文量最高的机构,共发表了20篇文章。中心性较强的前3个机构分别是巴黎公共援助医院[Assistance Publique Hopitaux Paris (APHP)]、圣保罗大学(Universidade de Sao Paulo)和安格利亚鲁斯金大学(Anglia Ruskin University)。 图4中机构与机构之间的连线较少,这表明世界各地的机构仍然需要加强它们在不同地区之间的合作。可以观察到图中的大多数机构类型是学校,表明高频重复经颅磁刺激领域的临床研究数量可能不足。 2.4 高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究作者发文量及合作分析 以“合作作者”为节点,阈值选择g-index(k=3)、Top N=50,得到节点数64、连线数74的作者合作网络图谱(图6)。共有64位作者为高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究做出了贡献,发文量前20的作者如图7所示,其中Chris Baeken发表的文章最多,有37篇,其次是Daniel M Blumberger(11篇)、Rudi De raedt(10篇)和Won Hyuk Chang(10篇)。在作者合作网络中,一些不同作者之间有清晰的集群,用不同的颜色表示。发文量靠前作者之间的连线较少,表明在高频重复经颅磁刺激领域几个有影响力研究小组之间的交流可能是有限的。大多数孤立的节点只有一种颜色,表明这些作者可能只在该领域发表过一次文章。Zafiris J Daskalakis的节点被多条不同颜色的连线穿过,包括橙色和橙黄色,表明他是高频重复经颅磁刺激领域的一名活跃作者,在该领域与其他作者有持续的联系和交流。在合作网络图中,节点的颜色与年份有关,如左下角的色彩渐变所示。从图6中可以看出,在最近一年的时间里,许多中国作者在该领域交流密切,如图中深红色的网络所示。来自比利时根特大学的Chris Baeken在发表的文章数量上领先,他与同为根特大学的Rudi De raedt合作发表了多篇文章。 2.5 高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究被引期刊分析 以“被引期刊”为节点,阈值选择g-index(k=5)、Top N=50,得到节点数161、连线数166的被引期刊图谱(图8)。共有161种期刊发表了高频重复经颅磁刺激相关论文,被引频次排名前5的期刊如表1所示。《CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY》(影响因子=3.7)的被引频次最高,"
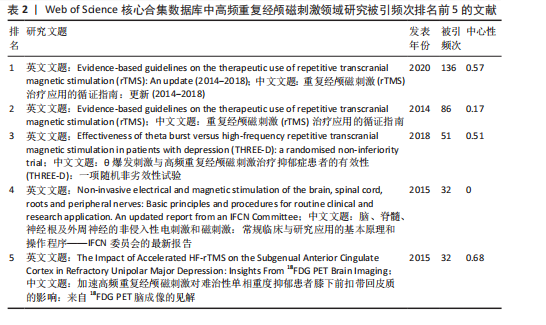
《BIOLOGICAL PSYCHIATRY》(影响因子=9.6)的中心性最强。《CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY》由ELSEVIER IRELAND LTD出版,主要发表临床神经生理学领域的研究成果与实践,不仅是国际临床神经生理学联合会的官方杂志,而且是众多神经生理学会的官方杂志,在神经生理学领域拥有良好的声誉和影响力,备受学者们的关注;该杂志还致力于推动神经系统疾病病理生理学相关研究的发展,积极传播相关的学术研究成果与报告。《BIOLOGICAL PSYCHIATRY》由ELSEVIER SCIENCE INC出版,是一本在神经科学和精神病学领域具有重要影响力的学术期刊。由此可以推断,高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究在过去10年中获得了广泛关注,《CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY》和《BIOLOGICAL PSYCHIATRY》在高频重复经颅磁刺激的发展中起着关键作用。在发文量相同的情况下,《BIOL PSYCHIAT》的被引频次最高,其次是《NEUROIMAGE》,说明这两家期刊是高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究的高质量期刊。 2.6 高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究文献共被引分析 以“被引文献”为节点,阈值选择g-index(k=6)、Top N=50,得到节点数224、连线数285的文献共被引图谱(图9)。由图9中可以看出,一些发表年份相近文章之间的连线较多,表明在该阶段这些文章共同得到学者们的认可。被引频次排名前5的文献如表2所示,说明这5篇文章的学术性高,影响力显著,具有较大的参考价值。Lefaucheur JP团队的研究在高被引参考文献中排名第一,说明他们的文章在该领域举足轻重,他们先于2014年发表了重复经颅磁刺激治疗应用的循证指南[18],并于2020年发表了更新的循证指南[5],这2篇文章的被引频次排名前二;他们评估了大量的临床证据,制定了涉及疼痛、运动障碍、脑卒中、肌萎缩侧索硬化症、多发性硬化症、癫痫、意识障碍、耳鸣、抑郁、焦虑症、强迫症和精神分裂症等众多神经和精神疾病的治疗指南[5,18],推动了高频重复经颅磁刺"
激领域的发展。还观察到Blumberger DM和Baeken C团队的研究出现在高被引参考文献中,说明了高频重复经颅磁刺激在抑郁症治疗方面的潜在价值[19-20]。 2.7 高频重复经颅磁刺激学科领域分析 以“学科”为节点,阈值选择g-index(k=6)、Top N=50,得到节点数70、连线数70的学科领域图谱(图10)。发文量前5的学科领域为神经科学(NEUROSCIENCES)、临床神经病学(CLINICAL NEUROLOGY)、精神病学(PSYCHIATRY),其频次分别为410,241和216,占总发文量的60.33%,说明高频重复经颅磁刺激领域的研究主要集中在神经系统疾病和精神疾病领域。中心性最强的3大学科是心理学与实验(PSYCHOLOGY, EXPERIMENTAL)、心理学(PSYCHOLOGY)和行为科学(BEHAVIORAL SCIENCES),说明它们与其他学科之间的交流更为密切,也表明高频重复经颅磁刺激能对人的心理和行为造成影响。 2.8 高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究关键词共现分析 以“关键词”为节点,阈值选择g-index(k=10)、Top N=50,得到节点数188、连线数241的关键词共现图谱(图11)。关键词共现和聚类分析能够深入揭示不同研究主题之间的关联性及密切程度,进而反映出研究领域中备受关注的热点议题、发展趋势及其内在联系[21-22]。出现频次排名前10的关键词如表3所示,这些结果展示了高频重复经颅磁刺激研究领域的研究热点和核心主题。图11中节点的大小表示关键词出现的频率。可以观察到较大的节点,例如“major depression”和“cortex”等表现出从蓝色到红色的梯度转变。这一现象表明,在过去近10年的时间里,高频重复经颅磁刺激领域的研究重点在于抑郁症的治疗和其在大脑皮层的作用机制。 2.9 高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究关键词聚类分析 关键词聚类是对关键词共现图谱进行扩展,通过概括提取出研究主题,并直观地展现其研究领域即聚类群,通过聚类群可以看出"

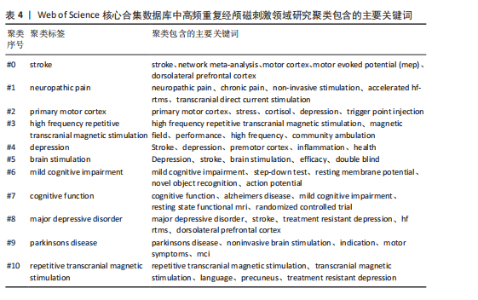
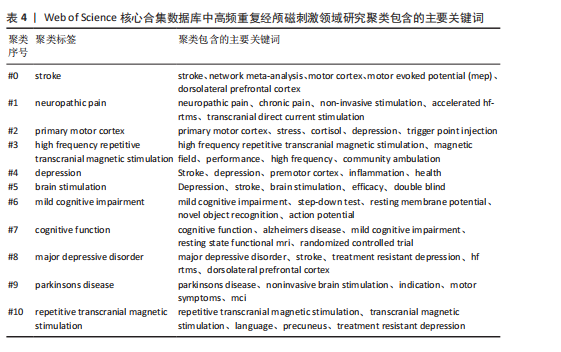
高频重复经颅磁刺激的热点分布状况。在关键词共现的基础上,选择LLR算法进行K选项的关键词聚类分析,得到如下的关键词聚类图谱(图12)。聚类模块性指数Modularity Q=0.765 6 (> 0.3),说明聚类结构显著,可清晰界定各个聚类的研究方向。聚类轮廓性指数S值Mean Silhouette=0.917 8(> 0.7),说明聚类效果十分合理且具有良好的同质性和较高的信度。每个聚类群所包含的主要关键词如表4所示。在图12中共有11个不同的聚类群,由不同的颜色表示,每个聚类群都由密切相关的短语组成,聚类群的标签以最具代表性的关键词命名,从而反映出这些聚类的主题;与聚类群标签关联的数字越小,则表明该聚类群中所包含的关键词就越多。过去10年中,高频重复经颅磁刺激领域的研究呈现出了聚集性、多元化和增速快的特征,该领域最具代表性的关键词是#0脑卒中、#1神经源性疼痛和#2初级运动皮质,这些关键词为把握未来的研究方向提供了一定的参考价值。 2.10 高频重复经颅磁刺激领域研究关键词突现 在关键词聚类基础上进行突现分析,得到25个突现词,如图13所示。突现词代表短期内频次发生显著变化的关键词,具有较高突现强度的词可以更好地预测未来的研究热点和前沿内容,这在一定程度上能够预测高频重复经颅磁刺激领域的发展趋势[12]。最新的前沿热点词有“轻度认知障碍”“损伤”及“工作记忆”,其中“轻度认知障碍”的突现强度最大,为3.67。值得注意的是,关键词“轻度认知障碍”的突现一直持续到2024年,表明在2021-2024年期间关于高频重复经颅磁刺激在轻度认知障碍领域应用的研究大幅激增。"

| [1] BARKER AT, JALINOUS R, FREESTON IL. Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet. 1985;1(8437):1106-1107. [2] HALLETT M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: a primer. Neuron. 2007;55(2): 187-199. [3] CAPPON D, DEN BOER T, JORDAN C, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) for geriatric depression. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;74:101531. [4] SHENG R, CHEN C, CHEN H, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for stroke rehabilitation: insights into the molecular and cellular mechanisms of neuroinflammation. Front Immunol. 2023; 14:1197422. [5] LEFAUCHEUR JP, ALEMAN A, BAEKEN C, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): An update (2014-2018). Clinical Neurophysiol. 2020; 131(2):474-528. [6] 唐莺莹,吴毅,王继军.重复经颅磁刺激的临床应用与操作规范上海专家共识[J].上海医学,2022,45(2):65-70. [7] 陈静,张长国,张红波,等.高频与低频重复经颅磁刺激治疗帕金森病的临床观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(5): 464-467. [8] KIM SY, SHIN SB, LEE SJ, et al. Factors Associated With Upper Extremity Functional Recovery Following Low-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Stroke Patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016;40(3):373-382. [9] MOHAMAD SAFIAI NI, MOHAMAD NA, BASRI H, et al. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation at dorsolateral prefrontal cortex for migraine prevention: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cephalalgia. 2022;42(10): 1071-1085. [10] SHIM J, LEE S. Effects of High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Combined with Motor Learning on Motor Function and Grip Force of the Upper Limbs and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with a Subacute Stroke. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(12):6093. [11] WEI L, ZHANG Y, WANG J, et al. Parietal-hippocampal rTMS improves cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease and increases dynamic functional connectivity of default mode network. Psychiatry Res. 2022;315:114721. [12] CHEN CM. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol. 2006;57(3):359-377. [13] ZHONG D, LI Y, HUANG Y, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Exercise on Cancer: A Bibliometrics Study and Visualization Analysis via CiteSpace. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:797902. [14] CHEN C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):5303-5310. [15] LIU F, CHEN N, WANG R, et al. Visual analysis of allergic rhinitis in children based on web of science and CiteSpace software. Front Pediatr. 2022;10:911293. [16] DING X, YANG Z. Knowledge mapping of platform research: a visual analysis using VOSviewer and CiteSpace. Electron. Commer. 2022;22(3):787-809. [17] ZHOU Y, HU Z, YUAN H, et al. CiteSpace-based visual analysis of hypothermia studies in surgical patients. Nursing Open. 2023;10(9):6228-6236. [18] LEFAUCHEUR JP, ANDRÉ-OBADIA N, ANTAL A, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;125(11):2150-2206. [19] BAEKEN C, MARINAZZO D, EVERAERT H, et al. The Impact of Accelerated HF-rTMS on the Subgenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Refractory Unipolar Major Depression: Insights From <SUP>18</SUP>FDG PET Brain Imaging. Brain Stimul. 2015;8(4):808-815. [20] BLUMBERGER DM, VILA-RODRIGUEZ F, THORPE KE, et al. Effectiveness of theta burst versus high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with depression (THREE-D): a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10131):1683-1692. [21] 高明波,韩婷.基于Web of Science的生酮饮食与肠道菌群研究文献计量学分析[J].中国微生态学杂志,2023,35(11):1257-1264+1271. [22] 闫伟娜.我国科普期刊研究的进展、热点与趋势:基于CiteSpace知识图谱的可视化分析[J].中国科技期刊研究,2024, 35(2):163-170. [23] SCHRIJVERS DL, BAEKEN C, DE RAEDT R,et al. The Impact of High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Fine Motor Functions in Medication-Resistant Major Depression. Neuropsychobiology. 2012;66(4):252-258. [24] WU GR, BAEKEN C. Exploring potential working mechanisms of accelerated HF-rTMS in refractory major depression with a focus on locus coeruleus connectivity. Eur Psychiatry. 2024;67(1):e70. [25] CHEN JM, ZHAO F, HONG JN, et al. Effect of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on swallowing function and pneumonia in poststroke dysphagia in rats. Brain Res. 2024;1832:148846. [26] ZHAO F, CHEN JM, SHAN YL, et al. Comprehensive assessment of HF-rTMS treatment mechanism for post-stroke dysphagia in rats by integration of fecal metabolomics and 16S rRNA sequencing. Front Cell Infect. 2024;14:8846. [27] FITZGERALD PB, DASKALAKIS ZJ. A practical guide to the use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of depression. Brain Stimul. 2012;5(3):287-296. [28] SCHUTTER DJ. Antidepressant efficacy of high-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation over the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in double-blind sham-controlled designs: a meta-analysis. Psychol Med, 2009;39(1):65-75. [29] 姜霖霖,牛陵川,王愉乐,等.高频重复经颅磁刺激对脑梗死后抑郁患者的影响[J].康复学报,2021,31(6):455-460. [30] 王铭琛,李作伟.高频重复经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中后抑郁的Meta分析[J].中医临床研究,2024,16(9):22-27. [31] CAULFIELD KA, FLEISCHMANN HH, GEORGE MS, et al. A transdiagnostic review of safety, efficacy, and parameter space in accelerated transcranial magnetic stimulation. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;152:384-396. [32] BAEKEN C, LEFAUCHEUR JP, VAN SCHUERBEEK P. The impact of accelerated high frequency rTMS on brain neurochemicals in treatment-resistant depression: Insights from (1)H MR spectroscopy. J Clin Neurosci. 2017; 128(9):1664-1672. [33] MURASE N, DUQUE J, MAZZOCCHIO R, et al. Influence of interhemispheric interactions on motor function in chronic stroke. Ann Neurol. 2004;55(3):400-409. [34] WANG Q, ZHANG D, ZHAO YY, et al. Effects of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the contralesional motor cortex on motor recovery in severe hemiplegic stroke: A randomized clinical trial. Brain Stimul. 2020;13(4):979-986. [35] DI PINO G, PELLEGRINO G, ASSENZA G, et al. Modulation of brain plasticity in stroke: a novel model for neurorehabilitation. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014;10(10):597-608. [36] BUETEFISCH CM. Role of the Contralesional Hemisphere in Post-Stroke Recovery of Upper Extremity Motor Function. Front Neurol. 2015;6:214. [37] HARRINGTON RM, CHAN E, ROUNDS AK, et al. Roles of Lesioned and Nonlesioned Hemispheres in Reaching Performance Poststroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2020;34(1):61-71. [38] 高飞,张玉阁,马琳,等.健侧半球高频重复经颅磁刺激对左侧大面积脑梗死后完全性失语的效果观察[J].华西医学, 2024,39(10):1625-1630. [39] KOMATSU T, HADA T, SASAKI N, et al. Effects and safety of high-frequency rTMS in subacute ischemic stroke patients. J Neurol Sci. 2024;462:123069. [40] LIU L, DING M, WU J F, et al. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation promotes ipsilesional functional hyperemia and motor recovery in mice with ischemic stroke. Cerebral Cortex. 2024; 34(3):bhae074. [41] LUO J, FENG Y, HONG Z, et al. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation promotes neural stem cell proliferation after ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(8):1772-1780. [42] DU J, YANG F, HU J, et al. Effects of high- and low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor recovery in early stroke patients: Evidence from a randomized controlled trial with clinical, neurophysiological and functional imaging assessments. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;21: 101620. [43] GUO Z, JIN Y, BAI X, et al. Distinction of High- and Low-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on the Functional Reorganization of the Motor Network in Stroke Patients. Neural Plast. 2021;2021:8873221. [44] ANDRÉ-OBADIA N, MAGNIN M, GARCIA-LARREA L. Theta-burst versus 20 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in neuropathic pain: A head-to-head comparison. J Clin Neurosci. 2021;132(10): 2702-2710. [45] DIAO Y, XIE Y, PAN J, et al. The Effectiveness of High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Patients with Neuropathic Orofacial Pain: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Neural Plast. 2022;2022:6131696. [46] JIN Y, XING G, LI G, et al. High Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Therapy For Chronic Neuropathic Pain: A Meta-analysis. Pain Physician. 2015;18(6): E1029-1046. [47] MYLIUS V, AYACHE SS, TEEPKER M, et al. [Transcranial magnetic stimulation and motor cortex stimulation in neuropathic pain]. Schmerz (Berlin, Germany). 2012; 26(6):655-660. [48] QUESADA C, POMMIER B, FAUCHON C, et al. New procedure of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for central neuropathic pain: a placebo-controlled randomized crossover study. Pain. 2020;161(4):718-728. [49] TSAI YY, WU WT, HAN DS, et al. Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review. Life (Basel, Switzerland). 2023;13(2):0258. [50] YOKOE M, MANO T, MARUO T, et al. The optimal stimulation site for high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: A double-blind crossover pilot study. J Clin Neurosci. 2018; 47:72-78. [51] KANG X, ZHANG B, DU W, et al. High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Regulates Astrocyte Activation by Modulating the Endocannabinoid System in Parkinson’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(8):5121-5134. [52] PAPALLO S, DI NARDO F, SICILIANO M, et al. Functional Connectome Controllability in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment after Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. J Clin Med. 2024;13(18):5763. [53] YUAN L Q, ZENG Q, WANG D, et al. Neuroimaging mechanisms of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for treatment of amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a double-blind randomized sham-controlled trial. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(4):707-713. [54] WANG T, GUO Z, WU H, et al. High-Frequency rTMS Could Improve Impaired Memory in Mild Cognitive Impairment Patients in China: A Randomized Controlled Study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2023; 37(4):296-302. |
| [1] | Sun Yajie, Zhao Xinchen, Bo Shuangling. Spatiotemporal expression of bone morphologic protein 7 in mouse kidney development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1156-1161. |
| [2] | Wang Mingqi, Feng Shiya, Han Yinhe, Yu Pengxin, Guo Lina, Jia Zixuan, Wang Xiuli. Construction and evaluation of a neuralized intestinal mucosal tissue engineering model in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 892-900. |
| [3] | Wang Jie, Huang Rui, Zhang Ye, Shou Zhaoxi, Yao Jie, Liu Chenxi, Liao Jian. Role and mechanism of probiotics in peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 901-907. |
| [4] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [5] | Liang Haobo, Wang Zeyu, Ma Wenlong, Liu Hao, Liu Youwen. Hot issues in the field of joint revision: infection, rehabilitation nursing, bone defect, and prosthesis loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1963-1971. |
| [6] | Lyu Liting, Yu Xia, Zhang Jinmei, Gao Qiaojing, Liu Renfan, Li Meng, Wang Lu. Bibliometric analysis of research process and current situation of brain aging and exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [7] | Xie Liugang, Cui Shuke, Guo Nannan, Li Aoyu, Zhang Jingrui. Research hotspots and frontiers of stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [8] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [9] | Li Huijun, Li Huangyan, Zhang Yeting. Physical activity and cognition in older adults: research hotspot and topic evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1073-1080. |
| [10] | Dang Xiaowen, Huang Hailiang, Huang Lei, Wang Yajie . Research frontiers and hotspots of carbon nanomaterials in biomedical field over the past 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 752-760. |
| [11] | Ma Yucong, Ouyang Zhengzheng, Liu Xiaojie, Yang Sifei. Tracking of research trends and hotspots in medical magnesium alloy materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7470-7480. |
| [12] | Wang Ziheng, Wu Shuang. Oxidative stress-related genes and molecular mechanisms after spinal cord injury: data analysis and verification based on GEO database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6893-6904. |
| [13] | Guo Haizhen, Cong Zidong, Zhao Yuke, Li Xiaofeng, Yu Lu, Qian Shule, Wang Runying, Du Wuxun. Development of patch clamp technology in the past 10 years: visual analysis based on CiteSpace and VOSviewer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6717-6726. |
| [14] | Wang Wanchun, , Yi Jun, Yan Zhangren, Yang Yue, Dong Degang, Li Yumei. 717 Jiedu Decoction remodels homeostasis of extracellular matrix and promotes repair of local injured tissues in rats after Agkistrodon halys bite [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6457-6465. |
| [15] | Hu Shujuan, Liu Dang, Ding Yiting, Liu Xuan, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang. Ameliorative effect of walnut oil and peanut oil on atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6482-6488. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||