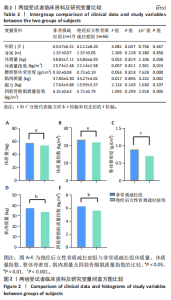
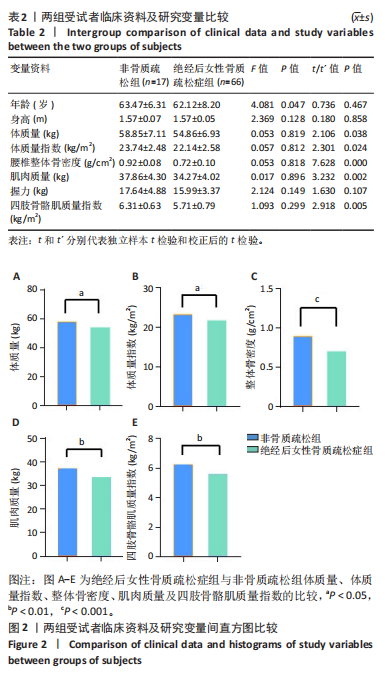
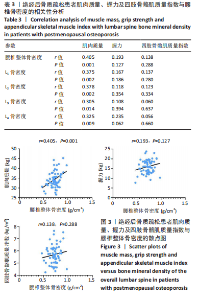
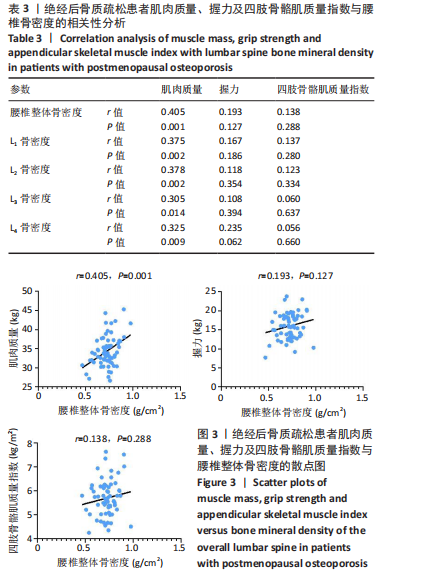
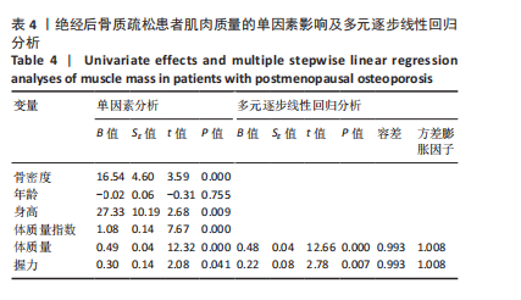
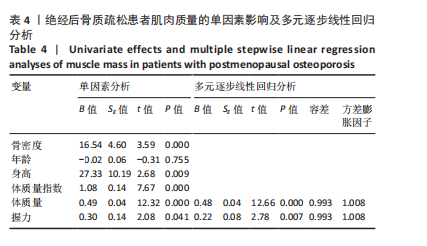
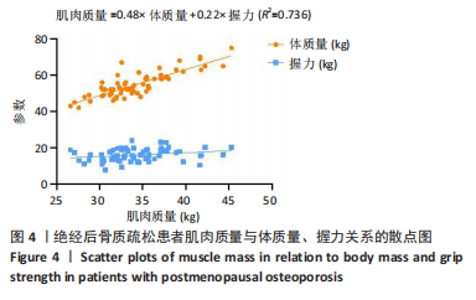
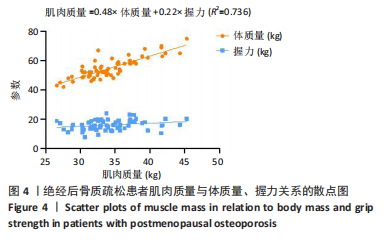
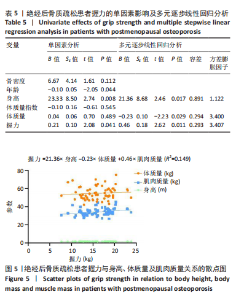
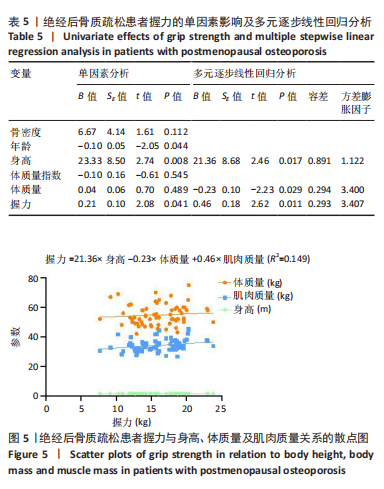
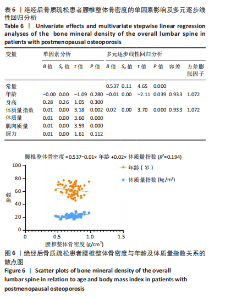
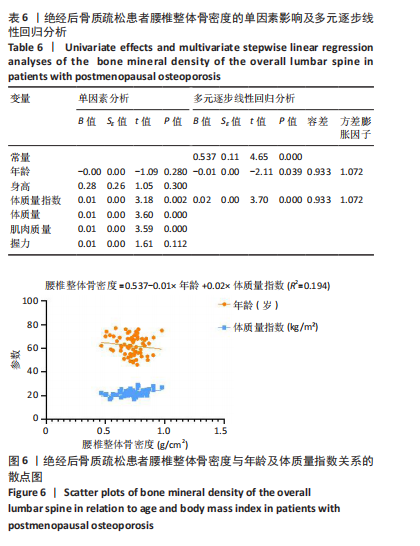
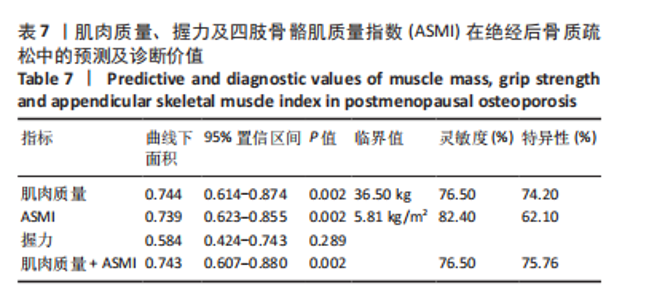
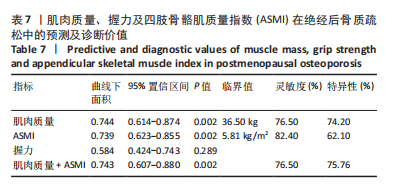
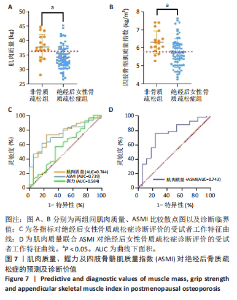
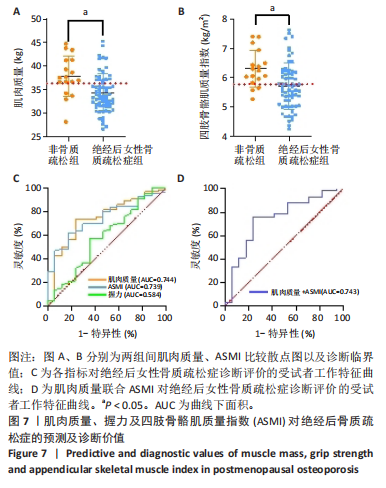
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1073-1080.doi: 10.12307/2026.039
Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index
Yang Zhijie1, Zhao Rui1, Yang Haolin1, Li Xiaoyun1, Li Yangbo1, Huang Jiachun2, Lin Yanping2, Wan Lei2, Huang Hongxing2
- 1The Third Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 2The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510378, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-11Accepted:2025-01-09Online:2026-02-18Published:2025-06-20 -
Contact:Huang Hongxing, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510378, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Yang Zhijie, MS, Physician, The Third Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82274551 (to HHX); Fundamental and Applied Basic Research Fund of Guangdong Province, No. 2023B1515230001 (to HHX); Huang Hongxing Guangdong Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Practitioner Inheritance Workshop, No. (2018)5 (to HHX); Self-selected Topic of Chinese Medicine Policy Research for Deepening Medical Reform at the Monitoring and Statistics Center of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. YGZXKT2024347 (to HJC); Osteoporosis and Bone Mineral Salt Disease Young and Middle-aged Physician Excellent Talent Cultivation Program and Bethune-Shiyao Osteoporosis Scientific Research Fund Project, No. GX2021C02 (to HJC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] LASKOU F, FUGGLE NR, PATEL HP, et al. Associations of osteoporosis and sarcopenia with frailty and multimorbidity among participants of the Hertfordshire Cohort Study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1): 220-229. [2] PARK HY, JUNG WS, KIM SW, et al. Relationship Between Sarcopenia, Obesity, Osteoporosis, and Cardiometabolic Health Conditions and Physical Activity Levels in Korean Older Adults. Front Physiol. 2021;12: 706259. [3] LIU Y, SONG Y, HAO Q, et al. Global prevalence of osteosarcopenic obesity amongst middle aged and older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Osteoporos. 2023;18(1): 60. [4] CACCIATORE S, MASSARO C, LANDI F. Preventing Osteoporosis, Sarcopenia and Obesity to Care about Quality of Life. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2023;27(1): 87-90. [5] DONG Y, YUAN H, MA G, et al. Bone-muscle crosstalk under physiological and pathological conditions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024;81(1): 310. [6] 何海洋, 杨嘉玲, 雷迅. 绝经后女性骨质疏松症患病率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2024,27(11):1370-1379. [7] 柴波, 冯皓宇, 常强, 等. 中国各地区绝经后骨质疏松症患病率及骨密度测量检出率分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2020,26(9):792-796. [8] KANIS JA, MELTON LR, CHRISTIANSEN C, et al. The diagnosis of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 1994;9(8):1137-1141. [9] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会, 章振林. 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J]. 中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691. [10] ZHENG M, WAN Y, LIU G, et al. Differences in the prevalence and risk factors of osteoporosis in chinese urban and rural regions: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):46. [11] THE L. Population ageing in China: crisis or opportunity? Lancet. 2022; 400(10366):1821. [12] 邓力军, 周高晋, 段蔚楠, 等. 自然绝经后女性体重、体重指数与骨密度的关系[J]. 浙江医学,2020,42(3):266-269. [13] KIM JG, HONG JY, PARK J, et al. Risk of fracture according to temporal changes of low body weight changes in adults over 40 years: a nationwide population-based cohort study. BMC Public Health. 2023; 23(1):948. [14] TANG G, FENG L, PEI Y, et al. Low BMI, blood calcium and vitamin D, kyphosis time, and outdoor activity time are independent risk factors for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1154927. [15] YOUNESI AL, KASHANIAN M, NAJMI Z, et al. Risk factors of osteoporosis and osteopenia in postmenopausal women based on the L2-L4 BMD T score of the lumbar spine: a study in Iran. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2023;39(1):2205959. [16] LI HL, SHEN Y, TAN LH, et al. Association between BMI and osteoporotic fractures at different sites in Chinese women: a case-control retrospective study in Changsha. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):187. [17] LIU HF, MENG DF, YU P, et al. Obesity and risk of fracture in postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Ann Med. 2023;55(1):2203515. [18] JANG SY, PARK J, RYU SY, et al. Low muscle mass is associated with osteoporosis: A nationwide population-based study. Maturitas. 2020; 133:54-59. [19] LEE Y, JE S, KIM HR, et al. Association between Fractures and Low Muscle Mass in Korean Menopausal Women: Data from Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey (2010-2011). J Menopausal Med. 2023;29(2):66-72. [20] QIN H, JIAO W. Correlation of muscle mass and bone mineral density in the NHANES US general population, 2017-2018. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(39):e30735. [21] 陈伟银, 李瑞莉, 黄汉超. 女性年龄与骨密度、骨质疏松的关系及发生骨质疏松的影响因素分析[J]. 中国实用医药,2024,19(1):60-63. [22] 袁嘉尧, 林燕平, 林贤灿, 等. 中老年人体成分与骨密度的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(15):2394-2399. [23] RIVIATI N, DARMA S, REAGAN M, et al. Relationship between Muscle Mass and Muscle Strength with Bone Density in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2024. doi: 10.4235/agmr.24.0113. [24] 蔺海山, 米尔阿里木·木尔提扎, 李鹏, 等. 绝经后女性髋部骨折患者骨骼肌肌纤维特点与骨密度的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(20):3144-3149. [25] HAN H, CHEN S, WANG X, et al. Association between muscle strength and mass and bone mineral density in the US general population: data from NHANES 1999-2002. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):397. [26] SUI H, DOU J, SHI B, et al. The reciprocity of skeletal muscle and bone: an evolving view from mechanical coupling, secretory crosstalk to stem cell exchange. Front Physiol. 2024;15:1349253. [27] LIN YH, CHEN HC, HSU NW, et al. Hand grip strength in predicting the risk of osteoporosis in Asian adults. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(2): 289-294. [28] MCGRATH RP, KRAEMER WJ, VINCENT BM, et al. Muscle Strength Is Protective Against Osteoporosis in an Ethnically Diverse Sample of Adults. J Strength Cond Res. 2017;31(9):2586-2589. [29] CHOI JY, YANG YM. Analysis of the association between osteoporosis and muscle strength in Korean adults: a national cross-sectional study. J Health Popul Nutr. 2023;42(1):97. [30] XU X, XU N, WANG Y, et al. The longitudinal associations between bone mineral density and appendicular skeletal muscle mass in Chinese community-dwelling middle aged and elderly men. Peer J. 2021;9: e10753. [31] QIN H, JIAO W. Correlation of muscle mass and bone mineral density in the NHANES US general population, 2017-2018. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(39):e30735. [32] MAEDA K, IMATANI J, NARAZAKI S, et al. Bone mineral density, limb muscle mass, muscle strength, and exercise capacity are reduced in female patients with distal radius fractures when the unaffected side grip strength is less than 18 kg. J Orthop Sci. 2023;28(6):1279-1284. [33] CHAN J, LU YC, YAO MM, et al. Correlation between hand grip strength and regional muscle mass in older Asian adults: an observational study. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22(1):206. [34] CHOE YR, JEONG JR, KIM YP. Grip strength mediates the relationship between muscle mass and frailty. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(2):441-451. [35] TAVARES N, RODRIGUES BC, ARRUDA S, et al. Untangle the relationship of muscle mass and bone mineral content on handgrip strength: Results of ELSA-Brasil. Cien Saude Colet. 2023;28(11):3191-3204. [36] KARSENTY G, OLSON EN. Bone and Muscle Endocrine Functions: Unexpected Paradigms of Inter-organ Communication. Cell. 2016; 164(6):1248-1256. [37] TAGLIAFERRI C, WITTRANT Y, DAVICCO MJ, et al. Muscle and bone, two interconnected tissues. Ageing Res Rev. 2015;21:55-70. [38] SEVERINSEN M, PEDERSEN BK. Muscle-Organ Crosstalk: The Emerging Roles of Myokines. Endocr Rev. 2020;41(4): 594-609. [39] ZHAO Z, YAN K, GUAN Q, et al. Mechanism and physical activities in bone-skeletal muscle crosstalk. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14: 1287972. [40] 黄宏兴, 史晓林, 李盛华, 等. 肌少-骨质疏松症专家共识[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(11):1561-1570. [41] PAPAGEORGIOU M, SATHYAPALAN T, SCHUTTE R. Muscle mass measures and incident osteoporosis in a large cohort of postmenopausal women. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019;10(1):131-139. |
| [1] | Sun Jiahe, Shi Jipeng, Zhu Tianrui, Quan Helong, Xu Hongqi. Effect of exercise intervention in elderly individuals with sarcopenia and its comorbidities: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 997-1007. |
| [2] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [3] | Zhou Jiajun, Ma Fei, Leng Yebo, Xu Shicai, He Baoqiang, Li Yang, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Tang Chao, Wang Qing, Zhong Dejun. Assessing distribution characteristics and clinical significance of vertebral fractures in patients with osteoporosis based on whole spine MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1883-1889. |
| [4] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [5] | Jiang Siqi, Huang Huanhuan, Yu Xinyu, Peng Ying, Zhou Wei, Zhao Qinghua. Meta-analysis of dose-effect of exercise on improving muscle health in community-dwelling older adults with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6295-6304. |
| [6] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei. Causal association between metabolites and sarcopenia: a big data analysis of genome-wide association studies in the European population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6369-6380. |
| [7] | Wang Runzheng, Fu Su, Dong Chao, Li Dongzhe, Wang Yongkui. Relationship between bone mineral density and lumbar disc degeneration in middle-aged and elderly men and postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5079-5085. |
| [8] | Qiao Zhengji, Chai Niubing, Zheng Luyao, Gao Yunna, Wang Yang. Effect of whole‑body vibration training on bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: a meta‑analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5195-5202. |
| [9] | Chen Jiayi, Li Huijing, Nong Yuxuan, Yin Yunfang, Liu Xiaobo, Chen Yue, Hu Xiaoshen, Zhong Dongling, Li Juan, Liu Tianyu, Jin Rongjiang. Meta-analysis of the correlation between phase angle and sarcopenia and its diagnostic indexes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2575-2589. |
| [10] | Liu Kedi, Chen Yongxi, Qin Haibiao, Guo Shenghui, Qin Zhongshe, Meng Juewei, Cui Shanlin, Fan Junhong. Causal relationship between peripheral blood cells and osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2605-2613. |
| [11] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Chen Lidan, Lu Wei, Zhang Zheng, Zhang Yunli, Chen Jiayong . Relationship between hypertension and osteoporosis in different racial groups [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2614-2622. |
| [12] | Jiang Nan, Fu Haonan, Hao Yuhan, Chen Zhilin, Zhu Zhiqing, Xu Feng, Yu Dong. Causal association between cathepsins and bone mineral density: two-way Mendelian randomization analyses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2623-2630. |
| [13] | Yang Cekai, Cai Zhuoyan, Chen Ming, Liu Hao, Weng Rui, Cui Jianchao, Zhang Shuncong, Yao Zhensong. Relationship between degeneration of paraspinal muscle and refractures in postmenopausal women treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1414-1419. |
| [14] | Xiaheida·Yilaerjiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun, Reyila·Kuerban, Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Chen Xin. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the distribution pattern of stress in bone tissues with different characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1277-1282. |
| [15] | Kaiyisaier•Abudukelimu, Maimaitimin•Abulimiti, Li Lei, Yang Xiaokai, Zhang Yukun, Liu Shuai. Effect of lumbar CT values in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in women patients with lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 945-949. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||