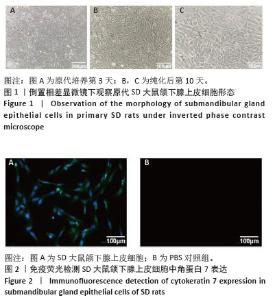
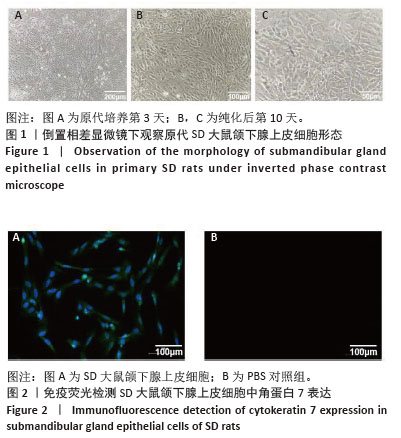
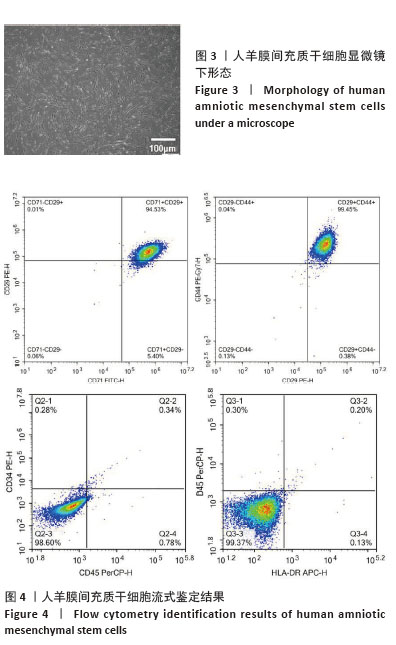
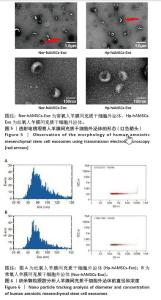
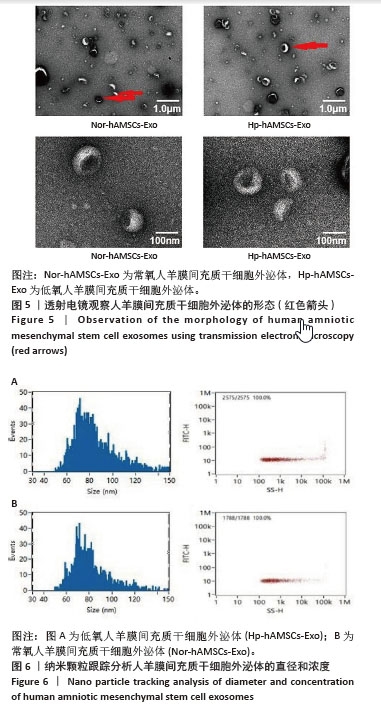
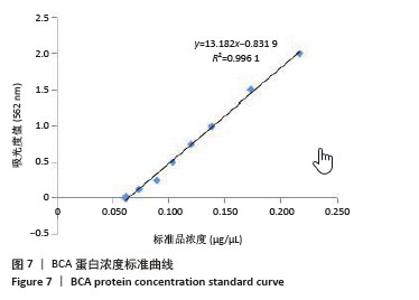
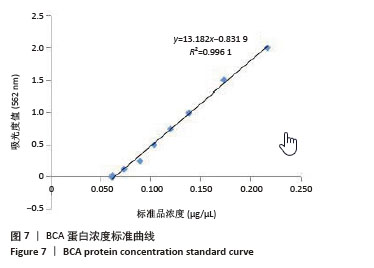
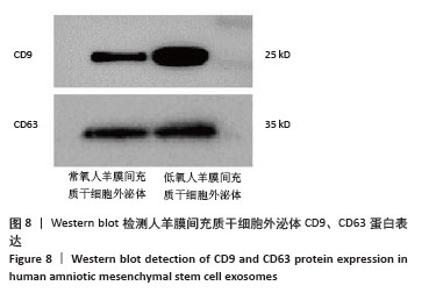
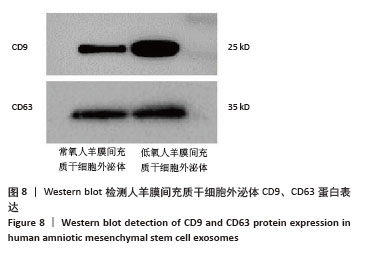
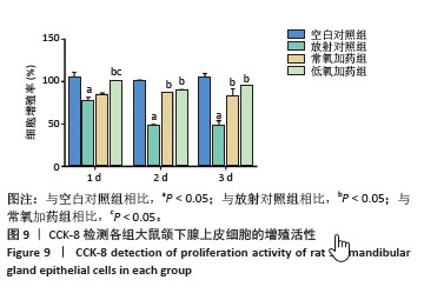
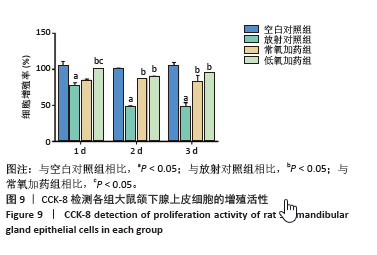
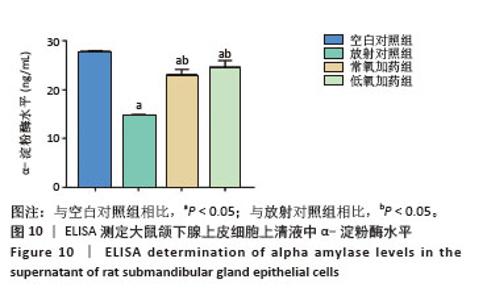
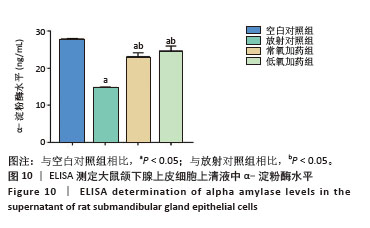
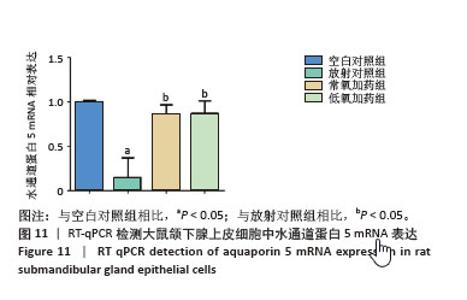
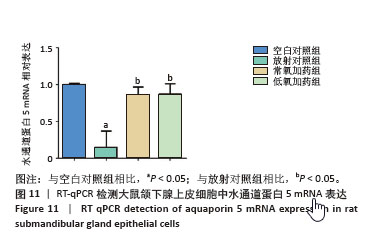
[1] RADES D, WARWAS B, GERULL K, et al. Prognostic Factors for Complete Recovery From Xerostomia After Radiotherapy of Head-and-Neck Cancers. In Vivo. 2022;36(4):1795-1800.
[2] KHOURY ZH, SULTAN AS. Prosthodontic implications of saliva and salivary gland dysfunction. J Prosthodont. 2023;32(9):766-775.
[3] LI Y, LI X, PANG R, et al. Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment of Radiotherapy-Induced Xerostomia: A Review. J Oncol. 2022;2022: 7802334.
[4] 田越,连启航,冯梅,等.唾液腺放射损伤发病机制及其防治的研究进展[J].肿瘤预防与治疗,2024,37(9):809-816.
[5] 黄桂林.放射性唾液腺功能损伤的再生医学研究:从干细胞到无细胞治疗[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2022,32(2):71-76.
[6] MARINKOVIC M, TRAN ON, WANG H, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cells offer a new paradigm for salivary gland regeneration. Int J Oral Sci. 2023;15(1):18.
[7] HEZAM K, WANG C, FU E, et al. Superior protective effects of PGE2 priming mesenchymal stem cells against LPS-induced acute lung injury (ALI) through macrophage immunomodulation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):48.
[8] 王丽丽,杨紫恩,欧阳明玥,等.间充质干细胞来源的外泌体在放射性肺损伤中的保护作用[J].中国辐射卫生,2025,34(1):13-20.
[9] LEAL-MARIN S, KERN T, HOFMANN N, et al. Human Amniotic Membrane: A review on tissue engineering, application, and storage. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(8):1198-1215.
[10] MALDONADO VV, PATEL NH, SMITH EE, et al. Clinical utility of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in regenerative medicine and cellular therapy. J Biol Eng. 2023;17(1):44.
[11] MOUSAEI GHASROLDASHT M, SEOK J, PARK HS, et al. Stem Cell Therapy: From Idea to Clinical Practice. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5): 2850.
[12] CHEN X, SU C, WEI Q, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Mice by Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization via the microRNA-146a-5p/NOTCH1 Axis. Immunol Invest. 2022;51(7):1975-1993.
[13] 王英鑫.低氧预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞修复放射性涎腺损伤功能的研究[D].遵义:遵义医学院, 2018.
[14] 孔维平.低氧预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞对放射性损伤鼠涎腺上皮细胞修复作用的研究[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2020.
[15] 唐建宏,张霓霓,黄桂林,等.不同体积分数氧气预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞的生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(15): 2318-2324.
[16] VIZOSO FJ, EIRO N, CID S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9):1852.
[17] QIAN W, HUANG L, XU Y, et al. Hypoxic ASCs-derived Exosomes Attenuate Colitis by Regulating Macrophage Polarization via miR-216a-5p/HMGB1 Axis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2023;29(4):602-619.
[18] 崔田宁,张霓霓,龙远铸,等.低氧预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞外泌体修复放射性损伤唾液腺的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2022, 38(12):1145-1150.
[19] 张敏,张霓霓,黄桂林,等.人羊膜间充质干细胞外泌体修复大鼠放射性颌下腺损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(36):7804-7815.
[20] SONG W, LIU H, SU Y, et al. Current developments and opportunities of pluripotent stem cells-based therapies for salivary gland hypofunction. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024;12:1346996.
[21] 曹璐.大鼠颌下腺上皮细胞放射性损伤模型的建立与评估[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2019.
[22] 骆勤亮,张霓霓,龙远铸,等.硝基油酸经 Nrf2/HO-1 通路对放射性损伤大鼠颌下腺上皮细胞的抗氧化损伤作用[J].口腔医学研究, 2022,38(12):1139-1144.
[23] 林培琦,骆勤亮,张立刚,等.硝基油酸对大鼠下颌下腺上皮细胞放射损伤的保护机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(26):5520-5527.
[24] HADE MD, SUIRE CN, MOSSELL J, et al. Extracellular vesicles: Emerging frontiers in wound healing. Med Res Rev. 2022;42(6):2102-2125.
[25] HAGHIGHITALAB A, DOMINICI M, MATIN MM, et al. Extracellular vesicles and their cells of origin: Open issues in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1090416.
[26] MA M, CUI G, LIU Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles, osteoimmunology and orthopedic diseases. PeerJ. 2023;11: e14677.
[27] HULDANI H, ABDALKAREEM JASIM S, OLEGOVICH BOKOV D, et al. Application of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells as potential therapeutic tools in autoimmune and rheumatic diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;106:108634.
[28] GAO S, CHEN T, HAO Y, et al. Exosomal miR-135a derived from human amnion mesenchymal stem cells promotes cutaneous wound healing in rats and fibroblast migration by directly inhibiting LATS2 expression. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):56.
[29] 张琪,于湄,刘磊,等.工程化外泌体研究现状与临床转化的挑战[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(19):3052-3060.
[30] 赵吉逢,高伟宸,王晓乐,等.间充质干细胞来源外泌体治疗骨关节炎的研究进展[J].临床骨科杂志,2024,27(6):896-901.
[31] 赵炜,刘金明,杨磊婷,等.低氧预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞来源外泌体在改善血管衰老中的作用研究[J].口腔医学, 2023,43(6): 494-499.
[33] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
[33] 黄欣悦,龚旭,郭维维,等.外泌体在牙周再生应用的研究进展[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2024,40( 1):117-121.
[34] HU S, CHEN B, ZHOU J, et al. Dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes revitalize salivary gland epithelial cell function in NOD mice via the GPER-mediated cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling pathway. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):361.
[35] KIM JH, JEONG BK, JANG SJ, et al. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Ameliorates Radiation-Induced Salivary Gland Injury by Preserving Parasympathetic Innervation in Rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2260.
[36] 漆慧中,张霓霓,李壮壮,等.氧化应激致放射性唾液腺损伤的机制及治疗研究进展[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2025,46(1):130-134.
[37] 崔荣兴,战丽彬,孙晓霞,等.阴虚津亏模型小鼠颌下腺 AQP5 及 cAMP/PKA-CREB 信号通路的表达与意义[J].中华中医药学刊,2022, 40(6):149-153.
[38] KIM JM, CHOI ME, JEON EJ, et al. Cell-derived vesicles from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate irradiation-induced salivary gland cell damage. Regen Ther. 2022;21:453-459.
[39] ZAYED HM, KHEIR EL DIN NH, ABU-SEIDA AM, et al. Gingival-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy regenerated the radiated salivary glands: functional and histological evidence in murine model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):46.
[40] JEYARAM A, LAMICHHANE TN, WANG S, et al. Enhanced Loading of Functional miRNA Cargo via pH Gradient Modification of Extracellular Vesicles. Mol Ther. 2020;28(3):975-985. |