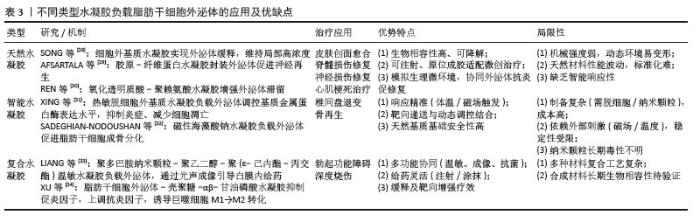
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3402-3411.doi: 10.12307/2026.203
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exosome loading mode of therapeutic adipose derived stem cells
Ji Demin, Ma Zhihong
- Department of Plastic Surgery and Burns, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Accepted:2025-09-16Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-26 -
Contact:Ma Zhihong, Chief physician, Department of Plastic Surgery and Burns, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Ji Demin, MS, Attending physician, Department of Plastic Surgery and Burns, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ji Demin, Ma Zhihong. Exosome loading mode of therapeutic adipose derived stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3402-3411.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 脂肪干细胞外泌体的作用机制 脂肪干细胞外泌体促进成纤维细胞迁移和增殖,同时刺激血管内皮细胞形成新生血管网显著缩短伤口愈合周期,调节胶原蛋白合成,减少瘢痕形成。YIN等[16]发现脂肪干细胞外泌体可以通过circ-Rps5/miR-124-3p轴调节巨噬细胞极化并促进糖尿病小鼠伤口愈合。LIANG等[17]证实脂肪干细胞外泌体通过转移miR-125a促进血管内皮细胞生成。WANG等[18]将脂肪干细胞外泌体通过小鼠尾静脉输注后,发现小鼠切口瘢痕体积缩小,Ⅲ型胶原与Ⅰ型胶原比例提高至1.8倍,有效抑制了成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞分化,减少α-平滑肌肌动蛋白表达,阻断纤维化进程,激活细胞外调节蛋白激酶/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路(磷酸化水平提升3.1倍),诱导皮肤真皮成纤维细胞表达基质金属蛋白酶3,促进细胞外基质动态重塑。 脂肪干细胞外泌体既促进前体细胞分化又抑制成熟细胞活性,维持骨重建动态平衡。LI等[19]发现脂肪干细胞外泌体通过递送miR-451a靶向抑制迁移抑制因子信号轴,重塑巨噬细胞极化平衡(M2/M1比例从0.8提升至3.6),进而改善炎性微环境并促进骨再生。REN等[20]则证实脂肪干细胞外泌体通过双重调控机制——抑制骨细胞凋亡及阻断核因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素信号轴,有效抑制骨细胞介导的破骨细胞生成。 脂肪干细胞外泌体诱导神经元细胞的轴突延伸,抑制髓鞘崩解进程,促进神经元轴突再生,加速周围神经的修复。尹刚等[21]构建了SD大鼠神经损伤模型,并于实验组大鼠尾静脉内注射脂肪干细胞外泌体进行干预,注射结束1周后处死大鼠并取损伤坐骨神经上下2 cm进行观察,结果发现:脂肪干细胞外泌体通过减少施万细胞凋亡、减轻细胞自噬并促进Büngner带形成等,在周围神经损伤修复过程中起重要作用。 脂肪干细胞外泌体对心肌梗死损伤的心肌细胞表现出更显著的保护作用。LIU等[22]发现缺氧预处理脂肪干细胞外泌体通过激活circ-Stt3b/miR-15a-5p/谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4信号通路并抑制铁死亡,从而有效改善心肌梗死后的心肌损伤。 脂肪干细胞外泌体调控免疫微环境,诱导T淋巴细胞程序性死亡,重塑巨噬细胞极化状态。BLAZQUEZ等[23]发现脂肪干细胞外泌体可显著抑制T淋巴细胞分化与活化过程,并降低体外刺激条件下T淋巴细胞的增殖活性及干扰素γ释放水平。DOMENIS等[24]也发现脂肪干细胞的抗炎和免疫抑制活性主要归因于炎症微环境的动态调控,当脂肪干细胞预先用促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α和干扰素γ处理时,脂肪干细胞外泌体中miR-34和miR-146的表达显著上调,通过靶向调控巨噬细胞微环境中的单核细胞,诱导M1型巨噬细胞向抗炎M2型极化。 综上所述,脂肪干细胞外泌体在创面修复、骨再生、神经再生与修复、心肌保护、免疫微环境调控等各个领域发挥了重要作用,见表1。"

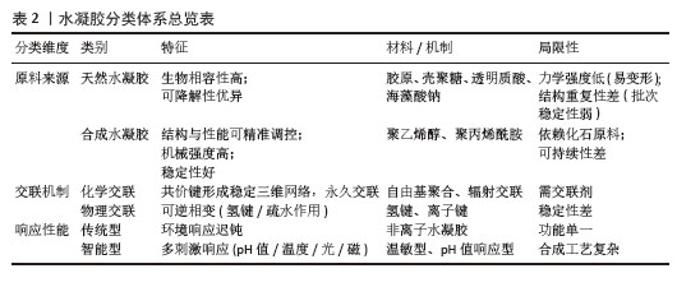
2.2 水凝胶递送系统 2.2.1 水凝胶的定义及特征 水凝胶作为一种新型高分子材料,是通过化学或物理交联技术将单体分子连接成三维亲水网络的聚合物体系,其独特的亲水性网状结构赋予了这类材料优异的吸水保水性能,同时具备生物软组织般的柔性特征。水凝胶发展历史可追溯至20世纪60年代,当时WICHTERLE团队[25]首次开发出聚羟乙基甲基丙烯酸甲酯水凝胶材料,通过自由基聚合工艺将2-羟乙基甲基丙烯酸甲酯单体交联成凝胶状物质,并成功应用于隐形眼镜制造领域。 2.2.2 水凝胶的分类 水凝胶依据原料来源、交联机制及响应性能可分为三大体系:①按原料来源划分:可分为天然与合成两大类,天然水凝胶以胶原、壳聚糖、透明质酸等天然高分子为基质,凭借优异的生物相容性和可降解性,在组织工程和药物缓释领域具有独特优势,但其力学强度较低、结构重复性差的局限性也制约了应用拓展;合成水凝胶如聚乙烯醇、聚丙烯酰胺等,则通过化学合成手段实现了结构与性能的精准调控,在机械强度、稳定性等方面显著优于天然材料,然而其单体多依赖化石资源,在环保性和可持续性方面存在短板。②从交联机制角度划分:可分为化学交联与物理交联两大类,化学交联通过共价键形成稳定的三维网络,赋予材料永久交联特性;物理交联则依赖氢键、范德华力等非共价作用,使凝胶在温度、离子强度等刺激下呈现可逆相变。③从响应性能角度划分:可分为传统型与智能型两大类,传统水凝胶对外界刺激反应迟钝,而智能水凝胶能够根据pH值、温度、光、磁场等信号发生结构或性能变化[26],这些智能特性使水凝胶在化学传感、精准医疗等领域展现出巨大潜力,推动其从传统材料向智能响应体系的创新升级[27]。各种不同类型水凝胶分类见表2。"
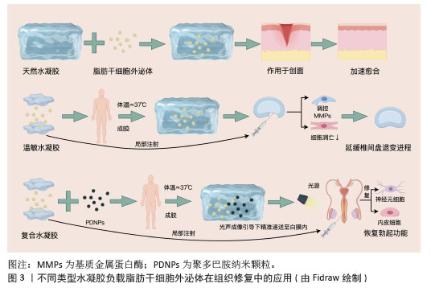
2.2.3 天然水凝胶负载脂肪干细胞外泌体 SONG等[28]研究报道了一种新型细胞外基质水凝胶外泌体(细胞外基质水凝胶)的开发,通过将脂肪干细胞外泌体载入细胞外基质水凝胶中构建而成。在伤口局部注射后,于生理温度(≈37 ℃)下形成水凝胶。脂肪干细胞外泌体从细胞外基质水凝胶中持续释放,从而在伤口部位维持较高的局部浓度,具有良好的生物相容性和可降解性。体内外实验结果均表明,细胞外基质水凝胶治疗可有效减轻炎症反应,促进血管生成、胶原沉积及细胞增殖迁移,进而加速伤口愈合进程。 AFSARTALA等[29]基于细胞外基质的胶原和纤维蛋白水凝胶封装脂肪干细胞外泌体,可促进急性脊髓损伤大鼠受损神经再生,并减轻脊髓损伤引起的中枢神经性疼痛。REN等[30]开发了一种可注射的氧化透明质酸-聚赖氨酸(OHA-PL)水凝胶,能够便捷负载脂肪干细胞外泌体,并提高其在生理条件下的滞留能力。透明质酸-聚赖氨酸-脂肪干细胞外泌体水凝胶通过微创方式移植到缺血心肌,可在心肌梗死早期清除细胞内外活性氧,调节巨噬细胞极化,减轻炎症反应;在心肌梗死后期可有效减少心肌纤维化和心室重构,促进血管生成,并恢复电生理功能。 天然水凝胶负载脂肪干细胞外泌体体系优势突出:①以细胞外基质、胶原等天然成分为基质,生物相容性与可降解性俱佳,能减少免疫排斥;②水凝胶自身可模拟生理微环境,与外泌体的抗炎、促修复功能形成协同效应;③可注射特性适配局部微创给药,原位成胶还能实现外泌体持续释放以维持靶部位高浓度,且在多领域均有治疗潜力,见图3。不过天然水凝胶负载脂肪干细胞外泌体的局限性亦不容忽视:①天然水凝胶机械强度较弱,在承重部位或动态环境中易降解变形;②天然材料来源差异可能造成性能波动,不利于标准化生产;③缺乏智能响应特性,对复杂病理微环境的动态适配能力有限,且部分研究对分子交互机制的解析不够深入。"
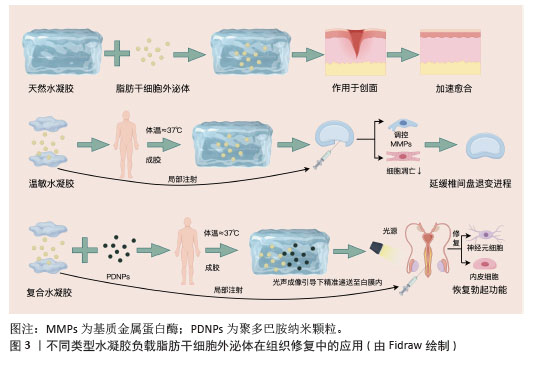
2.2.4 智能水凝胶负载脂肪干细胞外泌体 XING等[31]制备了一种热敏性脱细胞外基质水凝胶负载脂肪干细胞外泌体复合体系(dECM@exo)用以治疗椎间盘退变,这种热敏性水凝胶系统不仅能够通过原位凝胶化补充髓核细胞外基质的流失,还能为髓核细胞的生长提供适宜微环境。此外,该体系可持续稳定释放脂肪干细胞外泌体,通过精准调控基质金属蛋白酶的表达水平,实现基质合成与降解的动态平衡,同时,通过抑制炎症反应级联,显著减轻细胞凋亡现象,从而在体外实验中展现出良好的治疗效果。动物实验进一步证实,热敏性脱细胞外基质-脂肪干细胞外泌体水凝胶系统能够有效维持早期椎间盘微环境的稳态,显著延缓椎间盘退变的病理进程,见图3。 SADEGHIAN-NODOUSHAN等[32]将脂肪干细胞外泌体负载于含有1%钴铁氧体纳米颗粒(CoFe2O4)的海藻酸钠水凝胶支架上,通过碱性磷酸酶活性测定、茜素红染色和能量色散X射线光谱分析,评估磁性水凝胶复合材料在外部静磁场作用下对脂肪干细胞增殖与分化的影响。结果表明,负载脂肪干细胞外泌体的磁性海藻酸钠水凝胶支架不仅无细胞毒性,还能显著促进脂肪干细胞的增殖。此外,在磁场刺激下,负载脂肪干细胞外泌体的磁性海藻酸钠水凝胶支架对脂肪干细胞成骨分化表现出最强的促进作用,表现为更高的碱性磷酸酶活性和矿化程度。 智能水凝胶负载脂肪干细胞外泌体响应性精准可控,热敏性水凝胶靠体温触发成胶,磁性水凝胶受外磁场调控,实现外泌体精准递送,水凝胶的智能特性与外泌体的调控作用相辅相成;以天然基质或无毒材料为基础,生物安全性较高,且能针对性应对椎间盘退变、骨再生等特殊需求。不过智能水凝胶也存在缺陷:制备流程复杂,需处理脱细胞外基质或引入纳米颗粒,成本偏高且难以规模化生产;对刺激存在依赖,磁性水凝胶需持续磁场作用,热敏性水凝胶易受体内温度波动影响,稳定性受限;长期安全性存疑,磁性纳米颗粒的体内代谢路径及降解产物毒性尚未明确。 2.2.5 复合水凝胶负载脂肪干细胞外泌体 LIANG等[33]通过原位聚合法制备了一种负载聚多巴胺纳米颗粒的聚乙二醇-聚(ε-己内酯-丙交酯)(PDNPs-PELA)温敏水凝胶用于脂肪干细胞外泌体白膜内给药,该水凝胶在体温下发生溶胶-凝胶转变,外泌体被封装到水凝胶后,在2周内呈现持续释放行为。体内动物实验表明,水凝胶释放的外泌体可促进内皮细胞和神经元修复,增加海绵体内压,从而恢复勃起功能;由于温敏凝胶中的聚多巴胺纳米颗粒具有优异的光声性能,使水凝胶在实时光声成像引导下精准递送至白膜内;聚乙二醇-聚(ε-己内酯-丙交酯)温敏水凝胶作为可注射外泌体载体,在勃起功能障碍治疗中具有良好的效果,见图3。 XU等[34]利用壳聚糖及αβ-甘油磷酸交联形成水凝胶,壳聚糖具有良好的生物相容性、抗菌性和促进组织修复的特性,而αβ-甘油磷酸作为交联剂可调节水凝胶的温敏性,使其在体温下形成凝胶,便于局部注射或涂抹。将脂肪干细胞外泌体负载于壳聚糖-αβ-甘油磷酸水凝胶支架并作用于深度烧伤创面,结果发现,脂肪干细胞外泌体-壳聚糖-αβ-甘油磷酸水凝胶通过阻断核因子κB通路,抑制促炎因子(如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1α)的表达,同时上调抗炎因子(如白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β)和表皮生长因子的表达,从而减轻炎症反应,而且它可诱导M1型(促炎)巨噬细胞向M2型(抗炎、促修复)转化。 在复合水凝胶负载脂肪干细胞外泌体研究中,将温敏性、成像引导或抗菌特性与外泌体功能相结合,实现递送与治疗的协同增效;给药方式灵活多样,可注射或局部涂抹,能适配不同病灶的治疗需求;同时具备靶向性与缓释性,可维持外泌体的长期高效作用。不过其局限性也较为明显:制备过程涉及多种材料复合与纳米颗粒修饰,工艺复杂且成本偏高;部分合成材料(如聚乙二醇-聚ε-己内酯-丙交酯)的长期生物相容性仍有待验证。 水凝胶负载脂肪干细胞外泌体的复合递送系统,通过延长外泌体滞留时间与重塑损伤局部微环境,显著提升了组织修复疗效,它在协调炎症抑制与再生促进方面的作用尤为突出[35]。未来研究方向应集中于以下两点:①工艺标准化:运用微流控技术建立精准制备流程以提高批次稳定性;②生物安全性升级:引入可降解纳米元件(如酶响应型交联剂),规避长期体内蓄积风险,这些关键性突破将有力推动该系统的临床转化进程。不同类型水凝胶负载脂肪干细胞外泌体的应用及优缺点见表3。 "

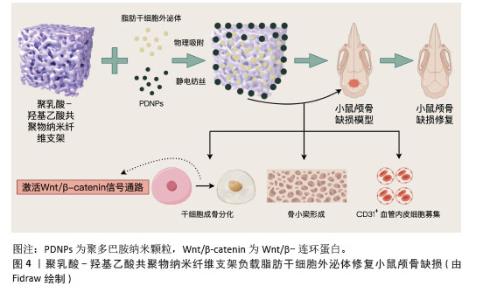
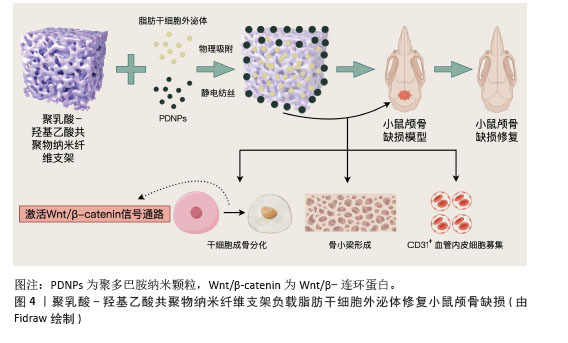
2.3 金属有机框架 2.3.1 金属有机框架定义及特征 金属有机框是一类通过无机金属单元(离子、离子簇或多核配合物)与有机配体自组装形成的多孔有机-无机杂化网络材料,其结构可延伸为一维、二维或三维[36]。在金属中心与有机配体通过配位键和共价键结合的过程中,会形成具有超高表面积和孔隙比率(可达90%)的金属有机框架晶体[37]。这类材料的制备方法相对简便,常见的合成手段包括溶剂热合成、电化学合成、机械研磨、微波与超声辅助合成以及高通量合成等[38]。此外,通过对金属有机框架进行合成后修饰,能够有效提升结构稳定性,精准调控功能特性,甚至赋予材料新的附加性能。金属有机框架整合了有机与无机组分的双重优势,其核心特点在于可通过灵活改变金属节点和(或)有机连接体的类型来调控材料的化学组成。由于组分在几何构型、尺寸大小及功能特性上具有高度可调性,金属有机框架的结构设计理论上具有无限可能性[39]。目前,已有大量金属有机框架材料被开发和研究,其中具有代表性的体系包括MIL(materials of institut lavoisier)系列、UiO(university of oslo)系列以及沸石咪唑酯骨架(zeolitic imidazolate frameworks,ZIF)系列,这种结构多样性使得金属有机框架在气体吸附、催化、药物递送等领域展现出广阔的应用潜力[40-41]。 2.3.2 金属有机框架负载脂肪干细胞外泌体 KANG等[42]成功开发了一种聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物/镁离子-没食子酸-金属有机框架复合支架(PLGA/Exo-Mg-GA MOF),通过结合脂肪干细胞外泌体、镁离子和没食子酸的协同作用,构建了独特的纳米结构界面,旨在同步提升材料的成骨诱导、血管生成促进及抗炎特性。实验数据表明,该复合支架在体外对人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化以及人脐静脉内皮细胞的血管形成均表现出显著的增强效应;进一步研究发现,支架中缓释的脂肪干细胞外泌体可被共培养细胞有效摄取,通过维持骨移植区域的微环境稳定、保障局部血供,进而加速成骨细胞分化进程并推动骨组织重建;动物实验方面,通过大鼠颅骨缺损模型验证了聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物/镁离子-没食子酸-金属有机框架复合支架在体内能够显著促进新生骨组织生成,并实现良好的骨整合效果。 金属有机框架负载脂肪干细胞外泌体的优势:结构与性能的调控灵活性突出,可通过组分设计实现功能的精准定制;多孔特性便于负载外泌体、离子等活性物质并实现缓释,从而达成多成分的协同效应;制备手段丰富且支持后期修饰,有利于优化材料稳定性并赋予其额外性能。不足之处在于:部分金属有机框架稳定性欠佳,体内长期应用可能产生不利影响;复合支架的制备涉及多组分整合,工艺复杂程度较高。 2.4 人工合成高分子聚合物支架 2.4.1 人工合成高分子聚合物支架定义及特征 人工合成高分子聚合物支架是通过化学合成方法制备的三维多孔结构材料,广泛应用于生物医学与组织工程领域。此类材料通常选择生物相容性良好的可降解或稳定高分子,如聚乳酸、聚乙醇酸、聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物及聚己内酯等,具备可调控降解速率、机械强度及生物功能的特性[43]。人工合成高分子聚合物的制备方法多样,包括静电纺丝法(构建纳米纤维模拟细胞外基质)、3D打印技术(定制复杂结构)、溶剂铸造/粒子沥滤法(调控孔隙率)及相分离法等,以满足不同应用需求[44]。这类支架的结构特点突出多孔性与可设计性,高孔隙率(50%–90%)和连通孔道支持细胞迁移与物质运输,孔径大小可根据组织再生需求(如骨组织工程需100–500 μm大孔径)灵活调整,通过表面功能化修饰(如接枝生长因子)或力学性能优化,可进一步提升生物相容性与细胞黏附能力。在应用方面,人工合成高分子聚合物支架已覆盖骨组织修复、药物缓释、神经再生及皮肤修复等 领域[45]。 2.4.2 人工合成高分子聚合物支架负载脂肪干细胞外泌体 GANDOLFI等[46]开发了一种负载脂肪干细胞外泌体的矿物增强型聚乳酸基骨修复材料,采用热致相分离技术制备了两种不同矿物配比的多孔支架(PLA-10CaSi-10DCPD和PLA-5CaSi-5DCPD),通过环境扫描电镜分析显示,支架具有直径10-30 μm的规则孔隙结构,且在模拟体液中浸泡28 d后仍能保持稳定的三维多孔形态,同时表面发生动态矿化反应,为成骨细胞提供了仿生微环境。体外实验表明,矿物掺杂显著增强了脂肪干细胞的成骨分化能力,其中PLA-10CaSi-10DCPD配方通过硅酸钙与二水合磷酸氢钙的协同作用表现出更优的生物活性;进一步研究发现,外泌体负载吸附于支架表面,通过旁分泌机制显著上调成骨相关基因(Ⅰ型胶原A1、骨桥蛋白、骨钙素等)的表达水平,与矿物掺杂产生协同效应;生物相容性测试显示,两种支架均支持细胞的黏附与增殖,其中高矿物含量支架在促进细胞外基质矿化方面表现突出。研究证实,将生物活性矿物与外泌体功能化相结合的策略,可通过模拟天然骨组织的成分与结构特征,有效激活干细胞的成骨分化潜能。 LI等[47]开发了一种基于脂肪干细胞外泌体的智能型骨修复系统,通过构建聚多巴胺修饰的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物纳米纤维支架,实现了生物活性因子的可控递送与骨再生微环境的精准调控;采用静电纺丝技术制备了具有仿生结构的聚多巴胺涂层聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物纳米纤维支架,并通过物理吸附法将外泌体稳定锚定于支架表面。体外实验显示,该复合体系可显著促进人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,表现为碱性磷酸酶活性提升3.2倍及成骨标志物基因表达上调(Runt相关转录因子2上调45%,骨钙素上调68%),同时增强细胞迁移能力(划痕愈合率提高28%);流式细胞术分析证实,脂肪干细胞外泌体通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进干细胞向成骨谱系分化;材料表征结果显示,聚多巴胺涂层使支架表面亲水性显著提高(接触角从125°降至48°),并形成具有纳米级粗糙度的仿生界面,有利于细胞黏附与外泌体的持续释放(缓释周期达21 d)。体内实验在小鼠颅骨缺损模型中验证了该系统的修复效能,术后12周Micro-CT检测显示新生骨体积达缺损面积的72%,较对照组提高40%;组织学分析显示,修复区域可见大量矿化骨小梁形成及血管化新生组织,免疫组化染色证实外泌体促进了CD31+血管内皮细胞的募集,见图4。"

人工合成高分子聚合物支架负载外泌体在骨修复及再生方面优势显著,其结构调控性强,可通过调整矿物比例、纤维形态或表面修饰,优化孔隙结构与生物活性,满足骨修复仿生需求;功能协同性好,聚合物力学支撑与外泌体成骨信号、矿物质生物活性多维度配合,提升修复效果。但也有局限:合成高分子降解速度需与骨再生周期匹配,否则易致力学失效或阻碍新骨形成;部分支架亲水性差,需表面修饰,增加制备复杂度;外泌体结合方式及释放规律需优化,以防突释;骨修复后力学强度及长期生物安全性仍待验证。 综上所述,各种不同类型递送系统负载脂肪干细胞外泌体时,因其材料特性,在组织修复(骨缺损、伤口、脊髓损伤等)中展现出协同增效作用,核心机制为延长外泌体滞留时间、调控局部微环境(抗炎、促血管生成等)。具体优势及局限性见表4。"

| [1] ZUK PA, ZHU M, MIZUNO H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228. [2] YANG S, SUN Y, YAN C. Recent advances in the use of extracellular vesicles from adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medical therapeutics. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):316. [3] FOTI R, STORTI G, PALMESANO M, et al. Senescence in Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Biological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Challenges. Int J Mol Sci. 2024; 25(15):8390. [4] FAN X, ZHANG Y, LIU W, et al. A comprehensive review of engineered exosomes from the preparation strategy to therapeutic applications. Biomater Sci. 2024;12(14):3500-3521. [5] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420. [6] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020; 367(6478):eaau6977. [7] RAHNAMA M, HEIDARI M, POURSALEHI Z, et al. Global Trends of Exosomes Application in Clinical Trials: A Scoping Review. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024;20(8): 2165-2193. [8] AL-MADHAGI H. The Landscape of Exosomes Biogenesis to Clinical Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19: 3657-3675. [9] TIENDA-VÁZQUEZ MA, HANEL JM, MÁRQUEZ-ARTEAGA EM, et al. Exosomes: A Promising Strategy for Repair, Regeneration and Treatment of Skin Disorders. Cells. 2023;12(12):1625. [10] HUSHMANDI K, SAADAT SH, RAEI M, et al. The science of exosomes: Understanding their formation, capture, and role in cellular communication. Pathol Res Pract. 2024;259:155388. [11] CHEN YF, LUH F, HO YS, et al. Exosomes: a review of biologic function, diagnostic and targeted therapy applications, and clinical trials. J Biomed Sci. 2024;31(1):67. [12] WANG Y, LI Q, ZHOU S, et al. Contents of exosomes derived from adipose tissue and their regulation on inflammation, tumors, and diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1374715. [13] KEMALOĞLU CA, DURSUN EN, YAY AH, et al. The Optimal Effective Dose of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes in Wound Healing. Ann Plast Surg. 2024;93(2): 253-260. [14] MOU C, XIA Z, WANG X, et al. Stem cell-derived exosome treatment for acute spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis based on preclinical evidence. Front Neurol. 2025; 16:1447414. [15] ABBASI R, ALAMDARI-MAHD G, MALEKI-KAKELAR H, et al. Recent advances in the application of engineered exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025;989:177236. [16] YIN D, SHEN G. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells regulate macrophage polarization and accelerate diabetic wound healing via the circ-Rps5/miR-124-3p axis. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024; 12(6):e1274. [17] LIANG X, ZHANG L, WANG S, et al. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci. 2016; 129(11):2182-2189. [18] WANG L, HU L, ZHOU X, et al. Author Correction: Exosomes secreted by human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote scarless cutaneous repair by regulating extracellular matrix remodelling. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):3245. [19] LI R, LI D, WANG H, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells regulate M1/M2 macrophage phenotypic polarization to promote bone healing via miR-451a/MIF. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):149. [20] REN L, SONG ZJ, CAI QW, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate hypoxia/serum deprivation-induced osteocyte apoptosis and osteocyte-mediated osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508(1):138-144. [21] 尹刚,刘蔡钺,林耀发,等.脂肪干细胞来源外泌体对周围神经损伤后再生作用的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018,32(12):1592-1596. [22] LIU J, WANG Z, LIN A, et al. Exosomes from Hypoxic Pretreatment ADSCs Ameliorate Cardiac Damage Post-MI via Activated circ-Stt3b/miR-15a-5p/GPX4 Signaling and Decreased Ferroptosis. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024;24(11): 1215-1225. [23] BLAZQUEZ R, SANCHEZ-MARGALLO FM, DE LA ROSA O, et al. Immunomodulatory Potential of Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Exosomes on in vitro Stimulated T Cells. Front Immunol. 2014; 5:556. [24] DOMENIS R, CIFÙ A, QUAGLIA S, et al. Pro inflammatory stimuli enhance the immunosuppressive functions of adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13325. [25] WICHTERLE O, LÍM D. Hydrophilic Gels for Biological Use. Nature. 1960;185(4706): 117. [26] FAN MH, PI JK, ZOU CY, et al. Hydrogel-exosome system in tissue engineering: A promising therapeutic strategy. Bioact Mater. 2024;38:1-30. [27] GUO L, FU Z, LI H, et al. Smart hydrogel: A new platform for cancer therapy. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2025;340:103470. [28] SONG Y, YOU Y, XU X, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Biopotentiated Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(30):e2304023. [29] AFSARTALA Z, HADJIGHASSEM M, SHIRIAN S, et al. The Effect of Collagen and Fibrin Hydrogels Encapsulated with Adipose Tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes for Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury in a Rat Model. Iran J Biotechnol. 2023;21(3):e3505. [30] REN Y, WANG W, YU C, et al. An injectable exosome-loaded hyaluronic acid-polylysine hydrogel for cardiac repair via modulating oxidative stress and the inflammatory microenvironment. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;275(Pt 2):133622. [31] XING H, ZHANG Z, MAO Q, et al. Injectable exosome-functionalized extracellular matrix hydrogel for metabolism balance and pyroptosis regulation in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):264. [32] SADEGHIAN-NODOUSHAN F, NIKUKAR H, SOLEIMANI M, et al. A smart magnetic hydrogel containing exosome promotes osteogenic commitment of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022;25(9):1123-1131. [33] LIANG L, SHEN Y, DONG Z, et al. Photoacoustic image-guided corpus cavernosum intratunical injection of adipose stem cell-derived exosomes loaded polydopamine thermosensitive hydrogel for erectile dysfunction treatment. Bioact Mater. 2021;9:147-156. [34] XU L, LIU D, YUN HL, et al. Effect of adipose-derived stem cells exosomes cross-linked chitosan-αβ-glycerophosphate thermosensitive hydrogel on deep burn wounds. World J Stem Cells. 2025;17(2): 102091. [35] CUI H, LI J. Hydrogel adhesives for tissue recovery. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2025;341:103496. [36] KHULOOD MT, JIJITH US, NASEEF PP, et al. Advances in metal-organic framework-based drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2025;673:125380. [37] WANG Y, GAO N, LI X, et al. Metal organic framework-based variable-size nanoparticles for tumor microenvironment-responsive drug delivery. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024;14(7):1737-1755. [38] 庆达,王建省,苏新悦,等.金属有机框架材料的制备及应用研究进展[J].化工新型材料,2024,52(1):65-70. [39] WANG D, YAO H, YE J, et al. Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Classification, Synthesis, Modification, and Biomedical Applications. Small. 2024;20(47):e2404350. [40] LEOI MWN, ZHENG XT, YU Y, et al. Redefining Metal Organic Frameworks in Biosensors: Where Are We Now? ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025;17(9):13246-13278. [41] LI W, CHEN J, GUO J, et al. Exploring the multifaceted roles of metal-organic frameworks in ecosystem regulation. J Mater Chem B. 2025;13(7):2272-2294. [42] KANG Y, XU C, MENG L, et al. Exosome-functionalized magnesium-organic framework-based scaffolds with osteogenic, angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties for accelerated bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;18: 26-41. [43] SULTANA N, COLE A, STRACHAN F. Biocomposite Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: Materials, Fabrication Techniques and Future Directions. Materials (Basel). 2024;17(22):5577. [44] TOLBERT JW, FRENCH T, KITSON A, et al. Solvent-cast 3D printing with molecular weight polymer blends to decouple effects of scaffold architecture and mechanical properties on mesenchymal stromal cell fate. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2024;112(9):1364-1375. [45] JIANG Z, ZHENG Z, YU S, et al. Nanofiber Scaffolds as Drug Delivery Systems Promoting Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(7):1829. [46] GANDOLFI MG, GARDIN C, ZAMPARINI F, et al. Mineral-Doped Poly(L-lactide) Acid Scaffolds Enriched with Exosomes Improve Osteogenic Commitment of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(3):432. [47] LI W, LIU Y, ZHANG P, et al. Tissue-Engineered Bone Immobilized with Human Adipose Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Promotes Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(6):5240-5254. [48] HONG P, YANG H, WU Y, et al. The functions and clinical application potential of exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):242. [49] SU H, CHAU H, LI Q, et al. Bridging the gap: clinical translation of adipose-derived stem cells - a scoping review of clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025;16(1):288. [50] RONG J, LI YY, WANG X, et al. Non-coding RNAs in adipose-derived stem cell exosomes: Mechanisms, therapeutic potential, and challenges in wound healing. World J Stem Cells. 2025;17(4):102917. |
| [1] | Liu Yang, Liu Donghui , Xu Lei, Zhan Xu, Sun Haobo, Kang Kai. Role and trend of stimuli-responsive injectable hydrogels in precise myocardial infarction therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2072-2080. |
| [2] | Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [3] | Guo Yuchao, Ni Qianwei, Yin Chen, Jigeer·Saiyilihan, Gao Zhan . Quaternized chitosan hemostatic materials: synthesis, mechanism, and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2091-2100. |
| [4] | Liu Hongjie, Mu Qiuju, Shen Yuxue, Liang Fei, Zhu Lili. Metal organic framework/carboxymethyl chitosan-oxidized sodium alginate/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes healing of diabetic infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [5] | Han Teng, Ma Hong, Yang Ruoyi, Luo Yi, Li Chao. Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived exosomal delivery of angiopoietin-2 is involved in tumor angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1755-1767. |
| [6] | Huang Jiawen, Pan Zhiyi, Xue Wenjun, Lian Yuanpei, Xu Jianda. Plant-derived vesicles and malignant tumor therapy: cross-species communication and modulation of host cell responses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1828-1838. |
| [7] | Wang Baiyan, Yang Shu, Wang Yiming, Wu Mengqing, Xiao Yu, Guo Zixuan, Zhang Boyi, Feng Shuying. Exosome-delivered CRISPR/Cas system enables gene editing in target cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1839-1849. |
| [8] | Wang Zhenze, Liu Fende, Zhang Rui, Li Wujun. Mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of arteriosclerosis obliterans of lower extremities: systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1869-1876. |
| [9] | Song Puzhen, Ma Hebin, Chen Hongguang, Zhang Yadong. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes combined with transforming growth factor beta 1 on macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1616-1623. |
| [10] | He Jiale, Huang Xi, Dong Hongfei, Chen Lang, Zhong Fangyu, Li Xianhui. Acellular dermal matrix combined with adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promotes burn wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1699-1710. |
| [11] | Xia Linfeng, Wang Lu, Long Qianfa, Tang Rongwu, Luo Haodong, Tang Yi, Zhong Jun, Liu Yang. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate blood-brain barrier damage in mice with septic encephalopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1711-1719. |
| [12] | Chen Yulin, He Yingying, Hu Kai, Chen Zhifan, Nie Sha Meng Yanhui, Li Runzhen, Zhang Xiaoduo , Li Yuxi, Tang Yaoping. Effect and mechanism of exosome-like vesicles derived from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. in preventing and treating atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781. |
| [13] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [14] | Zhan Lei, Wu Lina, Li Huan, Liu Min, Chen Tao, Pu Xiaobing, Zhou Changchun. Silk fibroin hydrogel loaded with icariin to promote tendon-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5178-5787. |
| [15] | Cao Yuqing, Guo Meiling, Liu Feng, Wei Junchao. Preparation, classification and application of polysaccharide-based hydrogels in skin damage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5257-5269. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||