Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3233-3241.doi: 10.12307/2026.087
Previous Articles Next Articles
Isolation, cultivation, identification, and induction of M1/M2 polarization in bone marrow-derived macrophages from C57BL/6 mice
Tan Yuhang1, 2, Li Bo1, 2, Tang Minghong1, 2, Sun Zeyu2, Luo Xu2
- 1Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-24Revised:2025-06-06Accepted:2025-07-03Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-24 -
Contact:Li Bo, Chief physician, Professor, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Tan Yuhang, Master candidate, Physician, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160419 (to LB); Guizhou Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Research Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Ethnic Medicine, No. QZYY-2024-114 (to SZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tan Yuhang, Li Bo, Tang Minghong, Sun Zeyu, Luo Xu. Isolation, cultivation, identification, and induction of M1/M2 polarization in bone marrow-derived macrophages from C57BL/6 mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3233-3241.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 小鼠BMDMs的基本形态特征 如图2所示,新分离的小鼠骨髓前体细胞在添加20 μg/L巨噬细胞集落刺激因子培养1 d后,细胞呈现圆形或近圆形,密集分布,多数以悬浮生长,尚未出现明显的贴壁特征,细胞较小且形态不规则或呈透明的圆形;培养3 d更换培养基以去除悬浮杂细胞,大部分细胞开始贴壁生长,细胞形态发生显著变化,细胞边界逐渐清晰,由最初的圆形逐渐转变为不规则多边形、椭圆形或长梭形,细胞密度增加,形态趋于一致;培养5 d,大部分细胞已贴壁,形态更加均匀,悬浮杂细胞明显减少,细胞呈现出梭形结构并延伸出突起,大小均匀一致,逐渐形成相互连接的网络;培养7 d,细胞已完全贴壁并分化为成熟的小鼠BMDMs,表现出典型的梭形和突起延展特征,细胞间连接紧密,分布均匀,形态一致,符合成熟巨噬细胞的形态特征,适合用于后续实验。"

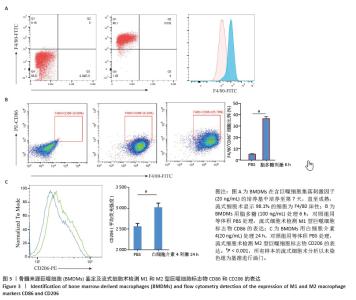
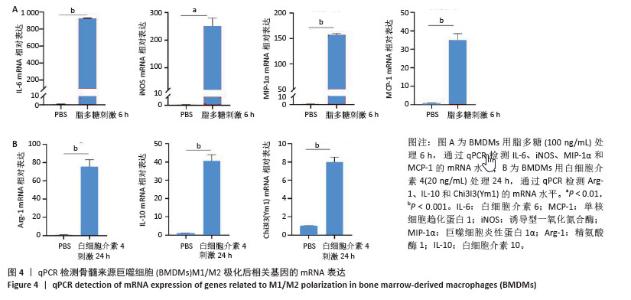
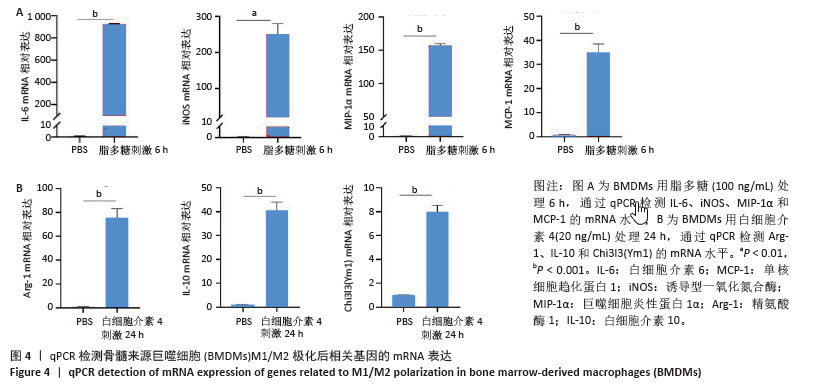
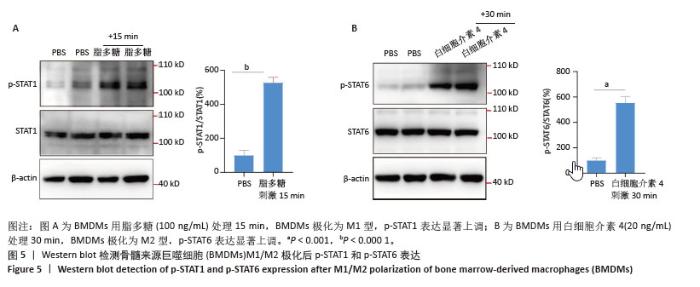
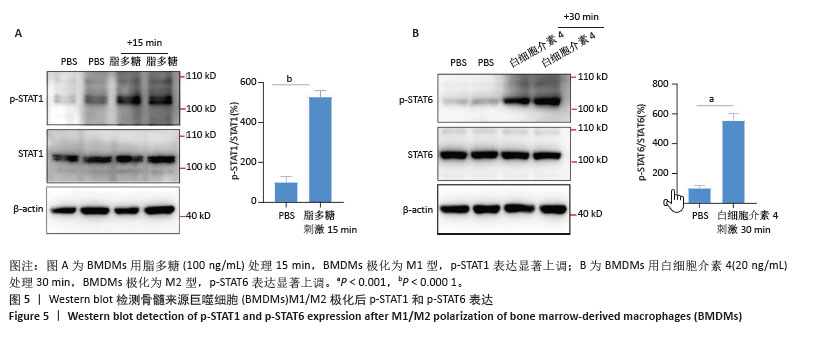
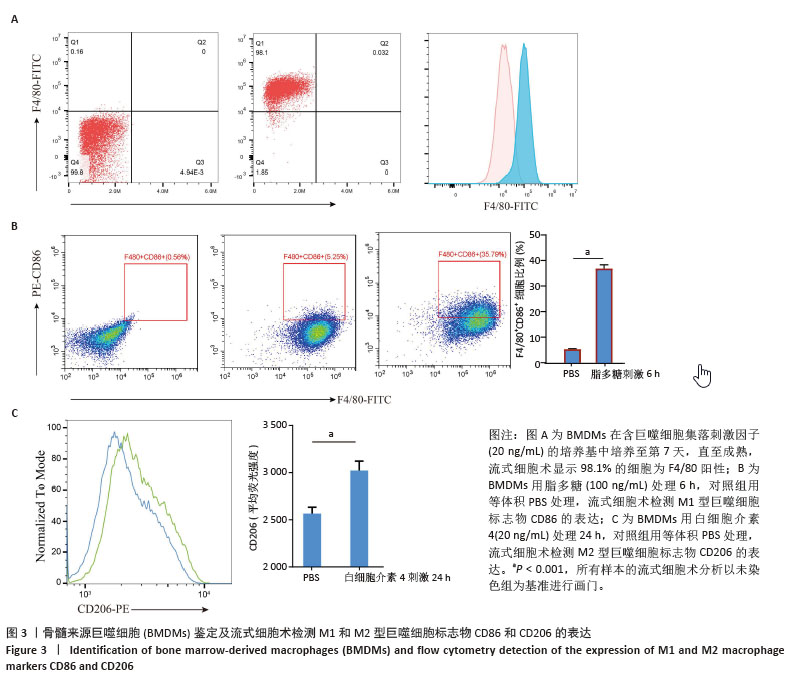
2.2 小鼠BMDMs鉴定及诱导为M1和M2型巨噬细胞后流式细胞术检测CD86和CD206的表达 收集成熟BMDMs,使用流式细胞术进行表型分析,检测巨噬细胞特异性标记物F4/80的表达,结果显示98.1%的成熟细胞呈现F4/80阳性,表明培养获得的细胞群体具有较高的纯度和成熟度。将BMDMs用100 ng/mL脂多糖刺激6 h,对照组用等体积PBS处理,巨噬细胞向M1型极化,流式细胞术检测结果显示小鼠M1型巨噬细胞表面标志物CD86的阳性率约为35%,与对照组相比具有显著差异。将BMDMs用20 ng/mL白细胞介素4刺激24 h,对照组用等体积PBS处理,巨噬细胞向M2型极化,流式细胞术检测结果显示小鼠M2型巨噬细胞表面标志物CD206平均荧光强度明显升高,与对照组相比具有显著差异,见图3。"
| [1] GORDON S, MARTINEZ FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. 2010;32(5):593-604. [2] ABDOLLAHI E, SAGHAFI N, HASANZADE M. Are M1 and M2 macrophages effectual players in pathological conditions. Proc Anticancer Res. 2022;6(3):34-41. [3] MURRAY PJ, ALLEN JE, BISWAS SK, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41(1):14-20. [4] KADOMOTO S, IZUMI K, MIZOKAMI A. Macrophage Polarity and Disease Control. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):144. [5] RUYTINX P, PROOST P, VAN DAMME J, et al. Chemokine-Induced Macrophage Polarization in Inflammatory Conditions. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1930. [6] SICA A, MANTOVANI A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(3):787-795. [7] BIDAULT G, VIRTUE S, PETKEVICIUS K, et al. SREBP1-induced fatty acid synthesis depletes macrophages antioxidant defences to promote their alternative activation. Nat Metab. 2021;3(9):1150-1162. [8] 高煜茹,王涛.肺泡巨噬细胞极化及凋亡在脓毒症急性肺损伤中作用机制的研究进展[J].中国现代医药杂志,2022,24(11):99-104. [9] CHEN R, ZHENG S, ZHAO X, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of macrophages by a nano-sized opsonization strategy to restore M1/M2 balance for osteoarthritis therapy. J Control Release. 2025; 380:469-489. [10] YU T, GAN S, ZHU Q, et al. Modulation of M2 macrophage polarization by the crosstalk between Stat6 and Trim24. Nat Commun. 2019; 10(1):4353. [11] SO Y, YIM D, KIM HK, et al. Functional Nanosheet Immunoswitches Reprogramming Innate Macrophages for Immunotherapy of Colorectal Cancer and Sepsis. ACS Nano. 2025;19(5):5165-5177. [12] 薛翔,刘红梅,邵旦兵,等.JAK/STAT信号通路调节机制的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(11):2161-2165. [13] YU J, LI P, LI Z, et al. Topical Administration of 0.3% Tofacitinib Suppresses M1 Macrophage Polarization and Allograft Corneal Rejection by Blocking STAT1 Activation in the Rat Cornea. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022;11(3):34. [14] 汤祥瑞,张勇,祝领,等.晚期糖基化产物通过RAGE/TLR4/STAT1信号通路诱导巨噬细胞M1型极化[J].安徽医科大学学报,2021, 56(5):751-756. [15] OH H, PARK SH, KANG MK, et al. Asaronic Acid Attenuates Macrophage Activation toward M1 Phenotype through Inhibition of NF-κB Pathway and JAK-STAT Signaling in Glucose-Loaded Murine Macrophages. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(36):10069-10078. [16] CHAO H, ZHENG L, HSU P, et al. IL-13RA2 downregulation in fibroblasts promotes keloid fibrosis via JAK/STAT6 activation. JCI Insight. 2023; 8(6):e157091. [17] BONELLI M, KERSCHBAUMER A, KASTRATI K, et al. Selectivity, efficacy and safety of JAKinibs: new evidence for a still evolving story. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83(2):139-160. [18] SEDANO R, MA C, JAIRATH V, et al. Janus Kinase Inhibitors for the Management of Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2022;18(1):14-27. [19] SCHLUNDT C, EL KHASSAWNA T, SERRA A, et al. Macrophages in bone fracture healing: Their essential role in endochondral ossification. Bone. 2018;106:78-89. [20] CHEN S, SAEED AFUH, LIU Q, et al. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):207. [21] CASSETTA L, POLLARD JW. Targeting macrophages: therapeutic approaches in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17(12):887-904. [22] SU P, LI O, KE K, et al. Targeting tumor‑associated macrophages: Critical players in tumor progression and therapeutic strategies (Review). Int J Oncol. 2024;64(6):60. [23] SINDER BP, PETTIT AR, MCCAULEY LK. Macrophages: Their Emerging Roles in Bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(12):2140-2149. [24] BATOON L, MILLARD SM, RAGGATT LJ, et al. Osteal macrophages support osteoclast-mediated resorption and contribute to bone pathology in a postmenopausal osteoporosis mouse model. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(11):2214-2228. [25] KAUR S, RAGGATT LJ, BATOON L, et al. Role of bone marrow macrophages in controlling homeostasis and repair in bone and bone marrow niches. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;61:12-21. [26] XU Y, YAN H, ZHANG X, et al. Roles of Altered Macrophages and Cytokines: Implications for Pathological Mechanisms of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:876269. [27] WEIVODA MM, BRADLEY EW. Macrophages and Bone Remodeling. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(3):359-369. [28] NASONOV EL, AVDEEVA AS, KOROTAEVA TV, et al.The role of interleukin 17 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Are there any prospects for the use of IL-17 inhibitors. Nauchno-Prakticheskaya Revmatologiya. 2023;61(2):165-180. [29] 曹文琪,冯秀芝,赵奕,等.巨噬细胞极化对2型糖尿病性骨质疏松症成骨-成血管偶联的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2026,30(4): 917-925. [30] 李平顺,王佳,田杰祥,等.由“伏毒-巨噬细胞极化-微炎症状态”路径探讨OP研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2025,31(2):222-228+312. [31] 张洁,肖天骄,李丽,等.白细胞介素4调控巨噬细胞极化及骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(25): 3960-3966. [32] 姚兰宣,王雪菲,刘洋,等.间充质干细胞及其衍生细胞外囊泡靶向巨噬细胞干预自身免疫性疾病[J].中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(31):6772-6781. [33] 王文涛,侯振扬,王熠军,等.Apelin-13抑制巨噬细胞M1极化缓解全身炎症性骨丢失[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(8):1548-1555. [34] MA PF, GAO CC, YI J, et al. Cytotherapy with M1-polarized macrophages ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating immune microenvironment in mice. J Hepatol. 2017;67(4):770-779. [35] UNUVAR PURCU D, KORKMAZ A, GUNALP S, et al. Effect of stimulation time on the expression of human macrophage polarization markers. PLoS One. 2022;17(3):e0265196. [36] MARTINEZ FO, GORDON S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:13. [37] SPRENKLE NT, SEREZANI CH, PUA HH. MicroRNAs in Macrophages: Regulators of Activation and Function. J Immunol. 2023;210(4): 359-368. [38] ZHANG X, YANG X, ZHANG S, et al. Wei-Tong-Xin exerts anti-inflammatory effects through TLR4-mediated macrophages M1/M2 polarization and affects GLP-1 secretion. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2023;75(4):574-584. [39] ALOBAID SM, ALSHAHRANI RM, ALONAZI AS, et al. Liraglutide Attenuates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy via the ILK/PI3K/AKT/PTEN Signaling Pathway in Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024;17(3):374. [40] CHATERJEE O, SUR D. Artificially induced in situ macrophage polarization: An emerging cellular therapy for immuno-inflammatory diseases. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;957:176006. [41] SZULC-KIELBIK I, KIELBIK M. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Reasons to Be Cheerful, Reasons to Be Fearful. Exp Suppl. 2022;113:107-140. [42] LIU M, LIU L, SONG Y, et al. Targeting macrophages: a novel treatment strategy in solid tumors. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):586. [43] YING W, CHERUKU PS, BAZER FW, et al. Investigation of macrophage polarization using bone marrow derived macrophages. J Vis Exp. 2013;(76):50323. [44] SAADE M, ARAUJO DE SOUZA G, SCAVONE C, et al. The Role of GPNMB in Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:674739. [45] OH H, PARK SH, KANG MK, et al. Asaronic Acid Inhibited Glucose-Triggered M2-Phenotype Shift Through Disrupting the Formation of Coordinated Signaling of IL-4Rα-Tyk2-STAT6 and GLUT1-Akt-mTOR-AMPK. Nutrients. 2020;12(7):2006. [46] PECKERT-MAIER K, LANGGUTH P, STRACK A, et al. CD83 expressed by macrophages is an important immune checkpoint molecule for the resolution of inflammation. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1085742. [47] LUO M, ZHAO F, CHENG H, et al. Macrophage polarization: an important role in inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 2024;15: 1352946. [48] YAO Y, XU XH, JIN L. Macrophage Polarization in Physiological and Pathological Pregnancy. Front Immunol. 2019;10:792. [49] HALIMANI N, NESTERCHUK M, ANDREICHENKO IN, et al. Phenotypic Alteration of BMDM In Vitro Using Small Interfering RNA. Cells. 2022; 11(16):2498. [50] TODA G, YAMAUCHI T, KADOWAKI T, et al. Preparation and culture of bone marrow-derived macrophages from mice for functional analysis. STAR Protoc. 2020;2(1):100246. [51] ZAJD CM, ZIEMBA AM, MIRALLES GM, et al. Bone Marrow-Derived and Elicited Peritoneal Macrophages Are Not Created Equal: The Questions Asked Dictate the Cell Type Used. Front Immunol. 2020;11:269. [52] FANG X, WU Y, QIN H, et al. Protocol for building an in vitro model of M2-like tumor-associated macrophages with lactic acid or conditioned medium from Lewis cells. STAR Protoc. 2024;5(2):103120. [53] YIN W, WANG JH, LIANG YM, et al. Neferine Targeted the NLRC5/NLRP3 Pathway to Inhibit M1-type Polarization and Pyroptosis of Macrophages to Improve Hyperuricemic Nephropathy. Curr Mol Med. 2025;25(1):90-111. |
| [1] | Song Puzhen, Ma Hebin, Chen Hongguang, Zhang Yadong. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes combined with transforming growth factor beta 1 on macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1616-1623. |
| [2] | Cai Ziming, Yu Qinghe, Ma Pengfei, Zhang Xin, Zhou Longqian, Zhang Chongyang, Lin Wenping. Heme oxygenase-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1624-1631. |
| [3] | Zou Yulian, Chen Chaopei, Huang Haixia, Lan Yuyan, Liu Min, Huang Ting. Resveratrol promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1669-1678. |
| [4] | Xia Linfeng, Wang Lu, Long Qianfa, Tang Rongwu, Luo Haodong, Tang Yi, Zhong Jun, Liu Yang. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate blood-brain barrier damage in mice with septic encephalopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1711-1719. |
| [5] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [6] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [7] | You Huijuan, Wu Shuzhen, Rong Rong, Chen Liyuan, Zhao Yuqing, Wang Qinglu, Ou Xiaowei, Yang Fengying. Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526. |
| [8] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [9] | Zhang Ye, An Zheqing, Xi Xin, Liu Xiaoyan, Hong Wei, Liao Jian. Zoledronic acid-loaded dissolvable microneedle patch inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclast differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5115-5124. |
| [10] | Xie Peisen, Guan Zhenpeng, Wei Xianjie, Zhang Keshi, Kang Qingyuan, Xiao Wentao, Guo Xiaoshuai. Cerium dioxide nanoparticles regulate expression of inflammatory factors in M1 macrophages and affect fibroblast co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 375-383. |
| [11] | Li Congcong, Wufanbieke·Baheti, Zhao Li, Chen Xiaotao, Kong Chuifan, Yu Min. Physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide/interleukin-4 composite coating materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 404-413. |
| [12] | Chen Yuanjun, Lin Sixing, Ji Lichun, Li Dongxiao, Liao Guangzhi, Lin Xingdong. Anti-inflammatory activity and mechanism of Lonicera japonica Thunb.-derived extracellular vesicle-like particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3308-3320. |
| [13] | She Xu, Li Xiaojiang, Huang Haixia, Wan Lingling, Luo Qingqing. Lipopolysaccharides regulate the function of human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3280-3287. |
| [14] | Liu Man, Zhang Kaiwei, Zhu Xu, Ruan Jinghua, Chen Jiunyi, Fei Ji. Mechanism of Shixiang plaster to promote healing of infectious wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2784-2794. |
| [15] | Shalayiding · Aierxiding, Gao Jian, Alimujiang · Abudourousuli, Kutiluke · Shoukeer, Aikebaierjiang · Aisaiti, Gulimire · Yilihamu, Jiang Kan, Aikeremujiang · Muheremu. Mechanisms by which macrophage polarization regulates bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2484-2490. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||