Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2484-2490.doi: 10.12307/2026.610
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanisms by which macrophage polarization regulates bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis
Shalayiding · Aierxiding1, Gao Jian1, Alimujiang · Abudourousuli1, Kutiluke · Shoukeer1, Aikebaierjiang · Aisaiti1, Gulimire · Yilihamu2, #br# Jiang Kan1, Aikeremujiang · Muheremu1 #br#
- 1The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-03-14Accepted:2025-06-20Online:2026-04-08Published:2025-08-28 -
Contact:Aikeremujiang · Muheremu, MD, Chief physician, Associate professor, doctoral supervisor, Master’s supervisor, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Shalayiding · Aierxiding, MS candidate, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2022D01C583 (to GJ); “Tianshan Talents” Medical and Health Care Training Program for Young and Middle-aged Key Talents, No. TSYC202301B107 (to GJ); Key Project of Open Subjects of Key Laboratory of the Ministry of Education, No. 2023A03 (to JK); Young Doctoral Project of “Tianchi Talents” Introduction Program (to AM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shalayiding · Aierxiding, Gao Jian, Alimujiang · Abudourousuli, Kutiluke · Shoukeer, Aikebaierjiang · Aisaiti, Gulimire · Yilihamu, Jiang Kan, Aikeremujiang · Muheremu. Mechanisms by which macrophage polarization regulates bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2484-2490.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
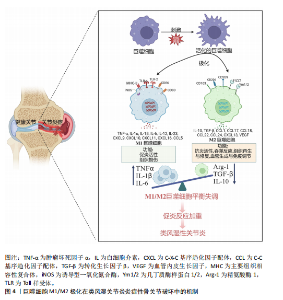
2.1 类风湿关节炎中M1巨噬细胞的调控作用 1882年,归功于具有通过激活Toll样受体和产生促炎和抗炎递质来识别、吞噬和破坏病原体的能力,Metchnikov首次把巨噬细胞描述为免疫系统的“大食者”,并认为是免疫系统的前哨细胞[18]。研究发现,巨噬细胞作为抗原递呈细胞,能够通过向初始T细胞呈递非自身抗原并释放细胞因子和生长因子,诱导Th1或Th2介导的免疫应答。此外,可塑性也是巨噬细胞的一个关键特征,巨噬细胞能够呈现异质表型,产生各种细胞极化亚群,这些巨噬细胞亚群不仅参与炎症的传播,还参与炎症的消退,这取决于它们的激活状态M1巨噬细胞(经典激活途径型)或M2巨噬细胞(替代激活途径型)[19]。越来越多的研究表明,M1和M2表型代表了巨噬细胞极化谱的极端,而其实际特征则存在于参与免疫调节或组织修复的“中间”表型,并由不同的代谢途径、细胞表面标志物和细胞因子产生定义[20]。科学家在过去几年揭示了M1/M2巨噬细胞在类风湿关节炎免疫反应中的作用(图3),发现类风湿关节炎的炎症过程主要由外周血和滑膜组织中的M1巨噬细胞介导和维持。M1巨噬细胞是促炎细胞,其特征在于高表达Ⅱ类主要组织相容性复合体、CD80、CD86、CD38和Toll样受体4,主要作用是负责促炎细胞因子的分泌,包括白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α以及趋化因子(如趋化因子受体7)[21]。当自身耐受性丧失时,炎症持续进化为慢性适应不良免疫反应。CD80/CD86是存在于M1巨噬细胞(以及其他细胞)上的共刺激分子,在免疫反应中起着重要作用,是表达在抗原呈递细胞表面的蛋白质,主要功能是与T细胞表面的CD28受体结合,促进T细胞的活化、增殖和分化[22]。 Toll样受体是指分布在抗原递呈细胞,包括巨噬细胞、自然杀伤细胞、淋巴细胞、内皮和上皮细胞以及成纤维细胞的细胞膜或胞质溶胶上的异源受体家族[23]。Toll样受体是宿主防御感染并识别病原体相关分子模式的最古老的免疫工具之一,类风湿关节炎中主要是Toll样受体2和Toll样受体4参与病原体识别[24]。Toll样受体4在巨噬细胞上表达,允许其识别类风湿关节炎中相关的内源性配体,例如天然关节蛋白和瓜氨酸化肽,并随后诱导细胞内信号转导,最终通过激活核因子κB信号传导途径促进促炎基因的表达[25-26]。通过从类风湿关节炎患者获得的单核细胞衍生巨噬细胞研究发现,Toll样受体4诱导的核因子κB信号通路激活,能够介导M1巨噬细胞的促炎活性,并产生和释放白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β[27]。在类风湿关节炎中,与M1巨噬细胞诱导的炎症相关的另一个重要途径涉及c-Jun氨基末端激酶/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、Janus激酶/信号转导和转录激活因子,这些激酶被促炎细胞因子激活并促进巨噬细胞的增殖和存活[28]。此外,类风湿关节炎关节滑膜中的肿瘤坏死因子 α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6也促进丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路的激活。"
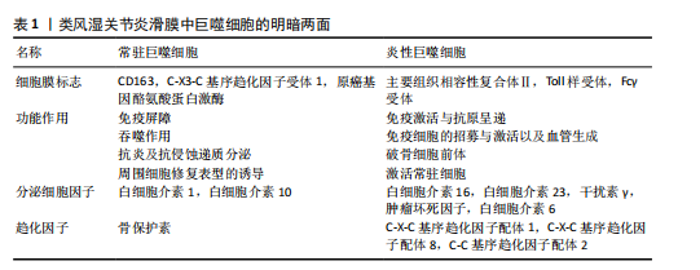
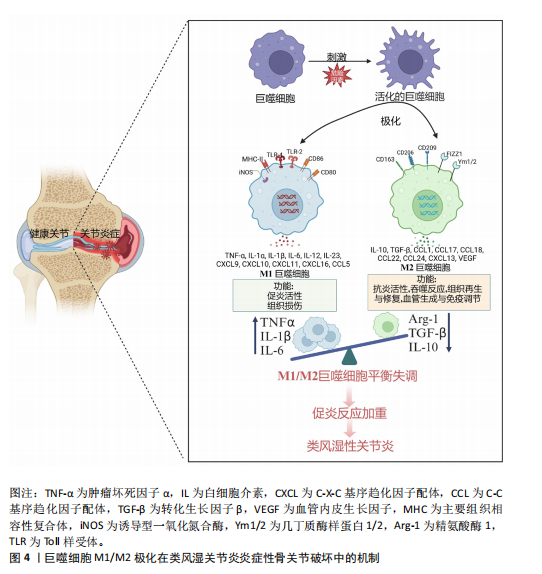
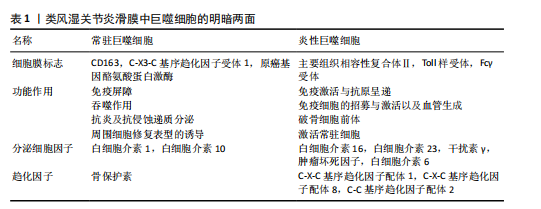
2.2 类风湿关节炎中M2巨噬细胞的调控作用 M2巨噬细胞高表达巨噬细胞清道夫受体(CD163、CD204)、甘露糖受体1(CD206)和CD209等[29]。M2巨噬细胞负责清除凋亡细胞、产生细胞外基质组分和趋化因子以及血管生成[30]。此外,白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β是由M2巨噬细胞内源性产生的分子,能够使免疫反应向组织修复模式转变[31]。CD163是一种在驻留组织巨噬细胞中高度表达的血红蛋白清除剂可溶性或膜结合受体,其有助于抗炎局部反应,降低血红蛋白水平并促进炎症消退[32]。CD206是一种甘露糖清道夫受体,主要存在于M2巨噬细胞和树突状细胞中,参与胶原内化和降解[33]。在类风湿关节炎中,腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶/α-乙酰辅酶A羧化酶能够促进巨噬细胞向M2极化,且促进巨噬细胞衍生趋化因子、CD206和白细胞介素10表达上调[34]。 2.3 M1和M2巨噬细胞在类风湿关节炎骨破坏中的作用 滑膜组织是类风湿关节炎患者关节炎症的主要区域,持续的慢性滑膜炎会导致骨与软骨的不可逆损伤。在滑膜炎中,关节滑膜组织细胞增多,滑膜增厚[35]。浸润性单核细胞衍生的巨噬细胞是滑膜炎发生和慢性化的基础细胞,它们能够协调免疫反应,释放炎症级联反应中涉及的细胞因子和酶,进而激活破骨细胞和成纤维细胞,导致关节破坏和疾病延续[10],这些巨噬细胞表达Toll样受体,主要是Toll样受体2,激活局部危险信号。在类风湿关节炎滑膜组织中,活化的M1巨噬细胞和Th1细胞之间的相互作用促进了促炎递质的产生,包括白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子 α、白细胞介素23、CXC趋化因子配体和C-C基序趋化因子配体,这种相互作用首先由主要组织相容性复合体Ⅱ介导,其次由共刺激分子CD80/CD86介导,后者在M1巨噬细胞中过表达(图4)[36]。 在类风湿关节炎的早期,这些递质有助于单核细胞源性巨噬细胞的召回和激活,使其从外周血进入滑膜组织,促进和维持炎症[37];在类风湿关节炎进展过程中,滑膜组织对炎性损伤做出反应,如炎性浸润、内层增生、新血管形成和血管翳形成,导致软骨破坏,见表1。 趋化因子受体7信号传导途径已被证明可诱导单核细胞迁移和M1极化。事实上,C-C基序趋化因子配体21/趋化因子受体7信号传导介导CD14+ CD86+单核细胞迁移,后者极化为M1巨噬细胞,并随之产生促炎细胞因子,主要是白细胞介素6和白细胞介素23。促炎性M1巨噬细胞的特征在于趋化因子受体的高表达,并且这些表达趋化因子受体7的巨噬细胞诱导和扩增Th17细胞分化[38]。与C-C基序趋化因子配体21/趋化因子受体7一样,白细胞介素23也是由滑膜组织中极化巨噬细胞分泌的另一种重要细胞因子,其诱导CD4+初始T细胞分化为Th17细胞,这些CD4+ "
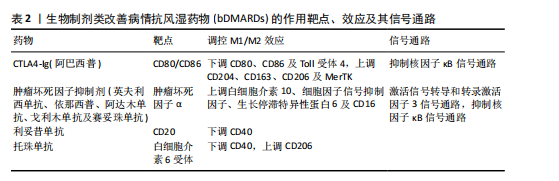
T细胞是白细胞介素17的主要产生者,而白细胞介素17可促进类风湿关节炎的发病,这些细胞因子与多种细胞类型(包括单核细胞/巨噬细胞)表面膜上的受体相互作用,激活炎症中涉及的细胞内信号传导途径,包括信号转导和转录激活因子、Janus激酶激活介导的信号传导途径[39]。最新研究证实,白细胞介素17和肿瘤坏死因子α协同作用诱导巨噬细胞产生促炎递质,包括白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和基质金属蛋白酶,使早期炎症向慢性关节炎进展[40]。炎性巨噬细胞通过产生和释放基质金属蛋白酶参与结缔组织的更新和关节面的侵蚀。促炎细胞因子和趋化因子的大量释放决定了滑膜微环境的急剧变化,并允许细胞毒性细胞的有效活化[41]。类风湿关节炎滑膜中大量存在的M1型巨噬细胞作为炎症的标志,反映了疾病活动性,因此,M1型巨噬细胞在靶器官水平的消耗可能是治疗反应的良好生物标志物[42]。 2.4 调控巨噬细胞极化的治疗策略及展望 滑膜组织中活化的促炎性巨噬细胞增加,是类风湿关节炎的早期标志(图4)[43]。因此,及时诊断后进行早期治疗是预防类风湿关节炎患者骨侵蚀、功能下降和过早死亡的必要措施,早期抑制巨噬细胞活化是类风湿关节炎有效且耐受性良好的治疗策略[44]。在“治疗机会窗”内实现早期缓解决定了更好的临床结果;相反,延迟开始治疗会导致症状持续时间延长和预后不良[45]。识别反映巨噬细胞群的特异性生化标志物可能是识别疾病活化状态的有用工具,并代表类风湿关节炎治疗的可能靶点,例如MerTK。在疾病缓解期的类风湿关节炎患者滑膜组织中检测到大量MerTK+ CD206+ CD163+ M2巨噬细胞,这些细胞的增加与滑膜变厚和血管炎呈负相关;值得注意的是,在健康滑膜组织中也观察到这些细胞的存在;相反,活动性类风湿关节炎患者的特征在于滑膜组织衬里层中存在MerTK-CD206-巨噬细胞。这项研究证实,关节滑膜组织以MerTK+ CD206+巨噬细胞(M2巨噬细胞)比例高为特征的患者,其疾病缓解能够得以维持;相反,在生物治疗停止后发作的类风湿关节炎患者中,这些M2巨噬细胞比例较 低[46]。这些结果表明,疾病缓解期类风湿关节炎患者和健康受试者的滑膜组织中M2表型的MerTK+巨噬细胞产生与炎症消退有关的脂质递质,并且它们过表达与局部免疫应答和稳态控制有关。 MerTK信号通路的诱导被认为是一种有希望的方法,可能促进类风湿关节炎患者的疾病缓解。然而,令人信服的证据表明糖皮质激素治疗与单核细胞衍生的巨噬细胞表面膜上MerTK表达增强之间存在正相关性,揭示这种治疗方法可以帮助减轻类风湿关节炎引起的炎症[47]。有研究指出,细胞代谢重编程可能是一种创新的治疗策略,可以减少M1巨噬细胞的生长,改变炎症环境,恢复M1和M2巨噬细胞比例平衡[48]。 在过去的几十年中,类风湿关节炎治疗发生了重大变化,突出了靶向治疗策略的关键作用,旨在为患者量身定制治疗方案,以更好地控制疾病活动。因此,对类风湿关节炎病理生理学的认识已成为开发有效和安全治疗的重要指导。基于这一点,越来越多的生物制剂类改善病情抗风湿药物(biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs,bDMARDs)已被开发出来,并已证实疗效[49]。事实上,由于bDMARDs能够干扰生物学过程,因此在非常早期阶段开始治疗,可以改变甚至逆转类风湿关节炎疾病进展[50]。 目前,在治疗类风湿关节炎时,没有针对巨噬细胞极化的特异性药物,主要是抑制巨噬细胞极化过程的某些方面,特别是炎症细胞因子的产生,包括肿瘤坏死因子 α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6。靶向单克隆抗体或可溶性受体的新型药物可能在治疗类风湿关节炎的炎症阶段更有效[42]。肿瘤坏死因子抑制剂(包括英夫利西单抗、依那西普、阿达木单抗、戈利木单抗和赛妥珠单抗)与可溶性和膜相关肿瘤坏死因子α结合,抑制参与介导促炎特性的细胞内信号通路的激活。托珠单抗通过与白细胞介素6受体相互作用抑制白细胞介素6介导的炎症,而白细胞介素1β的免疫和促炎作用与抑制阿那白滞素介导的受体结合形成对比,阿那白滞素是一种非糖基化重组形式的生理性白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂[51]。事实上,在最近针对一些bDMARDs的一项研究中,抗肿瘤坏死因子药物对类风湿关节炎患者促炎M1巨噬细胞的影响揭示了其间接调节这些细胞向M2表型极化的能力。有研究表明,抗肿瘤坏死因子药物不仅能抑制巨噬细胞的体外炎症功能,还能提高巨噬细胞的解毒功能,主要涉及白细胞介素10/信号转导和转录激活因子3信号轴 [52]。巨噬细胞在炎症背景下的这种极化转变有望提高各种bDMARDs在类风湿关节炎中的临床疗效[53],见表2。"
| [1] BROWN P, PRATT AG, HYRICH KL. Therapeutic advances in rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ. 2024;384:e070856. [2] RADU AF, BUNGAU SG. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Cells. 2021;10(11):2857. [3] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2):905. [4] NGO ST, STEYN FJ, MCCOMBE PA. Gender differences in autoimmune disease. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2014;35(3):347-369. [5] KIM H, CHO SK, KIM JW, et al. An increased disease burden of autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases in Korea. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020;50(3):526-533. [6] DI MATTEO A, BATHON JM, EMERY P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2023; 402(10416):2019-2033. [7] 赵军一,赵凤,曲冰佳,等.1990-2019年中国类风湿性关节炎疾病负担现状和趋势分析[J].中国卫生统计,2024,41(3): 344-348,353. [8] TURESSON C. Extra-articular rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013;25(3): 360-366. [9] AIN Q, ZEESHAN M, KHAN S, et al. Biomimetic hydroxyapatite as potential polymeric nanocarrier for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(12):2595-2600. [10] UDALOVA IA, MANTOVANI A, FELDMANN M. Macrophage heterogeneity in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(8):472-485. [11] WANG LX, ZHANG SX, WU HJ, et al. M2b macrophage polarization and its roles in diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 2019;106(2):345-358. [12] RANKIN LC, ARTIS D. Beyond Host Defense: Emerging Functions of the Immune System in Regulating Complex Tissue Physiology. Cell. 2018;173(3):554-567. [13] GAUTIER EL, SHAY T, MILLER J, et al. Gene-expression profiles and transcriptional regulatory pathways that underlie the identity and diversity of mouse tissue macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2012;13(11): 1118-1128. [14] WYNN TA, CHAWLA A, POLLARD JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013; 496(7446):445-455. [15] CUTOLO M, CAMPITIELLO R, GOTELLI E, et al. The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:867260. [16] HERB M, SCHATZ V, HADRIAN K, et al. Macrophage variants in laboratory research: most are well done, but some are RAW. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024; 14:1457323. [17] TARDITO S, MARTINELLI G, SOLDANO S, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Autoimmun Rev. 2019;18(11):102397. [18] DEGBOÉ Y, POUPOT R, POUPOT M. Repolarization of Unbalanced Macrophages: Unmet Medical Need in Chronic Inflammation and Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1496. [19] ROSS EA, DEVITT A, JOHNSON JR. Macrophages: The Good, the Bad, and the Gluttony. Front Immunol. 2021;12:708186. [20] MURAILLE E, LEO O, MOSER M. TH1/TH2 paradigm extended: macrophage polarization as an unappreciated pathogen-driven escape mechanism? Front Immunol. 2014;5:603. [21] ZHANG F, CHENG T, ZHANG SX. Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR): a potential new therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):187. [22] CUTOLO M, SOLDANO S, GOTELLI E, et al. CTLA4-Ig treatment induces M1-M2 shift in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages from healthy subjects and rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021; 23(1):306. [23] ZHANG Y, LIU J, WANG C, et al. Toll-Like Receptors Gene Polymorphisms in Autoimmune Disease. Front Immunol. 2021;12:672346. [24] CAO Y, LIU J, HUANG C, et al. Wilforlide A ameliorates the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization. J Pharmacol Sci. 2022;148(1):116-124. [25] 郭月丽,章涛,梅序桥. PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路与类风湿关节炎的相关性[J].广东医学,2017,38(14):2176-2179. [26] 刘琼,李永乐,董平,等. PI3K/Akt信号通路与类风湿关节炎相关性探讨[J].风湿病与关节炎,2021,10(3):62-66. [27] BRIZZOLARA R, MONTAGNA P, SOLDANO S, et al. Rapid interaction between CTLA4-Ig (abatacept) and synovial macrophages from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(5):738-740. [28] MALEMUD CJ, MILLER AH. Pro-inflammatory cytokine-induced SAPK/MAPK and JAK/STAT in rheumatoid arthritis and the new anti-depression drugs. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008;12(2):171-183. [29] SARADNA A, DO DC, KUMAR S, et al. Macrophage polarization and allergic asthma. Transl Res. 2018;191:1-14. [30] ABDELAZIZ MH, ABDELWAHAB SF, WAN J, et al. Alternatively activated macrophages; a double-edged sword in allergic asthma. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):58. [31] DERLINDATI E, DEI CAS A, MONTANINI B, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of human polarized macrophages: more than one role of alternative activation? PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0119751. [32] LILLIS AP, MURATOGLU SC, AU DT, et al. LDL Receptor-Related Protein-1 (LRP1) Regulates Cholesterol Accumulation in Macrophages. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0128903. [33] YU C, LIU H, GUO C, et al. Dextran sulfate-based MMP-2 enzyme-sensitive SR-A receptor targeting nanomicelles for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Deliv. 2022;29(1):454-465. [34] PARK SY, LEE SW, LEE SY, et al. SIRT1/Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase α Signaling Enhances Macrophage Polarization to an Anti-inflammatory Phenotype in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1135. [35] BOUTET MA, COURTIES G, NERVIANI A, et al. Novel insights into macrophage diversity in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(3):102758. [36] ELEMAM NM, HANNAWI S, MAGHAZACHI AA, et al. Role of Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunotargets Ther. 2020;9:43-56. [37] MURAYAMA MA, SHIMIZU J, MIYABE C, et al. Chemokines and chemokine receptors as promising targets in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1100869. [38] VAN RAEMDONCK K, UMAR S, PALASIEWICZ K, et al. CCL21/CCR7 signaling in macrophages promotes joint inflammation and Th17-mediated osteoclast formation in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(7):1387-1399. [39] SCHINOCCA C, RIZZO C, FASANO S, et al. Role of the IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Rheumatic Diseases: An Overview. Front Immunol. 2021;12:637829. [40] VAN HAMBURG JP, ASMAWIDJAJA PS, DAVELAAR N, et al. Th17 cells, but not Th1 cells, from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis are potent inducers of matrix metalloproteinases and proinflammatory cytokines upon synovial fibroblast interaction, including autocrine interleukin-17A production. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63(1):73-83. [41] ROSE BJ, KOOYMAN DL. A Tale of Two Joints: The Role of Matrix Metalloproteases in Cartilage Biology. Dis Markers. 2016;2016: 4895050. [42] YANG X, CHANG Y, WEI W, et al. Emerging role of targeting macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis: Focus on polarization, metabolism and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(7):e12854. [43] KINNE RW, STUHLMÜLLER B, BURMESTER GR, et al. Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Macrophages. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(6):224. [44] 付皖兰,曹云祥,黄传兵,等.巨噬细胞M1/M2型极化在类风湿关节炎中的研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2023,12(8): 59-64. [45] BULLOCK J, RIZVI SAA, SALEH AM, et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Brief Overview of the Treatment. Med Princ Pract. 2018; 27(6):501-507. [46] ALIVERNINI S, MACDONALD L, ELMESMARI A, et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 2020;26(8):1295-1306. [47] ZIZZO G, HILLIARD BA, MONESTIER M, et al. Efficient clearance of early apoptotic cells by human macrophages requires M2c polarization and MerTK induction. J Immunol. 2012;189(7):3508-3520. [48] ZHAO Q, CHU Z, ZHU L, et al. 2-Deoxy-d-Glucose Treatment Decreases Anti-inflammatory M2 Macrophage Polarization in Mice with Tumor and Allergic Airway Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2017;8:637. [49] OBENG JA, AMORUSO A, CAMASCHELLA GL, et al. Modulation of human monocyte/macrophage activity by tocilizumab, abatacept and etanercept: An in vitro study. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;780:33-37. [50] COMBE B, LOGEART I, BELKACEMI MC, et al. Comparison of the long-term outcome for patients with rheumatoid arthritis with persistent moderate disease activity or disease remission during the first year after diagnosis: data from the ESPOIR cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(4):724-729. [51] SCHATZ A, TRANKLE C, YASSEN A, et al. Resolution of pericardial constriction with Anakinra in a patient with effusive-constrictive pericarditis secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Cardiol. 2016; 223:215-216. [52] DEGBOÉ Y, RAUWEL B, BARON M, et al. Polarization of Rheumatoid Macrophages by TNF Targeting Through an IL-10/STAT3 Mechanism. Front Immunol. 2019;10:3. [53] 邹雪,张丽卿. Janus激酶抑制剂及其在类风湿关节炎治疗中的作用研究进展[J].山东医药,2022,62(31):107-110. |
| [1] | Song Puzhen, Ma Hebin, Chen Hongguang, Zhang Yadong. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes combined with transforming growth factor beta 1 on macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1616-1623. |
| [2] | Cai Ziming, Yu Qinghe, Ma Pengfei, Zhang Xin, Zhou Longqian, Zhang Chongyang, Lin Wenping. Heme oxygenase-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1624-1631. |
| [3] | He Jiale, Huang Xi, Dong Hongfei, Chen Lang, Zhong Fangyu, Li Xianhui. Acellular dermal matrix combined with adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promotes burn wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1699-1710. |
| [4] | Xia Linfeng, Wang Lu, Long Qianfa, Tang Rongwu, Luo Haodong, Tang Yi, Zhong Jun, Liu Yang. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate blood-brain barrier damage in mice with septic encephalopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1711-1719. |
| [5] | Cui Lianxu, Li Haomin, Xu Junrong, Tan Baodong, Lu Dahong, Peng Siwei, Wang Jinhui. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium on tissue repair after traumatic craniocerebral injury in miniature pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1730-1735. |
| [6] | Cao Yong, Teng Hongliang, Tai Pengfei, Li Junda, Zhu Tengqi, Li Zhaojin. Interactions between cytokines and satellite cells in muscle regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1808-1817. |
| [7] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [8] | Hou Chaowen, Li Zhaojin, Kong Jianda, Zhang Shuli. Main physiological changes in skeletal muscle aging and the multimechanism regulatory role of exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1464-1475. |
| [9] | You Huijuan, Wu Shuzhen, Rong Rong, Chen Liyuan, Zhao Yuqing, Wang Qinglu, Ou Xiaowei, Yang Fengying. Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526. |
| [10] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [11] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [12] | Zhang Di, Zhao Jun, Ma Guangyue, Sun Hui, Jiang Rong. Mechanism of depression-like behavior in chronic social defeat stress mice based on high-throughput sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1139-1146. |
| [13] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [14] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [15] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||