Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1569-1579.doi: 10.12307/2026.609
Previous Articles Next Articles
DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations
Wu Zhilin1, 2, He Qin1, Wang Pingxi1, Shi Xian1, Yuan Song1, Zhang Jun2, Wang Hao1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Dazhou Central Hospital, Dazhou 635000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Orthopedic Laboratory, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400014, China
-
Received:2024-12-09Accepted:2025-02-20Online:2026-02-28Published:2025-07-19 -
Contact:Wang Hao, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Dazhou Central Hospital, Dazhou 635000, Sichuan Province, China Co-corresponding author: Zhang Jun, Attending physician, Orthopedic Laboratory, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400014, China -
About author:Wu Zhilin, MD candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Dazhou Central Hospital, Dazhou 635000, Sichuan Province, China; Orthopedic Laboratory, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400014, China -
Supported by:the Orthopedic Special Research Project of Sichuan Medical Association, No. 2023AT19 (to WH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
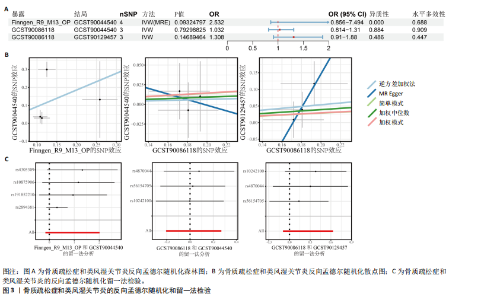
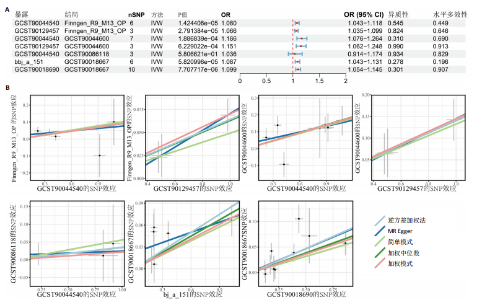
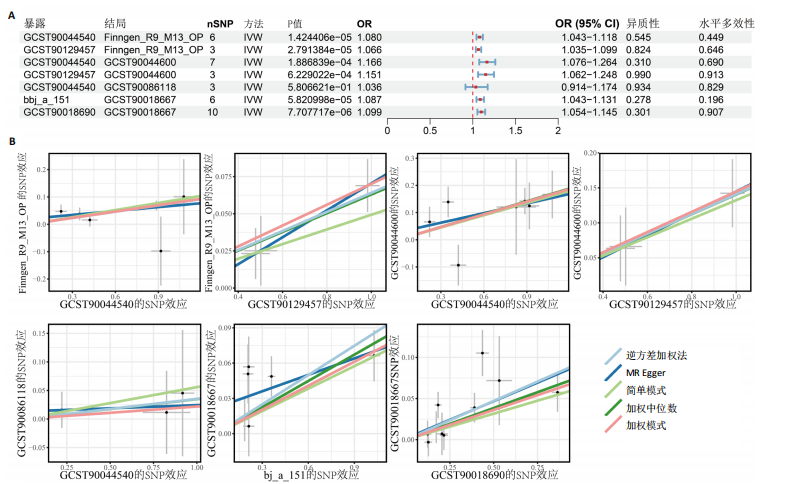
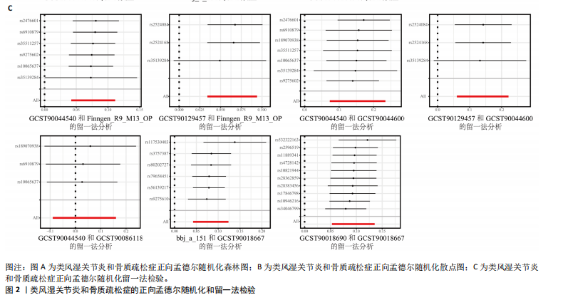
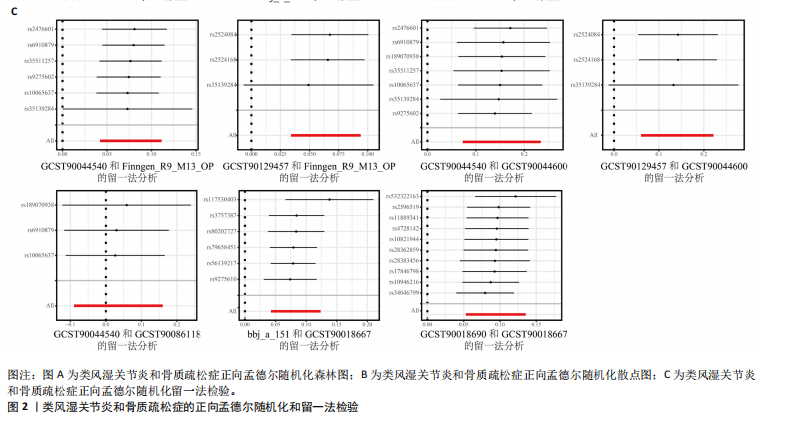
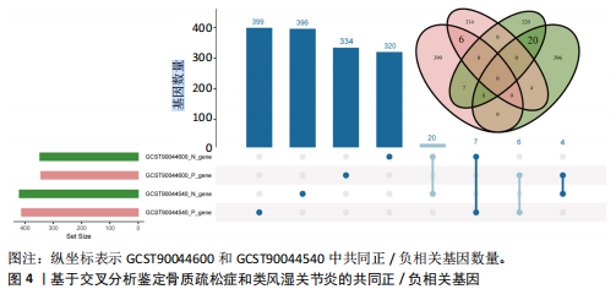
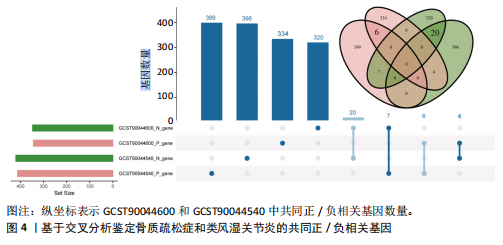
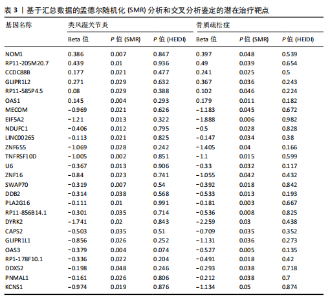
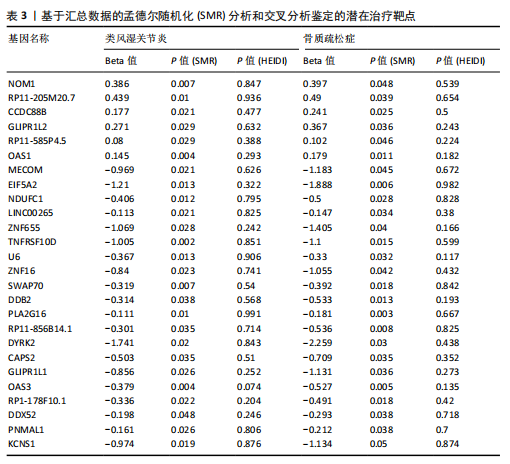
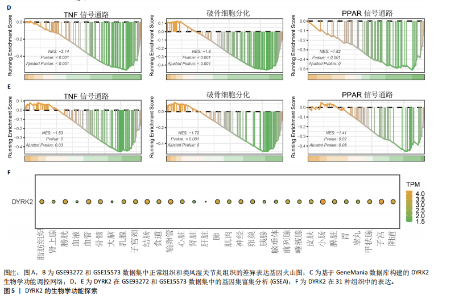
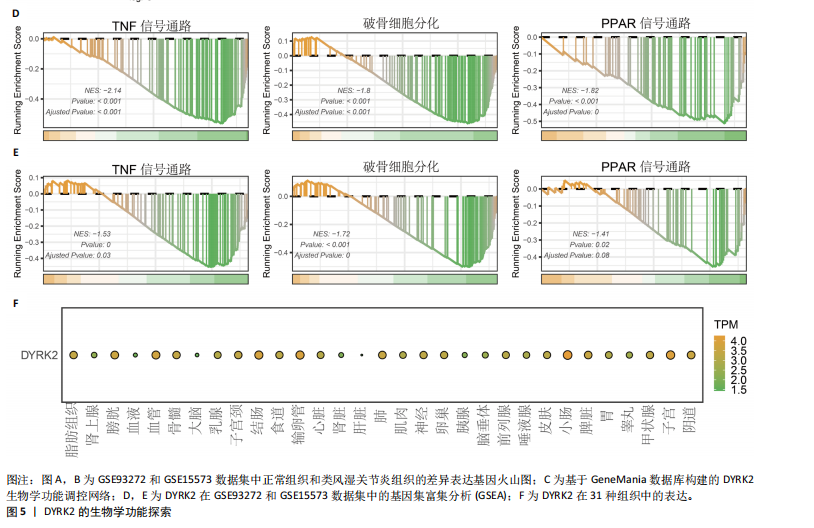
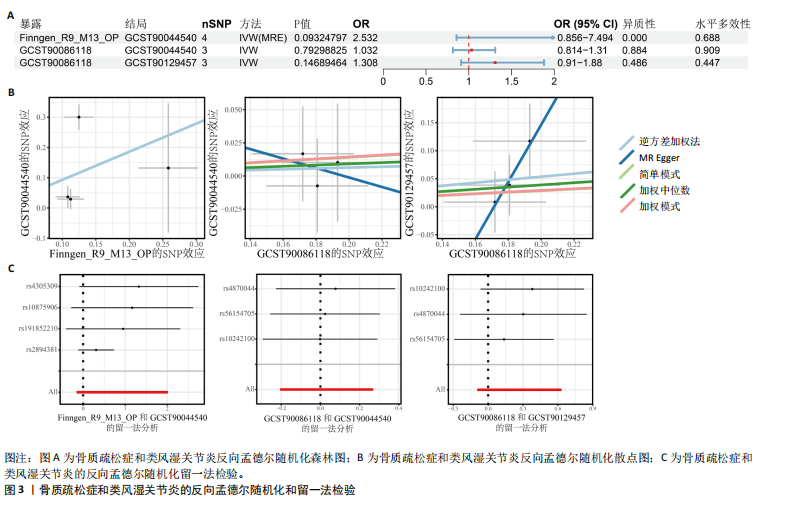
态性,并通过去除连锁不平衡从IEU Open GWAS 数据库筛选出满足孟德尔随机化三大假设的单核苷酸多态性,随后剔除F < 10的单核苷酸多态性,以避免结果偏倚,最后进行类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症间的正向双样本孟德尔随机化分析。结果显示,除外暴露GCST90044540和结局GCST90086118,其余孟德尔随机化分析证实类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症之间存在因果关系,并且呈显著正相关(图2A)。此外,散点图显示,其余4种算法(MR Egger法、简单模式法、加权中位数法和加权模式法)具有一致性,表明分析结果可靠(图2B)。阳性结果均通过Cochran’s Q检验、MR-Egger-Intercept检验和留一法检验,证明结果稳定且可靠(图2C)。 2.2 骨质疏松症和类风湿关节炎的反向孟德尔随机化分析 基于相同方式筛选出反向孟德尔随机化分析中与暴露因素(骨质疏松症)紧密相关且满足三大假设的单核苷酸多态性用于反向双样本孟德尔随机化分析。结果显示,尽管骨质疏松症与类风湿关节炎存在正相关趋势,但不存在明显因果关系(图3A)。散点图中各算法的不一致也证明骨质疏松症和类风湿关节炎之间不存在因果关系(图3B)。此外,敏感性分析结果表明骨质疏松症和类风湿关节炎的反向孟德尔随机化分析是可靠的(图3A和3C)。综上所述,类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症的正向孟德尔随机化分析中具有一致方向的OR值,并且大部分结果具有显著性;同时,骨质疏松症和类风湿关节炎的反向孟德尔随机化分析中未见阳性结果。因此,类风湿关节炎与骨质疏松症之间具有因果关系,并且类风湿关节炎与骨质疏松症的发生风险呈显著正相关。 2.3 潜在治疗靶点挖掘 基于SMR分析,该研究共获得与类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症正相关的基因分别为412和344个,负相关基因分别为421和347个。对正相关基因和负相关基因进行两两交叉分析,最终得到6个共同正相关基因和20个共同负相关基因,见图4。这些基因在类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症的调控中扮演桥梁作用,其中只有DYRK2的Beta值< -1.5,表明DYRK2与两种疾病具有紧密的联系(可能在两种疾病的共病机制中扮演着关键角色),并且是潜在的治疗靶点(表3)。 2.4 DYRK2的生物学功能探索 GSE93272和GSE15573数据集中的基因差异表达分析表明,DYRK2在类风湿关节炎中显著低表达(图5A,B),这表明DYRK2的表达可能是类风湿关节炎发病的机制之一。生物学功能分析表明DYRK2主要参与氨基酸的修饰(图5C)。此外,GSEA分析表明,DYRK2的表达对TNF信号通路、破骨细胞分化和PPAR通路具有抑制作用(图5D,E)。TNF信号通路是类风湿关节炎发病和进展的关键通路;破骨细胞分化和PPAR通路是骨质疏松发生的关键因素。因此,DYRK2低表达可能会导致这些通路的异常激活,进而导致类风湿关节炎的进展和骨质疏"
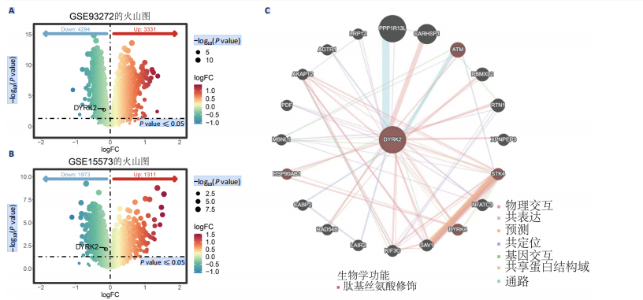
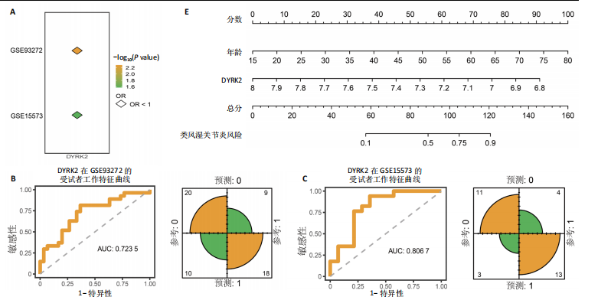
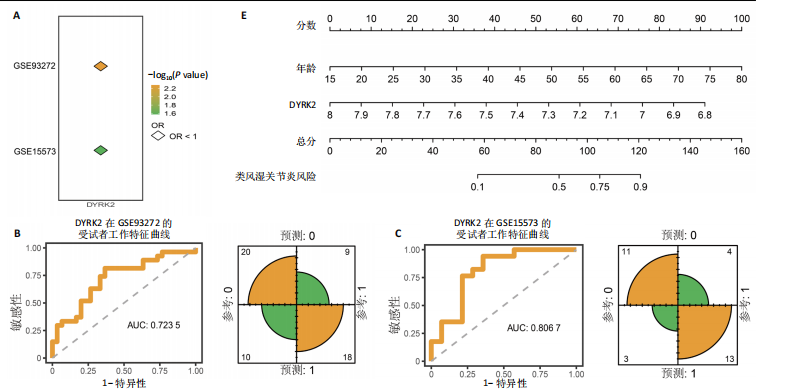
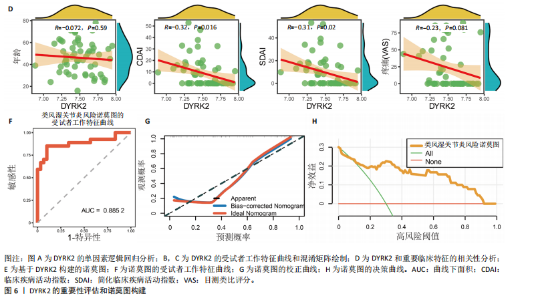
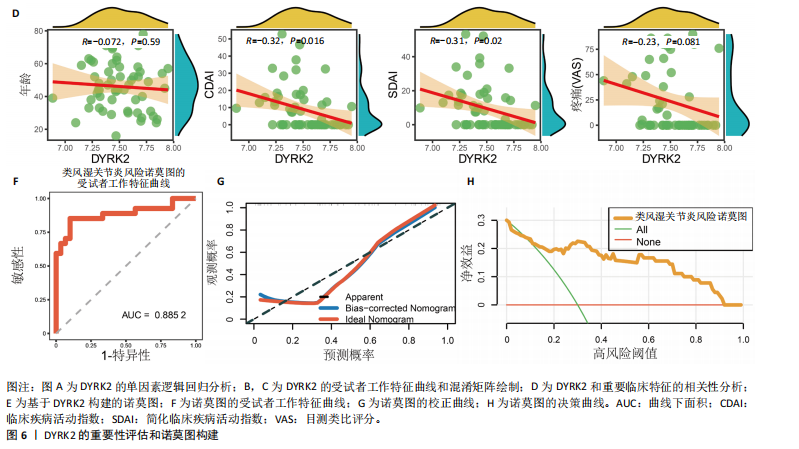
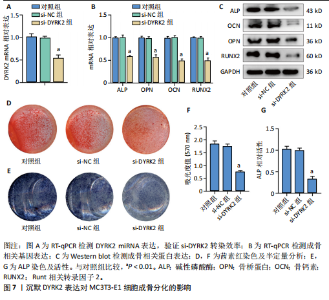
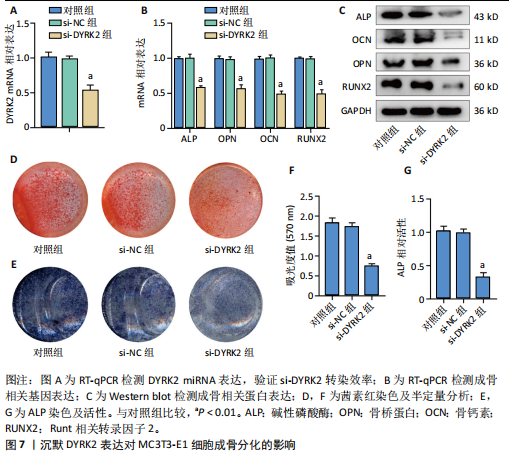
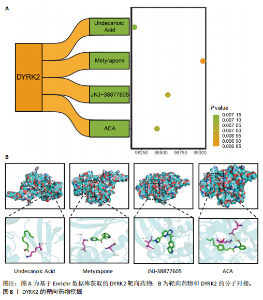
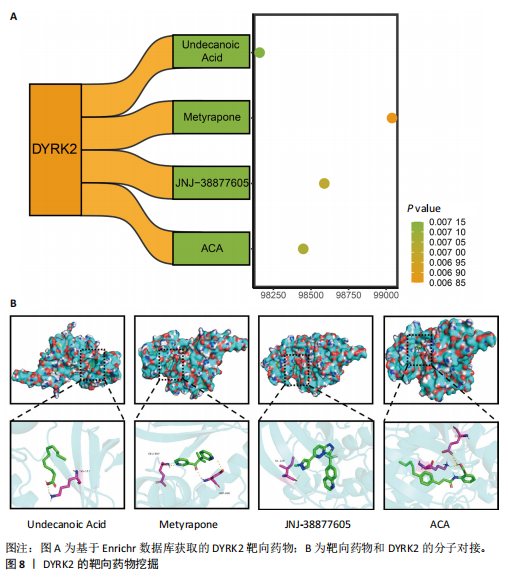
松症的发生。此外,GTEx数据库表明,DYRK2在骨髓中显著富集(图5F),在成骨分化中可能发挥重要作用。因此,上述结果表明,DYRK2是类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症的关键共病基因。 2.5 DYRK2的重要性评估和诺莫图构建 单因素逻辑回归结果显示,DYRK2在GSE93272和GSE15573两个数据集中具有显著意义(图6A);受试者工作特征曲线和混淆矩阵均显示DYRK2基因在两个数据集中表现出色。因此,DYRK2基因具有较好的类风湿关节炎风险预测性能(图6B,C)。此外,相关性分析表明,除年龄外,DYRK2的表达量与临床疾病活动指数(clinical disease activity index,CDAI)简化临床疾病活动指数(simplified disease activity index,SDAI )和目测类比评分(visual analogue scale,VAS)均呈显著负相关(图6D),这证实了该基因在临床中的重要性。最后,基于DYRK2和年龄特征,构建了一个诺莫图用于预测类风湿关节炎患病风险(图6E)。受试者工作特征曲线、矫正曲线和决策曲线证明该预测工具具有出色的预测性能(图6F-H)。 2.6 基于细胞实验验证DYRK2的生物学功能 如图7A所示,si-DYRK2转染成功,DYRK2表达明显下调。如图7B,C所示,在MC3T3-E1细胞中沉默DYRK2表达时,成骨相关基因(碱性磷酸酶、骨桥蛋白、骨钙素、Runt 相关转录因子2) mRNA和蛋白表达显著降低;同时,通过碱性磷酸酶染色和茜素红染色发现当DYRK2表达降低时,它能够显著抑制MC3T3-E1细胞的成骨分化和矿化(图7D-G),这表明DYRK2基因在成骨过程中起调控作用。 2.7 DYRK2的靶向药物挖掘和分子对接 基于Enrichr数据库挖掘出4种可靶向DYRK2的药物(图8A)。分子对接显示,4种药物的小分子均成功占据在DYRK2蛋白的分子口袋中(图8B),结合能分别为-23.85 kJ/mol (Undecanoic Acid)、-30.96 kJ/mol (Metyrapone)、-46.86 kJ/mol(JNJ-38877605)和-38.07 kJ/mol (ACA)。这些结果为类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症的靶向治疗提供了一定的前期理论依据。"

| [1] POURESMAEILI F, KAMALIDEHGHAN B, KAMAREHEI M, et al. A comprehensive overview on osteoporosis and its risk factors. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;14: 2029-2049. [2] JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(12):1726-1733. [3] JOHNSTON CB, DAGAR M. Osteoporosis in Older Adults. Med Clin North Am. 2020; 104(5):873-884. [4] VAN DER WOUDE D, VAN DER HELM-VAN MIL AHM. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors, and disease outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32(2):174-187. [5] LIU YQ, LIU Y, CHEN ZY, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis: a bi-directional Mendelian randomization study. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(10):14109-14130. [6] BASAT H, ESMAEILZADEH S, ESKIYURT N. The effects of strengthening and high-impact exercises on bone metabolism and quality of life in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2013;26(4):427-435. [7] TONG JJ, XU SQ, ZONG HX, et al. Prevalence and risk factors associated with vertebral osteoporotic fractures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2020; 39(2):357-364. [8] KWEON SM, SOHN DH, PARK JH, et al. Male patients with rheumatoid arthritis have an increased risk of osteoporosis: Frequency and risk factors. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(24):e11122. [9] LEE SG, PARK YE, PARK SH, et al. Increased frequency of osteoporosis and BMD below the expected range for age among South Korean women with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2012;15(3):289-296. [10] XUE AL, WU SY, JIANG L, et al. Bone fracture risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(36):e6983. [11] ADAMI G, SAAG KG. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: 2019 concise clinical review. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(6):1145-1156. [12] BIRNEY E. Mendelian Randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(4): a041302. [13] ZHU Z, ZHANG F, HU H, et al. Integration of summary data from GWAS and eQTL studies predicts complex trait gene targets. Nat Genet. 2016;48(5):481-487. [14] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621. [15] JIANG T, GILL D, BUTTERWORTH AS, et al. An empirical investigation into the impact of winner’s curse on estimates from Mendelian randomization. Int J Epidemiol. 2023;52(4):1209-1219. [16] DAVIES NM, HOLMES MV, DAVEY SMITH G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ. 2018;362:k601. [17] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using mendelian randomisation (STROBE-MR): explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2021;375:n2233. [18] HEMANI G, ZHENG J, ELSWORTH B, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. 2018;7:e34408. [19] KOTAKE S, UDAGAWA N, HAKODA M, et al. Activated human T cells directly induce osteoclastogenesis from human monocytes: possible role of T cells in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(5):1003-1012. [20] DANKS L, KOMATSU N, Guerrini MM, et al. RANKL expressed on synovial fibroblasts is primarily responsible for bone erosions during joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(6):1187-1195. [21] KOMATSU N, TAKAYANAGI H. Immune-bone interplay in the structural damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194(1):1-8. [22] WANG M, TIAN T, YU S, et al. Th17 and Treg cells in bone related diseases. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:203705. [23] PFEIFLE R, ROTHE T, IPSEIZ N, et al. Regulation of autoantibody activity by the IL-23-TH17 axis determines the onset of autoimmune disease. Nat Immunol. 2017;18(1):104-113. [24] HARRE U, LANG SC, PFEIFLE R, et al. Glycosylation of immunoglobulin G determines osteoclast differentiation and bone loss. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6651. [25] YEO L, TOELLNER KM, SALMON M, et al. Cytokine mRNA profiling identifies B cells as a major source of RANKL in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(11): 2022-2028. [26] HAUGEBERG G, UHLIG T, FALCH JA, et al. Bone mineral density and frequency of osteoporosis in female patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from 394 patients in the Oslo County Rheumatoid Arthritis register. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43(3):522-530. [27] SINIGAGLIA L, NERVETTI A, MELA Q, et al. A multicenter cross sectional study on bone mineral density in rheumatoid arthritis. Italian Study Group on Bone Mass in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000; 27(11):2582-2589. [28] HAUSER B, RICHES PL, WILSON JF, et al. Prevalence and clinical prediction of osteoporosis in a contemporary cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(10):1759-1766. [29] FASSIO A, IDOLAZZI L, JABER MA, et al. The negative bone effects of the disease and of chronic corticosteroid treatment in premenopausal women affected by rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatismo. 2016; 68(2):65-71. [30] JIN S, HSIEH E, PENG L, et al. Incidence of fractures among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(6):1263-1275. [31] CHEN B, CHENG G, WANG H, et al. Increased risk of vertebral fracture in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(45):e5262. [32] DOUGADOS M, SOUBRIER M, ANTUNEZ A, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and evaluation of their monitoring: results of an international, cross-sectional study (COMORA). Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(1):62-68. [33] RICHARDS JS, CANNON GW, HAYDEN CL, et al. Adherence with bisphosphonate therapy in US veterans with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(12):1864-1870. [34] OZEN G, KAMEN DL, MIKULS TR, et al. Trends and Determinants of Osteoporosis Treatment and Screening in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Compared to Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018;70(5):713-723. [35] TANDON V, DE LA VEGA L, BANERJEE S. Emerging roles of DYRK2 in cancer. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100233. [36] HE D, ZHENG S, CAO J, et al. CircCOX6A1 suppresses osteogenic differentiation and aggravates osteoporosis via miR-512-3p/DYRK2 axis. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):636. [37] GUTERMAN-RAM G, PESIC M, ORENBUCH A, et al. Dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 regulates osteoclast fusion in a cell heterotypic manner. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(1):617-629. |
| [1] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [2] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [3] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [4] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [5] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [6] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [7] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [8] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [9] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [10] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [11] | Zhou Jian, Zhang Tao, Zhou Weili, Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Shen Jie, Qian Li, Lu Ming. Effects of resistance training on quadriceps mass and knee joint function in patients with osteoporosis and sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1081-1088. |
| [12] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [13] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [14] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [15] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||