Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1311-1319.doi: 10.12307/2026.045
Previous Articles Next Articles
Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis
Liu Fengzhi1, Dong Yuna2, Tian Wenyi1, Wang Chunlei3, Liang Xiaodong1, Bao Lin4
- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Laizhou People’s Hospital, Laizhou 261400, Shandong Province, China; 3Wang Orthopaedic Hospital in Taian, Taian 271000, Shandong Province, China; 4The 960 Hospital of the Joint Logistics Support Force of the Chinese PLA, Jinan 250031, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-03Accepted:2025-02-15Online:2026-02-18Published:2025-06-28 -
Contact:鲍霖,主管技师,中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九六〇医院,山东省济南市 250031 通讯作者:梁晓东,博士,副教授,硕士生导师,山东中医药大学中医学院,山东省济南市 250355 https://orcid.org/0009-0006-6374-9512 (刘凤芝) -
About author:刘凤芝,女,山东省菏泽市人,汉族,山东中医药大学在读硕士,主要从事中药学方面的研究。
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
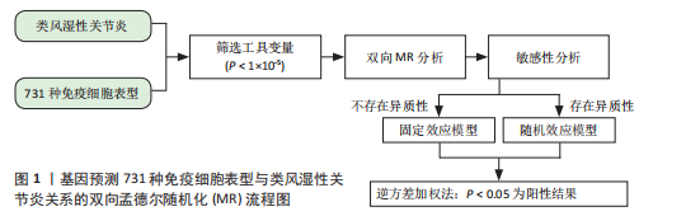
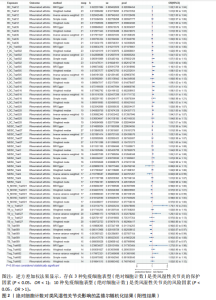
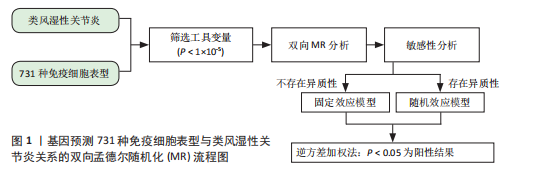
通过双样本孟德尔随机化分析,在Cochran’s Q检验的P > 0.05时,使用固定效应模型IVW估计免疫细胞特征与类风湿性关节炎之间的因果关系,发现共有68种免疫细胞表型与类风湿性关节炎存在因果关系,其中绝对细胞计数 13例、中位荧光强度 40例、形态学特征2例、相对细胞计数 13例。根据细胞分类,此次研究发现有15种B细胞、12种经典树突状细胞、9种成熟阶段T细胞(Maturation stages of T cell)、6种单核细胞(Monocyte)、7种髓系细胞(Myeloid cell)、6种TBNK细胞 (淋巴细胞亚群中的T细胞、B细胞和自然杀伤细胞)和13种调节性T细胞与类风湿性关节炎的发生存在因果关联。因而,此次研究根据7种免疫细胞的免疫特征将其分为4组。 2.1 绝对细胞计数对类风湿性关节炎的因果效应 如图2所示,IVW结果"
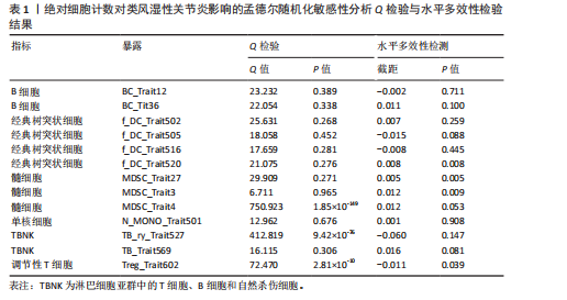
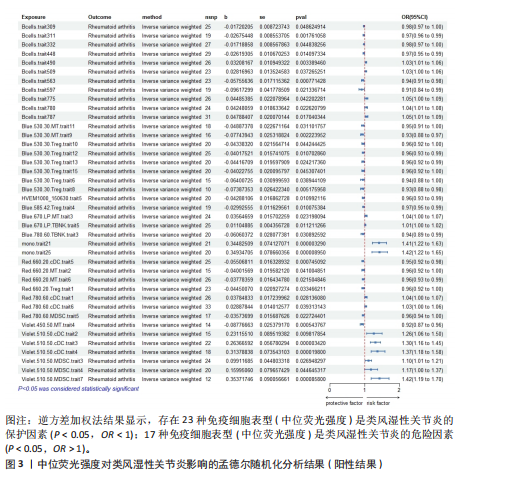
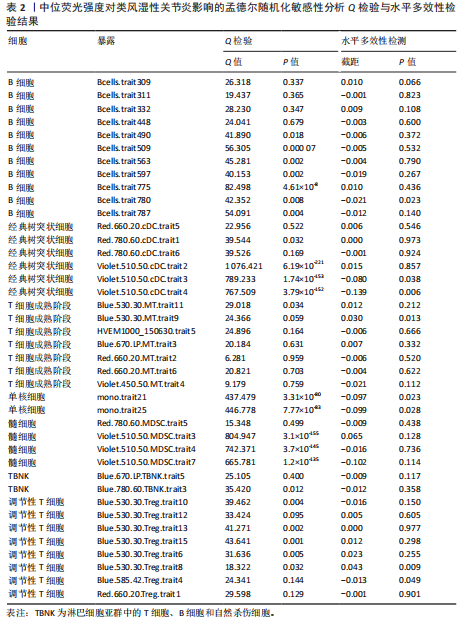
表明,13种免疫细胞表型中有3种是类风湿性关节炎的保护因素(P < 0.05,OR < 1),包括 MDSC_Trait4、N_MONO_Trait501和TB_Trait569;其他10种免疫细胞表型是类风湿性关节炎的风险因素,包括 BC_Trait12、BC_Trait36、f_DC_Trait502、f_DC_Trait505、f_DC_Trait516、f_DC_Trait520、MDSC_Trait27、MDSC_Trait3、TB_ry_Trait527 和 Treg_Trait602。 表1列出了敏感性分析的异质性检验和水平多效性分析结果。结果表明,除 MDSC_Trait4、TB_ry_Trait527 和 Treg_Trait602 存在强异质性(P远< 0.05)外,其他数据均不存在水平多效性,因此需要舍弃这些结果。 2.2 中位荧光强度对类风湿性关节炎的因果效应 如图3所示,IVW结果表明,40种免疫细胞表型中有23种是类风湿性关节炎的保护因素(P < 0.05,OR < 1);其他17个表型是类风湿性关节炎的危险因素(P < 0.05,OR > 1)。 表2列出了敏感性分析的异质性检验和水平多效性分析结果。结果显示,Bcells.trait780、Violet.510.50.cDC.trait3、Violet.510.50.cDC.trait4、Blue.530.30.MT.trait9、mono.trait21 mono.trait25、Blue.530.30.Treg.trait8和Blue.585.42.Treg.trait4 具有水平多重相关性,被排除在外。23种免疫细胞表型,如Bcells.trait490、Bcells.trait509等,具有很强的异质性(P < 0.05),因此被剔除。综合敏感性分析的结果,发现中位荧光强度中有15种免疫细胞表型与类风湿性关节炎的因果关系具有很强的可信度,包括B细胞Bcells.trait309、Bcells. trait311、Bcells.trait332和Bcells.trait448;cDC细胞Red.660.20.cDC.trait5 和 Red.780.60.cDC.trait6。T细胞的成熟阶段HVEM1000_150630.trait5、Blue.670.LP.MT.trait3、Red.660.20.MT.trait2、Red.660.20.MT.trait6和Violet.450.50.MT.trait4;髓系细胞Red.780.60.MDSC.trait5;TBNK细胞Blue.670.LP.TBNK.trait5;调节性T细胞Blue.530.30.Treg.trait12和"
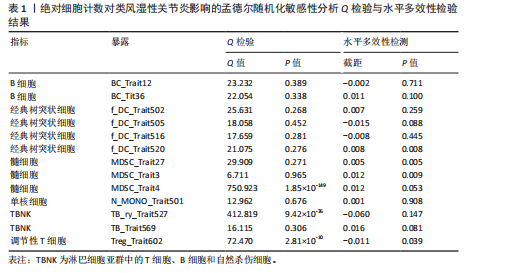
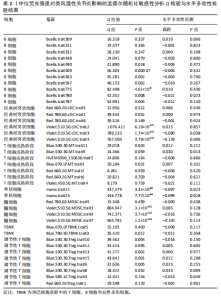
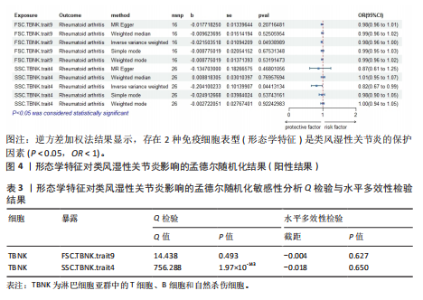
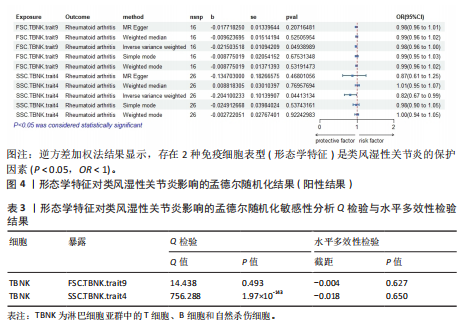
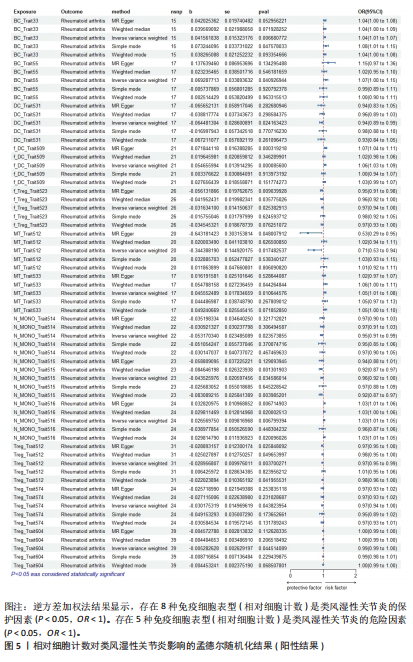
Red.660.20.Treg.trait1。具体因果关系如图2所示。 2.3 形态学特征对类风湿性关节炎的因果关系 如图4所示,IVW结果表明,形态学特征组的2种免疫细胞表型都是类风湿性关节炎的保护因素(P < 0.05,OR < 1)。 敏感性分析的异质性检验和横向多重共线性分析结果见表3。结果显示,除 SSC.TBNK.trait4 存在强异质性(P=1.97×10-143 < 0.05)外,其他数据均不存在水平多效性,因此需要舍弃这些结果。 2.4 相对细胞计数对类风湿性关节炎的因果效应 如图5所示,IVW 结果表明,13种免疫细胞表型中有8种是类风湿性关节炎的保护因素(P < 0.05,OR < 1);其余5种是类风湿性"
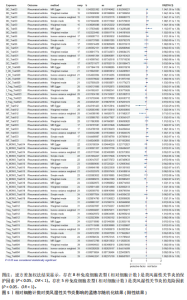
关节炎的危险因素(P < 0.05,OR > 1),包括BC_Trait33、BC_Trait55、f_DC_Trait509、MT_Trait533和N_MONO_Trait516。 敏感性分析的异质性检验和水平多效性分析结果如表4所示。结果表明,除了BC_Trait55、f_DC_Trait509、MT_Trait512和Treg_Trait604存在较强的异质性(P < 0.05),需要舍弃这些结果外,其他数据不存在水平多效性。 2.5 类风湿性关节炎对免疫细胞表型的因果效应 表5显示了IVW通过7组免疫细胞对类风湿性关节炎进行基因预测的结果,结果表明以下20种免疫细胞表型与类风湿性关节炎的发生呈正相关(OR > 1,P < 0.05),包括经典树突状细胞Violet.510.50.cDC.trait3、Violet.510.50.cDC.trait4、Violet.510.50.cDC.trait2和DC_Trait533;T细胞的成熟阶段MT_Trait513;单核细胞mono.trait25、mono.trait21、mono.trait54、mono.trait42、mono.trait50、mono.trait53和mono.trait16;髓系细胞Violet.510.50.MDSC.trait7、Violet. 510.50.MDSC.trait5和Violet.510.50.MDSC.trait4;TBNK 细胞f_MONO_Trait504、f_MONO_Trait503、TB_ry_Trait513、f_MONO_Trait505和RATIO_CD4_CD8B。其中,类风湿性关节炎的发病率会降低免疫细胞表型的浓度(OR < 1,P < 0.05),包括Treg细胞 Violet.510.50.Treg.trait2、Violet.510.50.Treg.trait5、Blue.530.30.Treg.trait21、Blue.530.30.Treg.trait11、Blue.530.30.Treg.trait12、Blue.530.30.Treg.trait15、Violet.510.50.Treg.trait3、Blue.530.30.Treg.trait13、Blue.530.30.Treg.trait14、Blue.530.30.Treg.trait8、Blue.530.30.Treg.trait7、Blue.530.30.Treg.trait22和Violet.510.50.Treg.trait4;B 细胞Bcells.trait514、Bcells.trait255、BC_Trait44、BC_Trait67、BC_Trait43和Bcells.trait282;T细胞的成熟阶段MT_Trait545和Blue.530.30. MT.trait11;髓系细胞Red.780.60.MDSC.trait5、Red.780.60.MDSC.trait14和Red.780.60.MDSC.trait7。结果显示,孟德尔随机化分析结果显示存在正向"
| [1] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, MCINNES IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet(London, England). 2016;388(10055):2023-2038. [2] HUANG J, FU X, CHEN X, et al. Promising Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:686155. [3] SMITH MH, BERMAN JR. What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? JAMA. 2022; 327(12):1194. [4] DERKSEN VFAM, HUIZINGA TWJ, VAN DER WOUDE D. The role of autoantibodies in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 2017;39(4): 437-446. [5] VAN DELFT MAM, HUIZINGA TWJ. An overview of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102392. [6] HU H, LUAN L, YANG K, et al. Burden of rheumatoid arthritis from a societal perspective: A prevalence-based study on cost of this illness for patients in China. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20(2):e13028. [7] VENETSANOPOULOU AI, ALAMANOS Y, VOULGARI PV, et al. Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis: genetic and environmental influences. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2022;18(9):923-931. [8] EDILOVA MI, AKRAM A, ABDUL-SATER AA. Innate immunity drives pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed J. 2021;44(2): 172-182. [9] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2): 905. [10] BROCK J, BASU N, SCHLACHETZKI JCM, et al. Immune mechanisms of depression in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023;19(12):790-804. [11] KAUR J, CAIRNS E, BARRA L. Restoring Balance: Immune Tolerance in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2023;50(8): 991-1001. [12] SHUAI Z, ZHENG S, WANG K, et al. Reestablish immune tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022; 13:1012868. [13] O’NEIL LJ, KAPLAN MJ. Neutrophils in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Breaking Immune Tolerance and Fue ling Disease. Trends Mol Med. 2019;25(3):215-227. [14] GORONZY JJ, SHAO L, WEYAND CM. Immune aging and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2010;36(2):297-310. [15] TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology in 2014: Two-faced immunology-from osteogenesis to bon e resorption. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(2):74-76. [16] DENG Z, ZHANG Q, ZHAO Z, et al. Crosstalk between immune cells and bone cells or chondrocytes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021; 101(Pt A):108179. [17] SEIFRITZ T, BRUNNER M, CAMARILLO RETAMOSA E, et al. BRD3 Regulates the Inflammatory and Stress Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts. Biomedicines. 2023;11(12):3188. [18] FILIPPIN LI, VERCELINO R, MARRONI NP, et al. Redox signalling and the inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;152(3):415-422. [19] CUPPEN BVJ, FU J, VAN WIETMARSCHEN HA, et al. Exploring the Inflammatory Metabolomic Profile to Predict Response to TNF-α Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PloS one. 2016;11(9):e0163087. [20] ATZENI F, ANTIVALLE M, PALLAVICINI FB, et al. Predicting response to anti-TNF treatment in rheumatoid arthritis pati ents. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8(5):431-437. [21] SANDERSON E, GLYMOUR MM, HOLMES MV, et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2022;2:6. [22] LI W, XU JW, CHAI JL, et al. Complex causal association between genetically predicted 731 immunocyte phenotype and osteonecrosis: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Int J Surg. 2024;110(6):3285-3293. [23] ORRÙ V, STERI M, SIDORE C, et al. Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and i nform therapy. Nat Genet. 2020;52(10):1036-1045. [24] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature. 2023;613(7944):508-518. [25] LI W, CHAI JL, LI Z, et al. No evidence of genetic causality between diabetes and osteonecrosis: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):970. [26] MACHIELA MJ, CHANOCK SJ. LDlink: a web-based application for exploring population-specific haplotype structure and linking correlated alleles of possible functional variants. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(21):3555-3557. [27] MORGAN SL. Counterfactuals, Causal Effect Heterogeneity, and the Catholic School Effect on Learning. Sociol Educ. 2001;74(4):341-374. [28] 许崇彦, 叶晨, 陈洋丽, 等. 基于孟德尔随机化探讨免疫细胞与散发型克雅氏病的因果关系[J]. 生物医学,2024,14(4): 624-636. [29] MEYER A, PARMAR PJ, SHAHRARA S. Significance of IL-7 and IL-7R in RA and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2022; 21(7):103120. [30] GORONZY JJ, ZETTL A, WEYAND CM. T cell receptor repertoire in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Rev Immunol. 1998;17(5-6):339-363. [31] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2): 905. [32] RAO DA, GURISH MF, MARSHALL JL, et al. Pathologically expanded peripheral T helper cell subset drives B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2017;542(7639):110-114. [33] GAO Y, CAI W, ZHOU Y, et al. Immunosenescence of T cells: a key player in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Res. 2022; 71(12):1449-1462. [34] KOTSCHENREUTHER K, YAN S, KOFLER DM. Migration and homeostasis of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:947636. [35] DELGADO-ARÉVALO C, CALVET-MIRABENT M, TRIGUERO-MARTINEZ A, et al. POS0367 NLRC4 and FC-γ-R crosstalk on cd1c+ dendritic cells differentially contributes to rheumatoid arthritis immunopathology. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:413. [36] WANG Z, ZHANG J, AN F, et al. The mechanism of dendritic cell-T cell crosstalk in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):193. [37] TAI Y, WANG Q, KORNER H, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of T Cells Activation by Dendritic Cells in Autoimmune Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:642. [38] YU MB, LANGRIDGE WHR. The function of myeloid dendritic cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37(7): 1043-1051. [39] SINGH A, BEHL T, SEHGAL A, et al. Mechanistic insights into the role of B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;99:108078. [40] WU F, GAO J, KANG J, et al. B Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Treatment Prospects. Front Immunol. 2021;12:750753. [41] KARMAKAR U, VERMEREN S. Crosstalk between B cells and neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunology. 2021; 164(4):689-700. [42] XIE Y, DING J, GAO J, et al. Triptolide reduces PD-L1 through the EGFR and IFN-γ/IRF1 dual signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;118:109993. |
| [1] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [2] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [3] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [4] | Bao Zhuoma, Hou Ziming, Jiang Lu, Li Weiyi, Zhang Zongxing, Liu Daozhong, Yuan Lin. Effect and mechanism by which Pterocarya hupehensis skan total flavonoids regulates the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 816-823. |
| [5] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [6] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [7] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [8] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [9] | Xie Peisen, Guan Zhenpeng, Wei Xianjie, Zhang Keshi, Kang Qingyuan, Xiao Wentao, Guo Xiaoshuai. Xie Peisen, Guan Zhenpeng, Wei Xianjie, Zhang Keshi, Kang Qingyuan, Xiao Wentao, Guo Xiaoshuai [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 375-383. |
| [10] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [11] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [12] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [13] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [14] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [15] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||