Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1558-1568.doi: 10.12307/2026.593
Previous Articles Next Articles
Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis
Huang Jie1, Zeng Hao1, Wang Wenchi1, Lyu Zhucheng1, Cui Wei2
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-01-13Accepted:2025-03-07Online:2026-02-28Published:2025-07-18 -
Contact:Cui Wei, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Huang Jie, MS candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Guipai Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance Innovation Team, No. 2022A004 (to CW [project participant]); Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Self-Funded Research Project, No. 20210579 (to CW); Project of Chinese National Medical Association, No. 2020MZ-040701 (to CW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
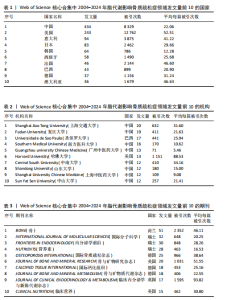
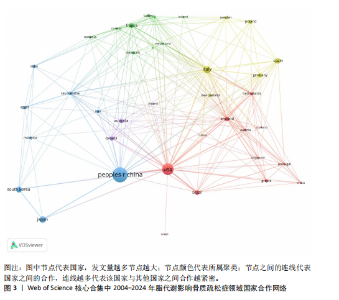
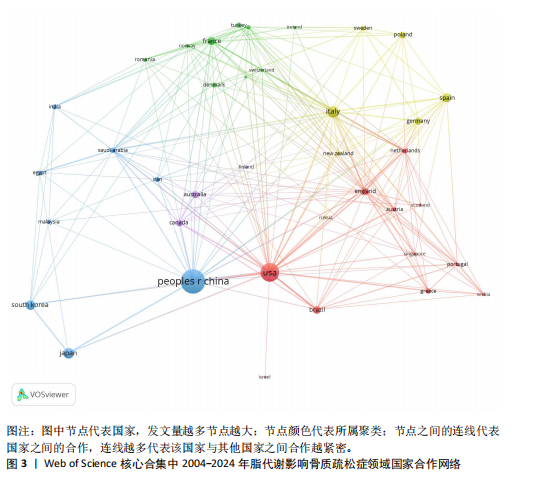
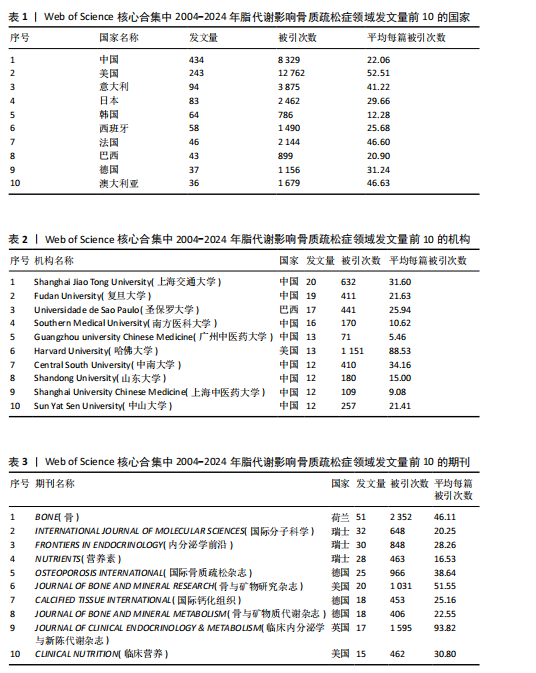
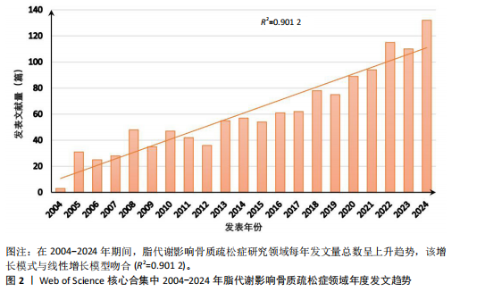
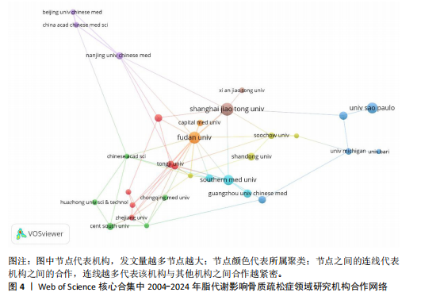
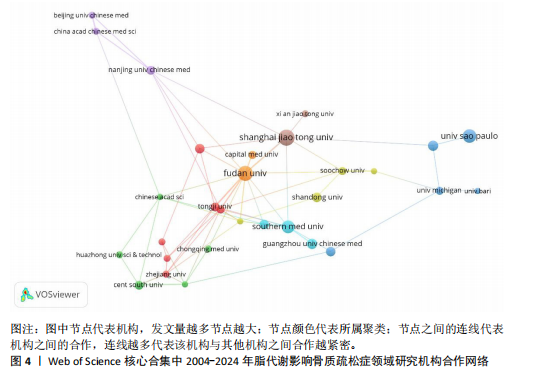
2.1 脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域年度发文量分析 数据统计显示,在脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域发文量最少的年份为2004年(3篇),最多的年份为2024年(132篇,因研究截止时间为2024-12-01,故发文总量仍有波动),在20年间呈显著增长的趋势。在2005-2012年期间发文量开始增加,但发文量仍保持在较低水平(均低于50篇),从2013年开始,每年发文量开始持续上升,在2015年和2019年有轻微向下波动,但发文量也均超过50篇,并且在2022-2024期间均保持在较高水平,于2024年达到峰值,见图2。表明脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域的科学研究在不断增加,尤其在近3年保持较高的热度,并且呈持续上升的趋势。 2.2 脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域国家分布 共有67个国家的研究人员参与了脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域论文的发表,其中,中国是发文量最高的国家(发文量为434篇),其次是美国(发文量为243篇),第三是意大利(发文量为94篇);论文总被引用次数排名第一的是美国,为12 762次,其次是中国的8 329次;发文量前10的国家中,篇均被引次数最多的是美国52.51次,其次是澳大利亚的46.63次,中国为22.06次,排名第8,见表1。结果显示,虽然中国在发文数量上领先于其他国家,但是在文章质量上略微低于其他国家,这可能与科研环境、投入资金和人为等因素有关。根据图谱显示,目前该领域的研究以中国和美国为主导,与其他国家相比较出现断层情况,但是,随着研究的不断深入,逐渐建立了以中美为主的合作研究网络,这将会减小各个国家在该领域的研究断层,见图3。 2.3 脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域发文机构分析 根据数据统计,截至2024年12月,共有1 905个科研机构发表了脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域的文章。在发文量前10的机构中,有8个来自中国,余下的2个机构分别是来自巴西的圣保罗大学(发文量为17篇)和美国的哈佛大学(发文量为13篇),值得注意的是,这两所大学虽然发文量相对中国的机构较少,但其被引次数均在前三,尤其是哈佛大学,被引次数为1 151次,说明其文章质量较其他机构高,为大多数学者所认同,见表2。中国的科研机构发文量的前3名分别是上海交通大学(发文量为20篇)、复旦大学(发文量为19篇)和南方医科大学(发文量为16篇),虽然占据主要地位,但仍需要加强文章质量的把控。同时,据图谱分析可知,目前在脂代谢影响骨质疏松症研究领域国内外科研机构的合作相对较少,应当加强国内外机构间的相互合作,见图4。 2.4 脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域发文期刊分析 对脂代谢影响骨质疏松症研究领域的发表期刊进行研究发现,共有52个相关期刊出版了脂代谢影响骨质疏松症相关的文献。在发文量前10的期刊中,8个来自欧洲的期刊,余下2个来自美国,中国的期刊未跻身前10,这表明在该领域的研究论文发表中以欧美国家期刊为主要阵地,国内的期刊与欧美国家之间还存在一定的差距,见表3。荷兰的《BONE(骨)》是发文量最多的期刊,为51篇,总"
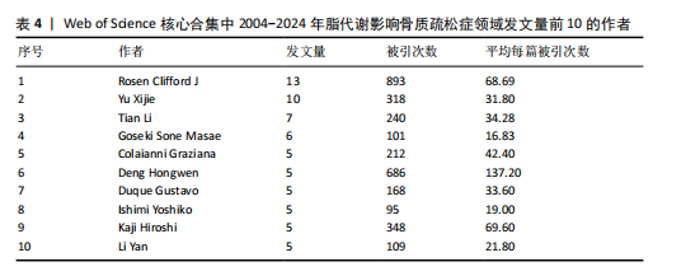
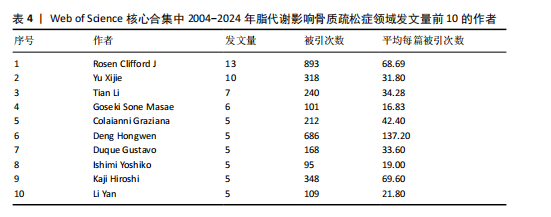
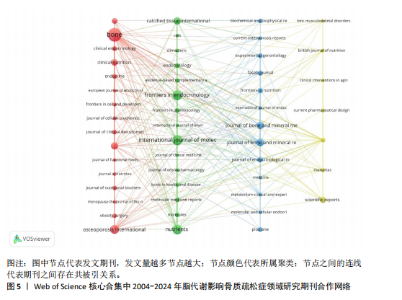
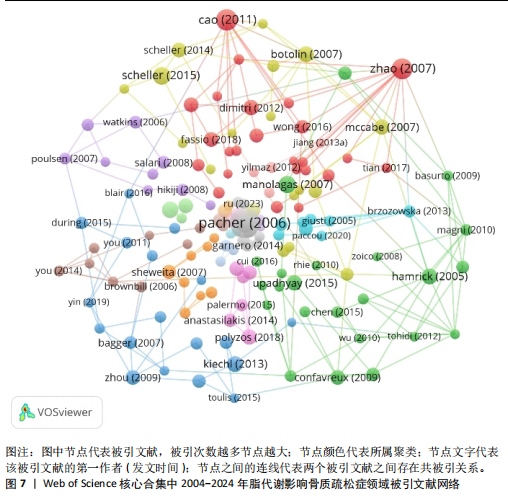
被引次数为2 352次,篇均被引次数为46.11,说明它是目前国际上该领域的权威杂志之一。值得注意的是,英国的《JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY & METABOLISM(临床内分泌学与新陈代谢杂志)》发文量虽然仅排名第9,但是其总被引次数(1 595次)和篇均被引次数(93.82次)均在前列,这在一定程度上揭示了该期刊受到大多数学者的普遍关注和认同,代表着未来研究的趋势。另外,根据图谱可知,国际上已经形成了以《BONE(骨)》《OSTEOPOROSIS INTERNATIONAL(国际骨质疏松杂志)》和《INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES(国际分子科学)》等期刊为主的欧美国家合作网络体系,而中国期刊在国际上的合作则存在不足,更应该加强国内外的合作联系,见图5。 2.5 脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域研究作者合作分析 普莱斯定律是指在某一领域的发表文献数量中,有一半的论文为一群高产作者所撰写,这些作者的数量约等于全部作者总数的平方根,计算公式是N=0.749×(Nmax)1/2,Nmax为该领域发文量最多作者的发文数量,因此N=4.86,即核心作者发文量应≥5篇。使用VOSviewer分析发现,汇总发文量前10的作者,其中Rosen发文量为13篇,排名第一,被引次数为893次,表明他在该领域研究的突出贡献;Deng虽然只发表了5篇文献,但文献篇均被引次数高达137.2次,可见该作者的研究和文章价值之高,见表4。另外,有些作者发文量虽低,但篇均被引次数却显著高于其他作者,如Gaudio(篇均被引次数93.33次)、Goulis(篇均被引次数84.66次)、Kawao(篇均被引次数83.33次)等,说明这些研究者的文章被大多数人认同,含金量较高,见表4。作者合作图谱显示,目前在脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域,研究者之间较为分散,主要是以本土研究员之间的合作为主,国际合作较少,尚未形成以某一研究者为主的国际合作研究团队,见图6。未来应当深化国际"

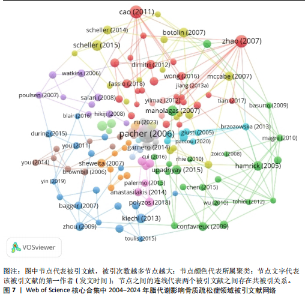
合作和学术交流,构建国际研究团队,博采众长,发挥其独有优势。 2.6 脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域高被引文献分析 文献的被引次数可以在一定程度上代表其学术成果在行业内的影响力和含金量,同时也能反映该领域内的研究热点和未来的趋势,通过对脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域高被引文献分析和文献被引图谱可知,在过去20年间,PACHER于2006年发表的论文总被引次数为1 581次,与第二名CAO于2011年发表的文章(总被引次数541次)相比,具有显著差异,形成了以PACHER所发表文献为核心的文献引用网络,见图7,这说明PACHER的研究不仅仅具有极高的价值,而且是该领域内的先行者和领军人物。 PACHER等[9]的综述探讨了内源性大麻素系统作为药物治疗的目标和现状,他总结得出:通过调节大麻素系统能够有效调节人体能量代谢,改善人体代谢相关疾病的发生,与此同时,大麻素拮抗剂有益于骨质疏松,能够调节人体骨量。CAO[10]认为肥胖通过多种机制影响骨骼代谢,例如由于成骨细胞和脂肪细胞都来源于间充质干细胞,脂肪细胞过多堆积则抑制成骨分化和骨形成;肥胖能促进体内慢性炎症的发生,上调炎细胞因子,从而促进破骨细胞活性和骨吸收;高脂饮食影响肠道钙吸收,影响骨骼形成。ZHAO等[11]通过测量2个种族之间的全身脂肪含量、脂肪百分比、体质量指数和骨量等数据,得出结论:脂肪量与骨量之间呈负相关,脂肪量的增加对骨量是无益的。VITALE等[12]对具有雌激素活性的异黄酮进行综述并表明,异黄酮对前列腺癌、心血管疾病和骨质疏松具有预防和缓解症状的作用,而不同的存在形式会对异黄酮的生物活性具有影响。SCHELLER等[13]通过动物实验揭示,骨髓脂肪细胞的发育、调节、脂肪细胞的大小等存在区域特异性差异,而且骨质疏松与骨髓脂肪细胞不饱和度的减少存在关联。MORRIS[14]通过详细综述7种Sirtuins蛋白发现,激活并提高"

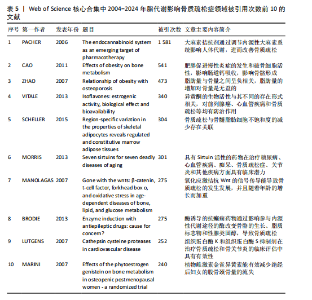
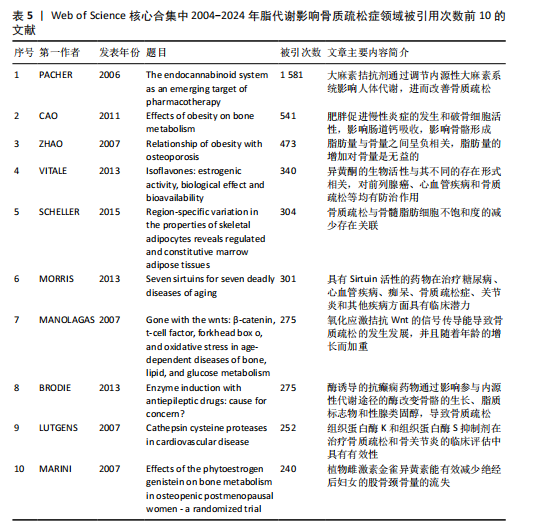
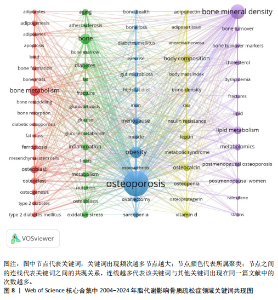
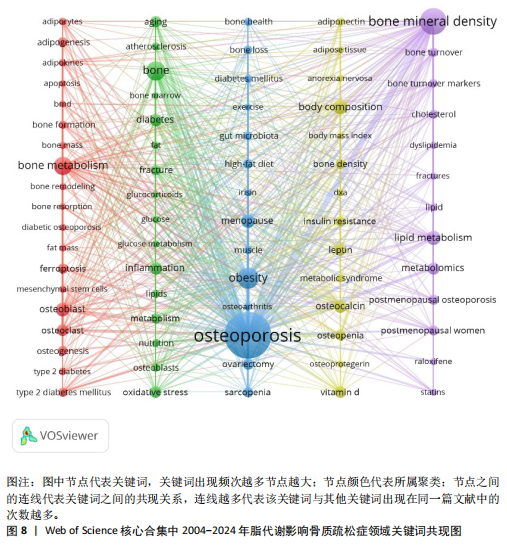
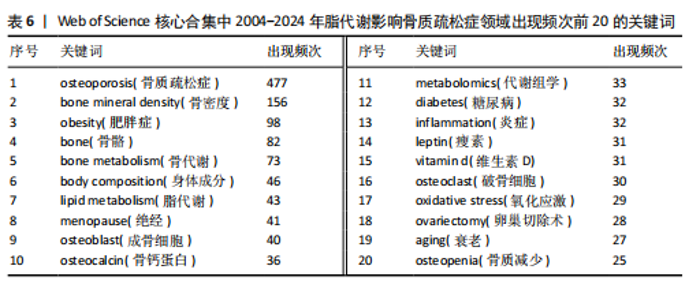
Sirtuin活性的药物在治疗糖尿病、心血管疾病、痴呆、骨质疏松症、关节炎和其他疾病方面具有临床潜力,但在癌症中激活该蛋白家族却是有害的。MANOLAGAS等[15]通过串联与年龄相关的氧化应激和叉头框蛋白O、Wnt/β-catenin信号传导、骨质疏松及代谢综合征等的特征推测:随着年龄的增长,氧化应激拮抗Wnt的信号传导不仅能导致骨质疏松症的发生发展,同时还可能导致相关的疾病发生,如高脂血症、动脉粥样硬化、胰岛素抵抗等。BRODIE等[16]认为常用的酶诱导抗癫痫药物具有广泛的不良反应,能影响多种参与内源性代谢途径的酶,改变骨骼的生长、脂质标志物和性腺类固醇,导致骨质疏松、心血管疾病和性功能障碍等合并症的发生。LUTGENS等[17]总结得出,组织蛋白酶K和组织蛋白酶S缺乏能减轻动脉粥样硬化,同时他们的抑制剂在治疗骨质疏松和骨关节炎的临床评估中具有有效性。MARINI等[18]通过一项随机试验揭示了植物雌激素金雀异黄素对绝经后妇女的股骨颈密度有积极作用,能减少骨量的流失。见表5。 2.7 脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域关键词分析 2.7.1 关键词共现分析 关键词是一篇文章的内容和结论的高度概括和凝练,有利于读者准确快速地了解文章的主题,是论文写作中至关重要的一环。利用VOSviewer总结出该领域2 534个关键词并构建了关键词共现网络可知,检索词骨质疏松症和脂代谢分别出现了477次和43次,排名第1和第7;此外,出现频次最高的关键词分别是骨密度、肥胖症、骨骼、骨代谢、身体成分,属于该领域内的热门研究话题,见表6和图8。随着社会物质条件的改善,肥胖已逐渐成为现代人的一大困扰,而脂代谢紊乱是肥胖发生的主要因素,在引起肥胖发生的同时还对骨密度和骨代谢起着重要影响,因此,越来越多的研究人员对脂代谢影响骨质疏松症之间的关系展开不同程度的研究。 2.7.2 关键词聚类分析 使用Citespace软件对脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域的关键词进行聚类分析并生成聚类图谱,该聚类模块的值Q=0.335 6,平均轮廓值S=0.676 8,由于Q > 0.3且S > 0.5,可以认为关键词聚类结构显著且聚类结果同质性可。共形成#0 bone mineral density (骨密度)、#1 ferroptosis(铁死亡)、#2 gut microbiota(肠道菌群)、#3 bone marrow(骨髓)、#4 postmenopausal women (绝经后妇女)、#5 lipid metabolism(脂代谢)、#6 postmenopausal osteoporosis(绝经后骨质疏松)7个有意义的聚类,见图9。各聚类板块间连线密集,说明各聚类间存在密切联系,其中,聚类#0 bone mineral density(骨密度)是最受关注的聚类,骨质疏松症患者的骨密度是该领域的热点,聚类#1、#2、#3、#5主要是讨论与骨质疏松"

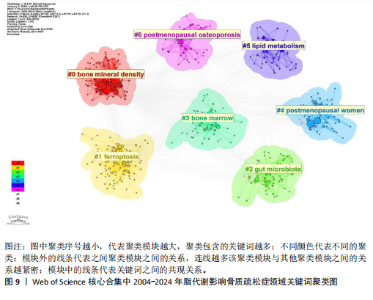
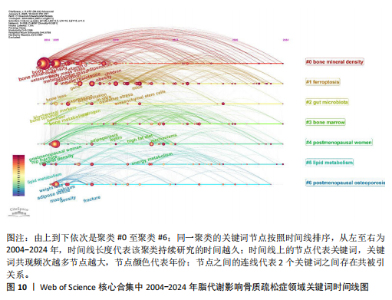
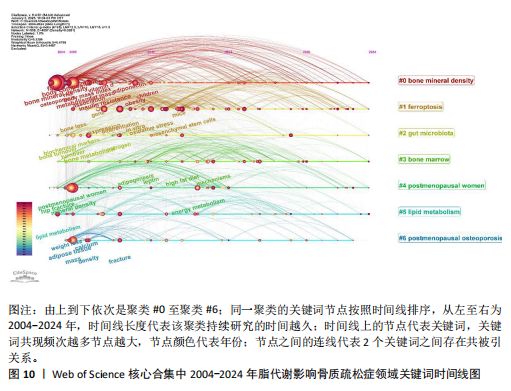
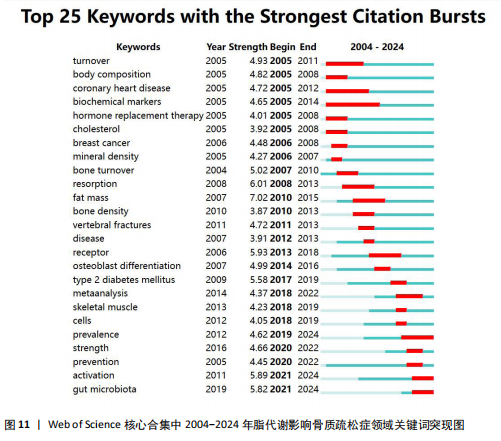
症相关并能对其产生影响的机制或途径,聚类#4、#6则表明骨质疏松症的多发人群为绝经后妇女。 2.7.3 关键词时间线分析 根据聚类分析生成脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域的关键词时间线图,可按照时间线观察不同聚类的研究进展。如图10所示,#0 bone mineral density(骨密度)是持续时间最长的聚类,时间跨度从2004年延续至2024年,该聚类下的body composition(身体成分)、fat(脂肪)和body mass index(体重指数)等与脂代谢相关的关键词与#0 bone mineral density(骨密度)的关系密切,被广泛研究。而#6 postmenopausal osteoporosis(绝经后骨质疏松)在近年来的研究热度有所下降;此外,根据关键词聚类图和关键词时间线图可以推测,ferroptosis(铁死亡)、gut microbiota(肠道菌群)和lipid metabolism(脂代谢)是该领域中的最新研究前沿。 2.7.4 关键词突现分析 关键词突现图主要分析在某一时间段内该领域中的研究焦点话题。如图11所示,在脂代谢影响骨质疏松症领域关键词突现强度最大的是fat mass(脂肪量),主要在2010-2015年间为广大学者所研究和关注;突现时间最长的关键词是biochemical markers(生物化学标记物);prevention(预防)、strength(强度)、meta analysis(荟萃分析)3个关键词中,前两者在2020-2022年见显现了突现强度,而后者在2018-2022年显现,三者出现时间较晚,这表明在未来可能会有更多的相关研究,并且以荟萃分析的形式出现;目前仍处于有意义的突现关键词为prevalence(流行)、activation(激活)、gut microbiota(肠道菌群),随着时间的推移,该领域的研究由骨质疏松症与脂代谢本身的机制或影响因素转移到与之相联系的研究领域,研究人员更加注重由细节到整体的研究。"

| [1] BETANCUR JF, PEREZ LE, BOLANOS-LOPEZ JE, et al. High and very high risk of osteoporotic fracture in Colombia, 2003-2022: identifying diagnostic and treatment gaps. Arch Osteoporos. 2024;19(1):52. [2] SUN C, HE W, WANG L, et al. Studies on the Role of MAP4K2, SPI1, and CTSD in Osteoporosis. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024.doi:10.1007/s12013-024-01621-1. [3] ZHANG J, HU W, ZOU Z, et al. The role of lipid metabolism in osteoporosis: Clinical implication and cellular mechanism. Genes Dis. 2024;11(4):101122. [4] LIU H, LIU S, JI H, et al. An adiponectin receptor agonist promote osteogenesis via regulating bone-fat balance. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(6):e13035. [5] NATESAN V, KIM SJ. Lipid Metabolism, Disorders and Therapeutic Drugs-Review. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2021;29(6):596-604. [6] WANG X, ZHANG C, ZHAO G, et al. Obesity and lipid metabolism in the development of osteoporosis (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2024;54(1):61. [7] GUO J, HUANG Q, ZHOU Y, et al. Typing characteristics of metabolism-related genes in osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:999157. [8] BUKAR UA, SAYEED MS, RAZAK SFA, et al. A method for analyzing text using VOSviewer. MethodsX. 2023;11:102339. [9] PACHER P, BÁTKAI S, KUNOS G. The endocannabinoid system as an emerging target of pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol REV. 2006;58(3):389-462. [10] CAO JJ. Effects of obesity on bone metabolism. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;6:30. [11] ZHAO L, LIU Y, LIU P, et al. Relationship of obesity with osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(5):1640-1646. [12] VITALE DC, PIAZZA C, MELILLI B, et al. Isoflavones: estrogenic activity, biological effect and bioavailability. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2013;38(1):15-25. [13] SCHELLER EL, DOUCETTE CR, LEARMAN BS, et al. Region-specific variation in the properties of skeletal adipocytes reveals regulated and constitutive marrow adipose tissues. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7808. [14] MORRIS BJ. Seven sirtuins for seven deadly diseases of aging. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;56:133-171. [15] MANOLAGAS SC, ALMEIDA M. Gone with the Wnts:: β-catenin, T-cell factor, forkhead box O, and oxidative stress in age-dependent diseases of bone, lipid, and glucose metabolism. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21(11):2605-2614. [16] BRODIE MJ, MINTZER S, PACK AM, et al. Enzyme induction with antiepileptic drugs: cause for concern? Epilepsia. 2013;54(1): 11-27. [17] LUTGENS SPM, CLEUTJENS KBJM, DAEMEN MJAP, et al. Cathepsin cysteine proteases in cardiovascular disease. FASEB J. 2007;21(12):3029-3041. [18] MARINI H, MINUTOLI L, POLITO F, et al. Effects of the phytoestrogen genistein on bone metabolism in osteopenic postmenopausal women: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146(12):839-847. [19] JIANG Q, FENG Q. Editorial: Aging and health in China. Front Public Health. 2022; 10:998769. [20] HUANG L, WANG X, ZHOU W, et al. Hydrolyzed egg yolk peptide alleviates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by regulating lipid metabolism. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025;292:139223. [21] KIM D, KO S. Common Regulators of Lipid Metabolism and Bone Marrow Adiposity in Postmenopausal Women. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023;16(2):322. [22] HAN H, LI R, FU D, et al. Correlation between bone density, bone metabolism markers with lipid metabolism markers and body mass index. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):162. [23] WANG S, QIU Y, TANG C, et al. Early changes of bone metabolites and lymphocyte subsets may participate in osteoporosis onset: a preliminary study of a postmenopausal osteoporosis mouse model. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024; 15:1323647. [24] LIU T, YU H, WANG S, et al. Chondroitin sulfate alleviates osteoporosis caused by calcium deficiency by regulating lipid metabolism. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2023; 20(1):6. [25] ZHONG ZQ, CHEN YL, RUAN XL, et al. Lipidomics analysis of bone marrow in a mouse model of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024; 246:116212. [26] DENG D, PAN C, WU Z, et al. An Integrated Metabolomic Study of Osteoporosis: Discovery and Quantification of Hyocholic Acids as Candidate Markers. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:725341. [27] KOU J, HE C, CUI L, et al. Discovery of Potential Biomarkers for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Based on Untargeted GC/LC-MS. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:849076. [28] LIU L, LE PT, STOHN JP, et al. Calorie restriction in mice impairs cortical but not trabecular peak bone mass by suppressing bone remodeling. J Bone Miner Res. 2024; 39(8):1188-1199. [29] NANDY A, HELDERMAN RCM, THAPA S, et al. Enhanced fatty acid oxidation in osteoprogenitor cells provides protection from high-fat diet induced bone dysfunction. J Bone Miner Res. 2025;40(2):283-298. [30] HE H, ZHANG Y, SUN Y, et al. Folic Acid Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Osteoporosis Through the AMPK Signaling Pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 791880. [31] ZHANG L, WANG XZ, ZHANG X. Modulation of Intestinal Flora by Dietary Polysaccharides: A Novel Approach for the Treatment and Prevention of Metabolic Disorders. Foods. 2022;11(19):2961. [32] FENG R, WANG Q, YU T, et al. Quercetin ameliorates bone loss in OVX rats by modulating the intestinal flora-SCFAs-inflammatory signaling axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;136:112341. [33] GUO MY, LIU HJ, YU YT, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes. 2023;15(1):2190304. [34] ZHANG JJ, ZHANG QW, LIU H, et al. Soy-whey dual-protein alleviates osteoporosis of ovariectomized rats via regulating bone fat metabolism through gut-liver-bone axis. Nutrition. 2022;103-104:111723. [35] ZHANG K, YANG X, ZHAO Q, et al. Molecular Mechanism of Stem Cell Differentiation into Adipocytes and Adipocyte Differentiation of Malignant Tumor. Stem Cells Int. 2020; 2020:8892300. [36] YANG J, UEHARU H, MISHINA Y. Energy metabolism: A newly emerging target of BMP signaling in bone homeostasis. Bone. 2020;138:115467. [37] NANDY A, RICHARDS A, THAPA S, et al. Altered Osteoblast Metabolism with Aging Results in Lipid Accumulation and Oxidative Stress Mediated Bone Loss. Aging Dis. 2024;15(2):767-786. [38] ALIOLI CA, DEMESMAY L, LAURENCIN-DALACIEUX S, et al. Expression of the type 1 lysophosphatidic acid receptor in osteoblastic cell lineage controls both bone mineralization and osteocyte specification. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020;1865(8):158715. [39] LIU L, LIU H, LU X, et al. Palladium-Based Nanocomposites Remodel Osteoporotic Microenvironment by Bone-Targeted Hydrogen Enrichment and Zincum Repletion. Research (Wash D C). 2024;7:540. [40] WENG Z, YE J, CAI C, et al. Inflammatory microenvironment regulation and osteogenesis promotion by bone-targeting calcium and magnesium repletion nanoplatform for osteoporosis therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):314. [41] LIU X, SHAO J, LIAO Y, et al. Regulation of short-chain fatty acids in the immune system[J]. Front Immunol. 2023;14: 1186892. |
| [1] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [3] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [4] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [5] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [6] | Zhou Jian, Zhang Tao, Zhou Weili, Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Shen Jie, Qian Li, Lu Ming. Effects of resistance training on quadriceps mass and knee joint function in patients with osteoporosis and sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1081-1088. |
| [7] | Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [8] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [9] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [10] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [11] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [12] | Wang Meng, Lu Tan, Li Minjie, Liu Zhicheng, Guo Xiaoyong. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of anchors at different implantation depths under different bone density conditions in rotator cuff tears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 561-569. |
| [13] | Zhou Zixiang, Zhao Baoxiang. Research progress in the relationship between nontraumatic necrosis of the femoral head and lipid metabolism and its treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 680-690. |
| [14] | Xu Jiamu, Yang Cheng, Li Weimin, Wang Chunqing. Role and pathogenesis of pyroptosis and inflammatory factors in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 691-700. |
| [15] | Peng Hao, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. A visual analysis of research hotspots of H-type vessels in various bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 760-769. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||