Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 691-700.doi: 10.12307/2026.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and pathogenesis of pyroptosis and inflammatory factors in osteoporosis
Xu Jiamu1, Yang Cheng2, Li Weimin3, Wang Chunqing4
- 1School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Guizhou Hospital of Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Guiyang Fourth People's Hospital, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China; 4Department of Emergency Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-20Accepted:2025-02-06Online:2026-01-28Published:2025-07-05 -
Contact:Wang Chunqing, Associate professor, Chief physician, Department of Emergency Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Xu Jiamu, Master candidate, School of Clinical Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 82060271 and 82460300 (both to WCQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Jiamu, Yang Cheng, Li Weimin, Wang Chunqing. Role and pathogenesis of pyroptosis and inflammatory factors in osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 691-700.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
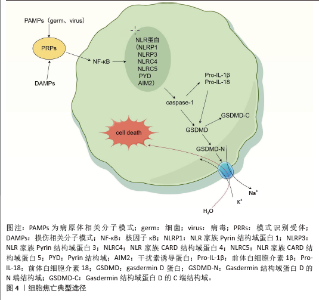
2.2 典型焦亡途径 焦亡由Caspase和Gasdermin(GSDM)家族介导,GSDM介导的焦亡是一种程序性细胞死亡机制,特征是细胞扩增最终导致细胞膜破裂,随后释放细胞内容物进一步放大炎症反应[20]。作为最具炎症性的死亡方式,焦亡可分为典型焦亡途径、非典型焦亡途径和其他GSDM介导的焦亡途径[21]。 在典型的焦亡途径中,模式识别受体可识别病原体相关分子模式或机体细胞释放的危险相关分子模式[22]。炎症信号通过细胞内核因子κB途径传递启动炎性小体的组装,在细胞内巩固为炎性小体复合物,该复合物的关键成分包括 NLR蛋白,如NLR家族pyrin结构域蛋白(NLR family pyrin domain-containing protein,NLRP)1、NLRP3、NLR家族CARD结构域蛋白4、NLR家族CARD结构域蛋白5、Pyrin 结构域及干扰素诱导蛋白等[23]。炎症小体复合物随后将前Caspase-1切割成酶活性形式[24],Caspase-1进一步处理GSDMD蛋白,将其切割成水溶性GSDMD -C端结构域和脂溶性GSDMD-N端结构域[25],n端结构域发生寡聚化,在细胞膜上形成可渗透孔。由于细胞内外钠离子和钾离子的渗透压不同,导致水通过渗透压梯度流入细胞,细胞膨胀、破裂并最终死亡[26](图4,该图由Figdraw绘制)。同时,Caspase-1切割和成熟炎症因子白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18前体,通过GSDMD孔将其释放到细胞外,细胞外炎症因子可以进一步募集免疫细胞,放大炎症反应并诱导焦亡,从而创造炎症微环境[27]。"
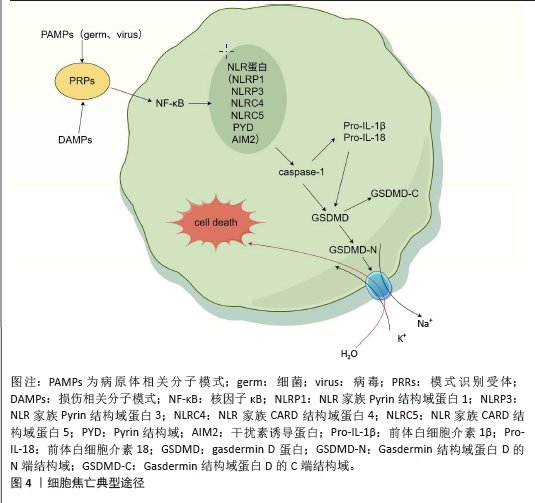
2.3 非典型焦亡途径 在非典型焦亡途径中,人类Caspase-4和Caspase-5与啮齿类Caspase-11具有同源性,均表达半胱天冬酶募集结构域。在非典型焦亡途径中,来自革兰阴性菌细胞壁的脂多糖直接被细胞质中的半胱天冬酶募集结构域识别,在干扰素g的参与下启动焦亡。细胞内胞质脂多糖通过活化的Caspase-4/5/11直接切割GSDMD,在细胞膜上形成GSDMD孔,最终导致焦亡[28](图5,该图由Figdraw绘制)。炎性Caspase—特别是人Caspase-4/5(小鼠Caspase-11)在不需要炎性小体传感器的情况下响应病原体刺激而被激活。脂多糖直接结合Caspase-4/11的半胱天冬酶募集结构域,通过寡聚物形成启动Caspase激活,一旦被激活,Caspase-4/5/11可以切割焦亡执行蛋白GSDMD,在n端产生插入细胞膜P30片段,导致细胞毒性作用[26,29]。例如,布鲁氏菌脂多糖激活Caspase-11介导的焦亡,通过杀死巨噬细胞和限制细菌存活来限制关节感染。与Caspase-1不同,Caspase-4/5/11不直接加工白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18,抑制Caspase-5并不会降低白细胞介素1β水平[29]。所以,在非典型焦亡途径里,人类 Caspase-4/5 与啮齿类 Caspase-11因同源且含CARD 结构域,能识别胞质脂多糖而活化,切割GSDMD引发焦亡,虽不加工白细胞介素1β等,却可借 GSDMD-N分化激活Caspase-1,触发炎症并影响细胞分化走向。"
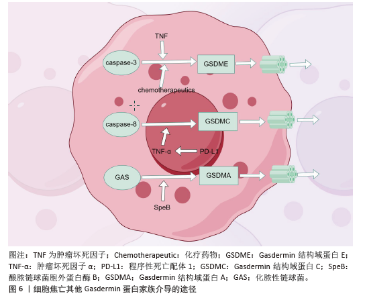
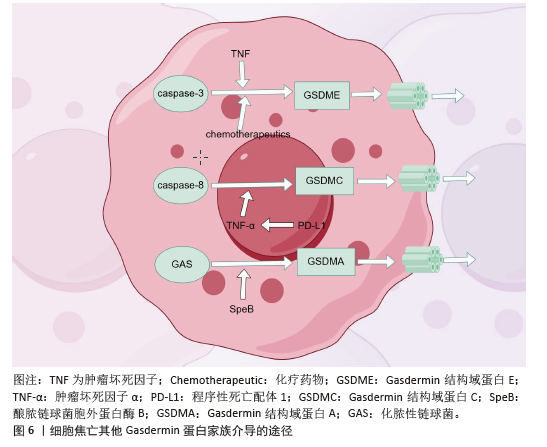
2.4 其他GSDM介导的焦亡途径 其他研究表明,在化疗药物或肿瘤坏死因子的刺激下,Caspase-3可以通过切割GSDME并从GSDME片段中产生膜孔来引发焦亡(图6,该图由Figdraw绘制)。在小鼠中沉默GSDME可改善化疗引起的组织损伤和体质量减轻,表明Caspase-3可能通过GSDME途径介导细胞焦亡[30]。另一项研究揭示,Caspase-8通过触发坏死性凋亡和焦亡诱导小鼠胚胎死亡,表明Caspase-8是一种控制细胞凋亡和焦亡的分子开关,同时在胚胎发育和成年期间避免组织损伤[31]。在癌细胞中,程序性死亡配体1可以将肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的细胞凋亡转化为焦亡,涉及Caspase-8和GSDMC[32]。化脓性链球菌也被认为是A族链球菌,产生酿脓链球菌胞外蛋白酶 B毒力因子,通过切割GSDMA诱导皮肤角质形成细胞死亡。然而,在骨病的背景下,其他途径介导的焦亡仍未得到充分探索。 "

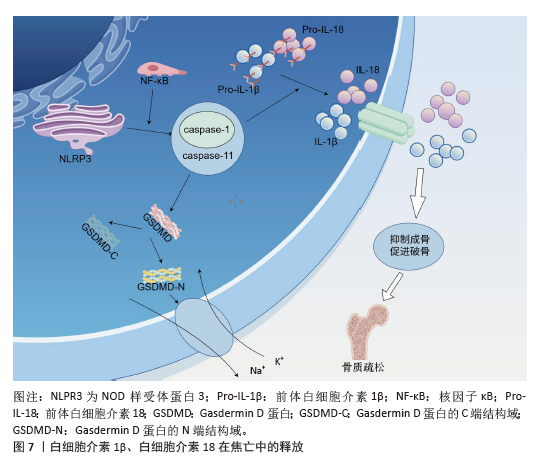
2.5 细胞焦亡与相关炎症因子参与骨质疏松症的发病机制 在骨质疏松症中,成骨细胞经历了大量由多种原因导致的程序性死亡事件,并释放NLRP3,它们在破骨细胞过度分化和骨吸收过度中起着关键作用。NLRP3在细胞焦亡过程中被激活,并将白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18的前体加工成成熟的形式,伴随细胞破裂释放到细胞外环境中,所有这些化合物都是焦亡的经典炎症因子。所以,焦亡主要通过激活NLRP3、分泌成熟的白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18参与骨质疏松的发病机制,下文将对此进行论证。 2.5.1 白细胞介素1β参与细胞焦亡介导骨质疏松症的发病机制 白细胞介素1配体家族有11个成员,白细胞介素1β被认为是多种炎症的主要治疗靶点。白细胞介素1β与其受体结合并启动白细胞介素1信号转导,包括丝裂原活化蛋白激酶级联和核因子κB通路,这些信号通路导致一些转录因子的激活,如c-Jun n端激酶、激活蛋白1、核因子κB和p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶[33]。将白细胞介素1β与其受体结合在T淋巴细胞、B淋巴细胞和巨噬细胞上可促进核因子κB 受体活化因子配体的产生,核因子κB受体活化因子配体与破骨细胞前体细胞的核因子κB 受体活化因子结合,有助于破骨细胞的分化和活化[34];此外,白细胞介素1β可以通过增加巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的产生来激活破骨细胞,抑制破骨细胞凋亡[35]。 白细胞介素1也被认为是肿瘤坏死因子介导成骨的重要递质。肿瘤坏死因子和白细胞介素1最初参与不同的信号通路,这些信号通路与核因子κB的激活和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶系统的刺激融合,因此,两种细胞因子的串连效应为破骨细胞生成提供了有效的信号,抑制成骨细胞功能,调节骨骼细胞的寿命。有研究报道,白细胞介素1通过直接刺激破骨细胞前体分化增强基质细胞核因子κB 受体活化因子配体表达,调控肿瘤坏死因子α的破骨作用[36]。 另一方面,白细胞介素1也对成骨细胞有影响,白细胞介素1a可以通过c-Jun n端激酶和p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶途径诱导MC3T3-E1细胞活力下降,抑制成骨细胞分化。研究发现,在成骨细胞中下调Toll样受体 4可降低白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平,随后由于炎症通路的抑制细胞活力提高;相反,在骨质疏松模型中,切除卵巢大鼠血清中白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的水平明显高于对照大鼠,间充质干细胞的分化也被阻断[37]。显然,成骨细胞在炎症环境中失去了它们的能力。 2.5.2 白细胞介素18参与细胞焦亡介导骨质疏松症的发病机制 作为白细胞介素1细胞因子超家族成员,白细胞介素18也通过Caspase-1的加工发挥作用[38-39]。在白细胞介素18与其受体结合后,白细胞介素18与白细胞介素1受体和Toll样受体共享信号通路并激活许多转录因子,如核因子κB、激活蛋白 1和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶。1999年,GRACIE等[40]发现白细胞介素18的mRNA和蛋白在类风湿关节炎患者关节中丰富,并证明白细胞介素18可以刺激干扰素γ、粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和肿瘤坏死因子α的显著产生。事实上,白细胞介素18在增加肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的产生中起着关键作用。白细胞介素18可以通过多种途径促进破骨细胞的分化,包括诱导干扰素g 的分泌以及作用于T淋巴细胞。 最初,干扰素g被描述为抗破骨因子,因为它在体外对破骨细胞的形成有强大的抑制作用,这一观点强化了干扰素g是骨吸收抑制剂的观点。然而,也有研究观察到干扰素g能促进骨吸收,导致骨质流失。作为一种有效的抗原呈递诱导剂,干扰素g也是T细胞活化的诱导剂,当体内干扰素g水平升高时,活化的T细胞分泌促破骨因子,抵消干扰素g的抗破骨作 用[28]。有研究发现,干扰素g在体内具有间接促破骨作用和直接抗破骨作用,而两种相反力量的净平衡偏向于骨吸收[41]。因此,在焦亡引起的炎症状态下,白细胞介素18通过增加干扰素g的产生来促进破骨细胞的生成。 2.5.3 NLRP3参与细胞焦亡介导骨质疏松症的发病机制 在炎症小体被激活之前,必须在巨噬细胞中诱导炎症反应,慢性炎症反应是炎症或自身免疫性疾病的主要危险因素[42]。如上所述,已知白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18在破骨细胞发生中产生多种作用,因此,NLRP3的过度激活可以通过加工白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18前体影响破骨细胞的形成(图7,该图由Figdraw绘制)。另外,NLRP3炎性小体的激活需要2个信号:核因子κB依赖途径和诱导寡聚化的激动剂,而核因子κB依赖通路在破骨细胞分化中具有重要意义,因此,炎症小体的过度激活将在炎症/自身免疫性疾病的发生和发展中发挥关键作用。 NLRP3通过影响成骨细胞直接抑制成骨,在炎症所致骨质疏松中起核心作用。有研究证实,成骨细胞表达NLRP3,其介导细菌诱导的细胞焦亡并参与炎症期间的骨质流失[43]。NLRP3被认为是骨质疏松引起的许多细菌感染所必需的[44]。当NLRP3炎性小体增加时,Caspase-1通路被激活,白细胞介素1和白细胞介素18的表达水平上调,导致成骨细胞死亡[45]。在缺乏雌激素的骨质疏松症中,没有观察到直接的细菌感染但NLRP3水平仍升高,成骨细胞活力显著降低,抑制或灭活NLRP3后骨质疏松症也得到缓解[46]。"
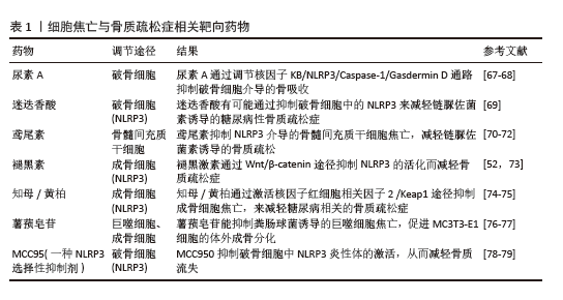
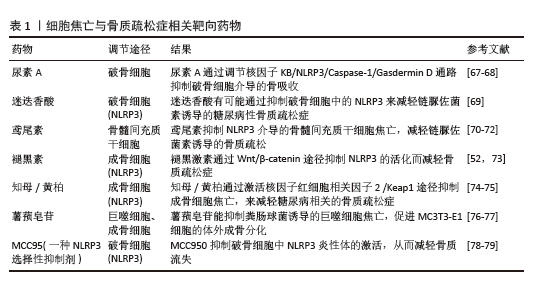
2.6 细胞焦亡与骨质疏松症相关性研究 2.6.1 通过细胞焦亡抑制成骨细胞参与骨代谢 骨细胞由成骨细胞产生。骨髓间充质前体细胞在转录因子顺序的作用下开始向骨祖细胞方向进行分化,最终逐步分化为骨细胞[47]。卵巢切除诱导的骨质疏松小鼠骨髓腔中观察到大量脂滴,表明骨质疏松症中脂肪生成分化比骨祖细胞分化更为明显。焦亡已被证明积极参与骨质疏松症[48]。在炎症环境下,骨髓间充质干细胞的活力和成骨分化能力减弱;在脂多糖刺激下,骨髓间充质干细胞中NLRP3和白细胞介素1β的表达显著增加,提示骨髓间充质干细胞的焦亡抑制成骨分化[49]。研究表明,丁酸钠Caspase-3/GSDME和骨保护素/核因子κB 受体活化因子配体轴诱导成骨细胞焦亡并抑制成骨,导致成骨分化减弱[50]。使用地塞米松处理骨髓基质细胞可诱导细胞焦亡,阻碍成骨分化,通过沉默Caspase-1基因可减弱地塞米松的作用[51]。卵巢切除小鼠成骨细胞中NLRP3、Caspase-1、凋亡相关斑点样蛋白和白细胞介素1β表达上调,提示卵巢切除通过促进成骨细胞焦亡来抑制成骨;褪黑素治疗减弱了成骨细胞焦亡,并通过Wnt/β-catenin途径促进骨形成[52]。在异位骨化模型中,巨噬细胞焦亡通过白细胞介素1β和含高迁移率族蛋白 B1的细胞外囊泡影响肌腱干细胞的衰老,导致异位骨化形成,提示巨噬细胞焦亡在骨代谢调节中发挥重要作用[53]。在肿瘤坏死因子α刺激下,成骨细胞MC3T3-E1发生焦亡,这是由Janus激酶-信号转导及转录激活因子3通路中的关键蛋白ELP2调节的;此外,ELP2蛋白通过激活NLRP3-GSDMD/GSDME通路抑制成骨分化[54]。雌激素缺乏通过促进Capase-1/GSDMD/白细胞介素8和白细胞介素1β焦亡途径抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,最终导致骨质疏松症,而NLRP3敲低促进骨形成[46]。上述研究提示,焦亡在成骨调控中具有重要作用,可通过直接或间接作用诱导成骨细胞焦亡来抑制成骨。 2.6.2 通过细胞焦亡促进破骨细胞参与骨代谢 破骨细胞由骨髓中的造血前体细胞衍生而来,多种系统性细胞因子与信号传导对破骨细胞的分化和成熟过程予以调控。成熟的破骨细胞具备多核特性,能够紧密黏附于骨表面,进而引发骨吸收现象。 脂多糖诱导骨髓巨噬细胞焦亡,导致炎症因子白细胞介素1β分泌,促进破骨细胞分化、增加骨吸收。然而,破骨细胞分化可被炎性小体抑制剂(MCC950和Z-YVAD-FMK)抑制[55]。研究表明,骨髓巨噬细胞中焦亡的发生可能会刺激白细胞介素1β的分泌,从而促进破骨细胞的分化和成熟[56]。模仿人类表型,NLRP3基因D301N位点突变型小鼠(NLRP3miceD301N)型表现出全身性炎症和炎症性骨丢失,这是由于破骨细胞通过肌动蛋白细胞骨架重组增加骨吸收[57]。与未感染骨相比,骨髓炎模型中焦亡相关蛋白的表达更高,因此,抑制焦亡可以通过减弱破骨细胞的异常激活来减轻骨髓炎引起的骨破坏[44]。在牙周炎模型中,NLRP3抑制剂格列本脲通过抑制焦亡降低焦亡相关蛋白的表达并逆转骨吸收[58]。GSDMD通过调控内体-溶酶体途径调节破骨细胞的骨吸收功能,从而维持骨稳态。在去卵巢小鼠模型中,GSDMD敲除小鼠的骨质流失更为严重,这表明焦亡调节破骨细胞中GSDMD对骨代谢的改变[59]。 综上所述,焦亡代表了一种先天性免疫死亡形式,其利弊取决于焦亡过程的持续时间。在焦亡的初始阶段,细胞通过这一机制释放出大量的炎症因子,细胞膜的破裂使细胞内病原体暴露于抗体,促进了它们被募集的巨噬细胞吞噬和破坏。然而,在Caspase和GSDMD介导的持续焦亡中,炎症因子大量分泌,包括肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18、白细胞介素6等,形成慢性免疫炎症微环境。在这种炎症免疫微环境下,免疫细胞持续分泌核因子κB 受体活化因子配体,从而增强对巨噬细胞破骨细胞分化的刺激,放大骨吸收;同时,骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力减弱,阻碍成骨细胞活性,破坏骨合成,并且成骨细胞分泌骨保护素的能力受到损害,将这种作用传递给破骨细胞。因此,成骨细胞和破骨细胞之间的信号相互作用变得失调,最终导致骨代谢稳态紊乱,并表现为多种无菌性和细菌性炎症性骨疾病。 2.6.3 细胞膜破裂与炎性小体激活在细胞焦亡中的核心作用 在细胞焦亡过程中,炎性小体首先被激活。以常见的 NLRP3 炎性小体为例,当细胞受到如氧化应激、高血糖、病原体感染等刺激时,模式识别受体 NLRP3会识别这些危险信号从而发生寡聚化,并与衔接蛋白ASC及Caspase-1前体结合形成NLRP3炎性小体复合物[26]。随后,该复合物激活Caspase-1,激活后的Caspase-1 可切割GSDM蛋白家族成员,如GSDMD,产生具有膜打孔活性的 GSDMD-N端结构域,这些GSDMD-N片段会在细胞膜上形成孔洞,导致细胞膜破裂,细胞膜破裂后,细胞内的炎性因子如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18 等大量释放到细胞外环境中。 2.6.4 细胞焦亡引发的慢性炎症微环境破坏骨代谢平衡 持续的细胞焦亡使得大量炎症因子,如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18、白细胞介素6 等持续分泌,形成慢性免疫炎症微环境。在这种环境下,免疫细胞持续分泌核因子κB受体活化因子配体,核因子κB 受体活化因子配体与破骨细胞前体细胞表面的核因子κB 受体活化因子结合,促进破骨细胞的分化、激活和存活,进一步增强骨吸收;同时,骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力在炎症环境下减弱,阻碍了成骨细胞的活性,破坏了骨合成[34];此外,成骨细胞分泌骨保护素的能力也受到损害,骨保护素是核因子κB 受体活化因子配体的天然拮抗剂,骨保护素分泌减少使得核因子κB 受体活化因子配体对破骨细胞的刺激作用无法有效被抑制,进一步加剧了骨吸收与骨形成的失衡,最终,这种骨代谢稳态的紊乱导致了骨质疏松症的发生与 发展。 2.6.5 细胞焦亡通过相关信号通路参与骨质疏松症 Nrf2/Keap1信号通路通过介导细胞焦亡参与骨质疏松症:核因子红细胞相关因子2(nuclear factor-erythroid 2 related factor 2,Nrf2)作为氧化-抗氧化平衡的关键调节剂,主要通过调控抗氧化基因的表达来维持细胞氧化还原的稳态。在应激或炎症条件下,Nrf2/Keap1信号传导在维持细胞稳态中起着至关重要作用。大量证据证实,暴露于高糖环境会抑制Nrf2/Keap1信号传导,导致氧化应激诱导、Caspase-1的激活及随后细胞的焦亡[60],这一级联最终导致骨重塑中断和骨质疏松加剧。相反,Nrf2/Keap1信号的激活保持了细胞氧化还原稳态,阻碍了骨质疏松的进展。在高脂肪诱导肥胖大鼠进行的药理学研究表明,知母/黄柏的活性成分具有通过上调Nrf2蛋白水平来抑制炎症反应的能力[61],所以知母/黄柏通过激活Nrf2/Keap1信号通路显示出减轻成骨细胞焦亡和抑制骨质疏松症进展的潜力。 PI3K/AKT信号通路通过介导细胞焦亡参与骨质疏松症:磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶 B(phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/protein kinase B,PI3K/AKT)信号通路是调节各种细胞类型的细胞增殖、分化、衰老和焦亡的关键信号通路。研究表明,木犀草素可以通过激活PI3K/AKT轴抑制氧化损伤、改善线粒体功能障碍和减轻GSDME介导的焦亡,进而预防卵巢切除诱导的骨质流失、改善骨代谢[62]。在机制上,卵巢切除通过抑制PI3K/AKT轴增强氧化损伤、诱导线粒体功能障碍,导致Caspase-3切割产生的GSDME-N增加,最终激活骨组织内成骨细胞的焦亡。相关研究提示,绝经后骨质疏松期间成骨细胞可能发生GSDME介导的焦亡,并且木犀草素治疗减少成骨细胞的焦亡依赖于PI3K/AKT的激活[62]。 核因子κB信号通路通过介导细胞焦亡参与骨质疏松症:核因子κB信号通路参与调节多种致病过程,在激活焦亡中起着关键作用。去泛素酶泛素特异性蛋白酶1对骨形成至关重要。研究发现,去泛素酶泛素特异性蛋白酶1通过肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6泛素化抑制NLRP3炎症小体,并通过核因子κB信号传导对氧化暴露做出反应[63]。去泛素酶泛素特异性蛋白酶1通过抑制核因子κB-NLRP3介导的细胞焦亡对MC3T3-E1细胞具有保护作用。 Nrf2/血红素加氧酶1信号通路通过介导细胞焦亡参与骨质疏松症:据研究表明,柚皮素是一种天然化合物,能调节Nrf2/血红素加氧酶1信号通路,对骨微结构产生积极影响[64]。在模拟微重力的小鼠模型和细胞实验中,模拟微重力会使小鼠骨微结构恶化,导致骨小梁数量减少、骨体积分数降低等,而柚皮素可激活Nrf2/血红素加氧酶1信号通路,上调Nrf2和血红素加氧酶1的表达,有效改善了模拟微重力导致的骨微结构损伤,有助于维持骨量;模拟微重力会激活NLRP3炎性小体,诱导成骨细胞焦亡,抑制成骨分化,进而影响骨微结构,柚皮素通过激活 Nrf2/血红素加氧酶1通路减少细胞内活性氧产生、纠正线粒体功能障碍,抑制NLRP3炎性小体相关焦亡通路[64]。细胞实验结果显示,柚皮素预处理显著降低了NLRP3等焦亡相关蛋白和mRNA表达水平,同时,柚皮素促进碱性磷酸酶、Runx2等成骨相关蛋白和基因的表达,增强成骨细胞分化能力,保护和改善骨微结构[64]。 2.7 细胞焦亡有可能成为骨质疏松症新的治疗靶点 早期的研究表明,雌激素缺乏可诱导炎症免疫微环境,在这种微环境的影响下骨代谢的平衡被破坏,最终导致骨质疏松症的发展,因此,中断这一循环来调节炎症免疫微环境,具有治疗骨质疏松的潜力。目前,骨质疏松症是通过抑制骨吸收和促进骨形成来控制的,常用的抗骨吸收药物包括双膦酸盐、雌激素受体调节剂和靶向核因子κB 受体活化因子配体的单克隆抗体[65],刺激骨形成的药物包括特立帕肽、维生素D、维生素K和其他小分子补充剂[66]。针对焦亡的直接抑制剂和间接药物都是可用的。该文概括了部分专门针对骨质疏松症背景下细胞焦亡的药物(表1)。 尿素A 是肠道微生物群产生的一种具有生物活性的代谢物,对细胞功能具有有益作用[67]。体内研究表明,8周尿素A灌胃可增加卵巢切除小鼠的骨量,尿素A通过抑制核因子κB受体活化因子配体驱动的破骨细胞激活实现骨量恢复,测序分析显示与尿素A介导的炎症因子表达减少有潜在的相关性。相反,体外研究结果显示,尿素A可以调节巨噬细胞极化、减轻炎症反应,从而抑制破骨细胞生成[68],这表明尿素A抑制焦亡诱导炎症的策略可能对骨质疏松症治疗有价值。 迷迭香酸是一种从植物中分离出来的天然酚酸化合物,具有很强的抗氧化活性。临床研究表明。迷迭香酸通过抑制破骨细胞中炎性体NLRP3的激活,改善链脲佐菌素诱导的大鼠糖尿病骨质疏松症,表明迷迭香酸可能在糖尿病骨质疏松症的治疗中发挥作用[69]。 鸢尾素是含纤维连接蛋白Ⅲ型结构域5的水解产物,经过内质网加工并分泌到血液中以调节能量代谢。鸢尾素水平与健康状况有很强的相关性,在肥胖、骨质疏松、骨量减少的患者中鸢尾素水平显著降低,而癌症患者中鸢尾素水平明显升高[70]。一项体内研究表明,8周的跑步方案导致小鼠体内鸢尾素水平升高,可能增加卵巢切除小鼠的骨矿物质密度[71]。随后的研究显示,通过运动和体内给药促进鸢尾素水平升高,可以减轻糖尿病小鼠炎症小体诱导的焦亡相关信号通路,从而阻止骨质流失[72]。这意味着鸢尾素在通过抑制焦亡减轻骨质疏松症方面具有潜在的治疗作用。褪黑素是一种主要由松果体分泌的吲哚胺,具有明显的昼夜节律。研究证实,褪黑素具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗肿瘤和抗衰老作用。褪黑素具有对抗骨关节炎进展的能力,可用于预防软骨变形、刺激软骨基质合成,这一推论强调了其对复杂骨代谢的有利影响[73]。研究发现,腹腔注射8周后,褪黑素以剂量依赖性的方式减轻了卵巢切除诱导的骨质疏松症;此外,体外使用褪黑素处理骨髓间质干细胞可促进其成骨分化,这种效果归因于通过Wnt/β-catenin途径抑制NLRP3炎性体激活,表明褪黑素有可能通过抑制骨髓间质干细胞的焦亡来改善雌激素缺乏引起的骨质疏松症[52]。 知母/黄柏是一种独特的中药组合,在治疗糖尿病骨质疏松症方面具有深远影响。在大鼠模型中口服知母/黄柏可减轻链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病骨质疏松症;此外,在糖尿病斑马鱼模型中,知母/黄柏治疗后表现出血糖降低、成骨细胞相关基因上调和破骨细胞相关基因下调[74]。随后的体内免疫荧光分析显示,知母/黄柏通过激活核因子红细胞相关因子2 /Keap1途径抑制成骨细胞焦亡,从而减轻链脲佐菌素诱导的大鼠糖尿病骨质疏松症[75]。 薯蓣皂苷是一种天然存在的生物活性甾体皂苷,对一系列疾病有保护作用,包括恶性肿瘤、代谢紊乱、器官损伤和人类传染病[76]。研究表明,薯蓣皂苷能抑制粪肠球菌诱导的巨噬细胞热亡,促进MC3T3-E1细胞的体外成骨分化[77]。这些发现表明皂苷在促进成骨特别是在对抗骨质疏松症方面具有潜在的效用。 MCC950是一种NLRP3选择性抑制剂,通过抑制ASC寡聚化和与NLRP3结合来抑制炎性小体的激活。MCC950已在自身免疫、心血管、代谢和其他疾病的动物模型中显示出治疗效果[78]。早期研究表明,MCC950可抑制巨噬细胞中NLRP3的激活并减少炎症因子白细胞介素1β的产生[79]。此外,MCC950治疗通过抑制破骨细胞活化有效减轻了年龄相关性骨质流失,这与NLRP3基因敲除小鼠的研究结果一致。这些结果表明,MCC950抑制破骨细胞中NLRP3炎性体的激活,从而减轻骨质流失。"
| [1] ASPRAY TJ, HILL TR. Osteoporosis and the Ageing Skeleton. Subcell Biochem. 2019;91: 453-476. [2] 杨城,李玮民,冉栋成,等.铁死亡与骨质疏松症[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(3): 554-562. [3] VANDENBROUCKE A, LUYTEN FP, FLAMAING J, et al. Pharmacological treatment of osteoporosis in the oldest old. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:1065-1077. [4] JOHNSTON CB, DAGAR M. Osteoporosis in Older Adults. Med Clin North Am. 2020; 104(5):873-884. [5] ABDALBARY M, SOBH M, ELNAGAR S, et al. Management of osteoporosis in patients with chronic kidney disease. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(11):2259-2274. [6] MIRZA F, CANALIS E. Management of endocrine disease: Secondary osteoporosis: pathophysiology and management. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015;173(3):R131-R151. [7] SOZEN T, OZISIK L, BASARAN NC. An overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2017;4(1):46-56. [8] 方志杰,马抢平,董万涛,等.肠道菌群与骨质疏松症的遗传关系:来自英国数据库211个肠道微生物群分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(18):3941-3947. [9] RAO Z, ZHU Y, YANG P, et al. Pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Theranostics. 2022;12(9):4310-4329. [10] ALMEIDA M, LAURENT MR, DUBOIS V, et al. Estrogens and Androgens in Skeletal Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 2017;97(1):135-187. [11] AWAD F, ASSRAWI E, LOUVRIER C, et al. Inflammasome biology, molecular pathology and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;187:133-149. [12] ZENG C, WANG R, TAN H. Role of Pyroptosis in Cardiovascular Diseases and its Therapeutic Implications. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(7): 1345-1357. [13] WU J, LIN S, WAN B, et al. Pyroptosis in Liver Disease: New Insights into Disease Mechanisms. Aging Dis. 2019;10(5):1094-1108. [14] YU P, ZHANG X, LIU N, et al. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):128. [15] LOVELESS R, BLOOMQUIST R, TENG Y. Pyroptosis at the forefront of anticancer immunity. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021; 40(1):264. [16] ALLEN KD, THOMA LM, GOLIGHTLY YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):184-195. [17] SAFIRI S, KOLAHI AA, HOY D, et al. Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(11):1463-1471. [18] WANG L, YU W, YIN X, et al. Prevalence of Osteoporosis and Fracture in China: The China Osteoporosis Prevalence Study. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(8):e2121106. [19] ZHOU M, WANG H, ZENG X, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;394(10204):1145-1158. [20] GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, AARONSON SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(3):486-541. [21] DU T, GAO J, LI P, et al. Pyroptosis, metabolism, and tumor immune microenvironment. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(8):e492. [22] JIANG D, CHEN S, SUN R, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Role in metabolic disorders and regulation by metabolic pathways. Cancer Lett. 2018;419:8-19. [23] PLACE DE, KANNEGANTI TD. Recent advances in inflammasome biology. Curr Opin Immunol. 2018;50:32-38. [24] BROZ P, DIXIT VM. Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16(7):407-420. [25] SHI J, ZHAO Y, WANG K, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature. 2015;526(7575):660-665. [26] SBORGI L, RUHL S, MULVIHILL E, et al. GSDMD membrane pore formation constitutes the mechanism of pyroptotic cell death. EMBO J. 2016;35(16):1766-1778. [27] ING J, WANG K, LIU W, et al. Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature. 2016;535(7610): 111-116. [28] WEITZMANN MN, PACIFICI R. The role of T lymphocytes in bone metabolism. Immunol Rev. 2005;208:154-168. [29] HE D, ZHOU M, BAI Z, et al. Propionibacterium acnes induces intervertebral disc degeneration by promoting nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis via NLRP3-dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;526(3): 772-779. [30] WANG Y, GAO W, SHI X, et al. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature. 2017; 547(7661):99-103. [31] NEWTON K, WICKLIFFE KE, MALTZMAN A, et al. Activity of caspase-8 determines plasticity between cell death pathways. Nature. 2019;575(7784):679-682. [32] HOU J, ZHAO R, XIA W, et al. PD-L1-mediated gasdermin C expression switches apoptosis to pyroptosis in cancer cells and facilitates tumour necrosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(10): 1264-1275. [33] DINARELLO CA. Overview of the interleukin-1 family of ligands and receptors. Semin Immunol. 2013;25(6):389-393. [34] ONO T, NAKASHIMA T. Recent advances in osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):325-341. [35] LACATIVA PG, FARIAS ML. Osteoporosis and inflammation. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2010;54(2):123-132. [36] WEI S, KITAURA H, ZHOU P, et al. IL-1 mediates TNF-induced osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(2):282-290. [37] FENG C, XIAO L, YU JC, et al. Simvastatin promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in rat model of osteoporosis through BMP-2/Smads signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020; 24(1):434-443. [38] GE Y, HUANG M, YAO YM. Recent advances in the biology of IL-1 family cytokines and their potential roles in development of sepsis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;45:24-34. [39] GONG W, SHI Y, REN J. Research progresses of molecular mechanism of pyroptosis and its related diseases. Immunobiology. 2020;225(2):151884. [40] GRACIE JA, FORSEY RJ, CHAN WL, et al. A proinflammatory role for IL-18 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1999;104(10): 1393-1401. [41] GAO Y, GRASSI F, RYAN MR, et al. IFN-gamma stimulates osteoclast formation and bone loss in vivo via antigen-driven T cell activation. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(1):122-132. [42] YI YS. Role of inflammasomes in inflammatory autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;22(1):1-15. [43] DOSTERT C, PETRILLI V, Van BRUGGEN R, et al. Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science. 2008;320(5876):674-677. [44] ZHU X, ZHANG K, LU K, et al. Inhibition of pyroptosis attenuates Staphylococcus aureus-induced bone injury in traumatic osteomyelitis. Ann Transl Med. 2019; 7(8):170. [45] GREENE E, FLEES J, DHAMAD A, et al. Double-Stranded RNA Is a Novel Molecular Target in Osteomyelitis Pathogenesis: A Translational Avian Model for Human Bacterial Chondronecrosis with Osteomyelitis. Am J Pathol. 2019; 189(10):2077-2089. [46] YANG C, SONG B, HAN L, et al. Study on the mechanism of NLRP3 effect on the skeleton of de-ovalized mice. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023;35:101496. [47] PLOTKIN LI, BELLIDO T. Osteocytic signalling pathways as therapeutic targets for bone fragility. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(10): 593-605. [48] WANG L, CHEN K, WAN X, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mesenchymal stem cells inhibits osteogenic differentiation and enhances adipogenic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;484(4): 871-877. [49] WANG X, JIANG M, HE X, et al. N‑acetyl cysteine inhibits the lipopolysaccharide‑induced inflammatory response in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by suppressing the TXNIP/NLRP3/IL‑1beta signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(4):3299-3306. [50] WU Z, DING Q, YUE M, et al. Caspase-3/GSDME-mediated pyroptosis leads to osteogenic dysfunction of osteoblast-like cells. Oral Dis. 2024;30(3):1392-1402. [51] RUAN H, ZHANG H, FENG J, et al. Inhibition of Caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis promotes osteogenic differentiation, offering a therapeutic target for osteoporosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;124(Pt B):110901. [52] XU L, ZHANG L, WANG Z, et al. Melatonin Suppresses Estrogen Deficiency-Induced Osteoporosis and Promotes Osteoblastogenesis by Inactivating the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;103(4): 400-410. [53] LI J, WANG X, YAO Z, et al. NLRP3-Dependent Crosstalk between Pyroptotic Macrophage and Senescent Cell Orchestrates Trauma-Induced Heterotopic Ossification During Aberrant Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(19):e2207383. [54] XIA C, OU S, YANG Y, et al. ELP2-NLRP3-GSDMD/GSDME-mediated pyroptosis is induced by TNF-alpha in MC3T3-E1 cells during osteogenic differentiation. J Cell Mol Med. 2023;27(24):4093-4106. [55] ALAM MI, MAE M, FARHANA F, et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome Negatively Regulates RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis of Mouse Bone Marrow Macrophages but Positively Regulates It in the Presence of Lipopolysaccharides. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6096. [56] WU YL, ZHANG CH, TENG Y, et al. Propionate and butyrate attenuate macrophage pyroptosis and osteoclastogenesis induced by CoCrMo alloy particles. Mil Med Res. 2022;9(1):46. [57] QU C, BONAR SL, HICKMAN-BRECKS CL, et al. NLRP3 mediates osteolysis through inflammation-dependent and -independent mechanisms. FASEB J. 2015;29(4): 1269-1279. [58] JIANG M, SHANG Z, ZHANG T, et al. Study on the role of pyroptosis in bone resorption induced by occlusal trauma with or without periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2022;57(3):448-460. [59] LI M, YANG D, YAN H, et al. Gasdermin D maintains bone mass by rewiring the endo-lysosomal pathway of osteoclastic bone resorption. Dev Cell. 2022;57(20): 2365-2380. [60] YING Y, JIN J, YE L, et al. Phloretin Prevents Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Dissociating Keap1/Nrf2 Complex and Inhibiting Oxidative Stress. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:774. [61] LIU F, FENG M, XING J, et al. Timosaponin alleviates oxidative stress in rats with high fat diet-induced obesity via activating Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting the NF-kappaB pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;909:174377. [62] CHAI S, YANG Y, WEI L, et al. Luteolin rescues postmenopausal osteoporosis elicited by OVX through alleviating osteoblast pyroptosis via activating PI3K-AKT signaling. Phytomedicine. 2024;128:155516. [63] SUN D, PENG Y, GE S, et al. USP1 Inhibits NF-kappaB/NLRP3 Induced Pyroptosis through TRAF6 in Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2022;22(4):536-545. [64] CAO S, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Naringenin can Inhibit the Pyroptosis of Osteoblasts by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Alleviate the Differentiation Disorder of Osteoblasts Caused by Microgravity. J Agric Food Chem. 2024;72(46):25586-25600. [65] DE MARTINIS M, SIRUFO MM, GINALDI L. Osteoporosis: Current and Emerging Therapies Targeted to Immunological Checkpoints. Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(37):6356-6372. [66] WANG H, LUO Y, WANG H, et al. Mechanistic advances in osteoporosis and anti-osteoporosis therapies. MedComm (2020). 2023;4(3):e244. [67] D’AMICO D, ANDREUX P A, VALDES P, et al. Impact of the Natural Compound Urolithin A on Health, Disease, and Aging. Trends Mol Med. 2021;27(7):687-699. [68] TAO H, LI W, ZHANG W, et al. Urolithin A suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and postmenopausal osteoporosis by, suppresses inflammation and downstream NF-kappaB activated pyroptosis pathways. Pharmacol Res. 2021;174:105967. [69] LI Q, TAO X, ZHANG Y. Rosmarinic acid alleviates diabetic osteoporosis by suppressing the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in rats. Physiol Int. 2022.doi: 10.1556/2060.2022.00154. [70] LIU S, CUI F, NING K, et al. Role of irisin in physiology and pathology. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:962968. [71] KAWAO N, IEMURA S, KAWAGUCHI M, et al. Role of irisin in effects of chronic exercise on muscle and bone in ovariectomized mice. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(4):547-557. [72] BEHERA J, ISON J, VOOR M J, et al. Exercise-Linked Skeletal Irisin Ameliorates Diabetes-Associated Osteoporosis by Inhibiting the Oxidative Damage-Dependent miR-150-FNDC5/Pyroptosis Axis. Diabetes. 2022; 71(12):2777-2792. [73] ZHANG Y, LIU T, YANG H, et al. Melatonin: A novel candidate for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;78: 101635. [74] XU P, LIN B, DENG X, et al. Anti-osteoporosis effects of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma / Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex herb pair and its major active components in diabetic rats and zebrafish. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022; 293:115269. [75] FU F, LUO H, Du Y, et al. AR/PCC herb pair inhibits osteoblast pyroptosis to alleviate diabetes-related osteoporosis by activating Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2023; 27(22):3601-3613. [76] BANDOPADHYAY S, ANAND U, GADEKAR VS, et al. Dioscin: A review on pharmacological properties and therapeutic values. Biofactors. 2022;48(1):22-55. [77] YIN W, LIU S, DONG M, et al. A New NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitor, Dioscin, Promotes Osteogenesis. Small. 2020;16(1):e1905977. [78] LI H, GUAN Y, LIANG B, et al. Therapeutic potential of MCC950, a specific inhibitor of NLRP3 inflammasome. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;928:175091. [79] NI B, PEI W, QU Y, et al. MCC950, the NLRP3 Inhibitor, Protects against Cartilage Degradation in a Mouse Model of Osteoarthritis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:4139048. |
| [1] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [2] | Zhou Jian, Zhang Tao, Zhou Weili, Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Shen Jie, Qian Li, Lu Ming. Effects of resistance training on quadriceps mass and knee joint function in patients with osteoporosis and sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1081-1088. |
| [3] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [4] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [5] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [6] | Wang Meng, Lu Tan, Li Minjie, Liu Zhicheng, Guo Xiaoyong. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of anchors at different implantation depths under different bone density conditions in rotator cuff tears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 561-569. |
| [7] | Yang Fengli, Zhou Chao, Xiong Wei, Zhou Yuxiang, Li Dengshun, Wang Xin, Li Zhanzhen. 3D printed poly-L-lactic acid bone scaffolds in repair of bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 507-515. |
| [8] | Yu Manya, Cui Xing. Contribution and interaction of various cells in bone marrow microenvironment to exosomal circular RNA associated with multiple myeloma bone disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 101-110. |
| [9] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [10] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [11] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [12] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [13] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [14] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [15] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

