Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1331-1340.doi: 10.12307/2026.015
Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets
Zhang Cuicui1, Chen Huanyu1, Yu Qiao2, Huang Yuxuan1, Yao Gengzhen2, Zou Xu2
- 1Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-16Accepted:2025-02-20Online:2026-02-18Published:2025-06-28 -
Contact:Zou Xu, MS, Chief physician, Professor, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Cuicui, MS candidate, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine High-level Key Discipline Construction Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine – Key Discipline Construction Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Talent Cultivation “Cardiology of Traditional Chinese Medicine,” No. [2023]85 zyyzdxk-2023160 (to ZX); State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Key Research Laboratory Construction Project, No. [2012]27 (to ZX [project participant]); Guangdong Provincial Chinese Medicine Bureau Project, No. [2020]1 (to ZX); Guangdong Provincial Chinese Medicine Bureau Project, No. 20223011 (to ZX); Guangzhou Science and Technology Program, Nos. 202201020290 (to ZX), 2023A03J0230 (to ZX [project participant]), and 2024A03J0040 (to YGZ); Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine TCM Academic Schools Inheritance Workshop Construction Project, No. [2013]233 (to ZX [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
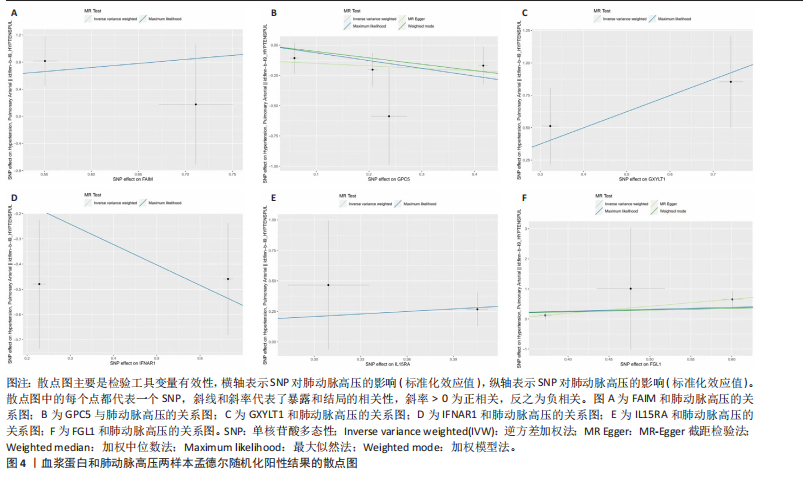
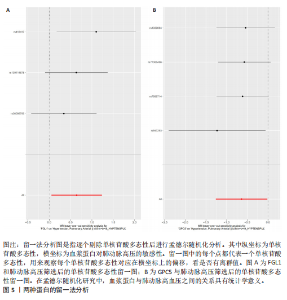
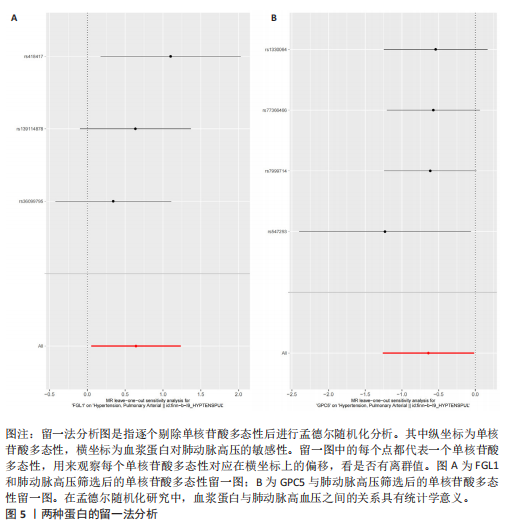
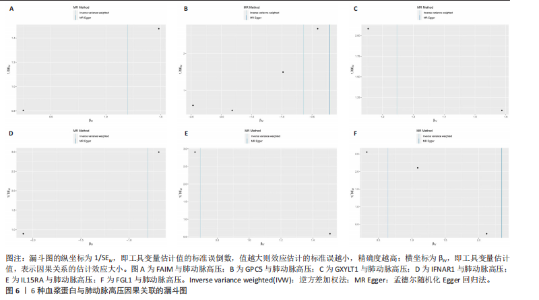
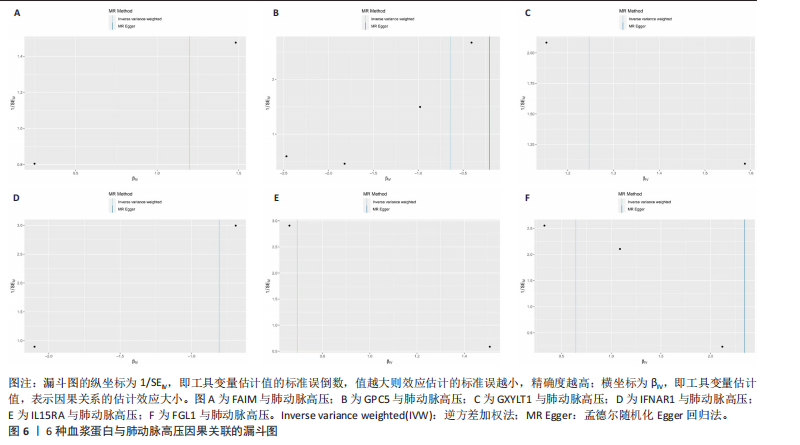
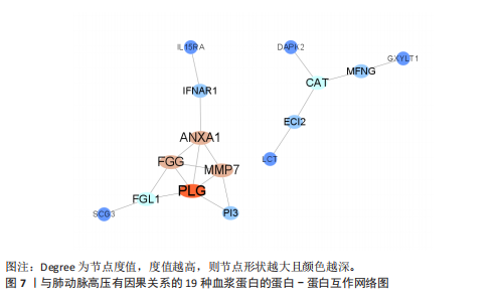
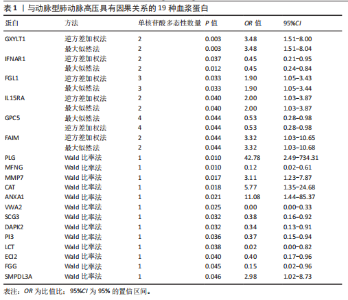
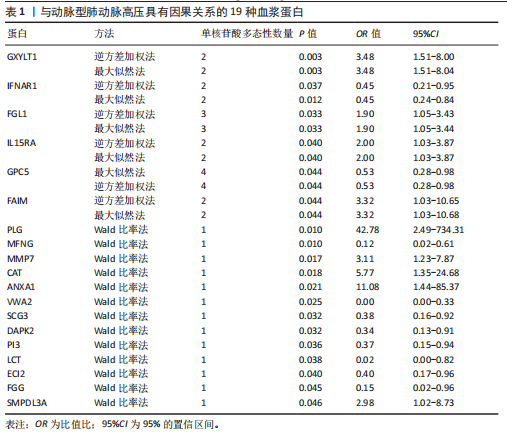
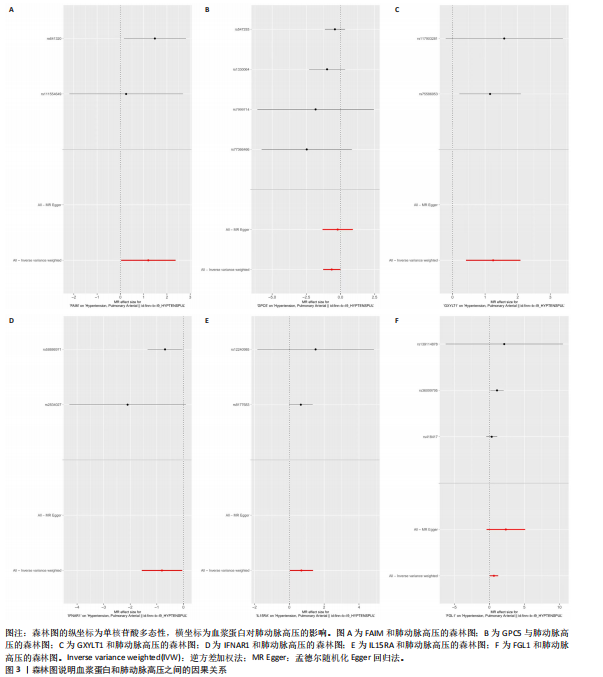
2.1 工具变量选取结果 根据研究采用的工具变量筛选标准,4 907种血浆蛋白共筛选出35 424个单核苷酸多态性,F值均> 10(F值最小为30),表明研究出现弱工具变量偏倚的影响较小。 2.2 孟德尔随机化分析结果 研究通过孟德尔随机化方法对血浆蛋白和动脉型肺动脉高压进行分析,结果显示,有19种血浆蛋白与动脉型肺动脉高压存在因果关系(P < 0.05)。共10种蛋白与动脉型肺动脉高压风险降低相关,分别为MFNG(OR=0.12,95%CI 0.02-0.61,P=0.01),IFNAR1(OR=0.45,95%CI 0.24-0.84,P=0.012), VWA2(OR=0.00,95%CI 0.00-0.33,P=0.025),SCG3(OR=0.38,95%CI 0.16-0.92,P=0.032),DAPK2(OR=0.34,95%CI 0.13-0.91,P=0.032),PI3(OR=0.37,95%CI 0.15-0.94,P=0.036),LCT(OR=0.02,95%CI 0.00-0.82,P=0.038),ECI2(OR=0.40,95%CI 0.17-0.96,P=0.04),GPC5 (OR=0.53,95%CI 0.28-0.98,P=0.044),FGG(OR=0.15,95%CI 0.02-0.96,P=0.045)。共9种蛋白与动脉型肺动脉高压风险升高相关,分别为GXYLT1(OR=3.48,95%CI 1.51-8.00,P=0.003),PLG(OR=42.78,95%CI 2.49-734.31,P=0.01),MMP7(OR=3.11,95%CI 1.23-7.87,P=0.017),CAT(OR=5.77,95%CI 1.35-24.68,P=0.018), ANXA1 (OR=11.08,95%CI 1.44-85.37,P=0.021),FGL1(OR=1.90,95%CI 1.05-3.43,P=0.033),IL15RA(OR=2.0,95%CI 1.03-3.87,P=0.04),FAIM(OR=3.33,95%CI 1.03-10.65,P=0.044),SMPDL3A(OR=2.98,95%CI 1.02-8.73,P=0.046),结果见表1和图3。 研究还使用加权中位数法、加权模式方法等对结果进行检验,结果显示其他4种方法结果与逆方差加权法一致,见图4。 2.3 敏感性分析结果 文章采用敏感性分析对孟德尔随机化分析结果进行异质性和水平多效性检验,确保结果的稳健性。MR-Egger截距检验结果中P均> 0.05 ,表明不存在异质性和水平多效性。留一法分析显示,逐个剔除单核苷酸多态性后,结果未见异常(图5)。漏斗图可见因果关系分布具有一定的对称性,未发现明显偏倚(图6)。Steiger检验结果中P均< 0.05,为TRUE,说明血浆蛋白与动脉型肺动脉高压之间不存在反向的因果关系,即支持暴露-结局方法的因果关系。 2.4 贝叶斯共定位分析结果 为了增强研究结果的可信度,排除混杂因素的影响,进行了贝叶斯共定位分析,结果显示,共有6种蛋白存在显著的遗传共定位(PPH4 > 0.8)。分别是PLG6(PPH4=1.0)、CAT(PPH4=0.87)、"
| [1] 王士伟,康龙丽.动脉型肺动脉高压治疗研究进展[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2024,45(4):493-502. [2] RUOPP NF, COCKRILL BA. Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Review. JAMA. 2022; 327(14):1379-1391. [3] ALAMRI AK, MA CL, RYAN JJ. Novel Drugs for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Where Are We Going? Drugs. 2023;83(7):577-585. [4] LAI YC, POTOKA KC, CHAMPION HC, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: the clinical syndrome. Circ Res. 2014;115(1):115-130. [5] GUIGNABERT C, TU L, LE HIRESS M, et al. Pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: lessons from cancer. Eur Respir Rev. 2013;22(130):543-551. [6] WEATHERALD J, BOUCLY A, PETERS A, et al. The evolving landscape of pulmonary arterial hypertension clinical trials. Lancet. 2022;400(10366):1884-1898. [7] SUN BB, MARANVILLE JC, PETERS JE, et al. Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome. Nature. 2018;558(7708):73-79. [8] ZHANG M, ZENG Q, ZHOU S, et al. Mendelian randomization study on causal association of IL-6 signaling with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2023;45(1):2183963. [9] TAN JS, YANG Y, WANG J, et al. Diabetes mellitus, glycemic traits, SGLT2 inhibition, and risk of pulmonary arterial hypertension: A Mendelian randomization study. Biosci Trends. 2024;18(1):94-104. [10] PIERCE BL, AHSAN H, VANDERWEELE TJ. Power and instrument strength requirements for Mendelian randomization studies using multiple genetic variants. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(3):740-752. [11] GUDJONSSON A, GUDMUNDSDOTTIR V, AXELSSON GT, et al. A genome-wide association study of serum proteins reveals shared loci with common diseases. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):480. [12] DAVEY SMITH G, HEMANI G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89-98. [13] FERKINGSTAD E, SULEM P, ATLASON BA, et al. Large-scale integration of the plasma proteome with genetics and disease. Nat Genet. 2021;53(12):1712-1721. [14] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature. 2023;613(7944):508-518. [15] ZHENG J, HABERLAND V, BAIRD D, et al. Phenome-wide Mendelian randomization mapping the influence of the plasma proteome on complex diseases. Nat Genet. 2020;52(10):1122-1131. [16] ARDLIE KG, KRUGLYAK L, SEIELSTAD M. Patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the human genome. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3(4): 299-309. [17] LEWONTIN RC. The Interaction of Selection and Linkage. I. General Considerations; Heterotic Models. Genetics. 1964;49(1):49-67. [18] PRITCHARD JK, PRZEWORSKI M. Linkage disequilibrium in humans: models and data. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;69(1):1-14. [19] 梁云.人类基因组中的连锁不平衡方式[J].国外医学(生理、病理科学与临床分册),2005,25(3):247-250. [20] PALMER TM, LAWLOR DA, HARBORD RM, et al. Using multiple genetic variants as instrumental variables for modifiable risk factors. Stat Methods Med Res. 2012; 21(3):223-242. [21] BURGESS S, SCOTT RA, TIMPSON NJ, et al. Using published data in Mendelian randomization: a blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors. Eur J Epidemiol. 2015;30(7):543-552. [22] ZHOU S, TAO B, GUO Y, et al. Integrating plasma protein-centric multi-omics to identify potential therapeutic targets for pancreatic cancer. J Transl Med. 2024; 22(1):557. [23] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016; 40(4):304-314. [24] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525. [25] GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, VUKCEVIC D, SCHADT EE, et al. Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014; 10(5):e1004383. [26] BAKER SK, STRICKLAND S. A critical role for plasminogen in inflammation. J Exp Med. 2020;217(4):e20191865. [27] DEFILIPPIS AP, CHERNYAVSKIY I, AMRAOTKAR AR, et al. Circulating levels of plasminogen and oxidized phospholipids bound to plasminogen distinguish between atherothrombotic and non-atherothrombotic myocardial infarction. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2016;42(1):61-76. [28] LIJNEN HR. Elements of the fibrinolytic system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:226-236. [29] FELDREICH T, NOWAK C, FALL T, et al. Circulating proteins as predictors of cardiovascular mortality in end-stage renal disease. J Nephrol. 2019;32(1):111-119. [30] TIAN Y, ZHAO Q, WU H, et al. VWA2 protein molecular mechanism predicts colorectal cancer: Promoting cell invasion and migration by inhibiting NK cell activation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;279(Pt 3):135394. [31] LEPPER PM, BALS R, WILKENS H. Natural killer cells in pulmonary arterial hypertension: a force on the dim or the bright side? Circulation. 2012;126(9):1020-1022. [32] ZHAO H, SONG J, LI X, et al. The role of immune cells and inflammation in pulmonary hypertension: mechanisms and implications. Front Immunol. 2024;15: 1374506. [33] WANG RR, YUAN TY, WANG JM, et al. Immunity and inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension: From pathophysiology mechanisms to treatment perspective. Pharmacol Res. 2022;180:106238. [34] KELLY L, MCGRATH S, RODGERS L, et al. Annexin-A1: The culprit or the solution? Immunology. 2022;166(1):2-16. [35] IBRAHIM YF, WONG CM, PAVLICKOVA L, et al. Mechanism of the susceptibility of remodeled pulmonary vessels to drug-induced cell killing. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014;3(1):e000520. [36] ARVIDSSON M, AHMED A, SÄLEBY J, et al. Plasma TRAIL and ANXA1 in diagnosis and prognostication of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm Circ. 2023; 13(3):e12269. [37] HENNIGS JK, BAUMANN HJ, LÜNEBURG N, et al. Fibrinogen plasma concentration is an independent marker of haemodynamic impairment in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Sci Rep. 2014;4: 4808. [38] ALAM SR, NEWBY DE, HENRIKSEN PA. Role of the endogenous elastase inhibitor, elafin, in cardiovascular injury: from epithelium to endothelium. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012; 83(6):695-704. [39] WANG J, SANMAMED MF, DATAR I, et al. Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 Is a Major Immune Inhibitory Ligand of LAG-3. Cell. 2019;176(1-2):334-347.e12. [40] THOMAS C, MORAGA I, LEVIN D, et al. Structural linkage between ligand discrimination and receptor activation by type I interferons. Cell. 2011;146(4):621-632. [41] IVASHKIV LB, DONLIN LT. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(1):36-49. [42] RATTHÉ C, GIRARD D. Interleukin-15 enhances human neutrophil phagocytosis by a Syk-dependent mechanism: importance of the IL-15Ralpha chain. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76(1):162-168. [43] WU Z, XUE HH, BERNARD J, et al. The IL-15 receptor {alpha} chain cytoplasmic domain is critical for normal IL-15Ralpha function but is not required for trans-presentation. Blood. 2008;112(12):4411-4419. [44] HUO J, XU S, LAM KP. FAIM: An Antagonist of Fas-Killing and Beyond. Cells. 2019;8(6): 541. [45] RIZZI M, TSCHAN MP, BRITSCHGI C, et al. The death-associated protein kinase 2 is up-regulated during normal myeloid differentiation and enhances neutrophil maturation in myeloid leukemic cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;81(6):1599-1608. [46] URATA Y, SAIKI W, TSUKAMOTO Y, et al. Xylosyl Extension of O-Glucose Glycans on the Extracellular Domain of NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 Regulates Notch Cell Surface Trafficking. Cells. 2020;9(5):1220. [47] PENG L, ZHAO M, LIU T, et al. A stop-gain mutation in GXYLT1 promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer via the MAPK pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(4):395. [48] SATO C, ZHAO G, ILAGAN MX. An overview of notch signaling in adult tissue renewal and maintenance. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012;9(2):227-240. [49] TAKEUCHI A, MIYAMOTO T, YAMAJI K, et al. A human erythrocyte-derived growth-promoting factor with a wide target cell spectrum: identification as catalase. Cancer Res. 1995;55(7):1586-1589. [50] CHEN L, DAI P, LIU L, et al. The lipid-metabolism enzyme ECI2 reduces neutrophil extracellular traps formation for colorectal cancer suppression. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):7184. [51] NÉMETH K, PLUMB GW, BERRIN JG, et al. Deglycosylation by small intestinal epithelial cell beta-glucosidases is a critical step in the absorption and metabolism of dietary flavonoid glycosides in humans. Eur J Nutr. 2003;42(1):29-42. [52] TRAINI M, QUINN CM, SANDOVAL C, et al. Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase acid-like 3A (SMPDL3A) is a novel nucleotide phosphodiesterase regulated by cholesterol in human macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289(47):32895-32913. [53] SHIN H, CHUNG H. SMPDL3A links cholesterol metabolism to the cGAS-STING pathway. Immunity. 2023;56(11):2459-2461. [54] TANG F, PACHECO MTF, CHEN P, et al. Secretogranin III promotes angiogenesis through MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018; 495(1):781-786. [55] ZHANG H, WANG G, YANG X, et al. Investigation of Gene Expression Profile of A549 Cells after Overexpression of GPC5 by High Throughput Transcriptome Sequencing. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016; 19(8):545-549. |
| [1] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [2] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [3] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [4] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [5] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [6] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [7] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [8] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [9] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [10] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [11] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [12] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [13] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [14] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [15] | Wang Xuepeng, , He Yong, . Effect of insulin-like growth factor family member levels on inflammatory arthritis: a FinnGen biobank-based analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7656-7662. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||