Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2784-2794.doi: 10.12307/2026.085
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of Shixiang plaster to promote healing of infectious wounds
Liu Man1, Zhang Kaiwei2, Zhu Xu2, Ruan Jinghua3, Chen Jiunyi2, Fei Ji2
- 1Graduate College, Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; 3School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2025-02-24Accepted:2025-05-29Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-05 -
Contact:Fei Ji, MS, Associate chief physician, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Liu Man, MS, Physician, Graduate College, Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Ethnic Medicine Science and Technology Research Project of Guizhou Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. QZYY-2023-013 (to FJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Man, Zhang Kaiwei, Zhu Xu, Ruan Jinghua, Chen Jiunyi, Fei Ji. Mechanism of Shixiang plaster to promote healing of infectious wounds[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2784-2794.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
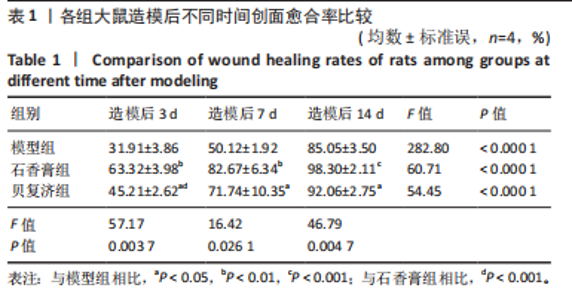
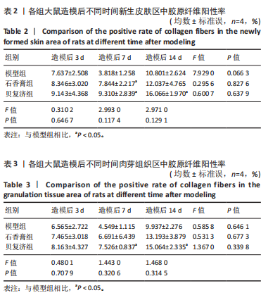
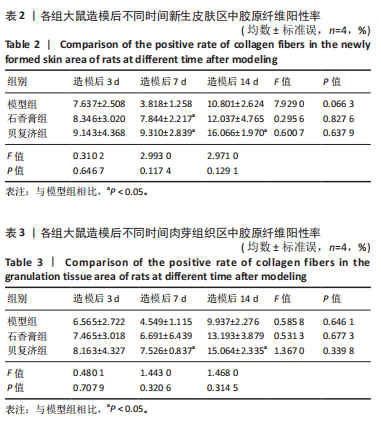
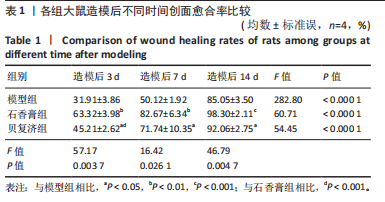
2.1 实验动物数量分析 36只大鼠全部造模成功,实验过程无死亡,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 创面愈合的宏观观察 在造模后的第3,7,14天,经药物干预后石香膏组大鼠创面愈合进展最快,无论是早期愈合率还是晚期愈合率都明显优于其他2组,贝复济组的愈合效果次之,但仍明显优于模型组。这些结果证明了石香膏在促进创面愈合方面的潜在疗效,见图1,表1。 2.3 苏木精-伊红及Masson染色检测组织病理学变化 2.3.1 苏木精-伊红染色 结果显示,模型组大鼠皮肤组织在伤后3 d出现大量炎性细胞,在伤后7,14 d炎性细胞浸润减少。石香膏组和贝复济组大鼠在3 d时创面处均出现大量炎性细胞和肉芽组织;14 d后"
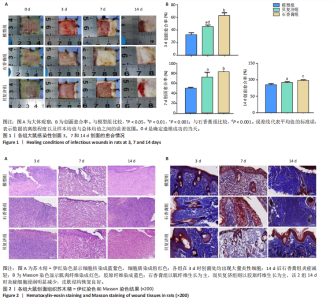
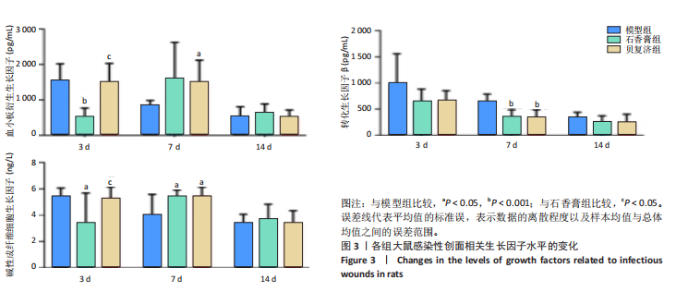
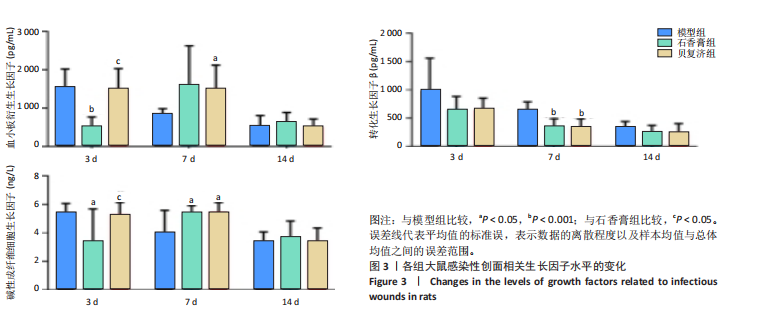
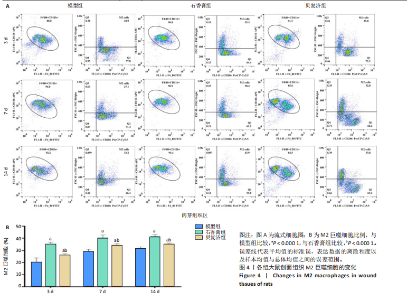
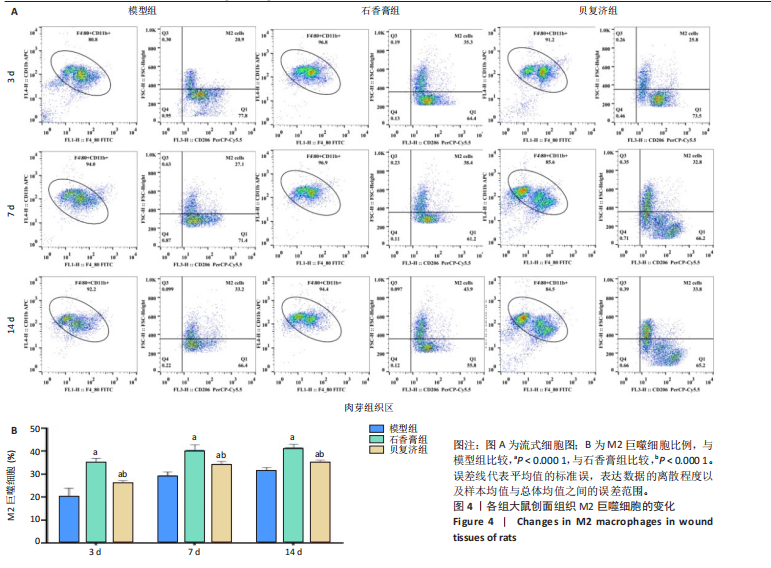
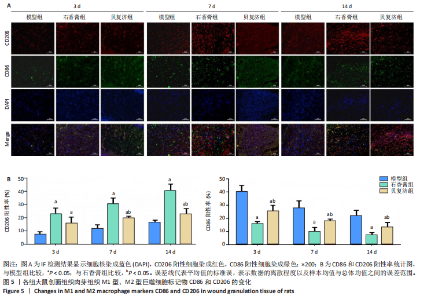
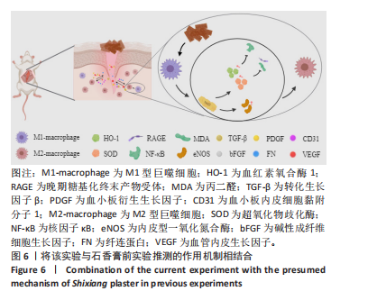
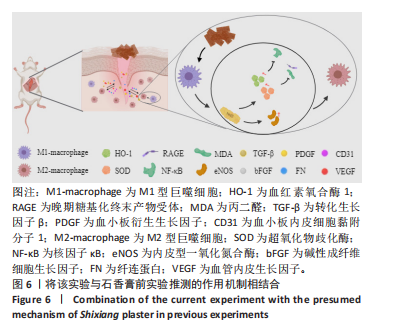
2.4 用酶联免疫吸附法测定组织中的相关生长因子水平 造模后3 d时,经药物干预后石香膏组的碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和血小板衍生生长因子的表达量比模型组显著降低;而相比石香膏组,贝复济组血小板衍生生长因子表达量显著升高。7 d时,石香膏和贝复济处理后转化生长因子β的表达量比模型组显著低,碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和血小板衍生生长因子表达量均显著增加。14 d时,各组之间未观察到显著差异。以上结果表明石香膏和贝复济对促进皮肤损伤修复相关因子的调节具有时效性差异,这可能与治疗后不同时间点皮肤修复过程的具体需求有关,见图3。 2.5 流式细胞术检测M2型巨噬细胞水平 结果揭示,对比模型组,石香膏和贝复济处理后均能显著增加创面组织中M2型巨噬细胞的水平。然而,在创面形成3,7,14 d,与石香膏组相比,贝复济组处理后的M2型巨噬细胞含量更低。表明两种药物都能促进M2型巨噬细胞增加,但贝复济的效果比石香膏弱,见图4。 2.6 荧光免疫术检测M2型巨噬细胞定位 通过免疫荧光检测观察3组给药后创面组织中M1型(Mark:CD86)和M2型(Mark:CD206)巨噬细胞的变化。正常皮肤中,这两种细胞标记物无显著变化。在创面形成后3,7,14 d的肉芽组织中,相较于模型组,石香膏和贝复济给药后均能显著增加CD206阳性率(P < 0.05),降低CD86阳性率(P < 0.05)。贝复济组的CD206阳性率在7,14 d低于石香膏组(P < 0.05),3 d差异不显著。在新生皮肤区,石香膏使CD206显著升高,而贝复济无显著效果。相比石香膏,贝复济在所有时间点CD206阳性率降低,CD86阳性率升高(P < 0.05)。表明石香膏和贝复济均能促进M2型巨噬细胞增加和M1型巨噬细胞减少,有利于抗炎和组织修复,但石香膏的效果更显著,见图5。"

| [1] FRYKBERGROBERT G. Challenges in the treatment of chronic wounds. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2015;4(9):560-582. [2] CLINTON A, CARTER T. Chronic wound biofilms: pathogenesis and potential therapies. Lab Med. 2015;46(4):277-284. [3] GJøDSBøL K, CHRISTENSEN JJ, KARLSMARK T, et al. Multiple bacterial species reside in chronic wounds: a longitudinal study. Int Wound J. 2006;3(3):225-231. [4] CHEN H, ZHANG J, HE Y, et al. Exploring the role of Staphylococcus aureus in inflammatory diseases. Toxins (Basel). 2022;14(7):464. [5] VOS T, ALLEN C, ARORA M, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1545-1602. [6] FALANGA V, ISSEROFF RR, SOULIKA AM, et al. Chronic wounds. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8(1):50. [7] OBAGI Z, DAMIANI G, GRADA A, et al. Principles of wound dressings: a review.Surg Technol Int. 2019;35:50-57. [8] VERDÚ-SORIANO J, CASADO-DÍAZ A, DE CRISTINO-ESPINAR M, et al. Hard-to-Heal Wound Healing: Superiority of Hydrogel EHO-85 (Containing Olea europaea Leaf Extract) vs. a Standard Hydrogel. A Randomized Controlled Trial. Gels. 2023;9(12):962. [9] VITSE J, TCHERO H, MEAUME S, et al. Silver sulfadiazine and cerium nitrate in ischemic skin necrosis of the leg and foot: Results of a prospective randomized controlled study. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2018;17(3):151-160. [10] ZHANG J, CHEN X, YU L, et al. The treatment of low leg nonischemic ulcers with a traditional Chinese-pharmaceutical medium: a randomized controlled multicenter clinical study. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2019;18(2):186-191. [11] 赵杰, 孙业祥. 浅析“煨脓长肉”理论在慢性难愈合创面中的作用机制及研究进展[J].中国烧伤创疡杂志,2024,36(6):425-428. [12] 刘曼, 张开伟. 基于“煨脓长肉”理念用石香膏促进慢性难愈性创面修复临床观察[J].实用中医药杂志,2024,40(3):423-425. [13] 凌一鸣, 费冀, 张开伟, 等. 中药石香膏对糖尿病大鼠慢性难愈合创面RAGE/NF-κBp65/eNOS mRNA表达影响的研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2019,25(7):913-917. [14] 凌一鸣, 费冀, 张开伟, 等. 石香膏对糖尿病慢性难愈合创面模型大鼠创面组织血管内皮细胞黏附分子1、核因子κB p65表达的影响[J].中医杂志,2020,61(7):619-625. [15] 费冀, 张开伟, 周一夫, 等. 石香膏干预糖尿病溃疡创面模型大鼠创面组织晚期糖基化终产物及其受体与内皮型一氧化氮合成酶表达的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(20):3196-3201. [16] 刘志伦, 关智宇, 蒋太平, 等. 石香膏干预大鼠感染难愈创面的愈合机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(26):4126-4131. [17] 李文华, 刘筱, 周雯婷, 等. 慢性难愈合创面动物模型制备方法的评价与选择 [C].第15届全国烧伤创疡学术会议论文汇编会议论文集,浏阳:2018. [18] 张晓倩, 王巍, 贾茹, 等. 炉甘石炮制前后治疗大鼠湿疹作用比较研究[J].广东化工,2022,49(2):31-32+40. [19] ASIF N, AMIR M, FATMA T. Recent advances in the synthesis, characterization and biomedical applications of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2023;46(10):1377-1398. [20] KHAJEHDEHI M, KHALAJ-KONDORI M, BARADARAN B.Molecular evidences on anti‐inflammatory, anticancer, and memory‐boosting effects of frankincense. Phytother Res. 2022;36(3):1194-1215. [21] BATIHA GE, WASEF L, TEIBO JO, et al. Commiphora myrrh: a phytochemical and pharmacological update. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023;396(3):405-420. [22] CAO B, WEI XC, XU XR, et al. Seeing the unseen of the combination of two natural resins, frankincense and myrrh: Changes in chemical constituents and pharmacological activities. Molecules. 2019;24(17): 3076. [23] SU X, HAO S, LI W, et al. Gardenia fruit and Eucommia leaves combination improves hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia via pancreatic lipase and AMPK-PPARαand Keap-1-Nrf2-HO-1 regulation. J Functional Foods. 2023;100:105394. [24] 白育军, 何希瑞, 白亚军, 等. 冰片及其酯/酰胺类衍生物的合成和活性研究进展[J].化学通报,2021,84(11):1173-1185. [25] PICKUP MJ. Pathophysiology of Wound Healing. Forensic and Legal Medicine. CRC Press. 2023:103-107. [26] PINTUCCI G, FROUM S, PINNELL J, et al. Trophic effects of platelets on cultured endothelial cells are mediated by platelet-associated fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Thromb Haemost. 2002;88(5):834-842. [27] NATH SG, RAVEENDRAN R. An insight into the possibilities of fibroblast growth factor in periodontal regeneration. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2014;18(3):289-292. [28] CATANZANO O, QUAGLIA F, BOATENG JS. Wound dressings as growth factor delivery platforms for chronic wound healing. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021;18(6):737-759. [29] FEI J, WANG LL, LIU M, et al. Study on the effect of Shixiang plaster on the expression of CD31, serum FN, and VEGF in a rat model with chronic wounds. Tradit Med Res. 2024;9:68-73. [30] SANZ-HORTA R, MATESANZ A, GALLARDO A, et al. Technological advances in fibrin for tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng. 2023;14: 20417314231190288. [31] GUO X, YANG L, DENG C, et al. Nanoparticles traversing the extracellular matrix induce biophysical perturbation of fibronectin depicted by surface chemistry. Nanoscale. 2024;16(12):6199-6214. [32] PANAGI I, THURSTON TL. Ready, STAT3, Go! Bacteria in the race for M2 macrophage polarisation. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2023;73:102285. [33] GAO X, LU C, MIAO Y, et al. Role of macrophage polarisation in skin wound healing. Int Wound J. 2023;20(7):2551-2562. [34] PENG Y, ZHOU M, YANG H, et al. Regulatory mechanism of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in the development of autoimmune diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2023;2023:8821610. [35] PANG J, MAIENSCHEIN-CLINE M, KOH TJ.Enhanced proliferation of Ly6C+ monocytes/macrophages contributes to chronic inflammation in skin wounds of diabetic mice. J Immunol. 2021;206(3):621-630. [36] CLARK RA. The molecular and cellular biology of wound repair. Springer Science & Business Media. 1996. [37] SANIN DE, GE Y, MARINKOVIC E, et al. A common framework of monocyte-derived macrophage activation. Sci Immunol. 2022;7(70): eabl7482. [38] GU M, LIU Y, ZHENG W, et al. Combined targeting of senescent cells and senescent macrophages: a new idea for integrated treatment of lung cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2024;106-107:43-57. [39] SAHA S, BUTTARI B, PANIERI E, et al. An overview of Nrf2 signaling pathway and its role in inflammation. Molecules. 2020;25(22):5474. [40] WANG L, HE C. Nrf2-mediated anti-inflammatory polarization of macrophages as therapeutic targets for osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:967193. [41] SOUSA AB, ÁGUAS AP, BARBOSA MA, et al.Immunomodulatory biomaterial-based wound dressings advance the healing of chronic wounds via regulating macrophage behavior. Regen Biomater. 2022; 9:rbac065. [42] REINKE J, SORG H. Wound repair and regeneration. Eur Surg Res. 2012;49(1):35-43. [43] MULLIN JA, RAHMANI E, KIICK KL, et al. Growth factors and growth factor gene therapies for treating chronic wounds. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023;9(3):e10642. [44] FANTIN A, VIEIRA J M, GESTRI G, et al. Tissue macrophages act as cellular chaperones for vascular anastomosis downstream of VEGF-mediated endothelial tip cell induction. Blood.2010;116(5):829-840. [45] DE PALMA M, BIZIATO D, PETROVA TV. Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(8):457-474. [46] FABRE T, BARRON AM, CHRISTENSEN SM, et al.Identification of a broadly fibrogenic macrophage subset induced by type 3 inflammation.Sci Immunol. 2023;8(82):eadd8945. [47] HUANG JG, REN JX, CHEN Y, et al. M2 macrophages mediate fibrotic scar formation in the early stages after cerebral ischemia in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(10):2208-2218. [48] YANG H, CHENG H, DAI R, et al. Macrophage polarization in tissue fibrosis. PeerJ. 2023;11:e16092. [49] SIM SL, KUMARI S, KAUR S, et al. Macrophages in skin wounds: functions and therapeutic potential. Biomolecules. 2022;12(11):1659. [50] HU M, YAO Z, XU L, et al. M2 macrophage polarization in systemic sclerosis fibrosis: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic effects. Heliyon. 2023;9(5):e16206. |
| [1] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [2] | Zhou Xinying, Sun Xinyue, Zhu Wenhao. Insulin-like growth factors and ischemic stroke: a genome-wide association analysis in European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2909-2919. |
| [3] | Cheng Xinqi, Shao Longhui, Shen Huaqiao, Liu Hongwei. Osteogenic and antibacterial effects of titanium alloy modified with copper-strontium binary doped calcium silicate coating [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4639-4646. |
| [4] | Tian Dongzi, Shen Weiwei, Li Wenshuai, Shi Jie, Deng Xiaowen, Zhao Zhengrong, Liu Dengke, Liu Taotao, Cai Maolin, Gao Qiuming. Construction and evaluation of a model of chronic osteomyelitis in sheep tibia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 2937-2942. |
| [5] | Qiu Xiaoming, Li Jidong, Kang Guan, Qiao Yongjie, Li Wenbo, Feng Qiangsheng, Zhen Ping, Lan Xu. Size of the borehole affects rabbit tibial osteomyelitis models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4429-4434. |
| [6] | Guo Pengda, Liu Keke, Duan Xin, Liu Zhaohui, Zhang Yuntao. Terpinen-4-ol with antibacterial properties promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 4006-4012. |
| [7] | Hu Jinlong, Quan Huahong, Wang Jingcheng, Zhang Pei, Zhang Jiale, Chen Pengtao, Liang Yuan. Effect of copper sulfide nanoparticles loaded thermosensitive hydrogel Pluronic F127 on infected wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1927-1931. |
| [8] | Feng Jianbo, Li Chencheng, Liu Jinyue, Wang Xiaomin, Peng Jiachen. Implantation of Kirschner wire with Staphylococcus aureus biofilm establishes a traumatic osteomyelitis model in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 700-705. |
| [9] | Zhao Yunan, Zhang Haobo, Sun Tao, Yang Xuejun. Hydrogel-based growth factors and drugs in the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: problems and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5525-5533. |
| [10] | Tang Kai, Zhao Wenhua, Shang Qi, Shen Gengyang, Zhang Zhida, He Jiahui, Zhang Peng, Yu Fuyong, Chen Guifeng, Ren Hui, Jiang Xiaobing, Yu Xiang. Effects of concentrated growth factors on the proliferation, osteogenic differentiation and migration of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4935-4939. |
| [11] | Yan Qifang, Xie Cuiliu, Yan Guowei. Effect of concentrated growth factor and bioceramic material iRoot BP on survival, proliferation and mineralization of human dental pulp cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3363-3368. |
| [12] | Zhou Yi, Liu Xiaoyan, Xiang Bingyan. Application advantages of concentrated growth factors in the field of tissue repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1631-1640. |
| [13] | Lin Miaoyuan, Li Yuwan, Liu Yi, Chen Bei, Zhang Li. Research hotspots and application value of tissue-engineered skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 153-159. |
| [14] | Xiu Yiping, Zhang Liyan, Qian Xueyi, Li Yan, Li Wantong. The clinical application of platelet-rich plasma to repair chronic refractory wounds: a retrospective study and literature retrieval evidence analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1231-1237. |
| [15] | Ma Jinchao, Liu Tiansheng, Liu Aipeng, Wang Hao, Wang Qi, Liang Yongjian, Wang Lin, Di Haiwei. Photodynamic antimicrobial chemotherapy for repairing a rabbit model of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1254-1259. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||