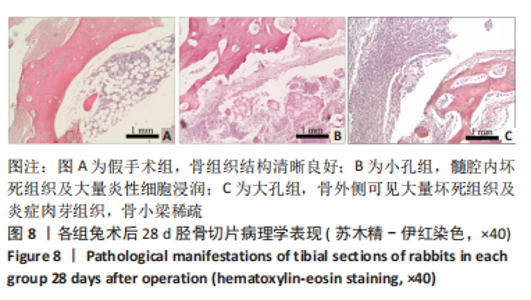
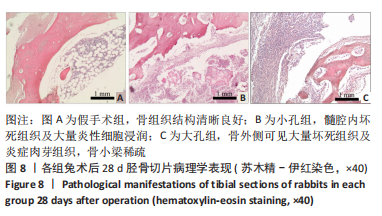
[1] LI S G, LIU Z, SUN TS, et al. VSD combined with fascio-cutaneous flap transferation staging operation to treat post-traumatic osteomyelitis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(6):516-519.
[2] TUCHSCHERR L, GERACI J, LOFFLER B. Staphylococcus aureus Regulator Sigma B is Important to Develop Chronic Infections in Hematogenous Murine Osteomyelitis Model. Pathogens. 2017;6(3):31.
[3] DE GRAAF H, SUKHTANKAR P, ARCH B, et al. Duration of intravenous antibiotic therapy for children with acute osteomyelitis or septic arthritis: a feasibility study. Health Technol Assess. 2017;21(48):1-164.
[4] PARK KH, CHO OH, LEE JH, et al. Optimal Duration of Antibiotic Therapy in Patients With Hematogenous Vertebral Osteomyelitis at Low Risk and High Risk of Recurrence. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(10):1262-1269.
[5] GEURTS J, HOHNEN A, VRANKEN T, et al. Treatment strategies for chronic osteomyelitis in low- and middle-income countries: systematic review. Trop Med Int Health. 2017;22(9):1054-1062.
[6] NORDEN CW. Experimental osteomyelitis. I. A description of the model. J Infect Dis. 1970;122(5):410-418.
[7] 陈金水, 廖肇山, 林松庆, 等. 兔股骨慢性骨髓炎模型的制作[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(49):7885-7889.
[8] 霍茜瑜, 闵昌敏, 袁琴, 等. 多重耐药鲍曼不动杆菌引起慢性骨髓炎的动物模型建立与评价[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志,2016,26(20): 2902-2905.
[9] 黄金亮, 唐辉, 范新宇, 等. 慢性难治性骨髓炎动物模型制备与鉴定[J]. 西南国防医药,2012,22(3):236-239.
[10] 袁承杰, 翁蔚宗, 周启荣, 等. 骨髓炎骨缺损动物模型构建研究进展[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(1):87-90.
[11] ROUX KM, COBB LH, SEITZ MA, et al. Innovations in osteomyelitis research: A review of animal models. Animal Model Exp Med. 2021; 4(1):59-70.
[12] 高正琴, 邢华, 孙怀昌, 等. 金黄色葡萄球菌对小鼠致病性的实验研究[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2003(2):27-29.
[13] 刘金月, 章猛奇, 卿明松, 等. 金黄色葡萄球菌性骨髓炎动物模型构建的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(14):2256-2262.
[14] QIU X, LI S, LI X, et al. Experimental study of β-TCP scaffold loaded with VAN/PLGA microspheres in the treatment of infectious bone defects. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;213:112424.
[15] 化昊天, 王新卫, 张磊, 等. 慢性骨髓炎的诊疗研究进展[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(2):132-136.
[16] 慕月晶, 王伟佳, 严海忠, 等. PCT检测在全身和局部细菌感染诊断中的临床应用[J]. 检验医学,2015,30(1):17-20.
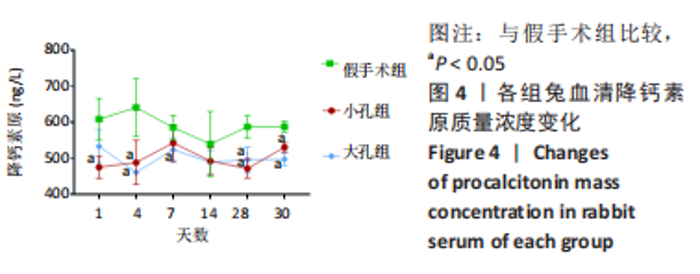
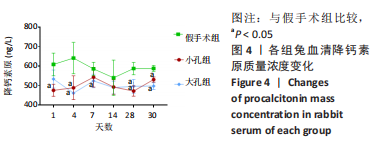
[17] 石婷婷, 李双庆, 梁利波. 降钙素原在感染中的应用及研究进展[J]. 中华全科医学,2018,16(4):620-625.
[18] 刘保光, 谢苗, 董颖, 等. 金黄色葡萄球菌研究现状[J]. 动物医学进展,2021,42(4):128-130.
[19] HORST SA, HOERR V, BEINEKE A, et al. A novel mouse model of Staphylococcus aureus chronic osteomyelitis that closely mimics the human infection: an integrated view of disease pathogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(4):1206-1214.
[20] HIENZ SA, SAKAMOTO H, FLOCK JI, et al. Development and characterization of a new model of hematogenous osteomyelitis in the rat. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(5):1230-1236.
[21] MORRISSY RT, HAYNES DW. Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis: a model with trauma as an etiology. J Pediatr Orthop. 1989;9(4):447-456.
[22] Privalov VA, Svetlakov AL, Kushakovskii OS, et al. An experimental model of suppurative osteomyelitis. Patol Fiziol Eksp Ter. 2000;(1):26-29.
[23] 王晓波, 郑欣, 陈一心. 感染性骨缺损动物模型的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2015,21(7):1158-1161.
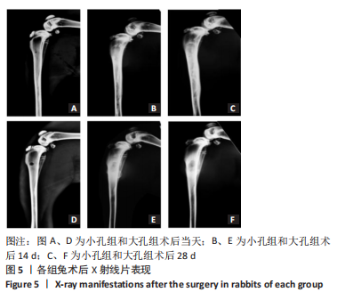
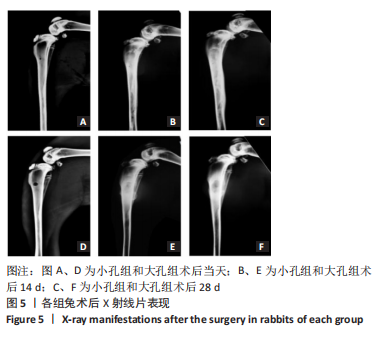
[24] XING J, HOU T, LUOBU B, et al. Anti-infection tissue engineering construct treating osteomyelitis in rabbit tibia. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013; 19(1-2):255-263.
[25] STEVENSON MC, SLATER JC, SAGI HC, et al. Diagnosing Fracture-Related Infections: Where Are We Now? J Clin Microbiol. 2022;60(2):e280720.
[26] YEN C, KAUSHIK S, DESAI SB. Image-guided percutaneous bone biopsy for pediatric osteomyelitis: correlating MRI findings, tissue pathology and culture, and effect on clinical management. Skeletal Radiol. 2022. doi: 10.1007/s00256-022-04131-4.
[27] SHAYEGAN A, ZUCCHI A, DE SWERT K, et al. Lipoteichoic acid stimulates the proliferation, migration and cytokine production of adult dental pulp stem cells without affecting osteogenic differentiation. Int Endod J. 2021;54(4):585-600.
[28] HU CC, CHANG CH, HSIAO YM, et al. Lipoteichoic Acid Accelerates Bone Healing by Enhancing Osteoblast Differentiation and Inhibiting Osteoclast Activation in a Mouse Model of Femoral Defects. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):5550.
[29] ODEKERKEN JC, WALENKAMP GH, BRANS BT, et al. The longitudinal assessment of osteomyelitis development by molecular imaging in a rabbit model. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:424652.
[30] 汪晓波, 李旭. MRI在诊断儿童长骨骨髓炎的应用价值[J]. 中国医学计算机成像杂志,2019,25(3):299-302.
[31] ZHANG W, LIN Y, ZONG Y, et al. Staphylococcus aureus Infection Initiates Hypoxia-Mediated Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 Upregulation to Trigger Osteomyelitis. mSystems. 2022;7(4):e38022. |