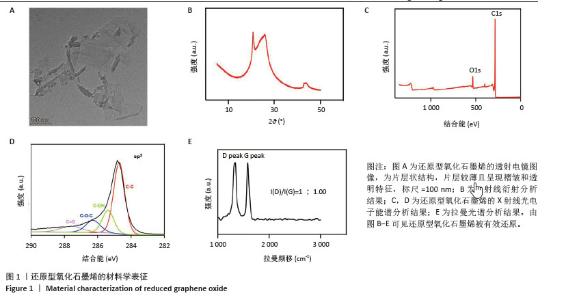
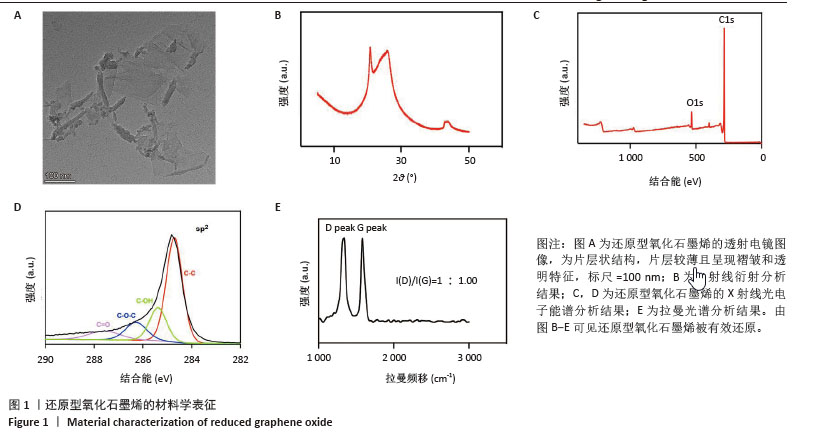
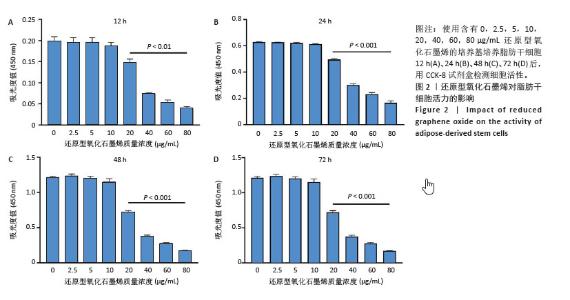
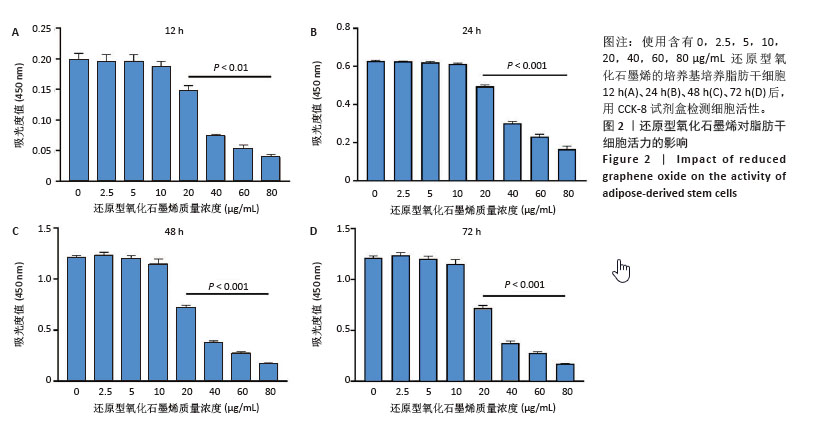
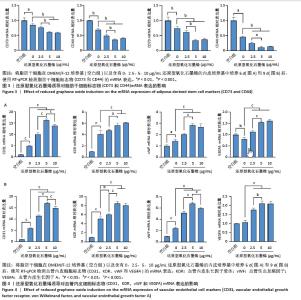
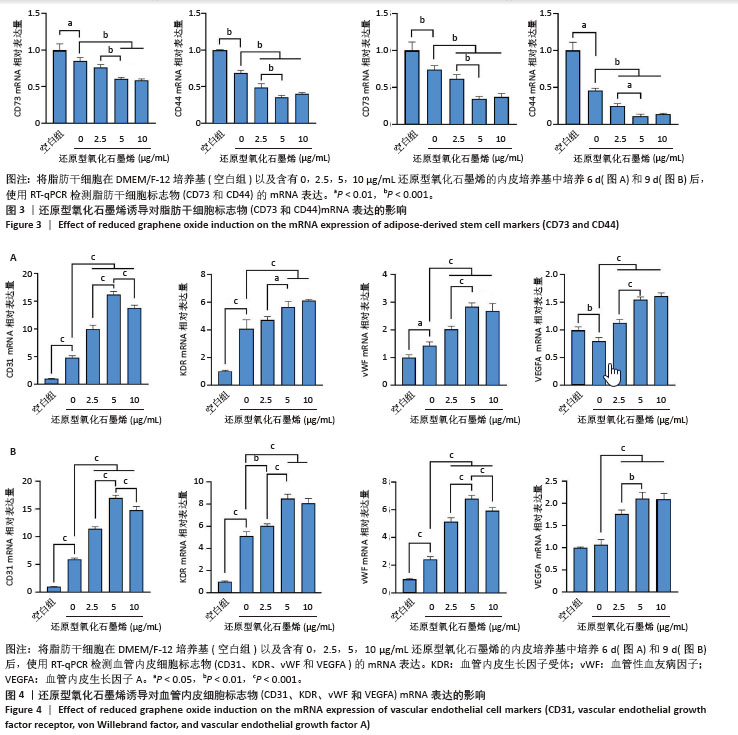
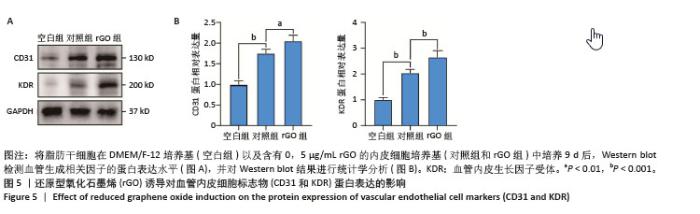
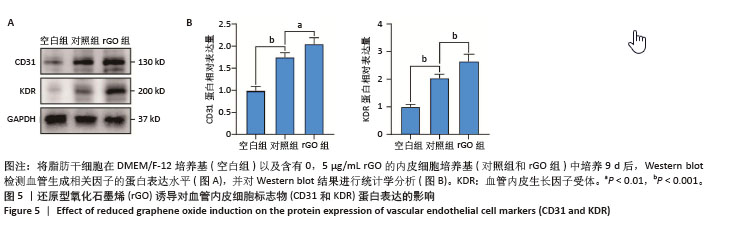
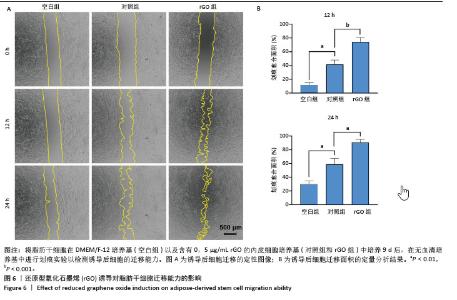
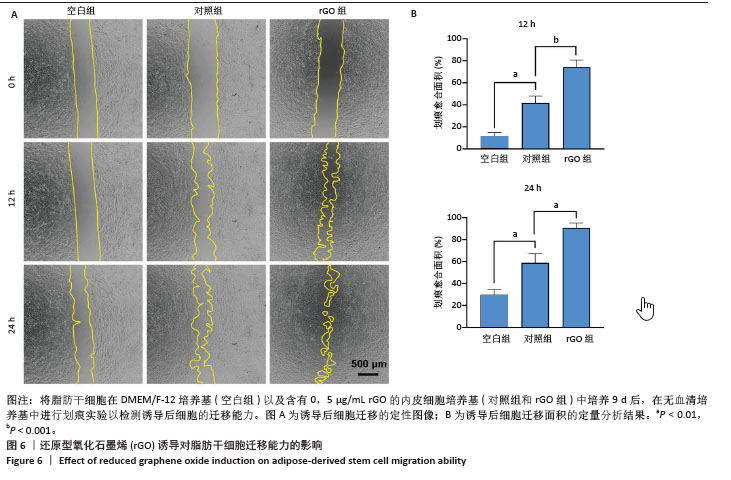
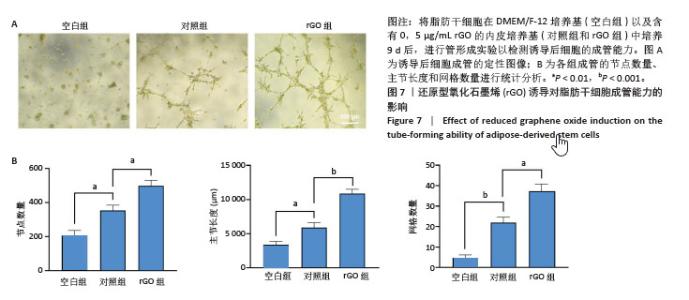
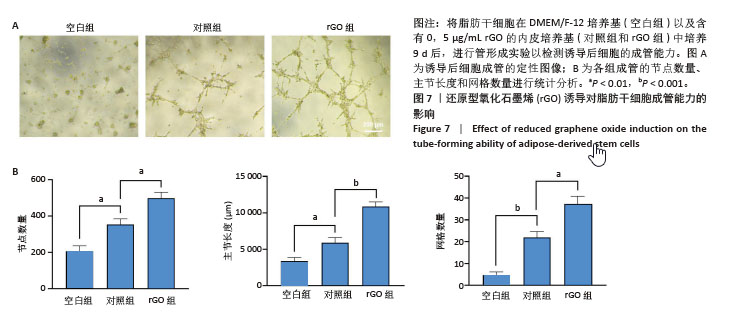
[1] ZHU J, DU Y, BACKMAN LJ, et al. Cellular Interactions and Biological Effects of Silk Fibroin: Implications for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Small. 2025;21(4):e2409739.
[2] AGHAZADEH Y, KHAN ST, NKENNOR B, et al. Cell-based therapies for vascular regeneration: Past, present and future. Pharmacol Ther. 2022; 231:107976.
[3] JUNG E, OU S, AHN SS, et al. The JNK-EGR1 signaling axis promotes TNF-α-induced endothelial differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells via VEGFR2 expression. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30(2):356-368.
[4] 沈荧怡,曹希萌,胥春.去分化脂肪细胞及其在口腔颌面部骨组织工程中应用的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2024,32(3):223-228.
[5] KANG H, FENG J, PENG Y, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue showed a more robust effect than those from the umbilical cord in promoting corneal graft survival by suppressing lymphangiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):328.
[6] 韩长杰,杨向群,张传森.脂肪干细胞的免疫学性质[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(27):5095-5098.
[7] HARASYMIAK-KRZYŻANOWSKA I, NIEDOJADŁO A, KARWAT J, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells show considerable promise for regenerative medicine applications. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2013;18(4): 479-493.
[8] QU Y, MU D, WANG Q, et al. Effects of Harvest Sites on Cryopreserved Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and ASC-Enriched Fat Grafts. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2020;44(6):2286-2296.
[9] OU L, TAN X, QIAO S, et al. Graphene-Based Material-Mediated Immunomodulation in Tissue Engineering and Regeneration: Mechanism and Significance. ACS Nano. 2023;17(19):18669-18687.
[10] KANG Y, LIU J, YIN S, et al. Oxidation of Reduced Graphene Oxide via Cellular Redox Signaling Modulates Actin-Mediated Neurotransmission. ACS Nano. 2020;14(3):3059-3074.
[11] MUKHERJEE S, SRIRAM P, BARUI AK, et al. Graphene Oxides Show Angiogenic Properties. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(11):1722-1732.
[12] HUNG HS, KUNG ML, CHEN FC, et al. Nanogold-Carried Graphene Oxide: Anti-Inflammation and Increased Differentiation Capacity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(8):2046.
[13] LEE J, MANOHARAN V, CHEUNG L, et al. Nanoparticle-Based Hybrid Scaffolds for Deciphering the Role of Multimodal Cues in Cardiac Tissue Engineering. ACS Nano. 2019;13(11):12525-12539.
[14] SHIN SR, ZIHLMANN C, AKBARI M, et al. Reduced Graphene Oxide-GelMA Hybrid Hydrogels as Scaffolds for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Small. 2016;12(27):3677-3689.
[15] LIN Z, WENG X, MA L, et al. Mechanistic insights into Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution by green reduced graphene oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019;550:1-9.
[16] THANGAVEL P, KANNAN R, RAMACHANDRAN B, et al. Development of reduced graphene oxide (rGO)-isabgol nanocomposite dressings for enhanced vascularization and accelerated wound healing in normal and diabetic rats. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;517:251-264.
[17] 李悦,刘巧玉,袁权,等.基于NOTCH1/DLL4通路的姜黄素联合生长因子促进ADSCs向血管内皮细胞分化[J].中药药理与临床, 2022,38(3):58-65.
[18] 曾玉,谢成伟,洪苑琪,等.含铜介孔生物活性玻璃的体外成血管及成骨性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(28):5941-5949.
[19] 孙安,毕翔宇,韩祥祯,等.联合应用血管内皮生长因子及血小板衍生生长因子BB干预骨髓间充质干细胞的血管化及增殖能力[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(1):1-6.
[20] 石婷婷,李少婷,于静侠,等.姜黄素调节HIF-1α/VEGF信号通路对牙髓干细胞活性及血管生成的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2025,41(2):72-76.
[21] PAN Y, LIN T, SHAO L, et al. Lignin/Puerarin Nanoparticle-Incorporated Hydrogel Improves Angiogenesis through Puerarin-Induced Autophagy Activation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:5095-5117.
[22] MIAO Y, CHEN Y, LUO J, et al. Black phosphorus nanosheets-enabled DNA hydrogel integrating 3D-printed scaffold for promoting vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;21:97-109.
[23] DOS SANTOS FKF, JÚNIOR AAMP, FILHO ALN, et al. Graphene and Natural Products: A Review of Antioxidant Properties in Graphene Oxide Reduction. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(10):5182.
[24] WANG R, LI C, WU J, et al. Coordination-Promoted Bio-Catechol Electro-Reforming toward Sustainable Polymer Production. J Am Chem Soc. 2023;145(33):18516-18528.
[25] XUE C, CAI W, WENG X, et al. A one step synthesis of hybrid Fe/Ni-rGO using green tea extract for the removal of mixed contaminants. Chemosphere. 2021;284:131369.
[26] 西南科技大学.红景天促进高海拔低氧环境下铁闪锌矿生物浸出的方法:CN202110697346.1[P].2021-08-24.
[27] ZHANG C, WANG X, FAN S, et al. Silk fibroin/reduced graphene oxide composite mats with enhanced mechanical properties and conductivity for tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;197:111444.
[28] GENG Y, YAO B, ZHONG W, et al. A General Strategy for Exceptionally Robust Conducting Polymer-Based Bioelectrodes with Multimodal Capabilities Through Decoupled Charge Transport Mechanisms. Adv Mater. 2025;37(16):e2417827.
[29] 陈曦,刘佳尚,洪华.氧化石墨烯氧化状态/横向尺寸对肝脏细胞死亡机制和炎症反应的影响[J].华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021,47(6):653-666.
[30] SIQUEIRA PR, SOUZA JP, VENTURINI FP, et al. rGO outperforms GO in generating oxidative stress and DNA strand breaks in zebrafish liver cells. Aquat Toxicol. 2023;262:106640.
[31] 李彤,杨雅茹,闵清,等.红景天苷提取、含量测定及药理作用研究进展[J].药物化学,2022,10(2):190-197. |