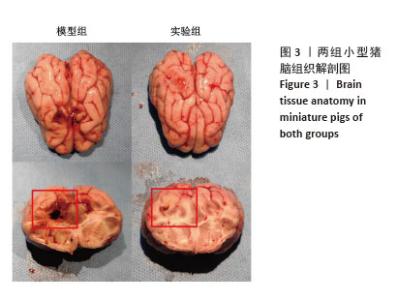
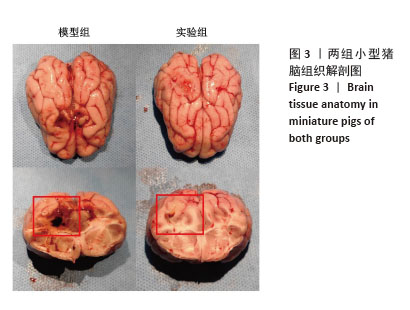
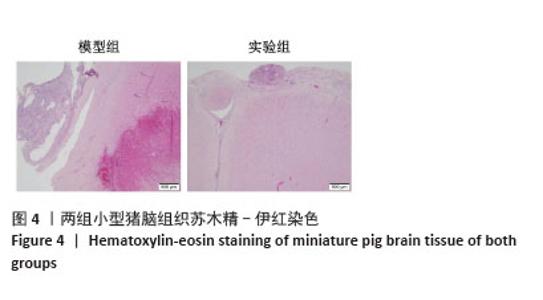
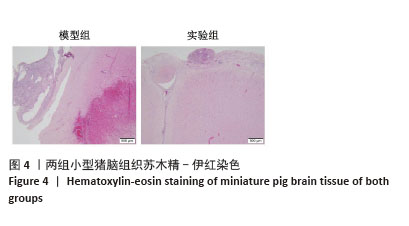
[1] BERNARD F. Neurotrauma and Intracranial Pressure Management. Crit Care Clin. 2023;39(1):103-121.
[2] ULYANKIN VE, MACHINSKY PA, VOROBIEV VG, et al. Main mechanisms of secondary ischemic brain damage formation in case of craniocerebral injury. Sud Med Ekspert. 2024;67(3):54-59.
[3] CUI L, SAEED Y, LI H, et al. Regenerative medicine and traumatic brain injury: from stem cell to cell-free therapeutic strategies. Regen Med. 2022;17(1):37-53.
[4] DEHGHANIAN F, SOLTANI Z, KHAKSARI M. Can Mesenchymal Stem Cells Act Multipotential in Traumatic Brain Injury? J Mol Neurosci. 2020;70(5):677-688.
[5] MU Z, QIN J, ZHOU X, et al. Synergistic effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells/neural stem cells and epidural electrical stimulation on spinal cord injury rehabilitation. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):26090.
[6] DING DC, CHANG YH, SHYU WC, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: a new era for stem cell therapy. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(3):339-347.
[7] CHEN Y, XU Y, CHI Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of refractory immune thrombocytopenia: a prospective, single arm, phase I trial. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):102.
[8] NOH CH, PARK S, SEONG HR, et al. An Exosome-Rich Conditioned Medium from Human Amniotic Membrane Stem Cells Facilitates Wound Healing via Increased Reepithelization, Collagen Synthesis, and Angiogenesis. Cells. 2023;12(23):2698.
[9] VACKOVCÁ I, KUBINOVÁ S. Stem cell conditioned medium for cell-free therapies. Cesk Fysiol. 2016;65(1):25-31.
[10] ROSOCHOWICZ MA, LACH MS, RICHTER M, et al. Conditioned Medium - Is it an Undervalued Lab Waste with the Potential for Osteoarthritis Management? Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(5):1185-1213.
[11] BOUCHE DJATCHE WH, ZHU H, et al. Potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived conditioned medium/secretome as a therapeutic option for ocular diseases. Regen Med. 2023;18(10):795-807.
[12] VIZOSO FJ, EIRO N, CID S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9):1852.
[13] LI J, YIN X, DU M, et al. Therapeutic effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and their conditioned medium on LPS-induced endometritis in mice. Tissue Cell. 2024;88:102346.
[14] OZKAN S, ISILDAR B, SAHIN H, et al. Comparative analysis of effects of conditioned mediums obtained from 2D or 3D cultured mesenchymal stem cells on kidney functions of diabetic rats: Early intervention could potentiate transdifferentiation of parietal epithelial cell into podocyte precursors. Life Sci. 2024;343:122543.
[15] LIU XY, WEI MG, LIANG J, et al. Injury-preconditioning secretome of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells amplified the neurogenesis and cognitive recovery after severe traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurochem. 2020;153(2):230-251.
[16] JHA KA, PENTECOST M, LENIN R, et al. Concentrated Conditioned Media from Adipose Tissue Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mitigates Visual Deficits and Retinal Inflammation Following Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):2016.
[17] LAFRENAYE AD, MONDELLO S, WANG KK, et al. Circulating GFAP and Iba-1 levels are associated with pathophysiological sequelae in the thalamus in a pig model of mild TBI. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):13369.
[18] GALIPEAU J, SENSÉBÉ L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):824-833.
[19] SEOK J, PARK HS, CETIN E, et al. The potent paracrine effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells mediates mitochondrial quality control to restore chemotherapy-induced damage in ovarian granulosa cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;172:116263.
[20] BEHZADIFARD M, ABOUTALEB N, DOLATSHAHI M, et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Conditioned Medium of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC-CM) as a Therapy for Ischemic Stroke Recovery: A Systematic Review. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(5):1280-1292.
[21] CHOI YJ, KIM WR, KIM DH, et al. Human umbilical cord/placenta mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium attenuates intestinal fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):69.
[22] L PK, KANDOI S, MISRA R, et al. The mesenchymal stem cell secretome: A new paradigm towards cell-free therapeutic mode in regenerative medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:1-9.
[23] ALIDOUST L, AKHOONDIAN M, ATEFI AH, et al. Stem cell-conditioned medium is a promising treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2023;452:114543.
[24] CHOUAIB B, HAACK-SØRENSEN M, CHAUBRON F, et al. Towards the Standardization of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome-Derived Product Manufacturing for Tissue Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(16):12594.
[25] LI L, NGO HTT, HWANG E, et al. Conditioned Medium from Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Culture Prevents UVB-Induced Skin Aging in Human Keratinocytes and Dermal Fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;21(1):49.
[26] KUSINDARTA DL, WIHADMADYATAMI H. Conditioned medium derived from bovine umbilical mesenchymal stem cells as an alternative source of cell-free therapy. Vet World. 2021;14(10):2588-2595.
[27] CAPIZZI A, WOO J, VERDUZCO-GUTIERREZ M. Traumatic Brain Injury: An Overview of Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Medical Management. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):213-238.
[28] BONSACK B, HEYCK M, KINGSBURY C, et al. Fast-tracking regenerative medicine for traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(7):1179-1190.
[29] FILIDOU E, KANDILOGIANNAKIS L, TARAPATZI G, et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fibrotic Effect of Immortalized Mesenchymal-Stem-Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium on Human Lung Myofibroblasts and Epithelial Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(9):4570.
[30] CHEN Y, LI J, MA B, et al. MSC-derived exosomes promote recovery from traumatic brain injury via microglia/macrophages in rat. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(18):18274-18296.
[31] LIU XYE, PARK E, BARRETTO T, et al. Effect of Human Umbilical Cord Perivascular Cell-Conditioned Media in an Adult Zebrafish Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Zebrafish. 2020;17(3):177-186.
|