Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (10): 1606-1612.doi: 10.12307/2024.316
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of melt electrowriting technology in tissue engineering
Jiang Yu1, He Feng2, Liu Huan3, Wu Ruixin4
- 1No. 3 Cadet Regiment, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Air Force Medical University, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China; 2State Key Laboratory of Military Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Shaanxi Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Department of Oral Surgery, Third Affiliated Hospital, Air Force Medical University, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China; 3Department of Stomatology, Xinqiao Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing 400037, China;
-
Received:2023-03-30Accepted:2023-05-10Online:2024-04-08Published:2023-08-21 -
Contact:Wu Ruixin, Attending physician, Lecturer, State Key Laboratory of Military Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Shaanxi Engineering Research Center for Dental Materials and Advanced Manufacture, Department of Periodontics, Third Affiliated Hospital, Air Force Medical University, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Jiang Yu, No. 3 Cadet Regiment, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Air Force Medical University, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82101013 (to WRX); Natural Science Basis Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China, No. 2022JQ-959 (to WRX); Natural Science Foundation Project of Chongqing, No. cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0638 (to LH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Yu, He Feng, Liu Huan, Wu Ruixin. Application of melt electrowriting technology in tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1606-1612.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
2.1 静电纺丝技术概述 2.1.1 静电纺丝的概念与分类 随着材料制造技术的发展,如3D生物打印、微流体纺丝、湿法纺丝、干法纺丝、静电纺丝等,纳米或微米纤维材料的制备变得越来越容易,其应用也越来越广泛,涵盖能源、催化、电子和光子设备、组织工程等众多领域[3]。其中,静电纺丝技术作为一种生产纳米纤维的有力工具,生产的纤维具有高比表面积、高孔隙率等特殊的性能,逐渐获得越来越多的关注。 关于静电纺丝概念的萌芽,最早可以追溯到1600年,WILLIAM GILBERT在研究中发现,在外部电场存在的条件下圆形水滴可以成为锥形。直到1964-1969年,GEOFFREY TAYLOR发表了一系列论文,才开创性地采用数学方式描述锥形液滴的形成过程,并提出了“泰勒锥”的概念:随着电场强度增加到临界水平,球形液滴克服表面张力,逐渐演变成锥形,发出液体射流[4]。上述发现为研究静电纺丝的机制奠定了基础。静电纺丝的两种基本形式为溶液静电纺丝和熔体静电纺丝。溶液静电纺丝通过有机溶剂的挥发产生纤维;熔体静电纺丝则通过直接加热形成熔融状态的聚合物,从而冷却沉积形成纤维,加热方式包括循环液、激光和电加热等。关于熔体静电纺丝的文章最早发表于20世纪80年代,相较于溶液静电纺丝,由于设备的复杂性和缺少对于纺丝机制的深入研究,熔体静电纺丝发展进程相对缓慢[5]。 传统的溶液静电纺丝设备主要由高压电源、注射泵、喷头和收集器构成,高压电场加载于喷头处,称为电极正接;熔体静电纺丝装置的特殊之处在于增添了额外的加热元件置于喷头处,而需要复杂的装置才能实现高压电源与加热元件的有效隔绝,因此熔体静电纺丝装置多采用电极反接的方式,即将高压电场加载于接收板,喷头接地[6]。熔体静电纺丝装置在加热元件的作用下将聚合物熔体液化,与溶液静电纺丝类似,聚合物从喷头处挤出的同时,通过外部施加高压电场使聚合物熔体产生表面电荷,随着电压的增加,液滴逐渐克服表面张力和黏弹性力形成射流,并经过冷却和固化沉积在收集器上[7]。整个过程可以分为连续的4个阶段:①液滴充电,泰勒锥形成;②增加电压,射流形成;③射流拉伸,进入鞭打不稳定阶段;④纤维的固化与收集[4]。 检索静电纺丝的相关文献可以发现,在组织工程领域尤其是在组织工程支架的制备与其有着密不可分的关系。良好的组织工程支架应具有良好的生物相容性、细胞浸润性、表面亲水性、开放的孔隙、一定的生物降解性和结构稳定性等优点[8]。静电纺丝生产的纳米纤维不仅具有高比表面积、高孔隙率,同时生产的纳米纤维结构在一定程度上可以模拟天然细胞外基质[9],而其中的熔体静电纺丝技术在组织工程支架制备方面表现出更优越的性能:首先,溶液静电纺丝有机溶剂的残留对细胞存在一定的毒性且不符合环保要求,熔体静电纺丝则不存在有机溶剂的残留问题[4];其次,用于熔体静电纺丝的聚合物具备较高的黏度和低导电性,使纤维射流阶段运动的路径较溶液静电纺丝更加稳定[10];此外,熔体静电纺丝工作效率高,并可以在一定程度上实现纤维的有序沉积,为制备出更加精细和特定形态的3D组织工程支架奠定了基础。但是,该技术制备的纤维直径相对于溶液静电纺丝较粗、对聚合物的要求高,这些缺点限制了其发展。在组织工程领域的研究中,熔体静电纺丝技术存在的主要问题是如何通过纤维的有序沉积形成特定的支架形态,以及如何提高细胞的浸润性和实现血管化[11]。 2.1.2 熔体静电纺丝技术发展 影响熔体静电纺丝过程的参数大致包括工艺(如熔体温度、外加电场、喷头尖端与收集器之间的距离、熔体进给率等)、材料(如聚合物熔体的黏度、种类等)、环境(温度、湿度)3方面参数[12-13],见表1。在该技术应用过程中,研究者对上述参数不断进行改进,其中SUN等于2006年正式提出的近场静电纺丝技术被认为是较为可靠的一种方法。近场静电纺丝技术通过改变喷头与收集器之间的距离,采用2D/3D运动收集平台,实现纤维的可控沉积和低电压纺丝:通过缩小喷头尖端和收集器之间的距离,在直线运动阶段完成纤维的沉积;同时通过平台移动速度和射流速度的匹配增加纤维沉积的可控性[3]。随着技术的不断改进,如通过采用多喷头增加纤维生产效率等,近场静电纺丝技术在能源、组织工程、可穿戴设备等领域获得越来越广泛的应用[14]。但是在组织工程支架制备过程中,随着纤维的不断沉积,近场静电纺丝技术中的过量电荷积累在纤维表面,支架的结构被扭曲破坏,限制了大体积和具有足够厚度支架的制备[15]。作为熔体近场静电纺丝的一种,熔体静电纺丝直写技术在组织工程领域的应用也面临着同样挑战。"
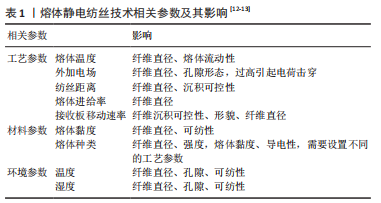
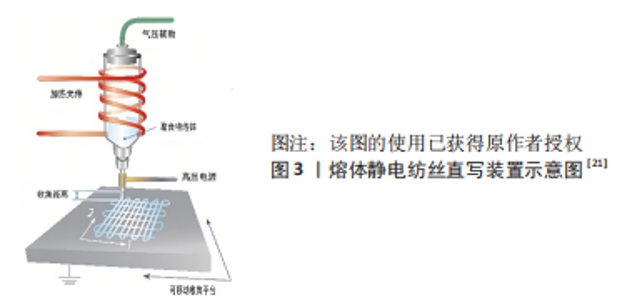
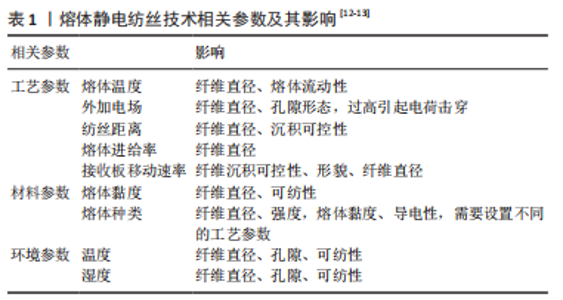
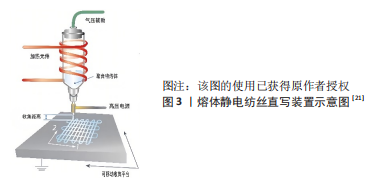
从表1中可以看出,不同参数对纤维直径都存在着或多或少的影响,而在不同的应用领域纤维直径也具有至关重要的作用,如在环境保护领域,纤维直径对于滤过膜的滤过效率有着十分重要的作用;在组织工程领域,不同的纤维直径影响着细胞的浸润、增殖、分化等行为。此外,针对不同的纤维制备要求,熔体静电纺丝装置已经发展出多种类别:多温度控制熔体静电纺丝用于增强和控制纤维尺寸和形态;气体辅助熔体静电纺丝可控制聚合物的降解;激光熔体静电纺丝可以减少高熔点聚合物的热降解;无针熔体静电纺丝可以高效、连续、大规模地生产纤维等[16]。熔体静电纺丝直写技术作为在此基础上发展起来的新兴技术,正在组织工程领域发挥着越来越重要的作用。 2.1.3 熔体静电纺丝直写技术的优势 熔体静电纺丝直写技术将熔体静电纺丝技术和基于熔融挤出的3D打印技术相结合,同时采用计算机辅助设计和控制[3]。熔体静电纺丝直写技术除了具备传统静电纺丝的优点外,还能够实现纤维的逐层精确沉积,可以更好地模拟天然组织的复杂结构;相较于其他3D打印技术,熔体静电纺丝直写技术可以生产直径更小的纤维,形成高度有序的多孔结构。熔体静电纺丝直写技术在实现纤维逐层精确沉积和支架3D结构的构建方面更具优势,在组织工程领域表现出巨大潜力[1]。2008年的一项研究,通过在熔体静电纺丝装置中使用可移动的x-y收集平台实现了图案化纤维的收集,同时实现了成纤维细胞在其表面的生长,初步进行了关于熔体静电纺丝直写技术及相关参数的研究[17]。DALTON等[17]通过熔体静电纺丝精确沉积聚(ε-己内酯)纤维,并第一次实现了连续纤维层沉积制备支架,其中实现连续写入的关键是将收集平台的移动速率与射流速度相匹配。BROWN等[18-19]采用熔体静电纺丝直写技术设计组织工程管状支架,并将原代人成骨细胞、间皮细胞以及小鼠成骨细胞接种于支架,支架表现出良好的细胞相容性,实现了细胞的浸润生长。FARRUGIA等[20]在该方法制备的支架上采用顶部接种成纤维细胞,实现了细胞的全层浸润生长。这些研究证明了该技术在调控细胞行为方面的优势及其在组织工程领域应用的可行性,同时也为此后复杂组织工程构建体的研究奠定了基础。熔体静电纺丝直写装置示意图[21],见图3。"
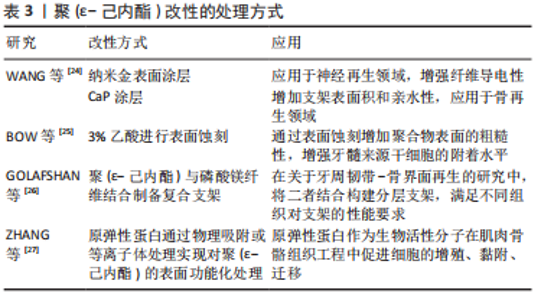
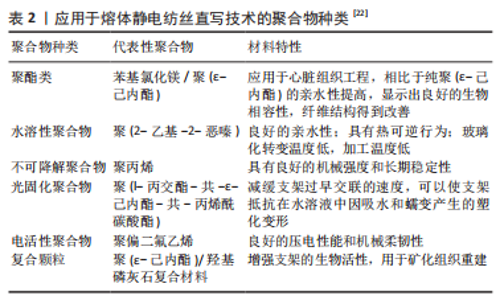
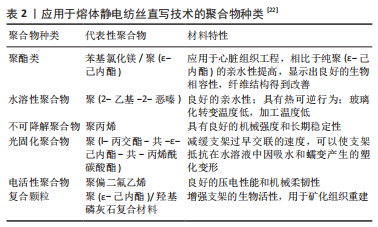
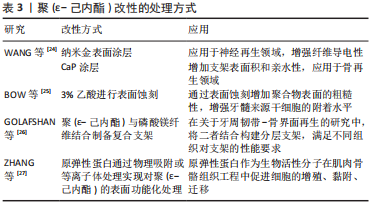
聚(ε-己内酯)作为应用最多的聚酯类聚合物,其优势表现在熔点低、热稳定性好、具有生物降解性、凝固快,其中按照药品生产质量管理规范生产的高纯度医用级聚(ε-己内酯)的精度和可控性更好[22],但聚(ε-己内酯)具有一定的疏水性,主要通过蛋白质沉积实现细胞的吸附和增殖,细胞浸润性较差,且缺乏生物活性信号[22]。为了克服这些缺点,在聚(ε-己内酯)的应用过程中已经采用了多种方法来改进其性能,包括:使用NaOH等试剂对聚(ε-己内酯)进行化学处理,通过等离子体处理在聚(ε-己内酯)表面形成含氧基团,通过引入活性基团增加细胞识别位点,与其他亲水性聚合物结合制备混合纤维等[23],见表3。其中,通过与其他聚合物结合制备混合纤维,实现不同聚合物间的性能互补结合是目前应用较多的一种方法。"
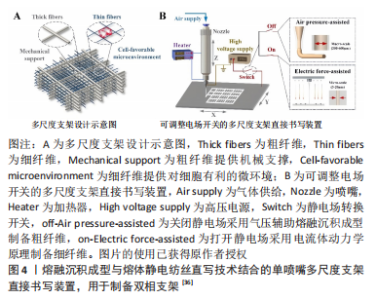
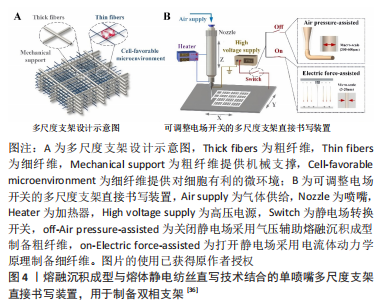
亲水性聚合物主要包括聚(2-恶唑啉)和聚(2-恶嗪),具有良好的生物相容性、剪切稀化特性、热响应特性和化学多功能性[28],通过熔体静电纺丝直写技术加工的纤维直径范围在8-138 μm[29],目前此类聚合物主要用于药物递送系统。基于此类生物墨水制备具有三维结构的水凝胶采用的交联方法包括物理交联、化学交联、借助酶促反应交联[30],其中紫外线照射、光引发剂、化学交联剂等对于细胞活性的影响仍存在争议,而关于聚(2-恶唑啉)和聚(2-恶嗪)的部分研究采用互补官能团实现原位化学交联。在一项关于聚(2-恶嗪)的研究中,通过借助呋喃和马来酰亚胺官能团实现Diels-Alder(DA)交联,一方面,聚合物在冷却沉积阶段可以自发进行化学交联,提高不同纤维层间的结合力,同时由于不存在其他化学添加剂,材料具有低细胞毒性,利于细胞的黏附和增殖;另一方面,由于交联具有热可逆性,部分不完全交联的官能团为材料的后处理修饰提供机会。相比于聚(2-恶唑啉),聚(2-恶嗪)玻璃化转变温度低,可以降低加工温度、减少热引起的副反应的发生、提高打印的连续性。此外,亲水性聚合物的膨胀程度与材料刚性相关,通过控制水解和改性程度进而影响聚合物的交联密度,或通过调整材料的亲水性来实现材料刚性的调整[31]。此类聚合物符合软组织所需的弹性和柔软性,交联保证了支架的尺寸稳定性,自身的特性保证了其具有可调节性,虽然目前其并未成功应用于临床,但随着研究的深入,在涉及软组织再生的组织工程领域其将发挥一定的作用。 目前应用较多的电活性聚合物包括聚(3,4-乙烯二氧噻吩)、聚吡咯、聚苯胺。在心脏、骨骼、平滑肌、神经组织工程领域,理想的构建体不仅需要有精确的形貌指导组织生长,同时还需要一定的电导率实现细胞之间的良好通信,促进细胞分化和组织再生[32]。掺入金属纳米颗粒是增强组织工程支架导电性的传统方法,但这种方法多数集中于体外研究,而关于其细胞毒性的体内研究仍然存在空白,限制了其在医疗实践中的应用[33]。目前电活性聚合物正引起越来越多的关注,但此类聚合物多不可降解,可印刷性差,常通过与其他种类聚合物结合构建具备良好导电性能和力学性能的生物支架。 羟基磷灰石作为骨组织中重要的无机成分对骨基质的重塑和产生具有十分重要的作用。在软骨组织工程中,常采用含羟基磷灰石颗粒的杂交生物材料促进软骨细胞的增殖和迁移、干细胞的软骨分化。 材料本身的性质影响构建体的生物活性和机械性能,而不同的印刷策略可以提高材料的可印刷性和形状稳定性,因此,在组织工程构建体的应用过程中,选择具有合适性质和功能的材料以及制定针对性的印刷策略是至关重要的。用于生物医学领域的材料对于生物相容性、降解性、机械强度、印刷性、凝固成型性、分子渗透性和仿生生物活性具有一定的要求[34],而在不同的生物医学应用中对材料性能的要求并不完全相同。开发更多的材料解决目前组织工程中的难题是应当关注的一个研究方向,而根据目前现有不同种类材料的性能实现一定的优化组合,制定合适的打印策略的重要性也不应被忽视。 2.2.2 熔体静电纺丝直写技术制备复杂结构支架 由于组织工程再生常常涉及多种组织、细胞,为了构建出更接近天然组织的分层复杂结构,实现多种细胞在空间的不同分布,近年来一些研究通过将不同打印技术或材料结合制备双相/多相支架,从而弥补各种技术的缺陷,这种方法的优势也获得了越来越多的关注[35]。 (1)熔体静电纺丝直写技术结合熔融沉积成型:熔体静电纺丝直写技术与熔融沉积成型的结合同时实现了支架对于机械强度和生物活性的要求。熔体静电纺丝直写技术可以产生微米至纳米尺度的纤维,如前所述,接近细胞大小的小尺度纤维有利于细胞的黏附和增殖,但机械强度不足使其应用受到一定的限制,而熔融沉积成型产生的粗纤维则具有足够的机械强度,通过两种技术的结合这一问题得到解决。GAO等[36]开发了一种单喷嘴多尺度支架直接书写装置,通过调整电压实现熔融沉积成型和熔体静电纺丝直写技术打印模式的切换,从而调整聚(ε-己内酯)支架的结构,同时平衡支架的机械强度和生物相容性,将骨髓间充质干细胞接种于支架上,结果表明相比于熔融沉积成型制备的大尺度支架,在该支架上的细胞表现出更好的生物学行为(图4)。通过两种技术的结合在一定程度上同时满足了支架的生物设计要求和力学设计要求。"

(2)熔体静电纺丝直写技术结合溶液静电纺丝:溶液静电纺丝可以产生小直径纤维,单独制备支架时,常由于纤维随机沉积和支架孔径过小而无法实现细胞的良好浸润,而熔体静电纺丝直写技术通过计算机控制可以实现纤维的定向沉积,并具有良好的孔隙率和一定的机械强度。JUNGST等[37]将溶液静电纺丝与熔体静电纺丝直写技术结合采用两步法制备双层管状支架,采用溶液静电纺丝制备内层致密的纤维网,实现了血管内皮的形成;熔体静电纺丝直写技术制备定向排列的外层纤维网以支持血管平滑肌细胞的分化,通过进行细胞共培养实现了细胞间的良好通信。 (3)熔体静电纺丝直写技术结合水凝胶:水凝胶作为经典的组织工程生物材料是细胞培养的重要载体,可以模拟天然细胞生长环境,具有出色的亲水性和水溶性,但机械性能不足限制了其发展[38]。通过熔体静电纺丝直写技术与水凝胶结合制备混合材料,水凝胶使支架表现出更好的生物相容性和合适的降解性,使细胞保持良好的生长,熔体静电纺丝直写技术制备的纤维保证了支架有足够的机械性能。该方法在骨和软骨再生、脉管系统形成、口颌面部组织工程中都发挥着一定的作用[38-40],见表4。"

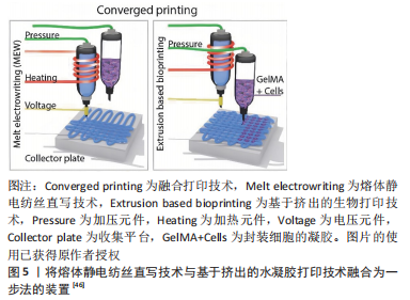
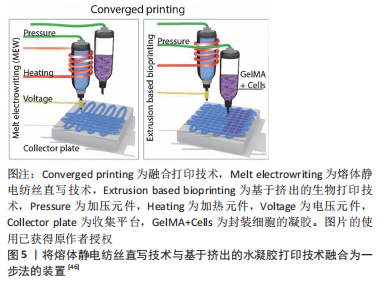
BAS等[45]采用通过熔体静电纺丝直写技术与水凝胶结合制备的支架结构,与无熔体静电纺丝直写技术支架增强的水凝胶相比弹性模量和拉伸强度均得到提升。上述复合支架的制备大多数是采用两步法制造,即通过基于挤出的生物打印技术制备用于细胞封装的水凝胶,然后将其嵌入熔体静电纺丝直写技术制备的纤维支架中实现复合支架的制备,但是两步法限制了支架设计的自由度以及所使用的材料种类和细胞类型。为了突破这些局限性,DE RUJITER等[46]首次将熔体静电纺丝直写技术和基于挤出的水凝胶打印技术结合到同一个装置,采用一步法在利用熔体静电纺丝直写技术制备纤维的同时,与细胞封装的水凝胶结合,实现了对打印过程的精准控制,并保证了细胞活力(图5)。"
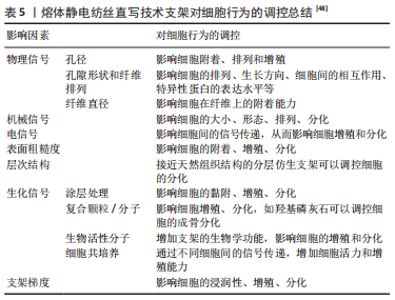
此外,通过改变设备自身参数,熔体静电纺丝直写技术可以实现多尺度的纤维直径制备。HRYNEVICH等[47]通过交替改变熔体静电纺丝直写技术参数,同时生产出直径在2-50 μm范围的纤维,在不改变电压的情况下,主要通过改变喷嘴的射流速度与收集器速度的匹配情况而进行纤维直径控制,实现多相支架的制备。ZIELI?SKI等[48]用熔体静电纺丝直写技术制备3层聚(ε-己内酯)支架,孔径分别为750,500和250 μm,相比于孔径均匀的支架表现出更好的细胞浸润和增殖,其中较大的孔隙保证了氧气和营养物质的有效运输,而较小的孔隙确保了支架足够的机械稳定性。 混合制造技术在组织工程领域的优势主要体现在以下几点:首先,混合制造方法为复杂和仿生组织工程支架的构建提供了解决办法,如脉管系统的构建;其次,通过不同技术的混合可以在保持支架生物力学性能的同时增加支架的孔隙率;同时,通过混合制造可以增加初始细胞密度,加快细胞增殖速率,缩短组织形成和成熟的时间[35]。总之,制备复杂组织结构支架需要充分考虑材料与细胞之间的相互作用,通过熔体静电纺丝直写技术与其他技术的结合,在不改变材料成分的条件下,充分结合各种方法的优势实现支架结构的调整,从而在保证支架力学性能的同时实现对细胞生物学行为的调控是一种可行的策略。 2.3 熔体静电纺丝直写技术支架调控细胞行为 组织工程支架需要满足细胞的定植、迁移、生长、分化和细胞外基质的沉积,支架的物理、化学、力学和生物学特性对支架-细胞的相互作用都会产生不同程度的影响[49],见表5。因此,优异的支架应具备良好的生物相容性、一定的可降解性、亲水性的表面、开放和足够的孔隙、足够的机械强度、合适的孔径和形状等性能[7-8]。为了能更好地指导细胞行为,支架需要提供特定的物理和生化信号促进组织形成,良好的支架设计是实现这些功能的前提。"
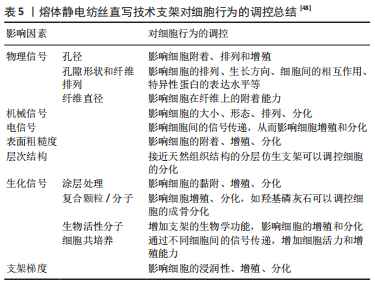

2.3.1 物理信号 支架提供的物理信号受到支架孔径、孔隙形状、纤维直径大小、孔隙率以及纤维排列等的影响,支架的机械性能、导电性、亲水性等都会导致细胞不同的生物学行为[36]。孔径和孔隙间的互连性被认为是影响细胞行为和组织再生的2个重要因素[38]。支架孔径在细胞附着、排列和增殖方面发挥着重要的作用[4]。相关研究发现,不同孔径对于细胞增殖速率和细胞形态的形成产生不同影响:小孔径具有更高的细胞接种效率,而大孔径和高孔隙率由于营养和氧气的有效运输表现出更高的增殖速率。此外,在小孔径(100 μm或更小)支架上的细胞形态多为圆形;而在较大孔径的支架,细胞会沿着纤维孔隙伸长生长[36]。关于孔径及其形态在骨组织再生中的作用,相关研究指出:大孔隙率(> 50 μm)对于血管的再生和骨组织的生长具有重要作用,小孔隙率(< 50 μm)则可以增加蛋白质的吸附[50] 。 此外,支架纤维直径、孔隙形状等对于细胞的黏附、增殖、分化也存在不同程度的影响[49]。在小直径纤维上,细胞表现出更快的迁移速度;在大直径纤维上,细胞表现出更远的迁移距离,细胞的伸长率增加[51]。不同的孔隙形状会对支架的力学性能产生一定的影响,六边形支架相比矩形支架拥有更好的弹性形变能力,在心肌组织工程中分别将六边形和矩形熔体静电纺丝直写技术支架用于培养诱导多能干细胞分化的心肌细胞,六边形支架诱导出更多的心脏标志物表达,反映出支架力学性能对细胞成熟存在一定的影响[48]。 2.3.2 生化信号 生化信号通常以可溶性或不溶性因子混合物的形式与支架相结合,从而调控细胞的生物学行为。生物活性分子(如生长因子、酶、药物、蛋白质等)的修饰在细胞-纤维的相互作用中发挥重要的作用。结合海藻酸酯甲基纤维素的聚(ε-己内酯)支架在软骨细胞的培养中表达出高水平的硫酸化糖胺聚糖,促进了软骨形成;将纤连蛋白和明胶等细胞外基质成分作为聚(ε-己内酯)支架的涂层,增强了细胞黏附、附着和毛细血管结构的形成;将生物活性乳蛋白与聚(ε-己内酯)混合,由于生物活性乳蛋白的免疫调节作用,如乳清蛋白的抗氧化作用和乳铁蛋白的抗炎作用,增强了细胞的浸润、生长和扩散,从而进一步促进组织再生[48]。 2.4 熔体静电纺丝直写支架重建血管和神经 在各种组织的再生过程中,早期血管的形成可以为组织的再生提供足够的营养。血管组织工程移植物目前面临的挑战是如何实现血管内细胞的分层分化,实现功能化血管的再生[52]。熔体静电纺丝直写技术可以实现支架形貌的精确控制,在血管组织工程移植物具有一定的优势。PENNINGS等[53]采用静电纺丝和熔体静电纺丝直写技术结合开发用于双层血管移植物的灌注两室生物反应器,实现了细胞层特异性分化,产生了类似天然组织的血管结构。为了得到具有仿生结构的血管系统模型,有研究采用牺牲模板法,用熔体静电纺丝直写技术生产具有低临界溶液温度的聚(2-环丙基-2-恶唑啉)支架,在嵌入水凝胶的过程中通过降温至25 ℃以下使纤维溶解,在水凝胶基质中形成相互交连的微脉管网络,实现了快速功能化血管内皮的生成[40]。 熔体静电纺丝直写技术在纳米和微米范围内可以实现对支架结构(孔径和形状、纤维铺设角度、高度)和纤维直径的高度可重复控制,制造具有高表面体积比的高度有序多孔支架。由于氧气和营养物质在组织内扩散极限是150-200 μm,实现组织血管化需要对血管网络的几何形状进行明确控制,即实现仿生制造需要构建复杂的分层结构,支架需要有明确的三维形貌[54]。因此,熔体静电纺丝直写技术在该领域具有很大的发展潜力。 在神经再生领域,熔体静电纺丝直写支架为神经再生提供3D环境,通过熔体静电纺丝直写技术制备的支架与基质结合创建用于神经再生的3D模型,实现了功能化神经元网格的形成[55]。HAMMERL等[56]通过熔体静电纺丝直写技术将金纳米颗粒与聚(ε-己内酯)纤维网格结合制备导电支架,促进神经突生长以进行神经再生。此外,熔体静电纺丝直写技术也可以定制具有不同形貌的神经引导导管修复周围神经损伤[57]。然而,熔体静电纺丝直写技术在神经再生领域的应用仍处于起步阶段,但支架在血管再生方面的优势将有助于为神经再生提供所需的营养[58];同时该技术可实现对支架设计的精确控制,这将为神经细胞的生长提供更好的指导。 总之,血管化和神经再生对于复杂组织结构的生理性重建具有重要的意义。如人体骨骼具有高度血管化结构和神经支配,骨组织再生关键在于成骨和血管化。在机体内,血管不仅为骨骼系统提供氧气等营养物质,去除骨骼中的代谢物,还为骨骼提供其他组织分泌的特定激素、生长因子和神经递质,维持骨细胞活性[59];神经系统通过神经肽、激素、细胞因子等参与成骨,通过靶向成骨细胞和破骨细胞的功能调节骨再生。目前的研究集中在神经束或骨植入材料在骨组织工程中的使用,关于协同促进神经骨骼再生的研究较少,设计出能同时满足神经和骨组织再生的支架具有一定的挑战[60]。 2.5 熔体静电纺丝直写支架重建软硬组织界面 2.5.1 牙周韧带-骨界面 颅颌面部的组织再生同时涉及软硬组织,各组织之间大小、结构、功能复杂,同时涉及血管、神经、骨骼和感觉器官等的重建。针对复杂结构的组织工程再生,目前研究通过多种生物打印技术的有效融合,构建用于复杂组织结构的支架/结构用以重建结构和功能之间的关系。如前所述,熔体静电纺丝直写技术在血管、神经、骨再生方面的潜力都为颅颌面部再生策略的实现奠定了基础。其中,牙周组织作为一个复杂的功能体,其再生涉及多种组织和细胞,牙周韧带-骨界面的再生具有极大的挑战,如何实现牙槽骨的再生以及重建功能性牙周韧带是牙周再生的最终目标[26]。 牙周炎作为严重影响人类健康的口腔疾病之一,目前临床应用引导组织再生和引导骨再生弥补牙周炎引起的组织破坏,通过天然材料(如Bio-Guide)或静电纺丝技术制备引导组织再生/引导骨再生膜,但由于静电纺丝纤维更多地聚集在2D平面,无法有效实现细胞的浸润生长和组织血管化,不能实现牙周组织真正意义上的生理性再生[61]。熔体静电纺丝直写技术可以构建高度有序的支架结构,实现特定支架形貌的构建。为了构建与天然牙周组织类似的复杂3D组织结构,同时实现软硬组织的协调生长,一些研究试图将熔体静电纺丝直写技术用于牙周组织再生的研究中,在牙周韧带再生和牙槽骨再生方面表现出一定的潜力。部分关于牙周组织再生的研究考虑通过设计具有针对牙周韧带和骨组织的特异性区域的支架,重建软硬组织界面,并最终实现具备功能的组织重建,同时血管化和神经再生在牙周组织工程中的作用也不应被忽视[11]。 相关研究通过熔体静电纺丝直写技术制备聚(ε-己内酯)双相支架,支架针对牙周韧带和骨再生的特点设计了2个不同的区域,符合不同组织各自特定的纤维结构和组成,实现了牙周韧带再生和在牙本质表面的附着,一定程度上实现了骨和牙周韧带之间的组织整合,为实现牙周组织功能性再生提供了可能[62]。近年来,多区室支架的发展为更好实现不同组织之间的浸润和整合提供了可能,借助于熔体静电纺丝直写支架的高精度设计策略,其在牙周韧带再生方面表现出巨大潜力。YAO等[63]采用熔体静电纺丝直写技术制备高度有序的多区室支架,支架分为骨区室、牙周韧带区室以及二者之间的过渡区域,实现了不同类型细胞(原代人成骨细胞和牙周膜成纤维细胞)的协调增殖和分化,为复杂的牙周缺损再生提供了可能。同时,熔体静电纺丝直写支架对于细胞行为的调控在牙周韧带-骨界面再生的过程中也发挥着一定的作用,通过制备具有不同的纤维排列、孔径、孔隙形态的支架,调控成骨和巨噬细胞极化,在以炎症为特征的牙周炎治疗中具有重要作用[64-65]。DAGHRERY及其团队[11]通过熔体静电纺丝直写技术制备特定结构的聚(ε-己内酯)支架,实现对人源性牙周韧带干细胞和巨噬细胞的分化指导,支架纤维排列高度有序,孔径为500 μm,采用氟化磷酸钙(F/CaP)涂层处理的条件下更有利于实现接近天然牙周组织结构的再生。 2.5.2 骨软骨界面 骨软骨界面由于缺少血管,受损后愈合能力有限,目前临床的治疗方法包括药物治疗和手术治疗,主要用于缓解受损后引起的疼痛和骨关节炎等症状。手术治疗包括自体软骨细胞移植、镶嵌式成形术、微骨折术等,但会导致纤维软骨瘢痕组织的生成,并不能阻止关节的进一步退化,因此如何实现骨软骨缺损的再生与修复是十分重要的[66]。骨软骨界面组织作为连接软骨和软骨下骨的过渡区域,具有复杂的解剖组成和独特的力学性质,生物活性支架在该领域具有一定的潜力,优异的仿生支架应具有与天然组织物理、化学、生理和机械特性吻合的分级结构。目前开发的支架主要包括离散梯度和连续梯度支架,离散梯度支架各层的物理和化学性质呈离散分布,在分层支架中通过调整可以形成层间连续梯度;连续梯度支架更接近天然组织结构,具有比离散梯度支架更优异的性能,但通过在支架上直接接种细胞模拟具有复杂组织结构和细胞成分的天然组织结构比较困难,相关支架制备具备一定的挑战[67]。 在骨软骨界面再生领域,通过多种技术的结合可以在一定程度上解决上述问题。熔体静电纺丝直写技术具有可以实现高精度纤维的多层沉积、具有多孔结构等特点,在软骨支架的制备中具有一定的优势。在分层软骨支架制备过程中,熔体静电纺丝直写技术可以更好地模拟天然软骨的多层不均匀结构,但其不能模拟骨软骨组织的区域异质性,应用具有一定的局限性。相关研究通过结合喷墨技术将预封装特异性细胞因子的微球喷洒到聚(ε-己内酯)支架上,构建多层复合支架,诱导骨髓间充质干细胞实现软骨分化;实验将转化生长因子β1、骨形态发生蛋白7、胰岛素样生长因子1封装在聚D,L-乳酸-共-乙二醇微球中,通过喷墨技术将其均匀喷洒在支架中,为骨髓间充质干细胞的分化创造适宜的微环境,模拟正常软骨组织的分层性能,促进了损伤的部分修复[68]。 熔体静电纺丝直写技术可以实现小直径纤维的精确控制组装,重建骨软骨组织的各向异性纤维结构,为构建具有空间分层和机械性能增强的仿生支架提供潜在的可能。相关研究开发了一种3层纤维水凝胶结构,通过熔体静电纺丝直写技术制造三嵌段聚合物网络,即聚(ε-己内酯)-嵌-聚(乙二醇)-嵌-聚(ε-己内酯)纤维,将兔骨髓间充质干细胞和封装有特异性生长因子的聚D,L-乳酸-共-乙二醇微球掺入到水凝胶混合材料中,逐层注入纤维中,制备出具有增强的机械性能和层特异性诱导活性的连续分层骨软骨结构,体内实验同时实现了软骨和软骨下骨的再生,为模拟天然骨软骨组织的空间分层结构,实现功能性骨软骨再生提供了一定的可能[69]。 综上所述,无论是血管、神经的再生,还是同时涉及软硬组织的界面再生,熔体静电纺丝直写技术都具有自身独特的优势,借助于计算机的辅助设计,一定程度满足了复杂组织再生对于支架形貌和设计精度的需求;同时在多种技术和材料的融合发展趋势下,混合制造技术也将引起越来越多的关注,为分层复杂组织支架设计提供更多可行的策略。"

| [1] LOEWNER S, HEENE S, BAROTH T, et al. Recent advances in melt electro writing for tissue engineering for 3d printing of microporous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:896719. [2] VESVORANAN O, ANUP A, HIXON KR. Current concepts and methods in tissue interface scaffold fabrication. Biomimetics (Basel). 2022;7(4):151. [3] KONG B, LIU R, GUO J, et al. Tailoring micro/nano-fibers for biomedical applications. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:328-347. [4] XUE J, WU T, DAI Y, et al. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications. Chem Rev. 2019;119(8):5298-5415. [5] HUTMACHER DW, DALTON PD. Melt electrospinning. Chem Asian J. 2011;6(1):44-56. [6] 李好义,贾紫初,刘宇亮,等.高压静电加载形式对聚合物熔体静电直写制备效果的影响[J].纺织学报,2023,44(4):32-37. [7] MUERZA-CASCANTE ML, HAYLOCK D, HUTMACHER DW, et al. Melt electrospinning and its technologization in tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2015;21(2):187-202. [8] KIM BS, PARK KE, KIM MH, et al. Effect of nanofiber content on bone regeneration of silk fibroin/poly(ε-caprolactone) nano/microfibrous composite scaffolds. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:485-502. [9] PARK SH, KIM TG, KIM HC, et al. Development of dual scale scaffolds via direct polymer melt deposition and electrospinning for applications in tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2008;4(5):1198-1207. [10] WUNNER FM, WILLE ML, NOONAN TG, et al. Melt electrospinning writing of highly ordered large volume scaffold architectures. Adv Mater. 2018;30(20):e1706570. [11] DAGHRERY A, FERREIRA JA, XU J, et al. Tissue-specific melt electrowritten polymeric scaffolds for coordinated regeneration of soft and hard periodontal tissues. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:268-281. [12] BUBAKIR M, LI H, BARHOUM A, et al. Advances in melt electrospinning technique.Handbook of Nanofibers,2017. [13] CHEN Z, LIU Y, HUANG J, et al. Influences of process parameters of near-field direct-writing melt electrospinning on performances of polycaprolactone/nano-hydroxyapatite scaffolds. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(16):3404. [14] HE XX, ZHENG J, YU GF, et al. Near-field electrospinning: progress and applications. J Phys Chem C. 2017;121(16):8663-8678. [15] NAZEMI MM, KHODABANDEH A, HADJIZADEH A. Near-field electrospinning: crucial parameters, challenges, and applications. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022;5(2):394-412. [16] IBRAHIM YS, HUSSEIN EA, ZAGHO MM, et al. Melt electrospinning designs for nanofiber fabrication for different applications: 10. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2455. [17] DALTON PD, JOERGENSEN NT, GROLL J, et al. Patterned melt electrospun substrates for tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2008;3(3): 034109. [18] BROWN TD, DALTON PD, HUTMACHER DW. Direct writing by way of melt electrospinning. Adv Mater. 2011;23(47):5651-5657. [19] BROWN TD, SLOTOSCH A, THIBAUDEAU L, et al. Design and fabrication of tubular scaffolds via direct writing in a melt electrospinning mode. Biointerphases. 2012;7(1-4):13. [20] FARRUGIA BL, BROWN TD, UPTON Z, et al. Dermal fibroblast infiltration of poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffolds fabricated by melt electrospinning in a direct writing mode. Biofabrication. 2013;5(2):025001. [21] CASTILHO M, FEYEN D, FLANDES-IPARRAGUIRRE M, et al. Melt electrospinning writing of poly-hydroxymethylglycolide-co-ε-caprolactone-based scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(18).doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700311. [22] KADE JC, DALTON PD. Polymers for melt electrowriting. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(1): e2001232. [23] CIPITRIA A, SKELTON A, DARGAVILLE TR, et al. Design, fabrication and characterization of pcl electrospun scaffolds—a review. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(26):9419-9453. [24] WANG Y, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z, et al. An injectable high-conductive bimaterial scaffold for neural stimulation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;195:111210. [25] BOW AJ, MASI TJ, DHAR MS. Etched 3d-printed polycaprolactone constructs functionalized with reduced graphene oxide for enhanced attachment of dental pulp-derived stem cells. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(12):2146. [26] GOLAFSHAN N, CASTILHO M, DAGHRERY A, et al. Composite graded melt electrowritten scaffolds for regeneration of the periodontal ligament-to-bone interface. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(10):12735-12749. [27] ZHANG M, WANG Z, ZHANG A, et al. Development of tropoelastin-functionalized anisotropic pcl scaffolds for musculoskeletal tissue engineering. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbac087. [28] TRACHSEL L, ZENOBI-WONG M, BENETTI EM. The role of poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazoline)s in hydrogels and biofabrication. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(8):2874-2886. [29] HOCHLEITNER G, HÜMMER JF, LUXENHOFER R, et al. High definition fibrous poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) scaffolds through melt electrospinning writing. Polymer. 2014;55(20): 5017-5023. [30] GHAVAMINEJAD A, ASHAMMAKHI N, WU XY, et al. Crosslinking strategies for 3d bioprinting of polymeric hydrogels. Small. 2020;16(35):e2002931. [31] NAHM D, WEIGL F, SCHAEFER N, et al. A versatile biomaterial ink platform for the melt electrowriting of chemically-crosslinked hydrogels. Mater Horiz. 2020;7(3):928-933. [32] RITZAU-REID KI, SPICER CD, GELMI A, et al. An electroactive oligo-edot platform for neural tissue engineering. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(42):2003710. [33] ASRI NAN, MAHAT MM, ZAKARIA A, et al. Fabrication methods of electroactive scaffold-based conducting polymers for tissue engineering application: a review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:876696. [34] XIAORUI L, FUYIN Z, XUDONG W, et al. Biomaterial inks for extrusion-based 3d bioprinting: property, classification, modification, and selection. Int J Bioprint. 2022; 9(2):649. [35] DALTON PD, WOODFIELD TBF, MIRONOV V, et al. Advances in hybrid fabrication toward hierarchical tissue constructs. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(11):1902953. [36] GAO Q, XIE C, WANG P, et al. 3D printed multi-scale scaffolds with ultrafine fibers for providing excellent biocompatibility. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;107: 110269. [37] JUNGST T, PENNINGS I, SCHMITZ M, et al. Heterotypic scaffold design orchestrates primary cell organization and phenotypes in cocultured small diameter vascular grafts. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(43):1905987. [38] DAGHRERY A, DE SOUZA ARAÚJO IJ, CASTILHO M, et al. Unveiling the potential of melt electrowriting in regenerative dental medicine. Acta Biomater. 2023;156:88-109. [39] GALARRAGA JH, LOCKE RC, WITHEREL CE, et al. Fabrication of msc-laden composites of hyaluronic acid hydrogels reinforced with mew scaffolds for cartilage repair. Biofabrication. 2021;14(1). doi:10.1088/1758-5090/ac3acb [40] RYMA M, GENÇ H, NADERNEZHAD A, et al. A print-and-fuse strategy for sacrificial filaments enables biomimetically structured perfusable microvascular networks with functional endothelium inside 3d hydrogels. Adv Mater. 2022;34(28):e2200653. [41] DE RUIJTER M, HRYNEVICH A, HAIGH JN, et al. Out-of-plane 3d-printed microfibers improve the shear properties of hydrogel composites. Small. 2018;14(8).doi: 10.1002/smll.201702773. [42] DILOKSUMPAN P, DE RUIJTER M, CASTILHO M, et al. Combining multi-scale 3d printing technologies to engineer reinforced hydrogel-ceramic interfaces. Biofabrication. 2020; 12(2):025014. [43] AMAGAT J, SU Y, SVEJSØ FH, et al. Self-snapping hydrogel-based electroactive microchannels as nerve guidance conduits. Mater Today Bio. 2022;16:100437. [44] AFGHAH F, IYISON NB, NADERNEZHAD A, et al. 3D fiber reinforced hydrogel scaffolds by melt electrowriting and gel casting as a hybrid design for wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(11):e2102068. [45] BAS O, DE-JUAN-PARDO EM, MEINERT C, et al. Biofabricated soft network composites for cartilage tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2017;9(2):025014. [46] DE RUIJTER M, RIBEIRO A, DOKTER I, et al. Simultaneous micropatterning of fibrous meshes and bioinks for the fabrication of living tissue constructs. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(7):e1800418. [47] HRYNEVICH A, ELÇI BŞ, HAIGH JN, et al. Dimension-based design of melt electrowritten scaffolds. Small. 2018;14(22):e1800232. [48] ZIELIŃSKI PS, GUDETI PKR, RIKMANSPOEL T, et al. 3D printing of bio-instructive materials: toward directing the cell. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:292-327. [49] WANG F, CAI X, SHEN Y, et al. Cell-scaffold interactions in tissue engineering for oral and craniofacial reconstruction. Bioact Mater. 2023;23:16-44. [50] PEREZ RA, MESTRES G. Role of pore size and morphology in musculo-skeletal tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;61:922-939. [51] JENKINS TL, LITTLE D. Synthetic scaffolds for musculoskeletal tissue engineering: cellular responses to fiber parameters. NPJ Regen Med. 2019;4:15. [52] DEVILLARD CD, MARQUETTE CA. Vascular tissue engineering: challenges and requirements for an ideal large scale blood vessel. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:721843. [53] PENNINGS I, VAN HAAFTEN EE, JUNGST T, et al. Layer-specific cell differentiation in bi-layered vascular grafts under flow perfusion. Biofabrication. 2019;12(1):015009. [54] BERTLEIN S, HIKIMOTO D, HOCHLEITNER G, et al. Development of endothelial cell networks in 3d tissues by combination of melt electrospinning writing with cell-accumulation technology. Small. 2018;14(2).doi: 10.1002/smll.201701521. [55] JANZEN D, BAKIRCI E, WIELAND A, et al. Cortical neurons form a functional neuronal network in a 3d printed reinforced matrix. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(9):e1901630. [56] HAMMERL A, DIAZ CANO CE, DE-JUAN-PARDO EM, et al. A growth factor-free co-culture system of osteoblasts and peripheral blood mononuclear cells for the evaluation of the osteogenesis potential of melt-electrowritten polycaprolactone scaffolds. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(5):1068. [57] ZHANG Z, JØRGENSEN ML, WANG Z, et al. 3D anisotropic photocatalytic architectures as bioactive nerve guidance conduits for peripheral neural regeneration. Biomaterials. 2020;253:120108. [58] PIEN N, KRZYSLAK H, SHASTRY KALLAJE S, et al. Tissue engineering of skeletal muscle, tendons and nerves: a review of manufacturing strategies to meet structural and functional requirements. Appl Mater Today. 2023;31:101737. [59] FILIPOWSKA J, TOMASZEWSKI KA, NIEDŹWIEDZKI Ł, et al. The role of vasculature in bone development, regeneration and proper systemic functioning. Angiogenesis. 2017;20(3): 291-302. [60] ZHANG Z, HAO Z, XIAN C, et al. Neuro-bone tissue engineering: multiple potential translational strategies between nerve and bone. Acta Biomater. 2022;153:1-12. [61] AYTAC Z, DUBEY N, DAGHRERY A, et al. Innovations in craniofacial bone and periodontal tissue engineering - from electrospinning to converged biofabrication. Int Mater Rev. 2022;67(4):347-384. [62] STAPLES R, IVANOVSKI S, VAQUETTE C. Fibre-guiding biphasic scaffold for perpendicular periodontal ligament attachment. Acta Biomater. 2022;150:221-237. [63] YAO Y, RAYMOND JE, KAUFFMANN F, et al. Multicompartmental scaffolds for coordinated periodontal tissue engineering. J Dent Res. 2022;101(12):1457-1466. [64] MONDADORI C, CHANDRAKAR A, LOPA S, et al. Assessing the response of human primary macrophages to defined fibrous architectures fabricated by melt electrowriting. Bioact Mater. 2023;21:209-222. [65] TYLEK T, BLUM C, HRYNEVICH A, et al. Precisely defined fiber scaffolds with 40 μm porosity induce elongation driven m2-like polarization of human macrophages. Biofabrication. 2020;12(2):025007. [66] YILDIRIM N, AMANZHANOVA A, KULZHANOVA G, et al. Osteochondral interface: regenerative engineering and challenges. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(3):1205-1223. [67] GAO H, PAN Q, DONG W, et al. Progress in osteochondral regeneration with engineering strategies. Ann Biomed Eng. 2022;50(10):1232-1242. [68] HAN Y, LIAN M, SUN B, et al. Preparation of high precision multilayer scaffolds based on melt electro-writing to repair cartilage injury. Theranostics. 2020;10(22):10214-10230. [69] QIAO Z, LIAN M, HAN Y, et al. Bioinspired stratified electrowritten fiber-reinforced hydrogel constructs with layer-specific induction capacity for functional osteochondral regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;266:120385. |
| [1] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [3] | Mei Jingyi, Liu Jiang, Xiao Cong, Liu Peng, Zhou Haohao, Lin Zhanyi. Proliferation and metabolic patterns of smooth muscle cells during construction of tissue-engineered blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [5] | Kong Jianda, Mu Yujing, Zhu Lei, Li Zhilin, Chen Shijuan. Mechanism of satellite cell regulation and its role in ecological niche signaling during skeletal muscle regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1105-1111. |
| [6] | Huang Yuxin, Liang Wenzi, Chen Xiuwen, Ni Na, Zhao Yinglin, Lin Changmin. Role of autophagy in hair regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1112-1117. |
| [7] | Shen Ziqing, Xia Tian, Shan Yibo, Zhu Ruijun, Wan Haoxin, Ding Hao, Pan Shu, Zhao Jun. Vascularized tracheal substitutes constructed by exosome-load hydrogel-modified 3D printed scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 697-705. |
| [8] | Wang Jianchun, Yang Shuqing, Su Xin, Wang Hongyuan. Different contents of B2O3 affect mechanical properties and bioactivity of bioactive glass scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 712-716. |
| [9] | Zhang Yihai, Shang Peng, Ma Benyuan, Hou Guanghui, Cui Lunxu, Song Wanzhen, Qi Dexuan, Liu Yancheng. Structural design and mechanical property analysis of trabecular scaffold of triply periodic minimal surface with a radial gradient [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 741-746. |
| [10] | Zhu Liwei, Wang Jiangyue, Bai Ding. Application value of nanocomposite gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels in different bone defect environments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [11] | Xu Rong, Wang Haojie, Geng Mengxiang, Meng Kai, Wang Hui, Zhang Keqin, Zhao Huijing. Research advance in preparation and functional modification of porous polytetrafluoroethylene artificial blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 759-765. |
| [12] | Yin Tong, Yang Jilei, Li Yourui, Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming. Application of core-shell structured nanofibers in oral tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 766-770. |
| [13] | Chen Xiaofang, Zheng Guoshuang, Li Maoyuan, Yu Weiting. Preparation and application of injectable sodium alginate hydrogels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
| [14] | Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu. Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [15] | Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu. Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||