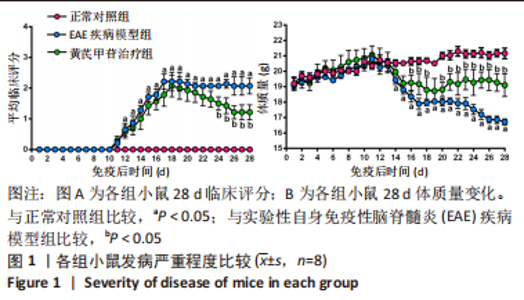
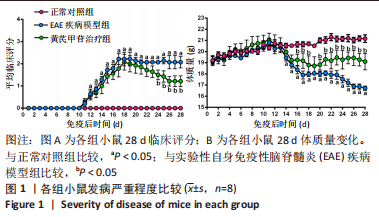
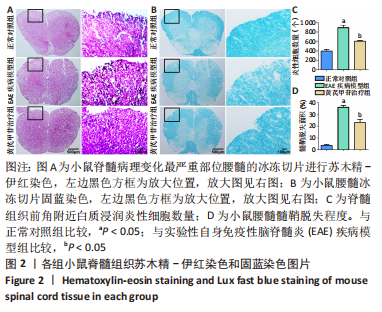
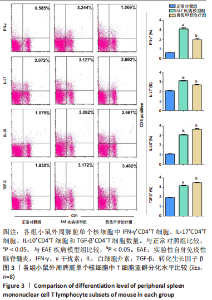
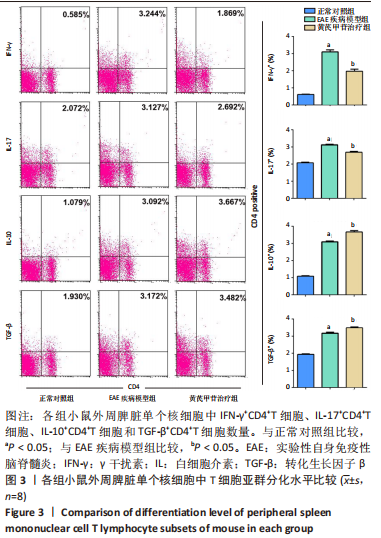
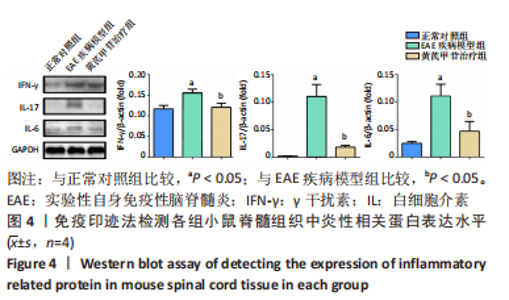
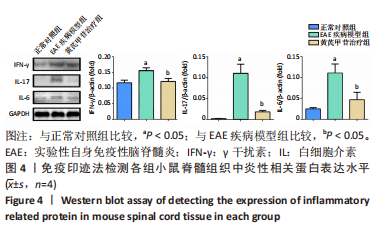
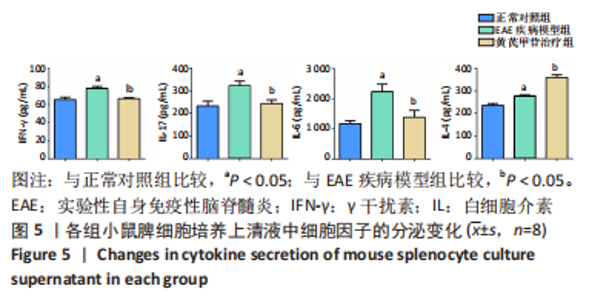
[1] 钟晓南,胡学强.《多发性硬化诊断和治疗中国专家共识(2018版)》解读[J].中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志,2019,26(2):80-83.
[2] 王金丽.NAD+通过调节骨髓源性抑制细胞的活性抑制实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的机制研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2020.
[3] LOTFI R, NASIRI KALMARZI R, RAJABINEJAD M, et al. The role of immune semaphorins in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: Potential therapeutic targets. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;95:107556.
[4] BAR-OR A, LI R. Cellular immunology of relapsing multiple sclerosis: interactions, checks, and balances. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(6):470-483.
[5] COULOUME L, MICHEL L. New concepts on immunology of Multiple Sclerosis. Presse Med. 2021;50(2):104072.
[6] VAN LANGELAAR J, RIJVERS L, SMOLDERS J, et al. B and T Cells Driving Multiple Sclerosis: Identity, Mechanisms and Potential Triggers. Front Immunol. 2020;11:760.
[7] HAUSER SL. Progress in Multiple Sclerosis Research: An Example of Bedside to Bench. JAMA. 2020;324(9):841-842.
[8] XIE H, YANG X, CAO Y, et al. Role of lipoic acid in multiple sclerosis. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28(3):319-331.
[9] 高颖,谢瑶,刘佳,等.多发性硬化的病机认识与分期辨治思路[J].北京中医药,2022,41(7):704-708.
[10] 马文玲,蒋晓静,胡睿,等.黄芪甲苷在免疫细胞方面的作用机制研究进展[J].中医临床研究,2022,15(14):145-148.
[11] 张丽红,郭敏芳,张慧宇,等.黄芪糖蛋白对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠血脑屏障作用的研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2019,48(10):878-882.
[12] 邢雁霞,刘斌钰,赵一锦,等.黄芪糖蛋白对EAE小鼠的神经保护作用及其修复机制分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(24):7-13.
[13] 李慧堂,张岱男,张新中,等.黄芪甲苷对大鼠创伤性脑损伤后脑水肿、炎症反应、细胞凋亡的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2022,31(9):1198-1223.
[14] YU J, GUO M, LI Y, et al. Astragaloside IV protects neurons from microglia-mediated cell damage through promoting microglia polarization. Folia Neuropathol. 2019;57(2):170-181.
[15] 刘建春,张红珍,李俊莲,等.黄芪总皂苷对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的神经保护及修复机制研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(11): 6700-6704.
[16] URBAN JL, KUMAR V, KONO DH, et al. Restricted use of T cell receptor V genes in murine autoimmune encephalomyelitis raises possibilities for antibody therapy. Cell. 1988;54(4):577-592.
[17] DE JONG JM, WANG P, OOMKENS M, et al. Remodeling of the interstitial extracellular matrix in white matter multiple sclerosis lesions: Implications for remyelination (failure). J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(7):1370-1397.
[18] BITTNER S, ZIPP F. Progression in multiple sclerosis - a long-term problem. Curr Opin Neurol. 2022;35(3):293-298.
[19] SHIN T, AHN M, KIM J, et al. Visual Dysfunction in Multiple Sclerosis and its Animal Model, Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: a Review. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(7):3484-3493.
[20] OLEK MJ. Multiple Sclerosis. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(6):ITC81-ITC96.
[21] GILMORE W, LUND BT, LI P, et al. Repopulation of T, B, and NK cells following alemtuzumab treatment in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):189.
[22] D’AMICO E, ZANGHÌ A, AVOLIO C. Injectable versus oral first-line multiple sclerosis therapies: knows and unknowns from observational studies. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(3):567-568.
[23] 胡妮娜,张晓娟.黄芪的化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J].中医药信息, 2021,38(1):76-82.
[24] 白宏,别蓓蓓,常翠翠,等.黄芪甲苷的药理活性研究进展[J].西北药学杂志,2022,37(3):198-202.
[25] LI S, DOU B, SHU S, et al. Suppressing NK Cells by Astragaloside IV Protects Against Acute Ischemic Stroke in Mice Via Inhibiting STAT3. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12:802047.
[26] 周怡锦,田新磊,祝志朋,等.黄芪甲苷通过抑制IL-6/JAK2/STAT3信号通路调节肺脾气虚反复呼吸道感染模型大鼠的Th17/Treg细胞平衡[J].中药材,2022,45(10):2473-2478.
[27] FENG H, ZHU X, TANG Y, et al. Astragaloside IV ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome‑mediated inflammation. Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(2):164.
[28] DOU B, LI S, WEI L, et al. Astragaloside IV suppresses post-ischemic natural killer cell infiltration and activation in the brain: involvement of histone deacetylase inhibition. Front Med. 2021;15(1):79-90.
[29] 赵彩萍,刘翠玲,梁爽,等.黄芪甲苷对脂多糖诱导人胃黏膜上皮细胞GES-1的抗炎作用及机制研究[J].中药新药与临床药理,2020,31(8):918-923.
[30] 杨睿,樊海军,张伟,等.黄芪甲苷在多发性硬化症模型动物中的保护作用及机制研究[J].中国药师,2022,25(7):1138-1144.
[31] 刘建春,张红珍,郭文娟,等.黄芪甲苷对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的防治作用[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(6):3119-3122.
[32] BASAK J, MAJSTEREK I. miRNA-Dependent CD4+ T Cell Differentiation in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis. Mult Scler Int. 2021;2021:8825588.
[33] CHÁVEZ MD, TSE HM. Targeting Mitochondrial-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species in T Cell-Mediated Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 703972.
[34] 丁月文,钱庭霖,刘祝贺,等.六味地黄汤通过树突状细胞Notch信号通路调节T细胞分化干预自身免疫性脑脊髓炎[J].安徽中医药大学学报,2022,41(1):54-58.
[35] RUDER J, DOCAMPO MJ, REX J, et al. Dynamics of T cell repertoire renewal following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in multiple sclerosis. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14(669):eabq1693.
[36] 韩振翔,侯臻臻,韩翔,等.醒神解郁汤对卒中后抑郁模型大鼠Th1/Th2及BDNF水平的影响[J].上海中医药杂志,2021,55(3):87-92.
[37] AMORIELLO R, GREIFF V, ALDINUCCI A, et al. The TCR Repertoire Reconstitution in Multiple Sclerosis: Comparing One-Shot and Continuous Immunosuppressive Therapies. Front Immunol. 2020;11:559.
[38] 刘振山,季哲,康自珍.Act1介导的IL-17信号通路与自身免疫性脑脊髓炎关系的研究进展[J].生命科学,2017,29(9):891-897.
[39] SERVAAS NH, ZAARAOUI-BOUTAHAR F, WICHERS CGK, et al. Longitudinal analysis of T-cell receptor repertoires reveals persistence of antigen-driven CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell clusters in systemic sclerosis. J Autoimmun. 2021;117:102574.
[40] ANSARI MA, NADEEM A, ALSHAMMARI MA, et al. Cathepsin B inhibitor alleviates Th1, Th17, and Th22 transcription factor signaling dysregulation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Exp Neurol. 2022;351:113997.
[41] 李红岩,侯振江,刘建凤,等.Th17/Treg细胞及其细胞因子在神经系统自身免疫性疾病中的研究进展[J].医学综述,2021,27(5):889-895,900.
[42] SALIGRAMA N, ZHAO F, SIKORA MJ, et al. Opposing T cell responses in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nature. 2019;572(7770): 481-487.
|