Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (25): 3949-3955.doi: 10.12307/2023.171
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and performance evaluation of calcium sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/ hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan multilayer dressing
Pan Wei, Li Shuyang, Liu Jinhui, Liang Cheng, Duan Ke, Chen Xingtao
- Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, School of Clinical Medicine of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2022-01-26Accepted:2022-05-14Online:2023-09-08Published:2023-01-17 -
Contact:Chen Xingtao, PhD, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, School of Clinical Medicine of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Pan Wei, Senior nurse, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, School of Clinical Medicine of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Doctoral Research Initiation Fund of Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, No. 20085 (to CXT); Doctoral Research Initiation Fund of Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, No. 20089 (to LSY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pan Wei, Li Shuyang, Liu Jinhui, Liang Cheng, Duan Ke, Chen Xingtao. Preparation and performance evaluation of calcium sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/ hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan multilayer dressing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 3949-3955.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

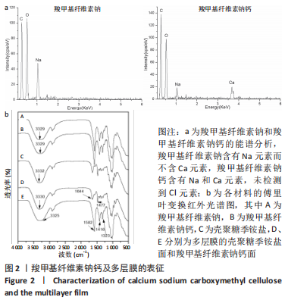
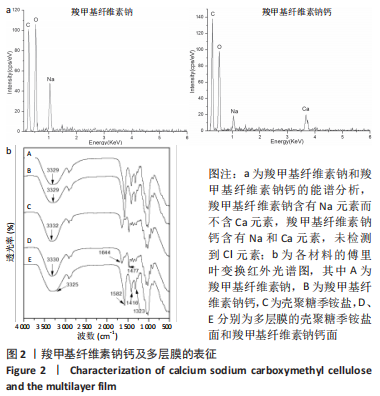
多层膜两面的傅里叶红外光谱见图2b所示。对于CMC-Ca面,3 325 cm-1左右的宽峰为O-H的伸缩振动峰;-COO-基团的不对称拉伸振动峰位于1 582 cm-1,而对称拉伸振动峰位于1 416,1 323 cm-1;与CMC-Ca相比,特征峰几乎不变。对于壳聚糖季铵盐面,3 330 cm-1左右的宽峰为O-H和N-H的拉伸振动峰;1 644,1 477 cm-1的2个峰分别对应于三甲基铵基中C=O的伸缩振动峰和C-H的弯曲振动峰;特征峰也与纯壳聚糖季铵盐几乎相同。结果与多层膜的设计预期相符。 多层膜(MF2)表面和断面的形貌,见图3所示,不同比例多层膜仅界面层位置有差别。两表面均显示均匀光滑的表面形貌,而断面则显示明显的分层结构,中间的界面层清晰可见(图中虚线框内)。对每层的能谱分析结果显示:壳聚糖季铵盐层(顶层)不含Na和Ca元素,富含Cl元素;CMC-Ca层(底层)不含Cl元素,富含Na和Ca元素;界面层(中间层)含有Na、Ca和Cl元素,与聚电解质复合物的特征相符。该结果与图2b中多层膜两面的傅里叶红外光谱结果相符,即多层膜的壳聚糖季铵盐面和CMC-Ca面的红外特征峰及元素组成与设计预期一致,进一步证明多层膜的结构与设计预期相符。"

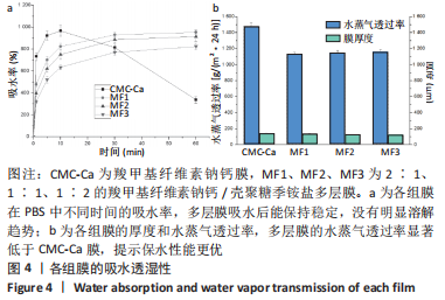
2.2 多层膜的吸水保湿性 CMC-Ca膜、多层膜在PBS中浸泡不同时间后的吸水率,见图4a所示。纯CMC-Ca膜在最初的10 min内迅速吸水溶胀,吸水率最高达967%,而后呈溶解趋势,导致测定的吸水率逐渐降低。3种多层膜在最初的10 min内也快速吸水,吸水速率低于CMC-Ca,随后吸水速率逐渐减缓并呈稳定趋势。与纯CMC-Ca膜的溶解趋势相比,多层膜在PBS中吸水后可稳定较长时间不溃散。CMC-Ca膜、多层膜的水蒸气透过率及厚度,见图4b所示。3种多层膜[约1 150 g/(m2·24 h)]的水蒸气透过率显著低于纯CMC-Ca膜[1 480 g/(m2·24 h)],且3种多层膜之间没有显著差异。考虑到所有膜的厚度几乎相同(约130 μm,与扫描电镜结果一致),聚电解质复合物界面层的存在可能是导致多层膜的水蒸气透过率较纯CMC-Ca膜降低(保湿性增加)的原因。"

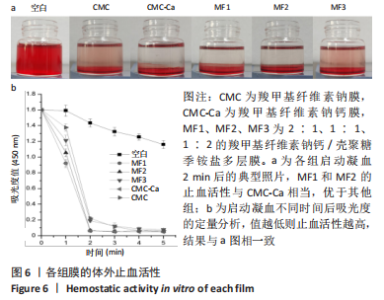
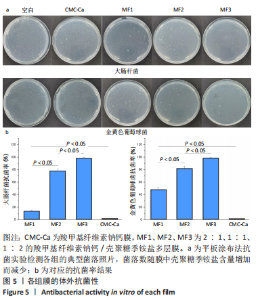
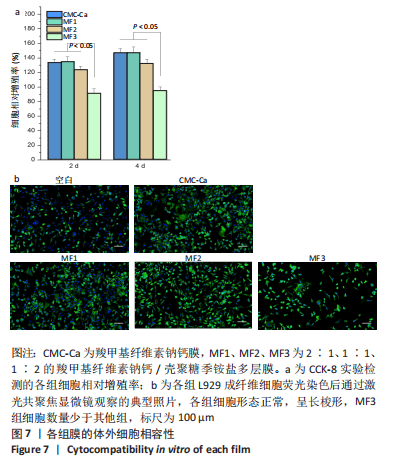
2.4 多层膜的体外凝血性 通过动态全血凝固实验研究了不同膜的促凝血能力,见图6。吸光度值越低代表在该时间点未凝固的红细胞越少,材料的促凝血能力就越强。与空白组相比,所有样品组在每个时间点吸光度值均较低,提示所有样品材料均有促凝血性能。此外,样品组的吸光度均在2 min内迅速降低,此后趋于平稳,说明凝血过程在2 min时基本完成(2 min时典型照片见图6a)。在每个时间点, CMC-Ca组的吸光度值均显著低于纯羧甲基纤维素钠膜,表明在羧甲基纤维素钠中引入钙离子可以显著提高止血活性。CMC-Ca组、MF1组和MF2组3组之间无显著差异,而MF3组的吸光度值显著高于上述3组。考虑到血液凝固发生在膜表面,这可能是由于MF1和MF2的CMC-Ca表面层厚度足够,故促凝血性能与纯CMC-Ca相近;而MF3较薄的CMC-Ca表面层则不足以支撑凝血(血液可能渗透进入聚电解质复合物界面层和壳聚糖季铵盐层)。"

| [1] NUUTILA K, ERIKSSON E. Moist Wound Healing with Commonly Available Dressings. Adv Wound Care. 2021;10(12):685-698. [2] VARAPRASAD K, JAYARAMUDU T, KANIKIREDDY V, et al. Alginate-based composite materials for wound dressing application:A mini review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;236:116025. [3] SOOD A, GRANICK MS, TOMASELLI NL. Wound Dressings and Comparative Effectiveness Data. Adv Wound Care. 2014;3(8):511-529. [4] KONG D, ZHANG Q, YOU J, et al. Adhesion loss mechanism based on carboxymethyl cellulose-filled hydrocolloid dressings in physiological wounds environment. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;235:115953. [5] HOMAEIGOHAR S, BOCCACCINI AR. Antibacterial biohybrid nanofibers for wound dressings. Acta Biomater. 2020;107:25-49. [6] SIMOES D, MIGUEL SP, RIBEIRO MP, et al. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018; 127:130-141. [7] HUANG WC, YING R, WANG W, et al. A Macroporous Hydrogel Dressing with Enhanced Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Capabilities for Accelerated Wound Healing. Adv Func Mater. 2020;30(21):2000644. [8] RAHIMI M, NORUZI EB, SHEYKHSARAN E, et al. Carbohydrate polymer-based silver nanocomposites: Recent progress in the antimicrobial wound dressings. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;231:115696. [9] PHAECHAMUD T, ISSARAYUNGYUEN P, PICHAYAKORN W. Gentamicin sulfate-loaded porous natural rubber films for wound dressing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;85:634-644. [10] MOGHADDAM MA, DI MARTINO A, SOPIK T, et al. Polylactide/Polyvinylalcohol-Based Porous Bioscaffold Loaded with Gentamicin for Wound Dressing Applications. Polymers. 2021;13(6):921. [11] FELGUEIRAS HP, AMORIM MTP. Functionalization of electrospun polymeric wound dressings with antimicrobial peptides. Colloids Surf B. 2017;156:133-148. [12] ZHOU D, YANG R, YANG T, et al. Preparation of chitin-amphipathic anion/quaternary ammonium salt ecofriendly dressing and its effect on wound healing in mice. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:4157-4169. [13] GHARIBI R, KAZEMI S, YEGANEH H, et al. Utilizing dextran to improve hemocompatibility of antimicrobial wound dressings with embedded quaternary ammonium salts. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;131:1044-1056. [14] AO H, JIANG W, NIE Y, et al. Engineering quaternized chitosan in the 3D bacterial cellulose structure for antibacterial wound dressings. Polym Test. 2020;86:106490. [15] PENG ZX, WANG L, DU L, et al. Adjustment of the antibacterial activity and biocompatibility of hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan by varying the degree of substitution of quaternary ammonium. Carbohydr Polym. 2010;81(2):275-283. [16] TAN H, MA R, LIN C, et al. Quaternized Chitosan as an Antimicrobial Agent: Antimicrobial Activity, Mechanism of Action and Biomedical Applications in Orthopedics. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(1):1854-1869. [17] FAN L, YANG J, WU H, et al. Preparation and characterization of quaternary ammonium chitosan hydrogel with significant antibacterial activity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;79:830-836. [18] RAHIMI M, AHMADI R, KAFIL HS, et al. A novel bioactive quaternized chitosan and its silver-containing nanocomposites as a potent antimicrobial wound dressing: Structural and biological properties. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101:360-369. [19] LUO F, SUN TL, NAKAJIMA T, et al. Oppositely charged polyelectrolytes form tough, self-healing, and rebuildable hydrogels. Adv Mater. 2015; 27(17):2722-2727. [20] GOMES NETO RJ, GENEVRO GM, PAULO LDA, et al. Characterization and in vitro evaluation of chitosan/konjac glucomannan bilayer film as a wound dressing. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;212:59-66. [21] CHEN X, YAN Y, LI H, et al. Evaluation of absorbable hemostatic agents of polyelectrolyte complexes using carboxymethyl starch and chitosan oligosaccharide both in vitro and in vivo. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(12): 3332-3344. [22] WAN ACA, CUTIONGCO MFA, TAI BCU, et al. Fibers by interfacial polyelectrolyte complexation - processes, materials and applications. Mater Today. 2016;19(8):437-450. [23] CHEN F, CAO X, CHEN X, et al. Calcium-modified microporous starch with potent hemostatic efficiency and excellent degradability for hemorrhage control. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(19):4017-4026. [24] CHEN X, LI S, YAN Y, et al. Absorbable nanocomposites composed of mesoporous bioglass nanoparticles and polyelectrolyte complexes for surgical hemorrhage control. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2020; 109:110556. [25] KIM GH, IM JN, KIM TH, et al. Preparation and characterization of calcium carboxymethyl cellulose/chitosan blend nonwovens for hemostatic agents. Text Res J. 2018;88(16):1902-1911. [26] MOEINI A, PEDRAM P, MAKVANDI P, et al. Wound healing and antimicrobial effect of active secondary metabolites in chitosan-based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;233:115839. [27] OP ‘T VELD RC, WALBOOMERS XF, JANSEN JA, et al. Design Considerations for Hydrogel Wound Dressings: Strategic and Molecular Advances. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26(3):230-248. [28] XUAN CK, HAO LJ, LIU XM, et al. Wet-adhesive, haemostatic and antimicrobial bilayered composite nanosheets for sealing and healing soft-tissue bleeding wounds. Biomaterials. 2020;252:120018. [29] OHTA S, NISHIYAMA T, SAKODA M, et al. Development of carboxymethyl cellulose nonwoven sheet as a novel hemostatic agent. J Biosci Bioeng. 2015;119(6):718-723. [30] SHI LX, LIU X, WANG WS, et al. A Self-Pumping Dressing for Draining Excessive Biofluid around Wounds. Adv Mater. 2019;31(5):1804187. [31] JAYAKUMAR R, PRABAHARAN M, KUMAR PTS, et al. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2011;29(3):322-337. [32] YANG Y, YANG S, WANG Y, et al. Anti-infective efficacy, cytocompatibility and biocompatibility of a 3D-printed osteoconductive composite scaffold functionalized with quaternized chitosan. Acta Biomater. 2016; 46:112-128. |
| [1] | Guan Zhenju, Xie Yonglin, Xiang Shougang, Zhang Chengdong, Li Xiaolong, Li Xingping, Pu Chao, Zhang Bo, Luo Xuwei, Xiao Dongqin. Preparation of polyphenol-mediated copper ion coating on titanium surface and antibacterial and antioxidant properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1997-2005. |
| [2] | Tan Junjie, Du Jiaheng, Wen Zhenyu, Yan Jiyuan, He Kui, Duan Ke, Yin Yiran, Li Zhong. Antibacterial magnesium oxide-calcium phosphate composite coating prepared by combining electrodeposition and sol-gel impregnation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(29): 4663-4670. |
| [3] | Dong Bo, Li Xiaoyu, Li Birong, Li Zhen, Wang Zixuan, Yin Zhaoyi, Meng Weiyan. 3D-printed scaffolds repair infected bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(29): 4685-4690. |
| [4] | Zheng Heishu, Zhang Yingjuan, Wei Yanhua, Huang Hui, Ma Xiangyu, Liao Hongbing. Antibacterial performance of cerium oxide nanoenzyme against Escherichia coli [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3496-3501. |
| [5] | Liu Yan, Zheng Xuexin. Performance of 3D-printed polylactic acid-nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan/doxycycline antibacterial scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3532-3538. |
| [6] | Wang Jinlei, Li Ke, Zhao Liang. Platelet-camouflaged silver nanoparticle hydrogel accelerates wound healing in type 1 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2659-2666. |
| [7] | Tang Ziyan, Gu Shunqiang, Chen Xiaoling, Wang Lei, Ma Chengbang, Zhou Mei, Chen Tianbao, Du Lina, Jin Yiguang. Recombinant expression and in vitro activity identification of a bioactive peptide QUB2984 from skin secretion of Agalychnis callidryas [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2675-2681. |
| [8] | Gang Fangli, Shi Rui, Ma Chunyang, Xiao Yi. Low-temperature condensation deposition method for 3D printing of bone tissue engineering poly-L-lactic acid/pearl powder composite scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2702-2707. |
| [9] | Bian Zhihong, Zhang Yuntao, Li Zeming, Hou Yudong. Potential of shikonin and its derivatives in oral soft and hard tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2747-2752. |
| [10] | He Wei, Zhou Zheng, Wu Lingling, Wang Kai, Mu Caiyun. Moxibustion and reduced graphene oxide/cerium dioxide nanocomposites for repairing infectious wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2307-2314. |
| [11] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [12] | Chen Chu, Ouyang Hougan, Zhu Xuying, Qi Yanzhe, Wang Zi. Biological changes of Waiguan acupoint in a rat model of psoriasis undergoing heat-sensitive moxibustion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5150-5154. |
| [13] | Li Yaohua, Zeng Fengjiao, Chen Bin, Fan Qin, Bai Guohui. Research advances in drug coatings for prevention of peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4912-4920. |
| [14] | Fan Haomei, Xiao Dongqin, Shi Feng, Luo Xuwei, Wei Jianlin, Zhuang Huadi, Liu Jinhui, Zhao Juhua. Preparation of calcium silicate microspheres loaded with epigallocatechin gallate and investigation on its antibacterial performance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4769-4775. |
| [15] | Wu Lihao, Shao Anliang, Xu Lin, Ren Kang, Wang Hongjian, Chen Liang, Xu Ling. Evaluation of immunotoxicity of the absorbable macroporous polysaccharides composite hemostatic material [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 329-334. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||