Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (30): 4912-4920.doi: 10.12307/2023.549
Research advances in drug coatings for prevention of peri-implantitis
Li Yaohua1, 2, Zeng Fengjiao2, 3, Chen Bin2, Fan Qin1, 3, Bai Guohui1, 2
- 1Stomatology College of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Special Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases Research, Higher Education Institutions in Guizhou Province, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 3Department of Implantology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-08-12Accepted:2022-09-27Online:2023-10-28Published:2023-04-03 -
Contact:Fan Qin, Master, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Stomatology College of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Implantology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Yaohua, Master candidate, Stomatology College of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Special Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases Research, Higher Education Institutions in Guizhou Province, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Plan Project of Zunyi, No. Zunyi Kehe HZ Zi (2022) 392 (to ZFJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yaohua, Zeng Fengjiao, Chen Bin, Fan Qin, Bai Guohui. Research advances in drug coatings for prevention of peri-implantitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4912-4920.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
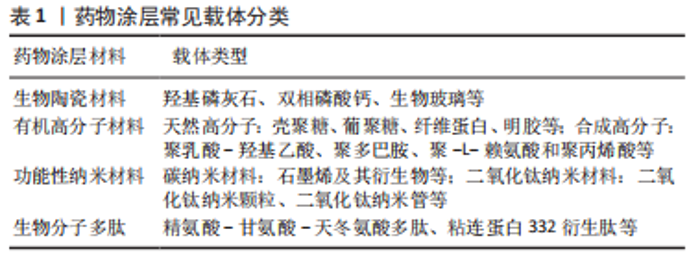
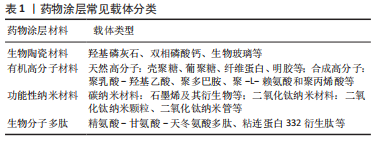
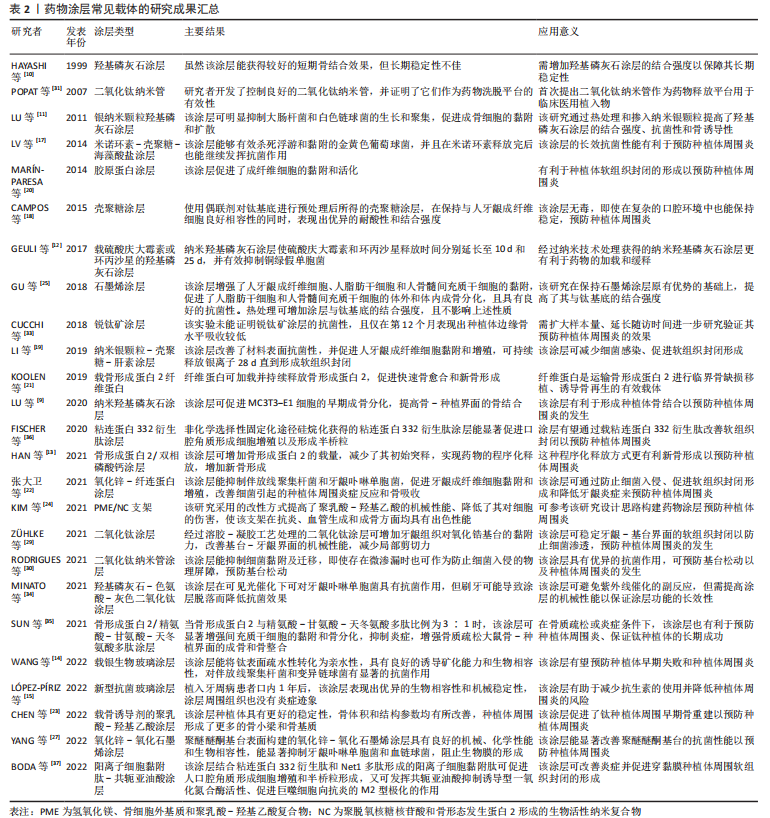
生物陶瓷材料:生物陶瓷材料是目前最经典、临床转化最多的材料,而常用于药物涂层预防种植体周围炎的主要包括羟基磷灰石、磷酸三钙和生物玻璃等。 羟基磷灰石是最具代表性、应用最广泛的生物陶瓷类材料,具有良好的热稳定性、生物降解性和骨诱导性,因此最常作为药物载体应用于种植体表面涂层。羟基磷灰石涂层可提高种植体表面粗糙度,增加骨组织和种植体之间的接触,促进新骨生长以形成种植体骨结合,有利于增强种植体周围骨组织对炎症的抵抗力[9]。但早期研究的羟基磷灰石涂层与基底材料的结合强度不足,且自身不具备抗菌性,易分层、剥脱而导致严重的边缘骨丧失甚至种植失败[10]。后来随着涂层技术改进、抗菌剂的载入研究者们逐渐克服了这一缺点,例如LU等[11]采用热处理提高了羟基磷灰石涂层的结合强度,并载入银纳米颗粒增加了涂层的抗菌性和骨诱导性。而经过纳米技术处理获得的纳米羟基磷灰石具有中空结构,可增大表面积并提高药物载量,更有利于药物的加载和缓释[12]。此外,由缓慢吸收的羟基磷灰石和快速吸收的磷酸三钙组成的双相磷酸钙,也具有更好的载药、释药性能,可程序化地释放负载药物,既有效避免了药物的初始突释,又能长期维持药物的释放,更有利于新骨的形成[13]。 生物玻璃是指能与活体骨组织或软组织形成直接连接的特殊玻璃。相对于羟基磷灰石,生物玻璃具有抗菌性,且机械强度更高。新型介孔生物活性玻璃因具有介孔通道结构,生物相容性更好,更有利于药物控释,逐渐受到研究者们的关注。WANG等[14]构建的载银介孔生物活性玻璃涂层能将钛表面疏水性转化为亲水性,提升了种植体表面的抗菌性、骨诱导性和生物相容性,有望用于预防种植体周围炎。但随着银含量的增加,该涂层结合强度下降,未来研究仍需进一步确定合适的载银含量,改善涂层结合强度,以便于实现临床转化。同样,生物玻璃与其他材料复合形成的新型抗菌玻璃涂层,也可获得更好的生物相容性和机械性能,避免涂层周围组织炎性反应,有助于减少抗生素的使用并降低种植体周围炎的风险[15]。 有机高分子材料:近年来大量天然及合成有机高分子材料因在体内可降解、生物相容性好而引起了研究者们的关注,广泛用作药物涂层载体预防种植体周围炎。 壳聚糖、葡聚糖、纤维蛋白及明胶等天然聚合物常作为载体用于构建药物涂层,其中壳聚糖因结构类似于透明质酸,具有多孔结构和良好的骨诱导性;其表面带正电荷,可与带负电的细菌表面相互作用,破坏细胞膜使胞内成分释放,发挥杀菌以及抑制生物膜形成的作用,最常作为药物涂层载体[16-17]。因为其本身具有抗菌性,所以涂层释放完抗菌药物后也能继续发挥抗菌作用。若使用偶联剂对钛表面进行预处理,可增加壳聚糖涂层与钛基底的结合强度和耐酸性,即使在酸性口腔环境(存在感染时)中也保持良好的稳定性[18]。另外,肝素具有抗炎作用,与多种生长因子具有亲和力,与壳聚糖复合可提升涂层的生物活性,可使涂层持续释放抗菌剂直到形成软组织封闭,减少了种植体周围感染的机会[19]。但未来研究需进一步模拟种植体周围环境,明确体内如血清蛋白等带负电荷的物质是否会影响壳聚糖涂层药物的释放,以推动其临床应用。 相比于壳聚糖,纤维蛋白生物活性更好,因为其具有精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸(arginyl-glycyl-aspartate,RGD)等生物黏附序列,可以与整合素结合促进细胞黏附和分化,常作为药物载体以改善种植体表面生物相容性[20-21]。纤维蛋白主要分为结构蛋白(胶原和弹性蛋白)及粘合蛋白(纤连蛋白和粘连蛋白)。其中,纤连蛋白还可以通过调控巨噬细胞分化状态,减少炎症因子的分泌,用于种植体/基台表面涂层可促进牙龈成纤维细胞的黏附和增殖,改善细菌引起的种植体周围炎症反应和骨吸收,因其自身不具备抗菌性,可载入抗菌药物,使涂层同时具有防止细菌入侵、促进软组织封闭形成和改善牙龈炎症的作用,从而预防种植体周围炎的发生[22]。 除了天然聚合物,近年来聚乳酸-羟基乙酸(polylactic acid hydroxy acetic acid,PLGA)、聚多巴胺、聚-L-赖氨酸和聚丙烯酸等合成高分子材料也常用作药物载体。其中PLGA研究最广泛、最具代表性。PLGA由聚乳酸和聚乙醇酸按照一定比例聚合而成,是一种无毒、获得美国食品药品监督管理局批准的聚合物。通过调整PLGA制备方法及制备时聚合物分子质量等参数,可对其载药量、药物缓释速率以及载体降解速率进行控制。有研究发现,将骨诱导剂加载于PLGA涂层能有效促进种植体周围早期骨重建,获得更快、更好的骨结合效果,更有利于预防种植体周围炎[23]。然而PLGA存在机械性能较弱、副产物在植入部位会形成酸性环境的缺点,为此研究者们将PLGA与碱性材料复合,以提高其机械性能、降低对细胞的伤害。例如,KIM等[24]将具有生物活性的聚脱氧核糖核苷酸/骨形成蛋白2纳米复合物加载于氢氧化镁、骨细胞外基质和PLGA形成的复合支架,使该支架在抗炎、血管生成和成骨方面均获得了出色性能。如果未来研究能参考此思路设计药物涂层,可能更有利于改善种植体周围炎症、促进种植体形成骨结合,增加种植体表面预防种植体周围炎的潜力。 功能性纳米材料:近年来随着纳米技术逐渐引入牙种植领域,大量的功能性纳米材料作为药物传递系统的载体用于种植体/基台表面涂层预防种植体周围炎,其中碳和二氧化钛纳米材料研究较为广泛。 碳纳米材料因为具有良好的机械性能、抗菌性和生物特性,作为药物载体可精确、及时释放药物。其中,以石墨烯及其衍生物为主的碳纳米材料涂层作为药物缓释系统,可将药物传递到手术创口,预防感染、促进创口愈合和种植体骨结合。研究者们通过改进涂层处理技术,可使石墨烯涂层在保持良好抗菌性和骨诱导性的同时,提高涂层与基底结合强度,避免涂层剥脱导致的不良反应[25]。氧化石墨烯是石墨烯的氧化物,具有抗菌、促进成骨和促进神经再生等作用,作为载体能辅助药物在涂层中的均匀分散[26];若其负载抗菌剂涂覆于基台表面,能更有效地抑制细菌生长,阻止生物膜形成,提高基台表面预防种植体周围炎的能力[27],但未来仍需进一步研究,以更好利用碳纳米材料的负载能力,并确定其应用于涂层的长期稳定性。 二氧化钛被认为是最有效的无机抗菌剂之一,将其应用于种植体/基台表面涂层,可利用其光催化活性降解种植体/基台表面有机污染物,提高材料表面亲水性和耐磨性,增加表面生物相容性和骨诱导性[28];同时二氧化钛涂层也可改善材料力学性能,减少局部剪切力,避免因血供不足而导致邻近组织缺氧坏死,降低发生种植体周围炎的风险[29]。有学者直接将二氧化钛纳米颗粒涂覆于基台表面,有效抑制了细菌的黏附和迁移,即使存在微渗漏时其也可作为防止细菌入侵的物理屏障,预防基台松动[30]。而二氧化钛纳米管是由大部分为锐钛矿相的片状钛酸盐组成的纳米级三维管状结构,因化学性质稳定、耐腐蚀,具有一端开口而另一端封闭的蜂窝状结构、高比表面积,自2007年POPAT等[31]首次提出将其作为一种全新的药物释放平台用于临床医用植入物以来,逐渐广泛用于构建药物涂层预防种植体周围炎。若将有机高分子材料膜覆盖于二氧化钛纳米管的管口,可增加其缓释效应,提高涂层生物相容性和抗菌性[32]。 然而一项关于锐钛矿涂层抗菌性的临床试验结果并未能证明其抗菌效应,仅在第12个月表现出更低的边缘骨吸收[33]。因此二氧化钛涂层的功效仍需延长随访时间、扩大样本量以进一步研究确认。另一点具有争议的是二氧化钛涂层的结合强度。理论上二氧化钛涂层直接构建于原有钛基底,不易剥脱和分层,可避免产生异物反应。而MINATO等[34]构建的羟基磷灰石-色氨酸-灰色二氧化钛涂层却会因为刷牙引起涂层脱落而降低涂层的抗菌效果。可能是羟基磷灰石-色氨酸复合物在增强二氧化钛涂层光催化作用的同时,影响了其结合强度,提示未来研究在掺入药物或复合其他材料增强涂层功能时,也要考虑到涂层的结合强度,以促进其临床推广。 生物分子多肽:与大分子蛋白载体相比,生物分子多肽在保持良好的载体活性的同时抗原性较低,可装载目的药物实现受体导向的靶向药物传递。其中,RGD多肽是细胞膜整合素的特异性配体,常利用其修饰材料表面可提高其生物相容性,促进成骨细胞黏附和迁移,有利于骨组织再生。当RGD多肽与骨形成蛋白2以适当的比例构建涂层时,二者可发挥协同作用,使得涂层增强干细胞的黏附及成骨分化,抑制炎症,促进骨质疏松症患者骨-种植界面的成骨和骨整合,降低其发生种植体周围炎的风险[35]。除RGD外,粘连蛋白332衍生肽(laminin 332 derived peptides,LamLG3)也常作为种植体穿黏膜部分/基台表面涂层,特异性地促进结合上皮的角质形成细胞增殖和形成半桥粒,改善软组织封闭的形成[36]。BODA等[37]将LamLG3和Net1多肽(来源于Netrin-1蛋白)共同组成的阳离子细胞黏附肽连接具有阴离子的共轭亚油酸形成的双功能涂层,除了促进软组织封闭的形成,还可通过共轭亚油酸抑制诱导型一氧化氮合酶的活性、促进巨噬细胞向抗炎的M2型极化以改善种植体周围炎症。 表2列举了羟基磷灰石、生物玻璃、壳聚糖、纤维蛋白、聚乳酸-羟基乙酸复合物、石墨烯以及二氧化钛纳米管等常见药物涂层载体均具有良好的生物相容性,都能够通过有效地加载和释放药物,可抑制细菌的黏附及生物膜的形成、减轻种植体周围组织炎症、促进新骨形成、减少炎性骨吸收以及增加软组织封闭的形成,实现对种植体周围炎的预防。但药物载体的长期稳定性以及所构建药物涂层有效性、安全性仍有待更多的临床试验来验证,以推进药物涂层的临床应用及推广。"
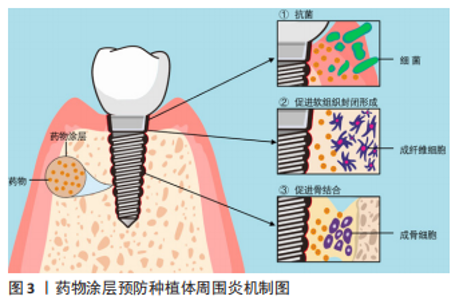
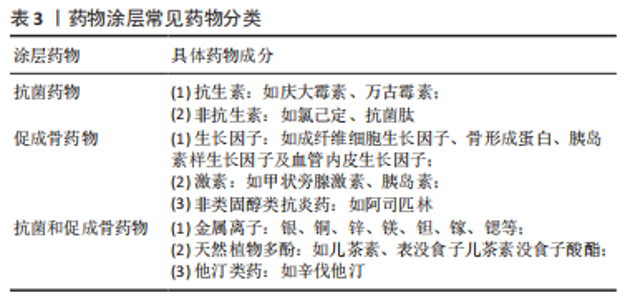
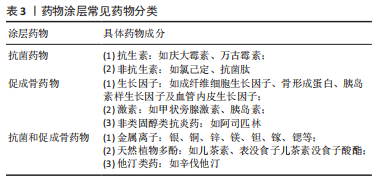
以上介绍的常见药物涂层载体均具有良好的生物相容性,都能够通过有效地加载和释放药物,实现对种植体周围炎的预防,但一些载体材料仍有待改进。首先,羟基磷灰石作为生物陶瓷材料的代表,具有良好的骨诱导性,最早应用于种植体表面涂层。近年来研究者们通过加载抗菌药物以及涂层技术的改进逐渐解决了羟基磷灰石涂层不具备抗菌性、与基底材料结合强度不足的缺点。而在有机高分子材料中,壳聚糖涂层自身具有抗菌性,应用较为广泛,但也需进一步研究明确壳聚糖涂层体内药物释放情况以及作用效果。相比壳聚糖,纤维蛋白的生物活性更好,可实现体内靶向药物运输,但需负载抗菌药物以提高其抗菌性。生物分子多肽作为药物载体与纤维蛋白具有相似的效果,而抗原性更低,也是预防种植体周围炎的潜力药物载体。PLGA是合成高分子药物载体的代表,能通过改变其降解速率控制药物的释放速率,但其本身同样不具备抗菌性,且降解副产物可能造成细胞损伤,需负载抗菌药、复合碱性材料以改善。另外,碳纳米材料作为药物涂层载体的新型材料,未来仍需进一步研究,以充分利用其负载能力,确保碳纳米涂层的长期稳定性。二氧化钛涂层本身具有抗菌性,但在加载药物或复合其他材料时,也要考虑到其结合强度,以保证其临床应用时获得良好的预防种植体周围炎的长期效果。 2.1.2 药物涂层相关药物 抗菌、促成骨和促软组织封闭等药物加载于上述载体并结合于种植体/基台表面,并释放于种植体周围发挥作用,可抑制细菌的黏附和增殖、阻止生物膜的形成,促进骨结合和软组织封闭形成,从而预防种植体周围炎的发生,见图3及表3。"
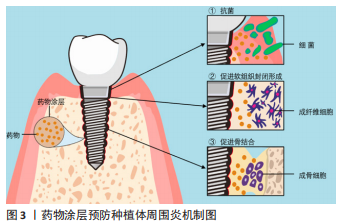
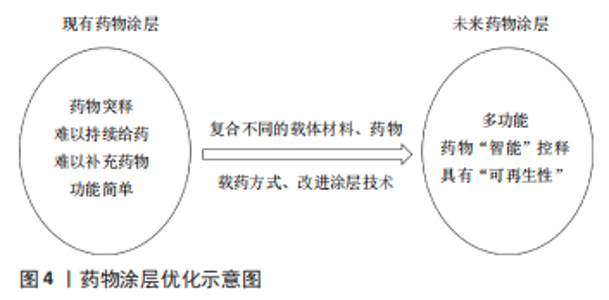
抗菌药物:近年来大量研究致力于将抗菌药物加载于种植体/基台表面以制备抗菌涂层,实现抗菌药物的局部释放,在致病菌形成生物膜的初始阶段,抑制细菌的黏附和聚集,阻止生物膜的形成,同时避免了全身应用存在的药物过敏、局部药物浓度低、易引起细菌耐药等缺点。抗菌药物主要分为抗生素和非抗生素两大类,非抗生素主要包括氯己定、抗菌肽等有机抗菌剂和金属离子等无剂抗菌剂。 抗生素是预防种植体术后早期感染以及治疗种植体周围炎的常用药。载抗生素涂层能有效抑制细菌黏附和共聚,阻碍生物膜形成,进而预防种植体周围炎的发生。四环素类抗生素是能抑制细菌蛋白质合成的广谱抗生素,掺入涂层可增加种植体/ 基台表面抗菌性[38]。同时四环素类抗生素还可抑制牙周组织胶原酶活性,减少牙槽骨吸收,未来可探索载四环素类抗生素的药物涂层对种植体周围骨组织和软组织的影响。若利用合适的药物载体负载抗生素,可改善药物载量和释放效果,更有效地抑制细菌生长,提升涂层预防种植体周围炎的能力[39]。也有报道指出,载万古霉素涂层可在全身药物负荷最小的情况下,预防细菌感染引起的骨破坏,促进种植体骨结合[40]。此外,卡苄西林、阿莫西林、头孢霉素、头孢菌素和妥布霉素等也可用于制作药物涂层[41]。 相对于抗生素,氯己定、氯二甲酚和聚六亚甲基双胍等有机抗菌剂不易引起细菌耐药,也可用于制备抗菌涂层预防种植体周围炎。其中,氯己定对革兰阳性菌、革兰阴性菌及真菌都有效,兼有抑菌和杀菌作用。细胞和临床研究都表明,载氯己定涂层能有效抑制抑制种植体周围炎相关病原菌的生长,阻止菌斑生物膜的形成,减少种植体周围组织的细菌负荷[42-43]。 抗菌肽是细胞生物自身防御系统产生的一种小分子多肽,耐酸性强,且具有良好的热稳定性。其抗菌谱广、杀菌迅速、低细胞耐受、无致畸作用、不易蓄积中毒和细胞选择性,为克服抗生素的副反应及产生的耐药菌提供了备选方案[44]。若将抗菌肽负载于种植体穿黏膜部分形成表面涂层,负载的抗菌肽可发挥抗菌作用直接预防种植体周围炎;还能促进牙龈上皮细胞和结缔组织细胞附着,形成软组织封闭,防止口腔内细菌进侵入软组织根方而影响骨结合,间接预防种植体周围炎;而这些细胞自身又可产生抗菌肽,继续发挥抗菌作用[45]。此外,载抗菌肽涂层还可抑制巨噬细胞的活化、下调促炎因子的表达并上调抗炎因子的表达,改善种植体周围组织炎症状态以促进骨结合过程[46]。然而真核生物抗菌肽存在对蛋白水解敏感、生理条件下活性低以及生产成本高的缺点。有研究报道原核生物抗菌肽(例如侧孢子菌素)可克服真核生物抗菌肽存在的这些问题,但其安全性仍需要进行更多动物体内实验来验证[47]。 促成骨药物:近年来许多研究者关注到将具有促成骨作用的药物加载于种植体表面,通过促进干细胞增殖、分化以及成骨细胞的增殖、黏附,增加种植体周围新骨形成,提高种植体周围骨组织对细菌性炎症的抵抗力;或者改善种植体周围组织炎症状态,抑制破骨细胞及炎症细胞的活动,减少种植体周围牙槽骨吸收。目前主要用于种植体/基台表面涂层的促成骨药物主要有包括生长因子、激素、非类固醇类抗炎药等。其中,一些药物还同时具有促软组织封闭形成的作用,有利于形成预防种植体周围炎的软组织屏障。 生长因子是体内自然产生的可以调节细胞生长及功能的生物活性分子,通过其与周围细胞外基质相互作用,将自身呈递给有特异性受体的细胞。种植体周围骨结合和软组织封闭的形成,需要多种生长因子的共同调节,各种生长因子功能不同。若将生长因子载入种植体/基台涂层,有利于形成种植体骨结合和软组织封闭,降低种植体周围炎的发生率。其中,成纤维细胞生长因子、骨形成蛋白、胰岛素样生长因子及血管内皮生长因子等常用于构建药物涂层[48],例如,成纤维细胞生长因子2涂层能有效促进人牙龈成纤维细胞增殖、黏附及细胞外基质的形成,益于形成软组织封闭[49]。若将不同功能生长因子组合也可发挥协同作用。如将胰岛素样生长因子1和骨形成蛋白2负载于涂层,可同时发挥胰岛素样生长因子1的促细胞增殖和骨形成蛋白2的促细胞分化作用,促进种植体植入术后伤口愈合和新骨形成[50]。 甲状旁腺激素和胰岛素等激素因为可以促进骨的合成代谢,有利于种植体周围骨形成,也是载入种植体表面涂层的潜力药物。甲状旁腺激素可促成骨、成血管,是治疗骨质疏松的常用药,若掺入涂层可促进早期种植体周围新骨形成,提高种植体骨结合强度,增强种植体稳定性,增加种植体周围骨组织对种植体周围炎的抵抗力[51]。胰岛素可调节糖代谢,是治疗糖尿病常用药,也具有应用于药物涂层的潜力。有研究报道,不管是糖尿病患者还是非糖尿病患者,局部缓释胰岛素都可以在不影响全身血糖水平情况下,加速伤口收缩、促进上皮再生和伤口愈合,并诱导干细胞成骨分化、增加种植体周围骨再生,从而提升种植体的早期稳定性[52-53]。 阿司匹林是典型的非类固醇类抗炎药,具有解热、镇痛、抗炎和抗血小板聚集的作用,但长期服用阿司匹林可能会增加种植术后出血风险。而近年来也有研究报道指出其应用药物涂层可通过持续稳定地释放阿司匹林,促进干细胞的增殖和成骨分化,抑制巨噬细胞M1向极化和RANKL介导的破骨细胞分化,改善种植体周围免疫微环境,促进种植体骨结合并改善炎性骨吸收[54]。那么可以推测载阿司匹林涂层可能也具有预防种植体周围炎的潜力。 抗菌及促成骨药物:近年来研究发现一些金属离子、天然多酚类化合物及他汀类药物同时具有抗菌、促成骨和/或软组织封闭形成的作用,因此许多研究者关注于将它们载入种植体/基台表面涂层,预防种植体周围炎的发生。 近年来研究表明,银(Ag)、铜(Cu)、锌(Zn)、镁(Mg)、钽(Ta)、铈(Ce)、镓(Ga)及锶(Sr)等金属离子不仅可以作为无机抗菌剂抑制或杀灭致病菌,还可以促骨结合和/或软组织封闭形成,因此常载入种植体表面涂层以减少种植体周围炎的发生[55–61]。银离子可通过改变细菌细胞壁通透性、干扰重要蛋白质、触发DNA凝结而发挥抗菌作用。若银离子与角蛋白结合形成复合涂层,不仅可改善基底材料的抗菌性,还可促进成牙龈纤维细胞细胞黏附和扩散,促进软组织封闭的形成[62]。而经过纳米技术得到的银纳米颗粒生物相容性更好、化学性质更稳定,不易引起细菌耐药,用于种植体/基台表面涂层可更有效地预防细菌感染[63]。与银离子相似,锌离子也因具有良好的抗菌性,能促进细胞增殖和分化,常用于种植体/基台表面涂层。研究者们通过在涂层表面构建二级结构,可使涂层在保持细胞毒性较低的同时,让锌离子早期迅速释放、后期维持释放以达到双重抗菌效果,延缓种植体周围炎的发展[57]。若将锌与锶等其他金属离子同时掺入涂层,也可进一步增强涂层的抗菌性和骨诱导性,促进种植体周围早期成骨和形成骨结合[61]。另外,改进涂层技术还可优化锌离子的释放速率,赋予钛基底表面细胞选择性,既能防止细菌的入侵,又能改善成纤维细胞的功能,促进软组织封闭的形成[64]。 植物天然合成的多酚化合物,具有抗菌、抗炎、抗氧化及抗癌等多种特点,常用于预防和治疗肥胖、糖尿病、炎性疾病和心血管疾病,近年来也逐渐用于构建药物涂层以预防种植体周围炎的发生。表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(epigallocatechin-3-gallate,EGCG)是茶多酚的主要成分,具有优异的抗氧化性,常掺入涂层保护细胞免于遭受由活性氧引起的氧化应激损伤,促进成骨细胞增殖、成骨分化和成骨相关基因表达以利于新骨形成,同时也能作为弱交联剂稳定涂层,若将EGCG与其他药物结合还可发挥协同作用。例如:EGCG与氯己定联合构建的药物涂层具有优异的抗菌性,即使在有菌环境下也能促进成骨细胞的黏附和增殖[65];而由氯化镁和EGCG形成的金属-多酚网络涂层协同发挥了镁离子和多酚促进成骨、抑制破骨的作用,促进了骨结合,提高骨-种植体接触率[66]。 他汀类药物是目前临床上用于降血脂的常见药物,近年研究发现其具有抗菌、抗炎、促成骨、促血管生成以及免疫调节作用,也可作为预防种植体周围炎的潜力药物。如载辛伐他汀的羟基磷灰石涂层具有良好抗菌性、骨诱导性及生物相容性,能够抑制细菌生物膜的形成,增加植入物周围成骨以促进骨结合,从而预防细菌引起的植入物相关感染[67]。也有研究报道辛伐他汀涂层可提高成纤维细胞和间充质干细胞活性,从而促进基台周围软组织封闭的形成,赋予基台表面预防种植体周围炎的能力[68]。 以上研究介绍的药物因为可以发挥抗菌、促成骨和软组织封闭形成的作用而具有应用于种植体/基台表面涂层的潜力。在载抗菌药物涂层中,传统抗生素涂层可能随着药物的释放,涂层储存的药量减少,当种植体周围药物浓度低于最低抑菌浓度时,可能失去抗菌作用,而长时间低浓度释放抗生素也可能存在细菌耐药的风险;以氯己定为代表的有机抗菌剂涂层相较而言不易引起细菌耐药,在临床试验中也取得了一定的效果,但仍需更长时间的随访观察进一步确定其预防种植体周围炎疗效;抗菌肽作为新型抗菌药,应用于药物涂层可获得双重抗菌效果,也可减少细菌耐药,然而其生产成本较其他抗菌药物高,在体内实际应用活性、稳定性、安全性仍需更多试验验证。 在促成骨的药物中,生长因子具有良好的生物活性,将不同的生长因子结合可同时促骨结合和软组织封闭的形成,但生长因子缺乏化学稳定性、生产成本高,阻碍了其应用;甲状旁腺激素、胰岛素、阿司匹林等原是治疗全身系统疾病的药物,均因具有促成骨作用而有望用于种植体表面药物涂层,但仍需进一步研究验证,以避免该类药物对全身产生不利影响。此外,一些金属离子、天然多酚化合物以及他汀类药物兼具抗菌、促进成骨和/或软组织封闭形成的功能,但部分金属离子浓度过高可能存在毒性,影响细胞的正常代谢,甚至产生全身作用,如银质成沉着病等;天然多酚化合物及他汀类药物近年来在药物涂层预防种植体周围炎方面的研究还较少,仍需要进一步研究以确定其有利作用。 总之,寻求具备良好的稳定性和生物相容性、能够促进骨生成甚至血管生成的药物载体以稳定地加载和释放药物,增加种植体/基台表面抗菌性、促进骨组织和软组织的愈合从而预防种植体周围炎的发生,是目前研究的热点。关于药物的选择,未来研究方向应针对不同患者的骨质或者根据患者全身状态(如健康或患有哪类疾病)选择不同的药物涂层,以实现种植体周围炎的个性化预防。 2.2 药物涂层的优化 目前的药物涂层大多具有良好的机械、热化学和生物性能,能够实现药物的有效加载和释放,但大多存在药物突释、功能简单、难以持续给药和药物补充的问题,需要进行相应地优化进一步提高其预防种植体周围炎的能力,见图4。"
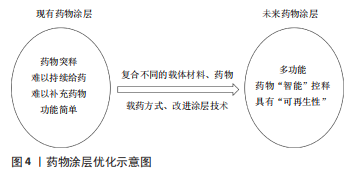

2.2.1 药物的“智能”控释 目前大多研究中,种植体/基台植入体内后,药物涂层就开始“自发”释放药物,甚至存在一个初始突释阶段,而突释之后药物释放量浓度骤然降低,难以维持有效浓度。而且一些药物(如金属离子)的早期突释可能导致局部药物的大量累积,甚至引起免疫毒性反应加重种植体周围炎症[69]。因此实现药物的“智能”(如pH值、温度、氧化还原、光、电、磁场或特异性酶触发释放)、持续释放,有利于把控药物疗效和毒性之间的平衡,是未来药物涂层预防种植体周围炎研究的重点。如载天然多酚化合物涂层需要在炎症态下释放更多的药物以发挥其抗氧化及抗炎作用,在生理状态下只释放少量药物以维持疗效[70]。此外在纳米管表面覆盖如海藻酸盐、钙磷、壳聚糖和胶原凝胶等膜结构以封闭管口,可增加药物的缓释效应,延长药物疗效[71]。 2.2.2 涂层的多功能化 目前研究的药物涂层也逐渐倾向于将不同的药物、载体材料复合,形成复合涂层,可改善单一药物或载体材料的不足,增强涂层某一功能或实现涂层的多功能化,实现从多方面预防种植体周围炎的发生。层层自组装技术可通过改变各层的成分从而增强某一功能或整合多种性能,为未来药物涂层的制备提供了新思路。例如,层层自组装技术复合抗菌肽和银纳米颗粒形成有机-无机两亲物的混合纳米涂层,在体内和体外均表现出更高的抗菌效力[72]。与此类似,羟基磷灰石、聚多巴胺及明胶形成的复合涂层也具有更优的亲水性和湿润性,不仅可促进牙龈成纤维细胞黏附相关基因的表达,而且能诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化和矿化,抑制变异链球菌的活性,调节巨噬细胞活性,使得该涂层同时获得了抗菌、抗炎、促骨结合和软组织封闭形成多种功能[73]。 2.2.3 涂层的“可再生” 目前所研究的大多药物涂层为“一次性”的,即随着时间的推移,负载药物逐渐消耗,难以持续稳定地释放药物以维持长期疗效。因此,需要研发一种“可再生”涂层,以期通过简单的方式对负载药物进行补充,维持药物涂层疗效。对于已经发生种植体黏膜炎,因软组织封闭破坏而导致暴露的种植体穿黏膜部分/基台表面,若是可以通过种植体周围冲洗重新实现涂层药物的加载,使其表面重获抗菌和软组织封闭形成的性能,就能使得种植体/基台再次“主动”对抗细菌进一步侵入,促进种植体周围组织再生,防止种植体周围黏膜炎进展为种植体周围炎[74]。 表4列举了各种抗生素、氯己定、抗菌肽、生长因子、激素、阿司匹林、金属离子、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯以及辛伐他汀等常见药物均可通过载入表面涂层,局部释放以发挥抗菌、抗炎、抗氧化、促骨结合和软组织封闭形成等作用,实现对种植体周围炎的预防。但载入涂层可能会削弱药物疗效,仍需进一步探索以实现药物的稳定释放,避免局部药物突释所造成的安全性问题,同样也需要更多的临床试验进行验证,实现对种植体周围炎的安全、有效及长期的预防。"

| [1] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [2] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [3] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [4] | Peng Hongcheng, Peng Guoxuan, Lei Anyi, Lin Yuan, Sun Hong, Ning Xu, Shang Xianwen, Deng Jin, Huang Mingzhi . Role and mechanism of platelet-derived growth factor BB in repair of growth plate injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [5] | Liu Haoyang, Xie Qiang, Shen Mengran, Ren Yansong, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Wang Weiguo . Application, research hotspots, and shortcomings of degradable zinc-based alloys in bone defect repair and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 839-845. |
| [6] | Yang Cheng, Li Weimin, Ran Dongcheng, Xu Jiamu, Wu Wangxiang, Xu Jiafu, Chen Jingjing, Jiang Guangfu, Wang Chunqing. Ferroptosis and osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 554-562. |
| [7] | He Kai, Xing Wenhua, Liu Shengxiang, Bai Xianming, Zhou Chen, Gao Xu, Qiao Yu, He Qiang, Gao Zhiyu, Guo Zhen, Bao Aruhan, Li Chade. Constructing a model of degenerative scoliosis using finite element method: biomechanical analysis in etiology and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 572-578. |
| [8] | Zheng Shanbin, Xia Tianwei, Sun Jiahao, Chen Zhiyuan, Cao Xun, Zhang Chao, Shen Jirong . Relationship between long non-coding RNA and osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2357-2367. |
| [9] | Zheng Ankai, Liu Ruiming, Xiang Qiuling. Application of stem cells in endothelialization of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 120-127. |
| [10] | Xie Qinglin, Zhang Xiaodong. Effect of bone marrow fat on bone metastasis and quantitative evaluation by magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 128-135. |
| [11] | Liu Ziyu, Geng Dandan, Zhang Runjiao, Liu Qing, Li Yibo, Wang Hongfang, Xie Wenmeng, Wang Wenyu, Hao Jiaxin, Wang Lei. Application of single-cell RNA sequencing technology in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 193-201. |
| [12] | Cheng Weilu, Wang Zehua, Zhang Yidan, Liu Yinghui. Application and regulatory challenges of organoid technology in medical field [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 202-210. |
| [13] | Bai Chen, Yang Wenqian, Meng Zhichao, Wang Yuze. Strategies for repairing injured anterior cruciate ligament and promoting graft healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1457-1463. |
| [14] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [15] | Lin Zeyu, Xu Lin. Research progress in gout-induced bone destruction mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||