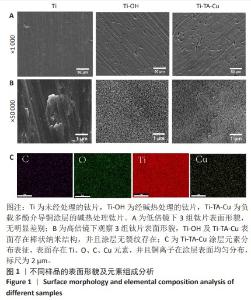
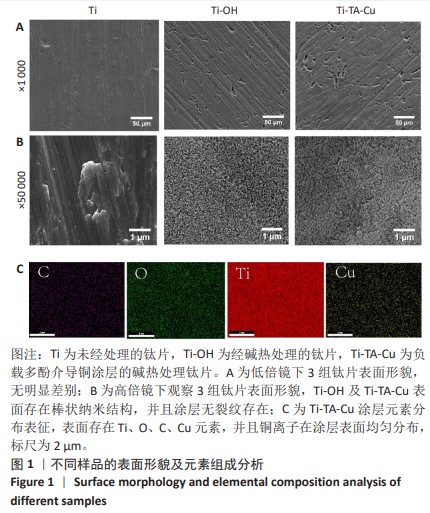
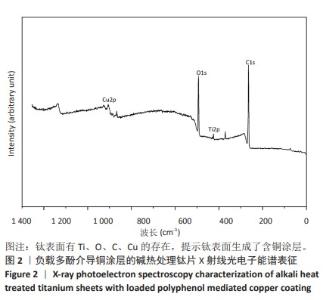
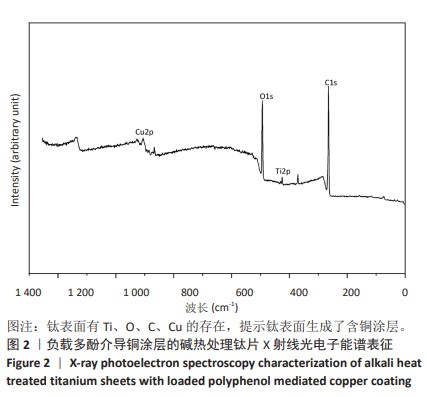
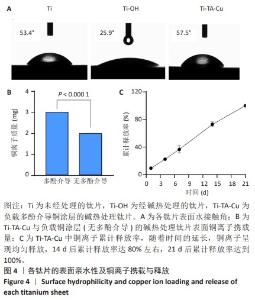
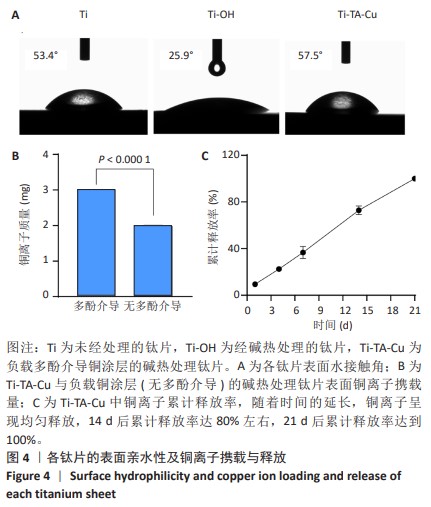
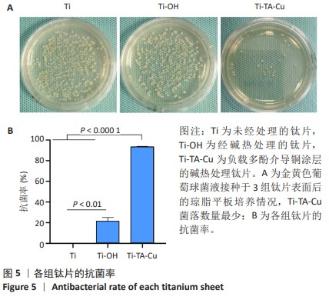
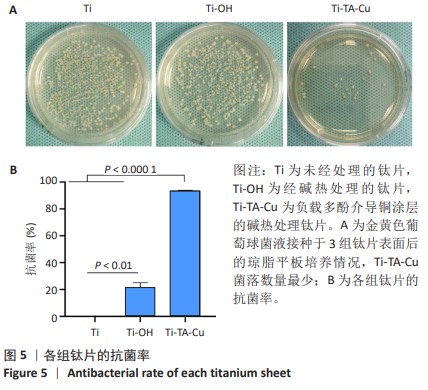
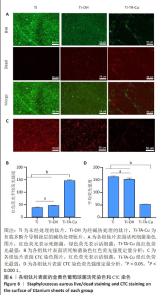
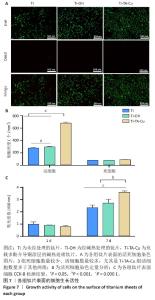
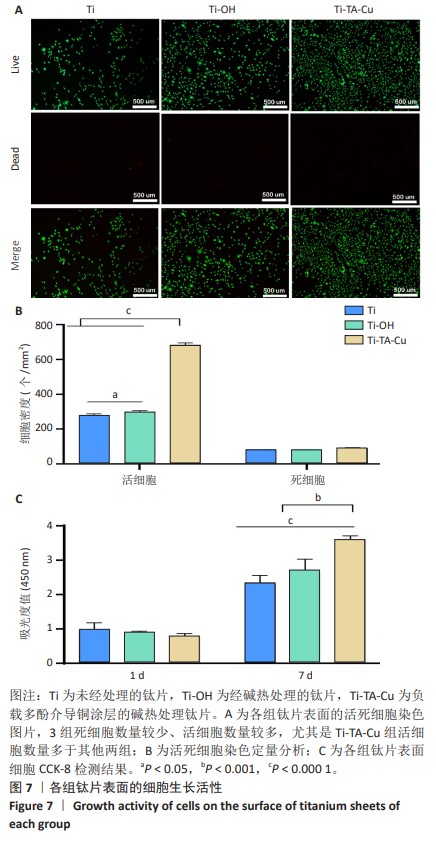
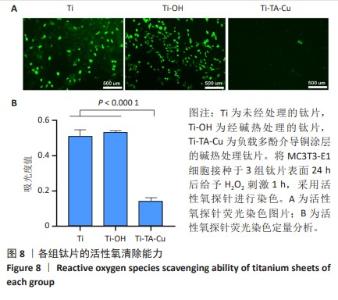
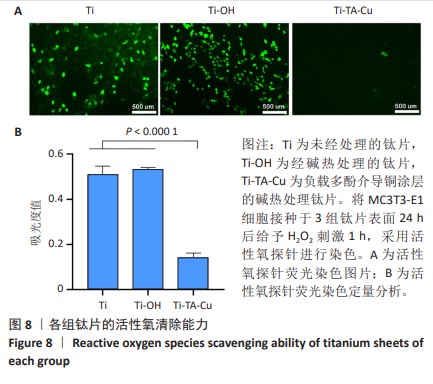
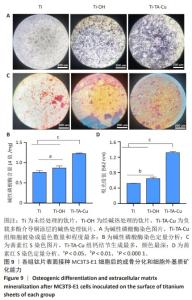
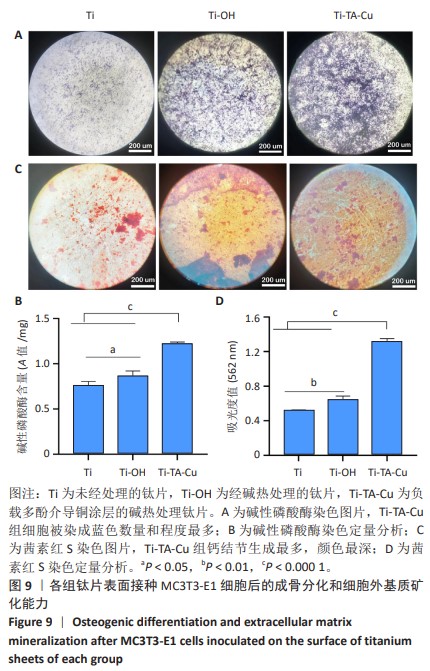
1] VACCA C, CONTU M P, ROSSI C, et al. In vitro Interactions between Streptococcus intermedius and Streptococcus salivarius K12 on a Titanium Cylindrical Surface. Pathogens. 2020;9(12):1069.
[2] ALBREKTSSON T, WENNERBERG A. On osseointegration in relation to implant surfaces. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21 Suppl 1:4-7.
[3] PELLEGRINI G, FRANCETTI L, BARBARO B, et al. Novel surfaces and osseointegration in implant dentistry. J Investig Clin Dent. 2018;9(4):e12349.
[4] WU B, TANG Y, WANG K, et al. Nanostructured Titanium Implant Surface Facilitating Osseointegration from Protein Adsorption to Osteogenesis: The Example of TiO(2) NTAs. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:1865-1879.
[5] XIAO J, ZHOU H, ZHAO L, et al. The effect of hierarchical micro/nanosurface titanium implant on osseointegration in ovariectomized sheep. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(6):1907-1913.
[6] DING M, HENRIKSEN SS, THEILGAARD N, et al. Assessment of activated porous granules on implant fixation and early bone formation in sheep. J Orthop Translat. 2016;5:38-47.
[7] RENSING C, GRASS G. Escherichia coli mechanisms of copper homeostasis in a changing environment. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2003;27(2-3):197-213.
[8] COSTERTON JW, STEWART PS, GREENBERG EP. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999;284(5418):1318-1322.
[9] CHOUIRFA H, BOULOUSSA H, MIGONNEY V, et al. Review of titanium surface modification techniques and coatings for antibacterial applications. Acta Biomater. 2019;83:37-54.
[10] YANG B, CHEN Y, SHI J. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Based Nanomedicine. Chem Rev. 2019;119(8):4881-4985.
[11] PERILLO B, DI DONATO M, PEZONE A, et al. ROS in cancer therapy: the bright side of the moon. Exp Mol Med. 2020;52(2):192-203.
[12] CHEUNG EC, VOUSDEN KH. The role of ROS in tumour development and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(5):280-297.
[13] BARCELOUX DG. Copper. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1999;37(2):217-230.
[14] ZHANG F, ZHOU M, GU W, et al. Zinc-/copper-substituted dicalcium silicate cement: advanced biomaterials with enhanced osteogenesis and long-term antibacterial properties. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(5):1060-1070.
[15] RONDANELLI M, FALIVA MA, INFANTINO V, et al. Copper as Dietary Supplement for Bone Metabolism: A Review. Nutrients. 2021;13(7):2246.
[16] GHOSH R, SWART O, WESTGATE S, et al. Antibacterial Copper-Hydroxyapatite Composite Coatings via Electrochemical Synthesis. Langmuir. 2019;35(17): 5957-5966.
[17] ZHANG X, LI Z, YANG P, et al. Polyphenol scaffolds in tissue engineering. Mater Horiz. 2021;8(1):145-167.
[18] KIM SW, KIM DB, KIM HS. Neuroprotective effects of tannic acid in the postischemic brain via direct chelation of Zn2+. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2022;26(4):183-191.
[19] KACZMAREK B. Tannic Acid with Antiviral and Antibacterial Activity as A Promising Component of Biomaterials—A Minireview. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(14):3224.
[20] REN Q, QIN L, JING F, et al. Reactive magnetron co-sputtering of Ti-xCuO coatings: Multifunctional interfaces for blood-contacting devices. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;116:111198.
[21] HU R, HE Y, HUANG M, et al. Strong Adhesion of Graphene Oxide Coating on Polymer Separation Membranes. Langmuir. 2018;34(36):10569-10579.
[22] RIVERA LR, COCHIS A, BISER S, et al. Antibacterial, pro-angiogenic and pro-osteointegrative zein-bioactive glass/copper based coatings for implantable stainless steel aimed at bone healing. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(5):1479-1490.
[23] SUTRISNO L, WANG S, LI M, et al. Construction of three-dimensional net-like polyelectrolyte multilayered nanostructures onto titanium substrates for combined antibacterial and antioxidant applications. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(32):5290-5302.
[24] DE MEO D, CECCARELLI G, IAIANI G, et al. Clinical Application of Antibacterial Hydrogel and Coating in Orthopaedic and Traumatology Surgery. Gels. 2021;7(3):126.
[25] CHO Y, HONG J, RYOO H, et al. Osteogenic Responses to Zirconia with Hydroxyapatite Coating by Aerosol Deposition. J Dent Res. 2015;94(3):491-499.
[26] XUE T, ATTARILAR S, LIU S, et al. Surface Modification Techniques of Titanium and its Alloys to Functionally Optimize Their Biomedical Properties: Thematic Review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:603072.
[27] ZENG Q, ZHU Y, YU B, et al. Antimicrobial and Antifouling Polymeric Agents for Surface Functionalization of Medical Implants. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(7):2805-2811.
[28] JACOBS A, RENAUDIN G, FORESTIER C, et al. Biological properties of copper-doped biomaterials for orthopedic applications: A review of antibacterial, angiogenic and osteogenic aspects. Acta Biomater. 2020;117:21-39.
[29] PATTANAYAK DK, KAWAI T, MATSUSHITA T, et al. Effect of HCl concentrations on apatite-forming ability of NaOH-HCl- and heat-treated titanium metal. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20(12):2401-2411.
[30] 杨砚,邹正中,田维嘉,等.不同类型铜合金板的杀菌特性[J].微生物学通报,2012,39(5):654-660.
[31] SATHISHKUMAR G, GOPINATH K, ZHANG K, et al. Recent progress in tannic acid-driven antibacterial/antifouling surface coating strategies. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(14):2296-2315.
[32] MA Z, REN L, LIU R, et al. Effect of Heat Treatment on Cu Distribution, Antibacterial Performance and Cytotoxicity of Ti–6Al–4V–5Cu Alloy. J Mater Sci Technol. 2015;31(7):723-732.
[33] WU S, XU J, ZOU L, et al. Long-lasting renewable antibacterial porous polymeric coatings enable titanium biomaterials to prevent and treat peri-implant infection. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3303.
[34] NORAMBUENA GA, PATEL R, KARAU M, et al. Antibacterial and Biocompatible Titanium-Copper Oxide Coating May Be a Potential Strategy to Reduce Periprosthetic Infection: An In Vitro Study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(3):722-732.
[35] MAHMOUDI-QASHQAY S, ZAMANI-MEYMIAN MR, SADATI SJ. Improving antibacterial ability of Ti-Cu thin films with co-sputtering method. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):16593.
[36] LIU X, TANG J, WANG L, et al. Mechanism of CuO nano-particles on stimulating production of actinorhodin in Streptomyces coelicolor by transcriptional analysis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):11253.
[37] HUANG Z, WANG D, SØNDERSKOV SM, et al. Tannic acid-functionalized 3D porous nanofiber sponge for antibiotic-free wound healing with enhanced hemostasis, antibacterial, and antioxidant properties. J Nanobiotechnol. 2023;21(1):190.
[38] ZHOU Z, XIAO J, GUAN S, et al. A hydrogen-bonded antibacterial curdlan-tannic acid hydrogel with an antioxidant and hemostatic function for wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;285:119235.
[39] KUMAR S, ROY DN, DEY V. A comprehensive review on techniques to create the anti-microbial surface of biomaterials to intervene in biofouling. Colloid Interface Sci Commun. 2021;43. doi:10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100464.
[40] HARRIS ED. A requirement for copper in angiogenesis. Nutr Rev. 2004;62(2): 60-64.
[41] GUO Z, XIE W, LU J, et al. Tannic acid-based metal phenolic networks for bio-applications: a review. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(20):4098-4110.
[42] LI H, GAO C, TANG L, et al. Lysozyme (Lys), Tannic Acid (TA), and Graphene Oxide (GO) Thin Coating for Antibacterial and Enhanced Osteogenesis. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3(1):673-684.
[43] LI L, TAN J, MIAO Y, et al. ROS and Autophagy: Interactions and Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015;35(5):615-621.
[44] SHEN X, FANG K, RU YIE KH, et al. High proportion strontium-doped micro-arc oxidation coatings enhance early osseointegration of titanium in osteoporosis by anti-oxidative stress pathway. Bioact Mater. 2022;10:405-419.
[45] XU Y, LUO Y, WENG Z, et al. Microenvironment-Responsive Metal-Phenolic Nanozyme Release Platform with Antibacterial, ROS Scavenging, and Osteogenesis for Periodontitis. ACS Nano. 2023;17(19):18732-18746.
[46] 秦祎雄,袁子健,谢山周,等.茶多酚对脂多糖刺激下成骨细胞增殖分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(35):5665-5669.
[47] LI Q, GAO Y, ZHANG J, et al. Crosslinking and functionalization of acellular patches via the self-assembly of copper@tea polyphenol nanoparticles. Regen Biomater. 2022;9:rbac030. |