Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (29): 4712-4722.doi: 10.12307/2023.663
Previous Articles Next Articles
Osteoimmunological effects of macrophages
Tian Yuyi, Liu Lihong
- The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410011, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2022-08-29Accepted:2022-09-28Online:2023-10-18Published:2022-12-02 -
Contact:Liu Lihong, MD, Chief physician, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410011, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Tian Yuyi, Master candidate, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410011, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:The National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82171581 (to LLH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Yuyi, Liu Lihong. Osteoimmunological effects of macrophages[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4712-4722.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
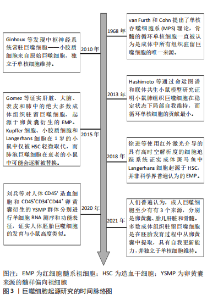
2.1 巨噬细胞的起源 巨噬细胞包括两类:一类是单核细胞来源的炎性巨噬细胞,通过血流输送到炎症部位;另一类是组织驻留巨噬细胞。组织驻留巨噬细胞根据解剖位置和功能表型的不同又分为大脑中的小胶质细胞、肝脏中的Kupffer细胞、皮肤中的Langerhans细胞、肺泡中的噬尘细胞、结缔组织中的组织巨噬细胞以及肠道、脾脏、胰腺、腹膜中的巨噬细胞等[2]。 自从1968年van Furth和Cohn提出了单核吞噬细胞系统(mononeuclear phagocyte system,MPS)理论,骨髓的循环单核细胞一直被认为是成体中所有组织驻留巨噬细胞的唯一来源[3]。然而,越来越多的研究与组织驻留巨噬细胞假定的单核细胞起源相冲突。例如,早在21世纪10年代就发现中枢神经系统常驻巨噬细胞——小胶质细胞来自原始巨噬细胞,独立于单核细胞维持[4]。2013年HASHIMOTO等[5]通过命运图谱和联体共生小鼠模型研究证明小鼠肺组织巨噬细胞在稳定状态下局部自我维持,而循环单核细胞的贡献最小。2015年GOMEZ PERDIGUERO 等[6]利用小鼠模型证实肝脏、大脑、表皮和肺中的绝大多数成体组织驻留巨噬细胞,起源于卵黄囊衍生的红细胞髓系祖细胞(erythro-myeloid progenitors,EMP)。Kupffer细胞、小胶质细胞和Langerhans细胞在1岁的小鼠中仅被造血干细胞轻微取代,而肺泡巨噬细胞在衰老的小鼠中可能会逐渐被替换。不过,该研究对于成体组织巨噬细胞的起源以及造血干细胞和非造血干细胞衍生的祖细胞的定性和定量贡献仍然不清楚。不过在2018年国内学者质疑了皮肤中的Langerhans细胞的EMP起源理论,其使用红外激光介导的具有高时空解析度的细胞追踪系统证实成体斑马鱼中Langerhans细胞起源于造血干细胞,并非科学界普遍认为的EMP[7]。以上研究主要以小鼠或斑马鱼为实验对象,虽然人们普遍认为巨噬细胞发育具有物种保守性,但人与小鼠或斑马鱼胚胎巨噬细胞发育是否相似缺乏明确证据。因此在2020年国内学者通过对人体CD45+造血细胞和CD45+CD34+CD44+卵黄囊衍生的髓样偏向祖细胞(yolk sac-derived myeloid-biased progenitors,YSMP)群体分别进行单细胞核糖核酸(ribonucleic acid,RNA)测序和功能表征,证实人体胚胎巨噬细胞的发育与小鼠高度类似,均存在原始造血巨噬细胞和CD45+CD34+CD44+人体YSMP两种非造血干细胞起源,其中YSMP可能是小鼠EMP在人体的对应细胞[8]。该研究为将来使用小鼠模型研究人体组织驻留巨噬细胞的发育和功能提供了依据。 尽管巨噬细胞的起源仍存在一些争议,但人们普遍认为,成人巨噬细胞至少有3个来源,分别是卵黄囊、胎儿肝脏和骨髓[9]。多数成体组织驻留巨噬细胞是在胚胎发育过程中从卵黄囊中提取,独立于单核细胞维持[10]。有关巨噬细胞起源研究的时间脉络图,见图3。虽然已经发现各个组织中驻留巨噬细胞具有不同的发育起源,但发育起源对于巨噬细胞的功能异质性的影响程度尚不清楚。因此,需要进一步研究组织巨噬细胞的生成、迁移、组织定植、成熟、凋亡和替换的具体过程,此外,组织局部环境多样性和个体遗传特异性对组织巨噬细胞的表型和功能的影响也需深入研究。"
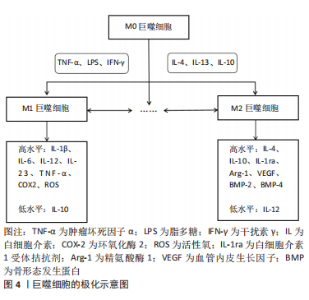
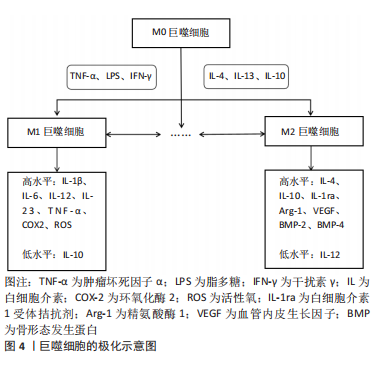
巨噬细胞是高度可塑的细胞,它们在各种微环境刺激下活化为促炎性M1和抗炎性M2两种表型,类似于辅助性T细胞的Th1/Th2命名法[11]。不过M1/2这种极端式二分法并不能反映体内巨噬细胞活化的复杂性和动态性,因此这个概念正在慢慢被巨噬细胞表型连续体所取代,但要注意的是M1/2术语仍在各类研究中广泛使用[12]。另外,在许多文章中M1和经典活化、M2和替代活化可以互换使用。对此有学者提出异议,其研究证实体内M1(=LPS+)和体外经典活化(LPS+干扰素-γ)以及体内M2(=LPS-)和体外替代活化(白细胞介素4)巨噬细胞的基因之间存在一些重叠,但更多的基因以相反或不相关的方式受到调节。因此,M1(=LPS+)巨噬细胞不等同于经典活化,M2(=LPS-)巨噬细胞也不等同于替代活化的巨噬细胞[13],这也因此解释了巨噬细胞体外实验中鉴定的大多数表面标志物与体内实验并不相符的现象。 进一步研究显示M2型还可细分为M2a(白细胞介素4/白细胞介素13诱导)、M2b(免疫复合物或Toll样受体激动剂诱导)、M2c(白细胞介素10诱导)[3]。除了上述3类M2亚群,还有一种在Toll样受体激动剂和腺苷的体外刺激下由M1巨噬细胞发展而来的血管生成M2样巨噬细胞亚型,被称为M2d[14]。另外肿瘤浸润巨噬细胞也表现出类似M2的表型,尽管它们的极化受到肿瘤环境和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(macrophage colony-stimulating factor,M-CSF)的刺激,但也被称为M2d[15]。还有一类M2巨噬细胞的特点是在凋亡细胞吞噬后分泌抗炎因子,它们被称为M2f(M2eff)巨噬细胞[16]。 巨噬细胞极化是一种动态过程,取决于局部微环境的变化,并由各种细胞内信号分子和通路调节。反之,当巨噬细胞表型发生变化时,它们表达的基因和分泌的细胞因子也会相应地发生变化,从而影响局部微环境[17]。M1巨噬细胞通常在肿瘤坏死因子α、脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS)或干扰素-γ的刺激下极化,产生高水平白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素12、白细胞介素23、肿瘤坏死因子(tumer necrosis factor,TNF)α、环氧化酶(cyclooxygenase,COX)-2、活性氧以及低水平的白细胞介素10。相反,M2巨噬细胞通常在白细胞介素4、白细胞介素13或白细胞介素10的诱导下极化,产生高水平白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10、白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂、精氨酸酶1、血管内皮生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白(bone morphogenetic protein,BMP)-2、骨形态发生蛋白4以及低水平的白细胞介素12[18-20]。有学者认为这两种巨噬细胞亚型在分泌介质的种类上没有明显差异,但在分泌物含量上会引起功能差异,例如,M2巨噬细胞仍然可以表达M1分泌物,但其水平低于M1巨噬细胞,反之亦然[21-22]。 即使上述巨噬细胞极化表型和细胞因子分泌存在争议,但人们仍普遍认为,M1巨噬细胞启动免疫反应并清除病原体和肿瘤细胞,参与急性炎症期,而M2巨噬细胞在后期组织愈合阶段起核心作用[23]。持续的高M1反应、M1的延长和缩短、M2的缺乏将导致慢性炎症、免疫反应延长、组织愈合延迟和生物材料整合失败等等。因此,如何利用巨噬细胞的可塑性并且精准调控巨噬细胞极化具有重要的治疗意义 。 由于细胞微环境的信号网络复杂,巨噬细胞极化的确切分子机制尚未完全阐明。目前已知的巨噬细胞极化的调节涉及腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(adenosine monophos-phate-activated protein kinase,AMPK)-哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR) 、Notch、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen activated protein kinase,MAPK)、Janus激酶(janus tyrosine kinase,JAK)-信号传导及转录激活蛋白(signal transducer and activator of transcription,STAT)、TNF、缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1)、核因子κB(nuclear factor kappa-B,NF-κB)、环磷酸腺苷(cyclic adenosine monophosphate,cAMP)、血管内皮生长因子、磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,PI3K)-蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,Akt)等多条信号通路。其中AMPK-mTOR、Notch和MAPK这3条信号通路在近几年受到较多关注,所以接下来将重点从AMPK-mTOR、Notch、MAPK 3条信号通路阐述巨噬细胞极化的调节机制。 2.2.1 AMPK-mTOR信号通路 mTOR是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,存在于mTORC1Cl(mTOR complex 1)和mTORC2(mTOR complex 2)两个不同的复合体中。关于mTOR在调节巨噬细胞活化中的作用,BYLES等[24]证明结节性硬化症蛋白复合体1(tuberous sclerosis complex 1,TSC1)缺失导致mTORC1激活,从而抑制白细胞介素4诱导的巨噬细胞M2极化。HAN等[25]证明依维莫司(mTOR抑制剂)通过抑制mTOR途径并提高mTOR上游蛋白Akt活性,从而导致M2巨噬细胞极化。与上述mTOR途径的激活会抑制巨噬细胞M2极化的结论不同,LI等[26]证实结直肠癌分泌的分泌蛋白组织蛋白酶K通过与Toll样受体4(Toll-like receptor 4,TLR4)结合激活mTOR途径,刺激肿瘤相关巨噬细胞的M2极化。此外,AMPK作为mTOR的上游调控因子,其激活被证实促进巨噬细胞M2极化[27-28]。更有研究证实AMPK-mTOR通路参与巨噬细胞M2极化。其中,XU等[29]研究表明膜联蛋白A1通过甲酰肽受体(formyl peptide receptor type 2,FPR2)/脂氧素A4受体(lipoxin A4 receptor,ALX)依赖性AMPK-mTOR通路,激活AMPK并抑制下游分子mTOR,抑制M1极化、促进M2极化,防止脑缺血再灌注损伤。YANG等[30]发现活性氧-AMPK-mTORC1-自噬途径参与非致死性声动力疗法介导的体外巨噬细胞的M1-M2极化。 2.2.2 Notch信号通路 进化保守的Notch信号通路由Notch受体、Notch配体、CSL(c-promoter binding protein-1,Suppressor of hairless,Lag1的合称)DNA结合蛋白、其他的效应物和Notch的调节分子等组成,可在发育过程中调控细胞增殖、凋亡和细胞命运决定并维持成人组织的稳态[31]。一般来说,Notch通路的激活与M1极化相关。据文献报道,Notch信号传导的下游介质miR-125a,分别通过调节抑制HIF-1α和干扰素调节因子4(interferon regulatory factor 4,IRF4)来主动增强M1并抑制M2极化[32]。国内学者研究发现冬凌草甲素通过抑制Notch途径诱导巨噬细胞极化转向抗炎表型,表现出有效的抗炎活性[33]。FENG等[34]在糖尿病足溃疡患者的发病机制和关键调节因子的研究中发现Notch1信号通路参与糖尿病患者中血管生成抑制剂KLIPREIN结合蛋白介导的巨噬细胞的募集和M1极化过程。还有研究表明非诺贝特通过抑制HIF-1α/Notch1途径来减少M1巨噬细胞募集,从而预防糖尿病肾病[35]。 2.2.3 MAPK信号通路 MAPK是一组进化保守的丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,可分为4个亚族:细胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal regulated kinase,ERK)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶38(mitogen activated protein kinase 38,p38)、C6N末端激酶(c-jun n-terminal kinase,JNK)和大丝裂原活化蛋白激酶1 (big map kinase 1,BMK1)(也称ERK5),调节细胞的生长、分化和凋亡等多种生理过程。近些年不少研究报道MAPK通路依赖性参与巨噬细胞M1极化过程。ZHENG等[36]在研究西他列汀对肝脏炎症的影响时发现西他列汀通过抑制JNK/激活蛋白-1 (activator protein-1,AP-1)信号通路和NF-κB转录活性抑制炎症并下调巨噬细胞M1极化。YANG等[37]研究表明姜黄素负载的壳聚糖-牛血清白蛋白新型纳米颗粒抑制TLR4-MAPK/NF-κB信号通路并进一步下调M1巨噬细胞极化。JIANG等[38]也发现吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶通过激活MAPK/ERK信号通路,促进烟曲霉性角膜炎的巨噬细胞极化为M1表型。还有研究表明MAPK通路的阻断与生长因子Progranulin抑制脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞M1极化过程有关[39]。 2.2.4 其他信号通路 还有一些信号通路被证实参与巨噬细胞极化的调控。NF-κB的激活被证实促进M1极化。其中,LI等[40]证实索拉非尼对NF-κB和AP-1活化的负调节是减轻脂多糖诱导的炎症反应的主要机制之一。HE等[41]证实PI3Kγ/NF-κB信号通路的激活参与黄芩素介导的癌症中巨噬细胞M1极化过程。同时有许多文献报道抑制NF-κB信号通路能够促进M2巨噬细胞极化。PENG等[42]证实miR-146a通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB信号通路促进M2巨噬细胞极化并加速糖尿病患者的伤口愈合。NING等[43] 证实纤连蛋白III型结构域蛋白5 (fibronectin type-III domain- containing protein 5,FNDC5)-骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体通过抑制NF-κB信号通路发挥抗炎作用并促进M2巨噬细胞极化。除NF-κB之外,Akt1激活被证实促进巨噬细胞M2极化[44]。IRF/STAT信号传导则被认为是调节巨噬细胞极化的中心途径,其中,干扰素激活IRF/STAT1信号通路使巨噬细胞极化为M1表型,而白细胞介绍4、白细胞介素13激活IRF/STAT6信号通路使巨噬细胞极化为M2表型[45],STAT3则被证实参与m6A甲基转移酶介导的M2巨噬细胞极化的过程[46]。 综上所述,AMPK、Akt1、STAT3/6的激活能促进巨噬细胞M2极化;mTOR、Notch、MAPK、NF-κB或STAT1的激活则促进M1极化。然而为了适应周围组织的微环境,巨噬细胞极化是短暂且可塑的。因此,进一步探索巨噬细胞极化的动态过程以及调控这一过程的详细分子机制,不仅利于理解巨噬细胞极化表型分类,而且对阐明巨噬细胞相关疾病的发生及发展机制和设计巨噬细胞极化的调控策略具有深远意义。 2.3 巨噬细胞的骨免疫学效应 2.3.1 骨免疫学概述 早在20世纪70年代初就有研究表明破骨细胞激活因子由人外周血白细胞分泌,从而提示骨骼系统和免疫系统之间具有密切联系[47]。而在2000年Arron和Choi首次提出“骨免疫学”一词,自此“骨免疫学”概念获得广泛关注——它强调免疫系统和骨骼系统的相互作用,其中包括不同的细胞以及参与细胞间通讯的介质和信号通路[48-49]。 作为一个复杂且高度动态的器官,骨由骨髓、骨质、骨膜、软骨、血管和神经组成,具有保护、支持、运动、造血及代谢功能[50]。骨稳态通过成骨细胞和破骨细胞活性之间的动态平衡来维持,是实现骨骼发育和修复的保障。其中成骨细胞主要负责骨形成,起源于骨髓中的间充质干细胞和骨骼干细胞,最终分化为骨细胞;破骨细胞主要功能是骨吸收,起源于造血干细胞,通过M-CSF和核因子κB受体活化因子配体 (receptor activator for nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)的相互作用分化为成熟的破骨细胞[51-52]。除上述骨骼细胞外,骨周围微环境中的炎症细胞、内皮细胞和施万细胞也参与骨骼发育和修复[53-55]。其中巨噬细胞在生理条件下的骨完整性和病理条件下的骨再生中起着关键作用,因此也引起了最多的讨论。骨的常驻巨噬细胞包括破骨细胞以及早在20世纪80年代就被观察到排列在骨表面的一组独立于破骨细胞的骨巨噬细胞(F4/80+)[56]。它们除了位于骨表面与成骨细胞相邻,直接调节成骨细胞功能并维持骨稳态,还存在于骨髓中,有利于维持骨内造血干细胞的局部微环境稳态[57-58]。 此外,感觉神经和交感神经对于骨修复中成骨分化、血管重建至关重要[59-60]。神经生长因子(nerve growth factor,NGF)是一种神经营养因子,参与感觉神经和交感神经的发育、维持和再生[61]。研究显示,局部注射β-NGF后促进软骨向骨的转化来加速软骨内骨折的修复[62],并且NGF介导的骨修复涉及相互作用的p75和酪氨酸激酶受体A(tyrosine kinase receptor A,TrkA)信号通路[63-67]。 近些年,越来越多的文献表明骨免疫效应涉及巨噬细胞和骨骼细胞的串扰。接下来将分别从巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞的串扰3个方面综述巨噬细胞的骨免疫学效应研究进展。 2.3.2 巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞 一方面,巨噬细胞影响间充质干细胞的增殖、分化、迁移和凋亡,有助于间充质干细胞介导的骨再生,但各种巨噬细胞表型对骨再生的影响仍在争论中,详见表1[68-72]。"

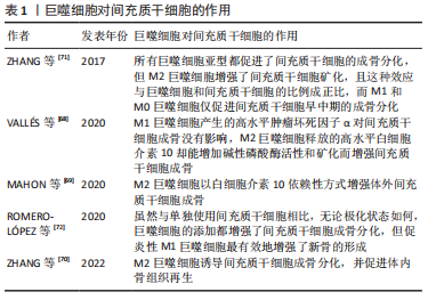
VALLéS等[68]研究了M1/2巨噬细胞释放的细胞因子(肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素10)对间充质干细胞成骨能力的影响,实验结果显示肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素10均可提高间充质干细胞的附着和迁移能力,但M1巨噬细胞的影响更为明显;不过,相较于M1巨噬细胞产生的高水平肿瘤坏死因子α对间充质干细胞成骨没有影响,M2巨噬细胞释放的高水平白细胞介素10却能增加碱性磷酸酶活性和矿化而增强间充质干细胞成骨。MAHON等[69]也得出M2巨噬细胞以白细胞介素10依赖性方式增强体内外成骨的结论。还有研究表明与星形或交错多细胞模式相比,间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞比例为2∶1的太极式空间分布模式的人工生物陶瓷支架可以为骨再生提供更有利的骨免疫环境,刺激巨噬细胞M2极化,诱导间充质干细胞成骨分化,并促进体内骨组织再生[70]。ZHANG等[71]系统地研究了不同巨噬细胞亚型对脂肪组织间充质干细胞增殖、分化和矿化的影响,认为所有巨噬细胞亚型都促进了间充质干细胞的成骨分化,但M2巨噬细胞增强了间充质干细胞矿化,且这种效应与巨噬细胞和间充质干细胞的比例成正比,而M1和M0巨噬细胞仅促进间充质干细胞早中期的成骨分化。与上述认为M2巨噬细胞更具有增强骨再生的优势的结论不同的是,ROMERO-LóPEZ等[72]认为虽然与单独使用间充质干细胞相比,无论极化状态如何,巨噬细胞的添加都增强了间充质干细胞成骨分化,但促炎性M1巨噬细胞最有效地增强了新骨的形成。 M1和M2表型在促进骨形成方面的相对重要性一直难以确定,结果可能取决于实验细节的设置,比如巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞共培养的数量比例或空间分布。总而言之,各种巨噬细胞亚型在间充质干细胞成骨中均具有积极作用,但不同巨噬细胞亚型增强成骨分化和骨再生效应的阶段和程度可能存在一定差异。 目前普遍认为M1巨噬细胞在炎症早期不可或缺,M2巨噬细胞则在骨再生后期具有较大优势,而对于骨再生最关键的是巨噬细胞表型的顺序激活和及时转换。LOI等[73]将巨噬细胞亚群以1∶1的比例直接与小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞(mouse embryo osteoblast precursor cells,MC3T3)共培养,结果所有巨噬细胞亚群均可增强MC3T3的成骨能力,并且在共培养72 h时对M1-MC3T3进行白细胞介素4处理可增强成骨能力。SCHLUNDT等[74]则证实在初始愈合阶段存在促炎性M1巨噬细胞,并且在预计软骨内骨化阶段被M2巨噬细胞取代;另外M2巨噬细胞似乎从周围肌肉侵入截骨间隙,提示M2巨噬细胞不是由骨髓驻留巨噬细胞提供。QIAO等[75]也证实了骨愈合过程中巨噬细胞表型的顺序激活模式对于生物材料诱导的骨再生非常重要。 另一方面,间充质干细胞也可以反过来影响巨噬细胞的功能,详见表2[76-80]。"
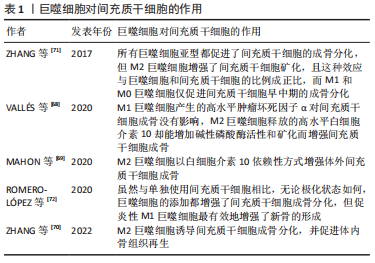
LUQUE-CAMPOS等[76]认为间充质干细胞可以调节巨噬细胞的代谢状态,从而改变其表型和功能。另外间充质干细胞被证明可以促进单核巨噬细胞向M2表型的极化,而M2表型分泌的高水平白细胞介素10可导致促使单核巨噬细胞分化为抗炎表型的正反馈通路的形成[77]。RANA等[78]观察到双相磷酸钙(biphasic calcium phosphate,BCP)生物材料和间充质干细胞共同植入大鼠颅骨缺损模型4周后经典单核巨噬细胞的数量增加,非经典单核巨噬细胞降低,认为骨再生归因于间充质干细胞介导的全面免疫调节。CHEN等[79]利用间充质干细胞的培养基上清液测定间充质干细胞对不同巨噬细胞亚群增殖、凋亡、极化和吞噬作用的影响,结果发现间充质干细胞对不同亚型巨噬细胞的体外作用是不同的,例如:间充质干细胞对巨噬细胞增殖无显著影响,但抑制M0巨噬细胞凋亡,并轻微诱导M1巨噬细胞凋亡;间充质干细胞轻微抑制M2巨噬细胞的吞噬作用,但对M1巨噬细胞没有显着影响。间充质干细胞除了以上对巨噬细胞产生直接的免疫调节作用外,还通过分泌趋化因子配体 (c-c motif chemokine ligand,CCL)2和CCL4等趋化因子调节巨噬细胞趋化性,以此增加巨噬细胞的募集[80]。 2.3.3 巨噬细胞与成骨细胞 当前研究大多围绕组织巨噬细胞以及巨噬细胞分泌的细胞因子证实巨噬细胞对成骨细胞的作用。CHANG等[81]发现骨巨噬细胞通常在骨表面形成冠状结构,与成骨细胞紧密相连,并且骨巨噬细胞耗竭会损害体外成骨细胞分化和矿化,而当成骨细胞在细胞外钙存在下与巨噬细胞共育时,矿床沉积量显著增加23倍。BATOON等[82]报道在膜内 (胫骨损伤)或软骨内 (股骨骨折)这两种骨损伤模型中,独立于破骨细胞的CD169巨噬细胞的耗竭都损害了骨修复,证明CD169巨噬细胞对于成骨细胞的维持至关重要,并在骨修复过程中促进膜内和软骨内骨化。至于骨巨噬细胞促进成骨的机制,WANG等[83]在大鼠Modic变化的终板骨硬化模型中发现终板骨硬化伴随着骨瘤数量的增加,且骨瘤通过抑瘤素M (oncostatin m,OSM)-STAT3 / Yes相关蛋白1(yes-associated protein 1,YAP1)信号轴有力地促进成骨细胞分化,而不是破骨细胞。活化的巨噬细胞通过分泌炎性细胞因子或生长因子双重调控成骨细胞的功能。肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6被证明负调节成骨细胞分化[84-86]。肿瘤坏死因子α还参与金属磨损诱导的假体周围骨质流失中成骨细胞的凋亡[87]。骨形态发生蛋白2则能刺激成骨细胞的分化和存活,有助于骨合成代谢过程[88]。 2.3.4 巨噬细胞与破骨细胞 破骨细胞作为人体内唯一的骨吸收细胞,对于骨代谢十分重要,它们是骨常驻巨噬细胞的一个亚群,与巨噬细胞是骨髓祖细胞的两种竞争性分化的结果[89]。不同于以往多数证实骨巨噬细胞支持成骨细胞功能的研究,最近的一项研究得出骨巨噬细胞支持破骨细胞介导的骨吸收功能的结论,提供了骨巨噬细胞参与骨质疏松症发病机制的初步证据[90]。不过,有关骨巨噬细胞与破骨细胞之间的关系还需进一步探索。巨噬细胞极化产生的细胞因子也会影响破骨细胞的形成和分化。具体来讲,M1型巨噬细胞分泌肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1等促炎因子,通过增加破骨细胞前体增殖分化或增强成骨细胞和其他细胞中的RANKL分泌直接或间接地促进破骨细胞形成和分化[91]。M2巨噬细胞分泌白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β1及骨形态发生蛋白2等抗炎因子和生长因子,对破骨细胞生成的影响并不一致。研究表明,白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β1抑制破骨细胞的形成和分化[92-93]。白细胞介素4通过两种主要机制抑制破骨细胞的生成:下调RANKL和上调成骨细胞中的骨保护素表达;抑制与破骨细胞分化相关的两条信号通路NF-κB和MAPK[94]。白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β1都通过减少活化T细胞核因子1(nuclear factor of activated T cells 1,NFATc1)表达来抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞生成[95-96]。骨形态发生蛋白2是破骨细胞和成骨细胞中对骨形态发生蛋白研究最多的,除了显示出对成骨细胞的积极作用外,还能直接刺激破骨细胞的分化或通过增加成骨细胞RANK表达间接促进破骨细胞分化和骨吸收[97]。此外,骨形态发生蛋白2也可以激活NFATc1转录因子,NFATc1通过RANKL的转录激活促进破骨细胞分化,形成正反馈通路[96]。 值得说明的是,目前的研究大多专注于巨噬细胞对破骨细胞或成骨细胞的影响,而忽略了骨免疫学强调的巨噬细胞和骨骼细胞的双向效应。因此为了更深入地理解及应用骨免疫学,未来有必要加强成骨细胞和破骨细胞对巨噬细胞影响的研究。 2.4 巨噬细胞的骨免疫学效应在骨修复中的应用 传统的骨缺损治疗方法存在诸多局限,例如自体骨移植的骨量有限且造成局部组织损伤;同种异体/异种移植物存在免疫排斥反应和医学伦理问题;金属植入物缺乏正常骨骼应有的生物学功能,且容易引起异物反应,不利于新骨生长等,由此开发具有免疫调节特性的生物材料甚至将其用于骨组织工程成为极具潜力的骨缺损治疗方案[98]。随着对骨免疫学领域的不断深入,研究人员发现通过干预巨噬细胞,调节局部免疫微环境是减轻植入物触发的异物反应、促进骨修复的关键手段,而并非是制造能够最大限度减少异物反应的惰性生物材料[99]。所以,用于调节巨噬细胞表型的各种生物材料修饰策略在近些年得到飞速发展。接下来将从多个方面回顾各种具有骨免疫调节特性的生物材料的设计策略。 2.4.1 生物材料表面理化性质修饰策略 最近的研究表明,生物材料的表面理化性质的修饰,包括刚度、粗糙度、孔径和亲水性等,都可以调节巨噬细胞的表型,详见表3[69-70,100-108]。"
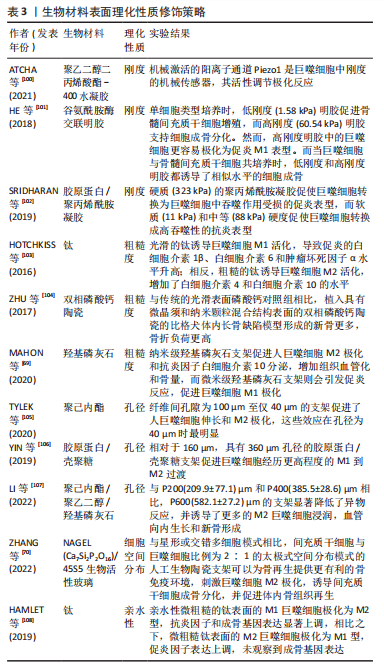

较硬的材料通常倾向于促进巨噬细胞M1极化。ATCHA等[100]发现巨噬细胞功能的刚度依赖性变化取决于机械敏感离子通道Piezo1。HE等[101]采用刚度可调型谷氨酰胺酶交联明胶研究支架材料刚度对巨噬细胞极化的影响,发现高硬度谷氨酰胺酶交联明胶中包封的巨噬细胞可以被调节成促炎表型,并间接支持骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。SRIDHARAN等[102]发现硬质的聚丙烯酰胺凝胶(323 kPa)促使巨噬细胞转换为巨噬细胞中吞噬作用受损的促炎表型,而软质(11 kPa)和中等(88 kPa)硬度促使巨噬细胞转换成高吞噬性的抗炎表型。然而,受到材料特性、刚度范围和实验模型差异等因素的影响,刚度对巨噬细胞极化的影响依旧非常复杂,需要通过进一步的体内外研究来定量分析。 表面粗糙度也是影响巨噬细胞极化的重要因素。HOTCHKISS等[103]报道,光滑的钛诱导巨噬细胞M1活化,导致促炎的白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6 和肿瘤坏死因子α水平升高,相反,粗糙的钛表面诱导巨噬细胞M2活化,增加了白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10的水平。由于天然骨组织的表面粗糙度约为32 nm,因此纳米级生物材料近年来也得到了广泛的研究。ZHU等[104]实验发现与传统的光滑表面双相磷酸钙对照组相比,植入具有微晶须和纳米颗粒混合结构表面的双相磷酸钙的比格犬体内长骨缺陷模型形成的新骨更多,骨折负荷更高。此外,在具有微晶须和纳米颗粒混合结构表面的双相磷酸钙与间充质干细胞共培养的体外实验中观察到促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平显著下调。此外,还有研究比较了微米级与纳米级羟基磷灰石颗粒免疫调节潜力的差异,证实米级羟基磷灰石颗粒促进人巨噬细胞M2极化和抗炎因子白细胞介素10分泌,增加组织血管化和骨量,而微米级羟基磷灰石功能化支架则会引发促炎反应,促进巨噬细胞M1极化[69]。 孔径也被证明是一种调节成骨的生物材料修饰策略。相对于容易形成局部氧气和营养物质缺乏环境的较小孔径,适宜的孔径能够诱导适度的缺氧环境,阻碍炎症反应,促进血管生成。TYLEK等[105]发现,纤维间孔隙为100 μm至仅40 μm的纤维支架促进了人巨噬细胞伸长和M2极化,这些效应在孔径为40 μm时最为明显。YIN等[106]发现相对于160 μm,具有360 μm孔径的胶原蛋白/壳聚糖支架促进巨噬细胞经历更高程度的M1到M2过渡。LI等[107]通过3D打印聚己内酯/聚乙二醇/羟基磷灰石生物活性支架的孔径对免疫反应和骨-生物材料整合影响的体内实验,发现与P200(209.9±77.1) μm和P400(385.5±28.6) μm相比,P600(582.1±27.2)μm的支架显著降低了异物反应,并诱导了更多的M2巨噬细胞浸润,血管向内生长和新骨形成。一般来说,巨噬细胞可以在大小从几十微米到几百微米的孔径中极化为M2表型,不过在实际应用时须注意在权衡生物材料孔径与机械强度的同时,针对不同材料特性的支架选择不同的最佳孔径。除此之外,有报道称人造骨生物陶瓷支架中巨噬细胞的空间分布也会影响巨噬细胞的功能,从而影响成骨[70]。 生物材料表面的亲水性等化学特性也会影响巨噬细胞的极化。一般来说,骨整合随着亲水性的增加而增强。HAMLET等[108]为了探究钛表面修饰对巨噬细胞表型和功能的影响,分别将M1和M2巨噬细胞在微粗糙和亲水性微粗糙钛表面上培养,结果发现亲水性微粗糙表面的M1巨噬细胞极化为M2型,抗炎因子和成骨基因表达显著上调,相比之下,微粗糙表面的M2巨噬细胞极化为M1型,促炎因子表达上调,未观察到成骨基因表达。 2.4.2 生物材料结合生物活性物质 除了支架表面理化性质修饰外,药物、细胞因子、金属离子、microRNA等单一或多种生物活性物质载入生物材料已被广泛用作调节巨噬细胞极化的有效策略,详见表4[109-120]。"
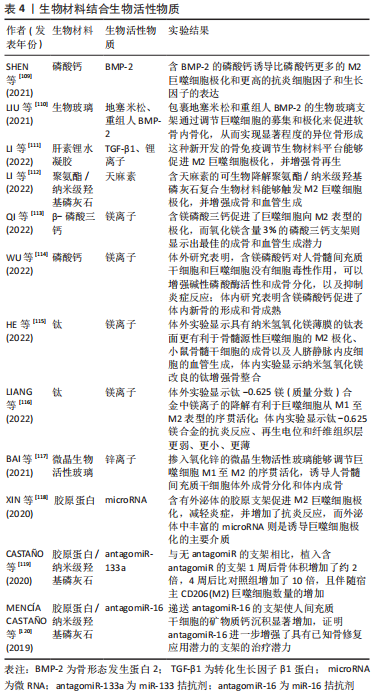

载入细胞因子(和)或药物已经成为生物材料调节炎症反应和成骨/血管生成能力的一种常用方法。例如,SHEN等[109]将BMP-2载入磷酸钙骨水泥中,证实BMP2-磷酸钙骨水泥诱导比磷酸钙骨水泥更多的M2表型极化和更高的抗炎细胞因子和生长因子的表达。LIU等[110]通过将抗炎药地塞米松载入含重组人BMP-2的多级多孔生物玻璃支架中并调节其释放动力学,通过软骨内骨化实现显著的异位骨形成。还有学者使用TGF-β1制造了一种促进M2巨噬细胞极化和成骨来引导骨再生的骨免疫性生物材料平台。该平台将含有TGF-β1的明胶-肝素微球 (microsphere,MS)载入可注射的肝素锂水凝胶中,其中水凝胶不仅充当MS/TGF-β1的递送载体,而且还作为促进成骨的锂离子释放基质,而TGF-β1的释放则引导巨噬细胞进行M2极化[111]。此外,中药天麻素也被应用于生物材料的修饰。LI等[112]开发了一种天麻素-可生物降解聚氨酯/纳米羟基磷灰石复合生物材料,这种生物材料能够触发M2巨噬细胞极化,并增强成骨和血管生成。 镁(Mg)是骨组织中的必需元素,在骨代谢中起着重要作用,也被应用于各种骨修复材料从而发挥免疫调节作用。QI等[113]在β-磷酸三钙支架中掺入不同含量的氧化镁,发现Mg-β-磷酸三钙促进了RAW264.7细胞向M2表型的极化,而氧化镁含量3%的β-磷酸三钙支架则显示出最佳的成骨和血管生成潜力。WU等[114]为了解决磷酸钙骨水泥中Mg降解过快的问题,开发了一种新型含Mg磷酸钙陶瓷,通过持续释放Mg离子,具有长期的机械稳定性和成骨作用。在另一项研究中,HE等[115]在钛(Ti)表面构建了能够持续释放Mg离子的纳米结构的薄膜,体外实验显示纳米Mg(OH)2薄膜更有利于骨髓源性巨噬细胞的M2极化、小鼠骨髓干细胞的成骨以及人脐静脉内皮细胞的血管生成,体内实验显示纳米Mg(OH)2改良的Ti骨整合增强。LIANG等[116]也将Mg离子掺入Ti金属中,并证实Ti-0.625 Mg(质量分数)合金中Mg离子的降解有利于巨噬细胞从M1至M2表型的序贯活化。除了以上提到的Mg离子和Li离子,锌离子也被掺入微晶生物活性玻璃以调节巨噬细胞表型的序贯活化,诱导人骨髓间充质干细胞体外成骨分化和体内成骨[117]。 最后,microRNA(miRNA)是参与基因调控的非编码小RNA分子,将其掺入生物材料中成为调控巨噬细胞极化的一种新兴策略。例如,XIN等[118]证实胶原支架/外泌体促进M2巨噬细胞极化,减轻炎症,并增加了抗炎反应,外泌体中丰富的miRNA则是诱导巨噬细胞极化的主要介质。CASTA?O等[119]利用antagomiR-133a开发了一种无需在植入前添加外源细胞的胶原-纳米羟基磷灰石-miRNA支架系统,结果显示与无antagomiR的支架相比,植入支架1周后实验组骨体积增加了约2倍,4周后比对照组增加了10倍,且伴随宿主CD206(M2)巨噬细胞数量的增加。与miR-133a相同的是,antagomiR-16也被载入胶原纳米羟基磷灰石支架,用于骨修复[120]。"

| [1] LEE CZW, GINHOUX F. Biology of resident tissue macrophages. Development. 2022;149(8):dev200270. [2] SCHLUNDT C, FISCHER H, BUCHER CH, et al. The multifaceted roles of macrophages in bone regeneration: A story of polarization, activation and time. Acta Biomater. 2021;133:46-57. [3] VAN FURTH R, COHN ZA. The origin and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1968;128(3):415-435. [4] GINHOUX F, GRETER M, LEBOEUF M, et al. Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science. 2010;330(6005):841-845. [5] HASHIMOTO D, CHOW A, NOIZAT C, et al. Tissue-resident macrophages self-maintain locally throughout adult life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes. Immunity. 2013;38(4):792-804. [6] GOMEZ PERDIGUERO E, KLAPPROTH K, SCHULZ C, et al. Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature. 2015;518(7540):547-551. [7] HE S, CHEN J, JIANG Y, et al. Adult zebrafish Langerhans cells arise from hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Elife. 2018;7:e36131. [8] BIAN Z, GONG Y, HUANG T, et al. Deciphering human macrophage development at single-cell resolution. Nature. 2020;582(7813): 571-576. [9] WU Y, HIRSCHI KK. Tissue-Resident Macrophage Development and Function. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;8:617879. [10] VAROL C, MILDNER A, JUNG S. Macrophages: development and tissue specialization. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:643-675. [11] PÉREZ S, RIUS-PÉREZ S. Macrophage Polarization and Reprogramming in Acute Inflammation: A Redox Perspective. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(7):1394. [12] NEGRESCU AM, CIMPEAN A. The State of the Art and Prospects for Osteoimmunomodulatory Biomaterials. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(6): 1357. [13] ORECCHIONI M, GHOSHEH Y, PRAMOD AB, et al. Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1084. [14] FERRANTE CJ, LEIBOVICH SJ. Regulation of Macrophage Polarization and Wound Healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2012;1(1):10-16. [15] CHANMEE T, ONTONG P, KONNO K, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages as major players in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers (Basel). 2014;6(3):1670-1690. [16] GRANEY PL, BEN-SHAUL S, LANDAU S, et al. Macrophages of diverse phenotypes drive vascularization of engineered tissues. Sci Adv. 2020; 6(18):eaay6391. [17] XIE Y, HU C, FENG Y, et al. Osteoimmunomodulatory effects of biomaterial modification strategies on macrophage polarization and bone regeneration. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(3):233-245. [18] LOI F, CÓRDOVA LA, ZHANG R, et al. The effects of immunomodulation by macrophage subsets on osteogenesis in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:15. [19] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440. [20] MARTIN KE, GARCÍA AJ. Macrophage phenotypes in tissue repair and the foreign body response: Implications for biomaterial-based regenerative medicine strategies. Acta Biomater. 2021;133:4-16. [21] MURRAY PJ. Macrophage Polarization. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017;79: 541-566. [22] BRÜNE B, WEIGERT A, DEHNE N. Macrophage Polarization In The Tumor Microenvironment. Redox Biol. 2015;5:419. [23] WANG Y, FAN Y, LIU H. Macrophage Polarization in Response to Biomaterials for Vascularization. Ann Biomed Eng. 2021;49(9): 1992-2005. [24] BYLES V, COVARRUBIAS AJ, BEN-SAHRA I, et al. The TSC-mTOR pathway regulates macrophage polarization. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2834. [25] HAN R, GAO J, ZHAI H, et al. RAD001 (everolimus) attenuates experimental autoimmune neuritis by inhibiting the mTOR pathway, elevating Akt activity and polarizing M2 macrophages. Exp Neurol. 2016;280:106-114. [26] LI R, ZHOU R, WANG H, et al.Gut microbiota-stimulated cathepsin K secretion mediates TLR4-dependent M2 macrophage polarization and promotes tumor metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26(11):2447-2463. [27] JING Y, WU F, LI D, et al. Metformin improves obesity-associated inflammation by altering macrophages polarization. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018;461:256-264. [28] WANG Z, LIU M, YE D, et al. Il12a Deletion Aggravates Sepsis-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Regulating Macrophage Polarization. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:632912. [29] XU X, GAO W, LI L, et al. Annexin A1 protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization via FPR2/ALX-dependent AMPK-mTOR pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):119. [30] YANG Y, WANG J, GUO S, et al. Non-lethal sonodynamic therapy facilitates the M1-to-M2 transition in advanced atherosclerotic plaques via activating the ROS-AMPK-mTORC1-autophagy pathway. Redox Biol. 2020;32:101501. [31] KOPAN R, ILAGAN MX. The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell. 2009;137(2):216-233. [32] ZHAO JL, HUANG F, HE F, et al. Forced Activation of Notch in Macrophages Represses Tumor Growth by Upregulating miR-125a and Disabling Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cancer Res. 2016;76(6):1403-1415. [33] XU L, LI L, ZHANG CY, et al. Natural Diterpenoid Oridonin Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis by Promoting Anti-inflammatory Macrophages Through Blocking Notch Pathway. Front Neurosci. 2019; 13:272. [34] FENG J, DONG C, LONG Y, et al. Elevated Kallikrein-binding protein in diabetes impairs wound healing through inducing macrophage M1 polarization. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):60. [35] FENG X, GAO X, WANG S, et al. PPAR-αAgonist Fenofibrate Prevented Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibiting M1 Macrophages via Improving Endothelial Cell Function in db/db Mice. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021; 8:652558. [36] ZHENG W, ZHOU J, SONG S, et al. Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 Inhibitor Sitagliptin Ameliorates Hepatic Insulin Resistance by Modulating Inflammation and Autophagy in ob/ob Mice. Int J Endocrinol. 2018; 2018:8309723. [37] YANG R, ZHENG Y, WANG Q, et al. Curcumin-loaded chitosan-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles potentially enhanced Aβ 42 phagocytosis and modulated macrophage polarization in Alzheimer’s disease. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2018;13(1):330. [38] JIANG N, ZHANG L, ZHAO G, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Regulates Macrophage Recruitment, Polarization and Phagocytosis in Aspergillus Fumigatus Keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020;61(8):28. [39] LIU L, GUO H, SONG A, et al. Progranulin inhibits LPS-induced macrophage M1 polarization via NF-кB and MAPK pathways. BMC Immunol. 2020;21(1):32. [40] LI X, XU M, SHEN J, et al. Sorafenib inhibits LPS-induced inflammation by regulating Lyn-MAPK-NF-kB/AP-1 pathway and TLR4 expression. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):281. [41] HE S, WANG S, LIU S, et al. Baicalein Potentiated M1 Macrophage Polarization in Cancer Through Targeting PI3Kγ/ NF-κB Signaling. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:743837. [42] PENG X, HE F, MAO Y, et al. miR-146a promotes M2 macrophage polarization and accelerates diabetic wound healing by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB axis. J Mol Endocrinol. 2022;69(2):315-327. [43] NING H, CHEN H, DENG J, et al. Exosomes secreted by FNDC5-BMMSCs protect myocardial infarction by anti-inflammation and macrophage polarization via NF-κB signaling pathway and Nrf2/HO-1 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):519. [44] XIAO M, BIAN Q, LAO Y, et al. SENP3 loss promotes M2 macrophage polarization and breast cancer progression. Mol Oncol. 2022;16(4): 1026-1044. [45] SICA A, MANTOVANI A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(3):787-95. [46] YIN H, ZHANG X, YANG P, et al. RNA m6A methylation orchestrates cancer growth and metastasis via macrophage reprogramming. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1394. [47] HORTON JE, RAISZ LG, SIMMONS HA, et al. Bone resorbing activity in supernatant fluid from cultured human peripheral blood leukocytes. Science. 1972;177(4051):793-795. [48] ARRON JR, CHOI Y. Bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408 (6812):535-536. [49] OKAMOTO K, NAKASHIMA T, SHINOHARA M, et al. Osteoimmunology: The Conceptual Framework Unifying the Immune and Skeletal Systems. Physiol Rev. 2017;97(4):1295-1349. [50] SCHLUNDT C, FISCHER H, BUCHER CH, et al. The multifaceted roles of macrophages in bone regeneration: A story of polarization, activation and time. Acta Biomater. 2021;133:46-57. [51] SALHOTRA A, SHAH HN, LEVI B, et al. Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(11):696-711. [52] GUDER C, GRAVIUS S, BURGER C, et al. Osteoimmunology: A Current Update of the Interplay Between Bone and the Immune System. Front Immunol. 2020;11:58. [53] MARUYAMA M, RHEE C, UTSUNOMIYA T, et al. Modulation of the Inflammatory Response and Bone Healing. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:386. [54] JONES RE, SALHOTRA A, ROBERTSON KS, et al. Skeletal Stem Cell-Schwann Cell Circuitry in Mandibular Repair. Cell Rep. 2019;28(11): 2757-2766.e5. [55] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014; 507(7492):323-328. [56] HUME DA, LOUTIT JF, GORDON S. The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80: macrophages of bone and associated connective tissue. J Cell Sci. 1984;66:189-194. [57] CHANG MK, RAGGATT LJ, ALEXANDER KA, et al. Osteal tissue macrophages are intercalated throughout human and mouse bone lining tissues and regulate osteoblast function in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 2008;181(2):1232-1244. [58] WINKLER IG, SIMS NA, PETTIT AR, et al. Bone marrow macrophages maintain hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) niches and their depletion mobilizes HSCs. Blood. 2010;116(23):4815-4828. [59] CAO J, ZHANG S, GUPTA A, et al. Sensory Nerves Affect Bone Regeneration in Rabbit Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(6):831-837. [60] LIU Z, SUH JS, DENG P, et al. Epigenetic Regulation of NGF-Mediated Osteogenic Differentiation in Human Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2022;40(9):818-830. [61] BRACCI-LAUDIERO L, DE STEFANO ME. NGF in Early Embryogenesis, Differentiation, and Pathology in the Nervous and Immune Systems. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2016;29:125-152. [62] RIVERA KO, RUSSO F, BOILEAU RM, et al. Local injections of β-NGF accelerates endochondral fracture repair by promoting cartilage to bone conversion. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):22241. [63] LI Z, MEYERS CA, CHANG L, et al. Fracture repair requires TrkA signaling by skeletal sensory nerves. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(12):5137-5150. [64] LEE S, HWANG C, MARINI S, et al. NGF-TrkA signaling dictates neural ingrowth and aberrant osteochondral differentiation after soft tissue trauma. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4939. [65] DELAY L, BARBIER J, AISSOUNI Y, et al. Tyrosine kinase type A-specific signalling pathways are critical for mechanical allodynia development and bone alterations in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. Pain. 2022;163(7):e837-e849. [66] XU J, LI Z, TOWER RJ, et al. NGF-p75 signaling coordinates skeletal cell migration during bone repair. Sci Adv. 2022;8(11):eabl5716. [67] FRANCO ML, NADEZHDIN KD, LIGHT TP, et al. Interaction between the transmembrane domains of neurotrophin receptors p75 and TrkA mediates their reciprocal activation. J Biol Chem. 2021;297(2):100926. [68] VALLÉS G, BENSIAMAR F, MAESTRO-PARAMIO L,et al. Influence of inflammatory conditions provided by macrophages on osteogenic ability of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):57. [69] MAHON OR, BROWE DC, GONZALEZ-FERNANDEZ T, et al. Nano-particle mediated M2 macrophage polarization enhances bone formation and MSC osteogenesis in an IL-10 dependent manner. Biomaterials. 2020;239:119833. [70] ZHANG B, HAN F, WANG Y, et al. Cells-Micropatterning Biomaterials for Immune Activation and Bone Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022; 9(18):e2200670. [71] ZHANG Y, BÖSE T, UNGER RE, et al. Macrophage type modulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose tissue MSCs. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;369(2):273-286. [72] ROMERO-LÓPEZ M, LI Z, RHEE C, et al. Macrophage Effects on Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenesis in a Three-Dimensional In Vitro Bone Model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2020;26(19-20):1099-1111. [73] LOI F, CÓRDOVA LA, ZHANG R, et al. The effects of immunomodulation by macrophage subsets on osteogenesis in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:15. [74] SCHLUNDT C, EL KHASSAWNA T, SERRA A, et al. Macrophages in bone fracture healing: Their essential role in endochondral ossification. Bone. 2018;106:78-89. [75] QIAO W, XIE H, FANG J, et al. Sequential activation of heterogeneous macrophage phenotypes is essential for biomaterials-induced bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;276:121038. [76] LUQUE-CAMPOS N, BUSTAMANTE-BARRIENTOS FA, PRADENAS C, et al. The Macrophage Response Is Driven by Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Metabolic Reprogramming. Front Immunol. 2021;12:624746. [77] WEISS ARR, DAHLKE MH. Immunomodulation by Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Mechanisms of Action of Living, Apoptotic, and Dead MSCs. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1191. [78] RANA N, SULIMAN S, MOHAMED-AHMED S, et al. Systemic and local innate immune responses to surgical co-transplantation of mesenchymal stromal cells and biphasic calcium phosphate for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2022;141:440-453. [79] CHEN B, NI Y, LIU J, et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exert Diverse Effects on Different Macrophage Subsets. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:8348121. [80] PAJARINEN J, LIN T, GIBON E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials. 2019;196:80-89. [81] CHANG MK, RAGGATT LJ, ALEXANDER KA, et al. Osteal tissue macrophages are intercalated throughout human and mouse bone lining tissues and regulate osteoblast function in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 2008;181(2):1232-1244. [82] BATOON L, MILLARD SM, WULLSCHLEGER ME, et al. CD169+ macrophages are critical for osteoblast maintenance and promote intramembranous and endochondral ossification during bone repair. Biomaterials. 2019;196:51-66. [83] WANG J, ZHENG Z, HUANG B, et al. Osteal Tissue Macrophages Are Involved in Endplate Osteosclerosis through the OSM-STAT3/YAP1 Signaling Axis in Modic Changes. J Immunol. 2020;205(4):968-980. [84] SUN W, MEEDNU N, ROSENBERG A, et al. B cells inhibit bone formation in rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing osteoblast differentiation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):5127. [85] KANESHIRO S, EBINA K, SHI K, et al. IL-6 negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation through the SHP2/MEK2 and SHP2/Akt2 pathways in vitro. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014;32(4):378-392. [86] HARMER D, FALANK C, REAGAN MR. Interleukin-6 Interweaves the Bone Marrow Microenvironment, Bone Loss, and Multiple Myeloma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;9:788. [87] HAMEISTER R, LOHMANN CH, DHEEN ST, et al. The effect of TNF-α on osteoblasts in metal wear-induced periprosthetic bone loss. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(11):827-839. [88] WU S, XIAO Z, SONG J, et al. Evaluation of BMP-2 Enhances the Osteoblast Differentiation of Human Amnion Mesenchymal Stem Cells Seeded on Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Collagen/Poly(l-Lactide). Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2171. [89] YANG D, WAN Y. Molecular determinants for the polarization of macrophage and osteoclast. Semin Immunopathol. 2019;41(5):551-563. [90] BATOON L, MILLARD SM, RAGGATT LJ, et al. Osteal macrophages support osteoclast-mediated resorption and contribute to bone pathology in a postmenopausal osteoporosis mouse model. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(11):2214-2228. [91] JUNG YK, KANG YM, HAN S. Osteoclasts in the Inflammatory Arthritis: Implications for Pathologic Osteolysis. Immune Netw. 2019;19(1):e2. [92] XU H, ZHAO H, LU C, et al. Triptolide Inhibits Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone Resorption In Vitro via Enhancing the Production of IL-10 and TGF-β1 by Regulatory T Cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:8048170. [93] TANAKA K, YAMAGATA K, KUBO S, et al. Glycolaldehyde-modified advanced glycation end-products inhibit differentiation of human monocytes into osteoclasts via upregulation of IL-10. Bone. 2019;128:115034. [94] MUÑOZ J, AKHAVAN NS, MULLINS AP, et al. Macrophage Polarization and Osteoporosis: A Review. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):2999. [95] TOKUNAGA T, MOKUDA S, KOHNO H, et al. TGFβ1 Regulates Human RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis via Suppression of NFATc1 Expression. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):800. [96] SUN Y, LI J, XIE X, et al. Macrophage-Osteoclast Associations: Origin, Polarization, and Subgroups. Front Immunol. 2021;12:778078. [97] BORDUKALO-NIKŠIĆ T, KUFNER V, VUKIČEVIĆ S. The Role Of BMPs in the Regulation of Osteoclasts Resorption and Bone Remodeling: From Experimental Models to Clinical Applications. Front Immunol. 2022;13:869422. [98] NIU Y, WANG Z, SHI Y, et al. Modulating macrophage activities to promote endogenous bone regeneration: Biological mechanisms and engineering approaches. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(1):244-261. [99] XIE Y, HU C, FENG Y, et al. Osteoimmunomodulatory effects of biomaterial modification strategies on macrophage polarization and bone regeneration. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(3):233-245. [100] ATCHA H, JAIRAMAN A, HOLT JR, et al. Mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1 modulates macrophage polarization and stiffness sensing. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3256. [101] HE XT, WU RX, XU XY, et al. Macrophage involvement affects matrix stiffness-related influences on cell osteogenesis under three-dimensional culture conditions. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:132-147. [102] SRIDHARAN R, CAVANAGH B, CAMERON AR, et al. Material stiffness influences the polarization state, function and migration mode of macrophages. Acta Biomater. 2019;89:47-59. [103] HOTCHKISS KM, REDDY GB, HYZY SL, et al. Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:425-434. [104] ZHU Y, ZHANG K, ZHAO R, et al. Bone regeneration with micro/nano hybrid-structured biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics at segmental bone defect and the induced immunoregulation of MSCs. Biomaterials. 2017;147:133-144. [105] TYLEK T, BLUM C, HRYNEVICH A, et al. Precisely defined fiber scaffolds with 40 μm porosity induce elongation driven M2-like polarization of human macrophages. Biofabrication. 2020;12(2):025007. [106] YIN Y, HE X T, WANG J, et al. Pore size-mediated macrophage M1-to-M2 transition influences new vessel formation within the compartment of a scaffold. Applied Materials Today. 2019;18:100466. [107] LI W, DAI F, ZHANG S, et al. Pore Size of 3D-Printed Polycaprolactone/Polyethylene Glycol/Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds Affects Bone Regeneration by Modulating Macrophage Polarization and the Foreign Body Response. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(18):20693-20707. [108] HAMLET SM, LEE RSB, MOON HJ, et al. Hydrophilic titanium surface-induced macrophage modulation promotes pro-osteogenic signalling. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30(11):1085-1096. [109] SHEN H, SHI J, ZHI Y, et al. Improved BMP2-CPC-stimulated osteogenesis in vitro and in vivo via modulation of macrophage polarization. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111471. [110] LIU Y, YANG Z, WANG L, et al. Spatiotemporal Immunomodulation Using Biomimetic Scaffold Promotes Endochondral Ossification-Mediated Bone Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(11):e2100143. [111] LI D, YANG Z, ZHAO X, et al. Osteoimmunomodulatory injectable Lithium-Heparin hydrogel with Microspheres/TGF-β1 delivery promotes M2 macrophage polarization and osteogenesis for guided bone regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2022;135:134991. [112] LI L, LI Q, GUI L, et al. Sequential gastrodin release PU/n-HA composite scaffolds reprogram macrophages for improved osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2022;19:24-37. [113] QI D, SU J, LI S, et al. 3D printed magnesium-doped β-TCP gyroid scaffold with osteogenesis, angiogenesis, immunomodulation properties and bone regeneration capability in vivo. Biomater Adv. 2022;136:212759. [114] WU J, LIU F, WANG Z, et al. The Development of a Magnesium-Releasing and Long-Term Mechanically Stable Calcium Phosphate Bone Cement Possessing Osteogenic and Immunomodulation Effects for Promoting Bone Fracture Regeneration . Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;9:803723. [115] HE Y, YAO M, ZHOU J, et al. Mg(OH)2 nanosheets on Ti with immunomodulatory function for orthopedic applications. Regen Biomater. 2022;9:rbac027. [116] LIANG L, SONG D, WU K, et al. Sequential activation of M1 and M2 phenotypes in macrophages by Mg degradation from Ti-Mg alloy for enhanced osteogenesis. Biomater Res. 2022;26(1):17. [117] BAI X, LIU W, XU L, et al. Sequential macrophage transition facilitates endogenous bone regeneration induced by Zn-doped porous microcrystalline bioactive glass. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(12):2885-2898. [118] XIN L, LIN X, ZHOU F, et al. A scaffold laden with mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for promoting endometrium regeneration and fertility restoration through macrophage immunomodulation. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:252-266. [119] CASTAÑO IM, RAFTERY RM, CHEN G, et al. Rapid bone repair with the recruitment of CD206+M2-like macrophages using non-viral scaffold-mediated miR-133a inhibition of host cells. Acta Biomater. 2020;109:267-279. [120] MENCÍA CASTAÑO I, CURTIN CM, DUFFY GP, et al. Harnessing an Inhibitory Role of miR-16 in Osteogenesis by Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Advanced Scaffold-Based Bone Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2019;25(1-2):24-33. |
| [1] | Sun Kexin, Zeng Jinshi, Li Jia, Jiang Haiyue, Liu Xia. Mechanical stimulation enhances matrix formation of three-dimensional bioprinted cartilage constructs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [3] | Wu Tianliang, Tao Xiuxia, Xu Hongguang. Influence of different bone mineral densities on cage subsidence after stand-alone oblique lateral interbody fusion: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1352-1358. |
| [4] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [5] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [6] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [7] | Bai Yulong, Li Zhonghai, Zhao Yantao, Xia Cencan, Shi Lei. History, current situation and prospect of tissue banks in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1306-1312. |
| [8] | Sun Jiajia, Zhu Haidi, Lu Yun, Zhang Kai. Comparison of bone metabolism markers between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [9] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [10] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [11] | Liu Jiaxin, Jia Peng, Men Yutao, Liu Lu, Wang Yeming, Ye Jinduo. Design and optimization of bone trabecular structure with triply periodic minimal surfaces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 992-997. |
| [12] | Yuan Hucheng, Ding Yongguo, Ma Xuehua, Ma Wenxin, Sun Jianmin, Wang Zili, Jin Weidong. Sustained releasing of pyrazinamide, capreomycin, moxifloxacin and amikacin loaded bone cement in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1017-1022. |
| [13] | Zhao Wei, Feng Wei, Yang Tieyi, Ren Wei, Wang Yuxin, Lyu Huicheng, Chang Zhiqiang, Feng Xiaodong, Wang Ziheng, Guo Shibing. Antibiotic bone cement intramedullary nail prepared using 3D printed mold for the treatment of long bone infection in lower limbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1023-1030. |
| [14] | Sun Jiangwei, Wang Junxiang, Baibujiafu·Yellisi, Dai Huijuan, Nijati·Turson. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in different smooth collar implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1004-1011. |
| [15] | Zhang Tingting, Liu Juan, Zhang Xu. Bioactivity of phase-transition lysozyme for surface modification of zirconia all-ceramic implant material mediating hydroxyapatite coating [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1043-1049. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||