Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (10): 1547-1552.doi: 10.12307/2023.305
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of chiral polyethyleneimine/graphene oxide/phenylalanine interface on adhesion and proliferation of multilineage-differentiating stress enduring cells
Zhou Jingjing1, 2, Sun Yixin1, 2, Sheng Yang1, 2, Zhang Rong1, 2
- 1School of Materials Science and Engineering, Changzhou University, Changzhou 213614, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Environmentally Friendly Polymeric Materials, Changzhou University, Changzhou 213164, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-04-02Accepted:2022-06-06Online:2023-04-08Published:2022-09-08 -
Contact:Sun Yixin, MD, Associate professor, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Changzhou University, Changzhou 213614, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Environmentally Friendly Polymeric Materials, Changzhou University, Changzhou 213164, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhou Jingjing, Master candidate, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Changzhou University, Changzhou 213614, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Environmentally Friendly Polymeric Materials, Changzhou University, Changzhou 213164, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Jingjing, Sun Yixin, Sheng Yang, Zhang Rong. Effects of chiral polyethyleneimine/graphene oxide/phenylalanine interface on adhesion and proliferation of multilineage-differentiating stress enduring cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1547-1552.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
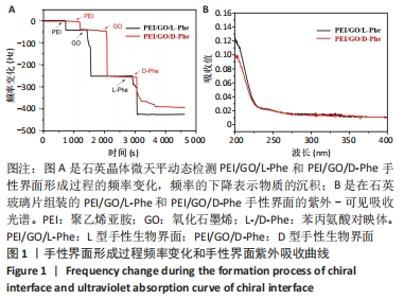
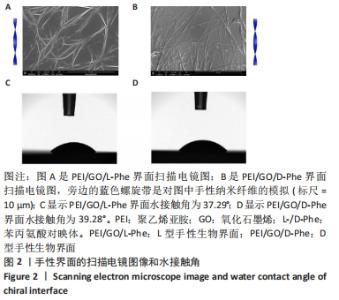
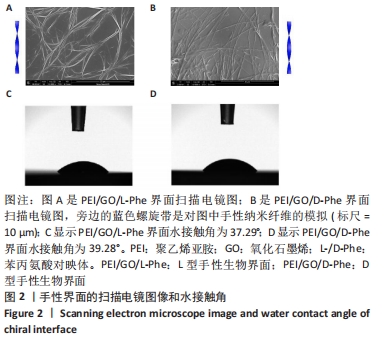
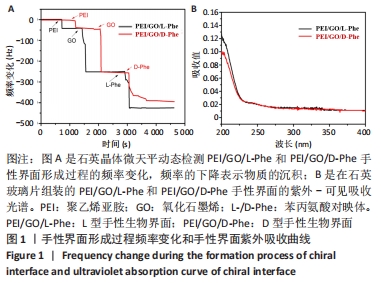
2.1 PEI/GO/Phe手性表面的性质和结构 首先,研究了PEI/GO/Phe界面在金涂层谐振器上的自组装,通过石英晶体微天平监测样品的频率变化,结果如图1A所示。在PEI/GO/Phe界面的构建过程中,频率的变化表明物质在基底(此处为石英金片)的沉积,根据Sauerbrey 方程的相关公式ΔM/A= (-C ·ΔF )/n可计算出沉积物质量[39],也可以看出频率变化与沉积物质量正相关。当不同的溶液通过蠕动泵流经石英金片表面时,石英晶体表面质量的变化会以频率变化直观展示出来;PEI、GO溶液以及Phe溶液依次通入石英金片后,随着时间的流逝,ΔF的数值不断下降,表明了3种物质在石英金片表面沉积,同时以上结果表明成功制备出PEI/GO/L-Phe和PEI/GO/D-Phe 2种手性界面。紫外-可见吸收光谱跟踪了PEI/GO/Phe的组装过程,结果也表明PEI/GO/Phe界面组装成功,见图1B。"
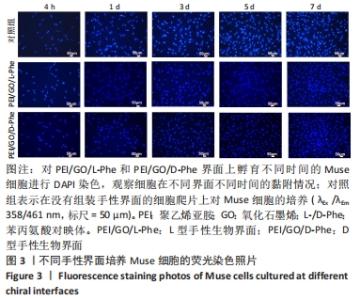
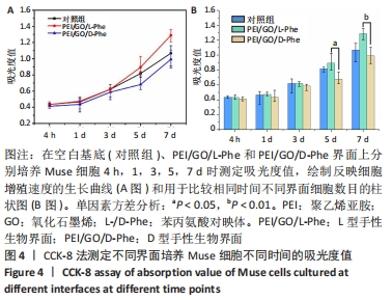
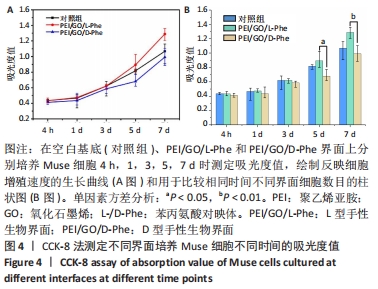
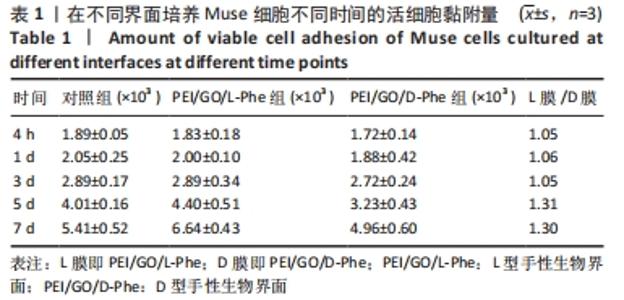
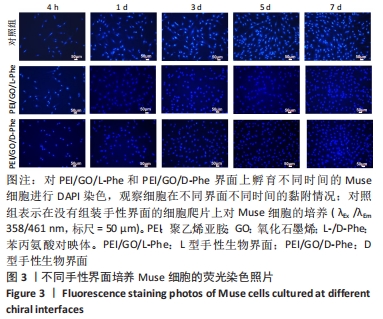
2.2 Muse细胞在手性生物界面上的黏附和增殖行为 手性生物界面孵育Muse细胞不同时间的DAPI染色结果见图3。首先通过CCK-8测试发现,Muse细胞的数量与吸光度值之间存在良好的线性关系(y=0.178 7x+0.103,R2=0.985 9,未在文中附标准曲线图)。结合图4和表1对Muse细胞在手性生物界面的生长状况进行解释,为下文方便叙述,PEI/GO/L-Phe简称为L膜,PEI/GO/D-Phe简称为D膜。在孵育的最初4 h,黏附在L膜上活细胞数目比D膜更多,L膜上活细胞数目是D膜的1.05倍。Muse细胞在手性生物界面上孵育24 h后并没有出现明显的增殖现象,但在第1-3天的时间段内细胞出现了明显的生长增殖,并且从第3天后增殖速度显著加快。L膜上黏附的Muse细胞总是比D膜上的多,见图4A,从表1可以看出第5天L膜上黏附的Muse细胞数目是D膜上细胞数目的1.31倍(P < 0.05),第7天L膜上活细胞黏附数目是D膜上的1.30倍(P < 0.01),这一比值和相关文献报道相近[33]。LIU等[33,40]在自组装手性纳米纤维水凝胶对细胞行为的调控研究中,将小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞(NIH 3T3)孵育在手性膜上4 h后,L膜上的活细胞黏附量比D膜上更多,孵育3 d后发现细胞的数目正比于原始的黏附量,高黏附量对实现高的细胞增殖量至关重要。实验中细胞培养7 d后,L膜上Muse活细胞黏附量是D膜上的1.30倍,正比于孵育4 h的活细胞黏附量(L膜/D膜:1.05/1),以上结果表明初期较高的活细胞黏附量对于后期Muse细胞增殖生长至关重要。"
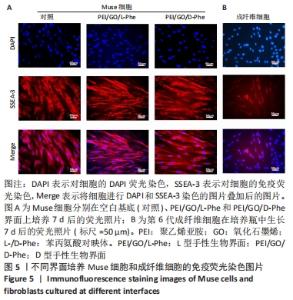
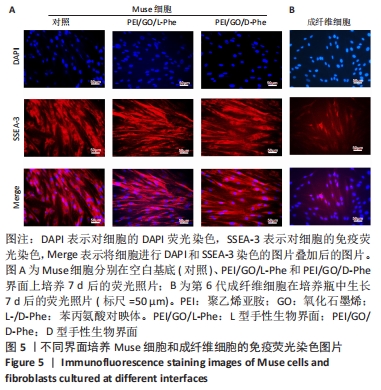
2.3 免疫荧光染色结果 有学者对人皮肤成纤维细胞和骨髓间质细胞进行了一系列应激实验,比如低营养、低血清、低氧、反复蛋白酶处理和长时间酶处理等,最后发现长时间酶处理是富集Muse细胞最有效的办法[41],所富集的Muse细胞表达干细胞表面多能性标记物,如SSEA-3、Nanog、Oct3/4和Sox2。在这项工作中,用胰蛋白酶处理成纤维细胞16 h后,获得的Muse细胞在手性界面培养7 d后,用DAPI和SSEA-3抗体对Muse细胞进行染色,从图5中看出,手性界面孵育多天的大多数Muse细胞在560 nm激发波下显示出强烈的红色荧光,对SSEA-3阳性表达。同时,可以看到视野中一部分成纤维细胞为SSEA-3抗体阳性,另一部分成纤维细胞对SSEA-3抗体呈阴性表达, 这进一步证明了长时间酶处理法富集Muse细胞的有效性。"
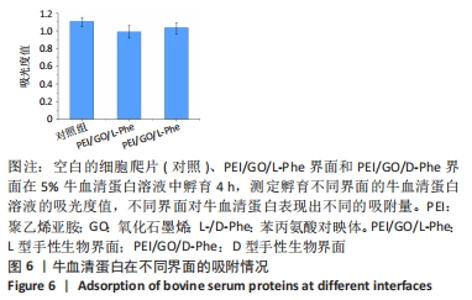
2.4 蛋白质在手性表面的吸附作用 细胞外膜上的蛋白质在调节细胞黏附和增殖方面起着重要作用。作为主要存在于细胞外基质和细胞表面的纤连蛋白,广泛参与了细胞迁移、黏附、增殖等细胞行为。例如,通过ELISA分析,纤连蛋白在L构型的纳米纤维膜上有较高的蛋白质吸附能力[33,42]。研究还表明,胎牛血清是细胞培养液中最重要的营养物质[43]。因此,研究了牛血清蛋白在不同手性界面上的吸附行为。在37 ℃和体积分数为5% CO2条件下,将不同的手性界面浸入牛血清蛋白溶液中4 h,用紫外可见光谱仪测量牛血清蛋白溶液的吸光度,见图6。与对照组相比,牛血清蛋白溶液在PEI/GO/L-Phe表面的吸光度下降得更多,表明PEI/GO/L-Phe表面比PEI/GO/D-Phe吸附了更多的蛋白质。"
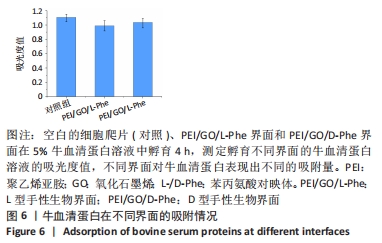

已有学者发现L-半胱氨酸(L-Cys)修饰的金表面上吸附了较多的胎牛血清白蛋白,D-半胱氨酸(D-Cys)修饰的金表面吸附的胎牛血清白蛋白就相对较少[32]。因此作者认为,在手性生物界面孵育Muse细胞的初始阶段,PEI/GO/L-Phe在其表面吸附了培养基中更多的蛋白质(胎牛血清白蛋白),进而PEI/GO/L-Phe具有更高的Muse细胞黏附量,进一步促进了细胞增殖,最后出现了PEI/GO/L-Phe和PEI/GO/D-Phe界面上Muse细胞数量的显著差异。还有可能是不同的手性界面相互作用向细胞释放不同的信号,从而导致不同的细胞底物相互作用,细胞和手性物质的相互作用机制仍需进一步的研究[44]。 "

| [1] LANGER R, TIRRELL DA. Designing materials for biology and medicine. Nature. 2004;428(6982):487-492. [2] HIGUCHI A, LING QD, CHANG Y, et al. Physical cues of biomaterials guide stem cell differentiation fate. Chem Rev. 2013;113(5):3297-3328. [3] 郑颖,邓诗碧,陈方.干细胞与再生医学技术发展态势研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2022,42(4):111-119. [4] MAO AS, MOONEY DJ. Regenerative medicine: Current therapies and future directions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(47):14452-14459. [5] SPILLER KL, KOH TJ. Macrophage-based therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;122:74-83. [6] KESHTKAR S, AZARPIRA N, GHAHREMANI MH. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):63. [7] OGURA F, WAKAO S, KURODA Y, et al. Human adipose tissue possesses a unique population of pluripotent stem cells with nontumorigenic and low telomerase activities: potential implications in regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(7):717-728. [8] KURODA Y, KITADA M, WAKAO S, et al. Unique multipotent cells in adult human mesenchymal cell populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(19):8639-8643. [9] WAKAO S, AKASHI H, KUSHIDA Y, et al. Muse cells, newly found non-tumorigenic pluripotent stem cells, reside in human mesenchymal tissues. Pathol Int. 2014;64(1):1-9. [10] FISCH SC, GIMENO ML, PHAN JD, et al. Pluripotent nontumorigenic multilineage differentiating stress enduring cells (Muse cells): a seven-year retrospective. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):227. [11] KURODA Y, WAKAO S, KITADA M, et al. Isolation, culture and evaluation of multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring (Muse) cells. Nat Protoc. 2013;8(7):1391-1415. [12] YAMASHITA T, KUSHIDA Y, WAKAO S, et al. Therapeutic benefit of Muse cells in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):17102. [13] NODA T, NISHIGAKI K, MINATOGUCHI S. Safety and Efficacy of Human Muse Cell-Based Product for Acute Myocardial Infarction in a First-in-Human Trial. Circ J. 2020;84(7):1189-1192. [14] YAMADA Y, MINATOGUCHI S, KANAMORI H, et al. Stem cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction - focusing on the comparison between Muse cells and mesenchymal stem cells. J Cardiol. 2022;80(1):80-87. [15] TAKAGI T, YOSHIMURA S, SAKUMA R, et al. Novel Regenerative Therapies Based on Regionally Induced Multipotent Stem Cells in Post-Stroke Brains: Their Origin, Characterization, and Perspective. Transl Stroke Res. 2017;8(6):515-528. [16] YU J, HU K, SMUGA-OTTO K, et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cells free of vector and transgene sequences. Science. 2009;324(5928): 797-801. [17] WAKAO S, KITADA M, KURODA Y, et al. Isolation of adult human pluripotent stem cells from mesenchymal cell populations and their application to liver damages. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;826:89-102. [18] WANG L, XIAO L, ZHANG RZ, et al. Effects of acrylate/acrylamide polymers on the adhesion, growth and differentiation of Muse cells. Biomed Mater. 2018;14(1):015003. [19] 李秀亚,盛扬,王圣依,等.蛋白芯片筛选用于培养Muse细胞的纤维蛋白原和明胶组合基质[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(21): 3312-3318. [20] TRAPPMANN B, GAUTROT JE, CONNELLY JT, et al. Extracellular-matrix tethering regulates stem-cell fate. Nat Mater. 2012;11(7):642-649. [21] MAMMOTO A, MAMMOTO T, KANAPATHIPILLAI M, et al. Control of lung vascular permeability and endotoxin-induced pulmonary oedema by changes in extracellular matrix mechanics. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1759. [22] GENTILE F, MEDDA R, CHENG L, et al. Selective modulation of cell response on engineered fractal silicon substrates. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1461. [23] WANG X, GAN H, ZHANG M, et al. Modulating cell behaviors on chiral polymer brush films with different hydrophobic side groups. Langmuir. 2012;28(5):2791-2798. [24] QUAH SP, ZHANG Y, FLUERASU A, et al. Techniques to characterize dynamics in biomaterials microenvironments: XPCS and microrheology of alginate/PEO-PPO-PEO hydrogels. Soft Matter. 2021;17(6):1685-1691. [25] ZHOU Q, GE L, GUIMARÃES CF, et al. Development of a Novel Orthogonal Double Gradient for High-Throughput Screening of Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Materials Interaction. Advanced Materials Interfaces. 2018;5(18):1800504-1800511. [26] ABARICIA JO, FARZAD N, HEATH TJ, et al. Control of innate immune response by biomaterial surface topography, energy, and stiffness. Acta Biomater. 2021;133:58-73. [27] SOTO VELIZ D, KUMMALA R, ABITBOL T, et al. Influence of mineral coatings on fibroblast behaviour: The importance of coating formulation and experimental design. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;208:112059. [28] JOSEPH G, ORME RP, KYRIACOU T, et al. Effects of Surface Chemistry Interaction on Primary Neural Stem Cell Neurosphere Responses. ACS Omega. 2021;6(30):19901-19910. [29] BAI CL, LIU MH. Implantation of nanomaterials and nanostructures on surface and their applications. Nano Today. 2012;7(4):258-281. [30] Mei Y, Saha K, Bogatyrev SR, et al. Combinatorial development of biomaterials for clonal growth of human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Mater. 2010;9(9):768-778. [31] SUN T, HAN D, RIEHEMANN K, et al. Stereospecific interaction between immune cells and chiral surfaces. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129(6):1496-1497. [32] YAO X, HU Y, CAO B, et al. Effects of surface molecular chirality on adhesion and differentiation of stem cells. Biomaterials. 2013;34(36): 9001-9009. [33] LIU GF, ZHANG D, FENG CL. Control of three-dimensional cell adhesion by the chirality of nanofibers in hydrogels. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014;53(30):7789-7793. [34] HU B, DENG J, ZHENG H, et al. Synthesis of Chiral Oligomer-Grafted Biodegradable Polyurethanes and Their Chiral-Dependent Influence on Bone Marrow Stem Cell Behaviors. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016;37(16):1331-1336. [35] DENG J, ZHENG HH, ZHENG XW, et al. Gold nanoparticles with surface-anchored chiral poly(acryloyl-L(D)-valine) induce differential response on mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis. Nano Research. 2016;9(12): 3683-3694. [36] PICCININI E, BLIEM C, REINER-ROZMAN C, et al. Enzyme-polyelectrolyte multilayer assemblies on reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistors for biosensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;92:661-667. [37] KWON D, KIM JS, CHA BH, et al. The Effect of Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) on Efficacy of Cellular Reprogramming for Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC) Generation. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(6):1025-1042. [38] WANG X, GAN H, SUN T. Chiral Design for Polymeric Biointerface: The Influence of Surface Chirality on Protein Adsorption. Adv Funct Mater. 2011;21(17):3276-3281. [39] OKUTAN M, DELIGOZ H. Effect of external salt addition on the structural, morphological and electrochemical properties of flexible PEDOT:PSS based LbL multilayered films. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2019;580(5):123695-123706. [40] MAHERALI N, SRIDHARAN R, XIE W, et al. Directly reprogrammed fibroblasts show global epigenetic remodeling and widespread tissue contribution. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1(1):55-70. [41] SUKHIKH GT, MALAITSEV VV, BOGDANOVA IM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2002;133(2):103-109. [42] HAN H, WANG K, FAN Y, et al. Enhancement of nitric oxide release and hemocompatibility by surface chirality of D-tartaric acid grafting. Applied Surface Science. 2017;425(15):847-854. [43] EITAN E, ZHANG S, WITWER KW, et al. Extracellular vesicle-depleted fetal bovine and human sera have reduced capacity to support cell growth. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:26373. [44] VOGEL V, SHEETZ M. Local force and geometry sensing regulate cell functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(4):265-275. |
| [1] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [2] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [3] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [4] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [5] | Li Rui, Liu Zhen, Guo Zige, Lu Ruijie, Wang Chen. Aspirin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and polydopamine modified titanium sheets improve osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 374-379. |
| [6] | Wang Huanhuan, Wang Qing, Tang Peng, Zhang Rui, Min Hongwei. Effects of extracorporeal shock wave on the proliferation and autophagy of chondrocytes from osteoarthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 252-257. |
| [7] | Zhang Rui, Liu Lan, Xie Defu, Lin Yingxi, Ren Hongjing, Yan Hong. Effect of adipose-derived stem cells stimulated by direct current electric field on refractory wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1484-1491. |
| [8] | Yang Xu, Wang Feiqing, Zhao Jianing, Zhang Chike, Liang Huiling, Qi Shasha, Wu Dan, Liu Yanqing, Tang Dongxin, Liu Yang, Li Yanju. Effects of multiple myeloma cell conditioned medium on proliferation and differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1514-1520. |
| [9] | Wang Zhaoxin, Nijati•Tursun, Dai Huijuan, Wang Junxiang, Xiaheida•Yilaljiang, Li Shuhui. Effect of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha on the biological behavior of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1521-1527. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Nie Minhai, Hu Xinyue, Liu Xuqian. Platelet-derived growth factor BB promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1534-1540. |
| [11] | Xing Guoyi, Sun Legang, Ma Xiangrui, Wang Wenlong. Regulation of Sema3A on oral mesenchymal stem cell function [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1626-1633. |
| [12] | Wei Yanzhao, Zheng Xiaohan, Gao Shijun, Huang Ting, Wei Xufang, Chen Xinxu, Zhao Zhenqiang. Expression of autocrine macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its receptors of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 34-41. |
| [13] | Yang Yan, Wang Jingxian, Zhang Ronghong, Li Chen, Fan Anran, Cui Dongbing, Wu Shumei. Effects of conditioned media of different sources on the proliferation of human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 49-53. |
| [14] | Lan Qian, Gu Yangcong, Xiao Xin, Bi Xueting, Li Na. Human periodontal ligament stem cells-derived exosomes interfere with the proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 54-58. |
| [15] | Zhang Jinglan, Zhang Binjing, Chen Yifei, Zhang Chenyue, Hu Zhiai, Hu Haikun. Biological effects of magnetic field on osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 145-151. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||