Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 461-469.doi: 10.12307/2023.049
Previous Articles Next Articles
Use of expanders and implants in breast reconstruction complicated with infection
Wang Kaiyu, Hu Peng, Wei Zairong, Huang Guangtao, Zhou Jian, He Guijia, Nie Kaiyu
- Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Tissue Injury Repair and Regenerative Medicine Co-sponsored by Province and Ministry, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-09-03Accepted:2021-10-18Online:2023-01-28Published:2022-06-01 -
Contact:Nie Kaiyu, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Tissue Injury Repair and Regenerative Medicine Co-sponsored by Province and Ministry, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wang Kaiyu, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Tissue Injury Repair and Regenerative Medicine Co-sponsored by Province and Ministry, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Kaiyu, Hu Peng, Wei Zairong, Huang Guangtao, Zhou Jian, He Guijia, Nie Kaiyu. Use of expanders and implants in breast reconstruction complicated with infection[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 461-469.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
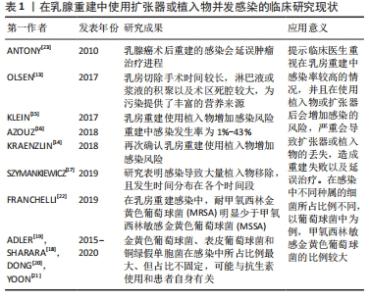
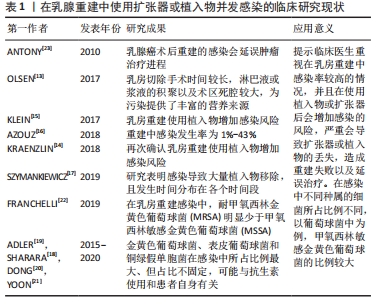
大多数的乳房手术被认为是清洁的,与其他乳房手术(如缩小乳房成形术)相比,乳房切除术后感染的发生率较高,可能是由于手术时间较长,淋巴液或浆液的积聚以及术区死腔较大,为污染提供了丰富的营养来源[13]。在乳房重建过程中,使用植入物会额外增加感染的风险[14-15],发生率为1%-43%[16],有报道称在一项研究中有83%的植入物移除都是由于感染所造成的,并且感染的发生时间分布在各个时间段[17]。乳房重建遍布于不同年龄段以及不同治疗需求的女性患者,其本身健康状态、生活习性或所接受的治疗均可能是发生感染的风险因素。在感染部位分离的病原菌中,革兰阳性菌与革兰阴性菌所占比例可能有所差异。在某些研究中发现金黄色葡萄球菌、表皮葡萄球菌和铜绿假单胞菌在感染中所占比例最大[18-20],但这些细菌的占比却并不固定,这些差异可以通过在不同医疗机构使用不同的预防性抗生素以及患者自身独特的微生物群来解释[21],其中耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus,MRSA)感染的比例远低于易感金黄色葡萄球菌(methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus,MSSA)[22]。感染的类型可能轻至单纯的皮肤红肿、发热,严重则可能出现深部感染,最终导致植入物的移出。在乳腺癌术后重建的感染还可能影响患者的肿瘤治疗进程[23],而且有证据表明,感染引起的局部炎症反应也可能增加5年疾病复发的风险。随着抗生素在某些方面的不当使用,会导致耐药菌不断出现,从而增加治疗难度,甚至会导致更严重的中毒性休克综合征。现将目前在乳腺重建中使用扩张器或植入物并发感染的现状作一总结,见表1。 "
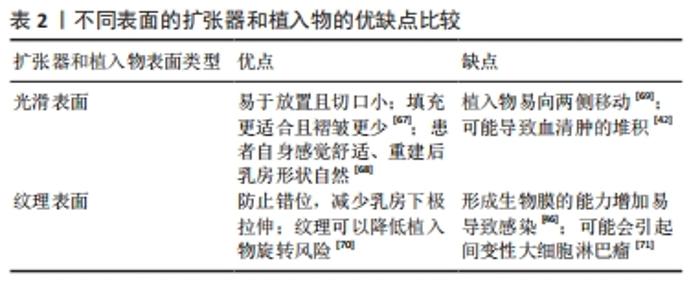
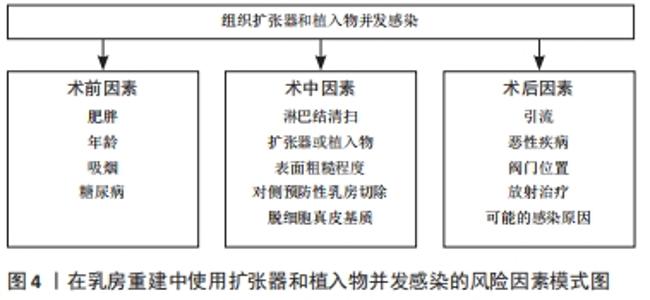
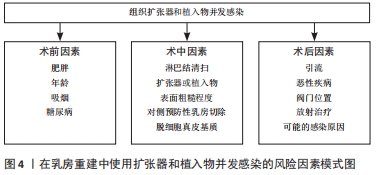
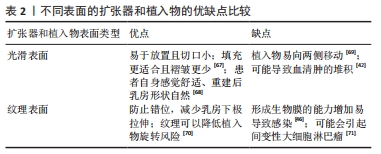
2.2 在乳房重建中使用组织扩张器及植入物并发感染的风险因素 2.2.1 术前因素 在使用植入物进行重建前存在许多导致感染的风险因素,包括患者年龄、吸烟、肥胖等,文章将此统称为术前因素,这些因素可能影响皮瓣的灌注、愈合和免疫功能,从而带来感染风险[15]。 年龄:目前65岁以上的乳腺癌患者占比将近 75% ,但极少为老年患者提供重建,虽然年龄始终是患者整体健康和耐受性的一个考虑因素,但大量的跨学科数据表明,患者的整体健康状况比单独的年龄更能评估手术结果是否成功。最近的一篇综述阐述了老年人群对乳房再造手术的耐受性良好,并发症发生率与年轻群体相当,但也有额外的证据表明,年龄大于65岁可能是基于植入物重建术后围术期并发症的独立危险因素[24],而且在使用脱细胞真皮基质进行乳房重建时,年龄不仅是发生感染的重要独立因素,也可能会增加重建失败的概率[23]。因此,年龄应看作是影响患者并发症发生的相关因素,但还需结合患者整体状况进行评估。 吸烟:吸烟可能是引起感染的重要因素,但由于吸烟者人数在病例总人群中所占比例较小,怀疑吸烟所造成的影响可能被低估[23]。 LEYNGOLD等[25]证实伤口裂开和皮瓣坏死没有增加感染概率,即使吸烟确实导致了伤口裂开和皮瓣坏死的发生,但是并非植入物感染的重要危险因素。HUANG等[26]则认为吸烟习惯是发生并发症高风险的有力预测指标,因为尼古丁作为一种血管收缩剂,会减少流向皮肤的血流量[27]。同时有研究者通过逻辑回归分析证实,吸烟者比不吸烟者具有更高平均动脉压水平[28],并且吸烟者比非吸烟者在并发症发生率方面相差近2倍以上[29]。 肥胖:肥胖可能对基于植入物的乳房重建的结果产生不利影响的重要原因, Hanwright等[30]研究发现通过以体质量指数≥30 kg/m2为标准界定肥胖与非肥胖,发现肥胖患者的感染率高于非肥胖者,而且巨乳症常常与肥胖有关,肥胖女性的乳房相对较大,需要更广泛的解剖,导致乳房切除术的皮瓣更大更长。从本质上讲,与较短的皮瓣相比,较长的皮瓣会减少血液供应,这会增加这些患者出现并发症的风险。此外,这些患者术后死腔更多,手术时间更长,所有这些都会增加并发症的可能性。术后血清肿也常见于肥胖症,初次手术后引流管移除后残留的血清肿可能是迟发性感染的诱因。有研究表明,肥胖导致的高体质量指数可能会增加扩张器术后感染的发生概率[25,31],体质量指数每增加一个点,晚期感染的风险就会增加 7%-8%[29,32],但这并不是引起感染的独立因素[33]。值得注意的是,BANUELOS等[34]发现与体质量指数无关的单纯乳房较大不是导致手术部位感染的主要原因,可能体质量指数在一定程度内的单纯乳房体积较大者由于体表面积较大,在不过分冗余的情况下可能有利于减少死腔和血肿堆积从而减少感染发生。 糖尿病:与肥胖相似,已有文献证实了糖尿病与乳房重建术后并发症之间的关联。糖尿病会导致基于植入物的乳房重建的伤口愈合并发症的风险更高[35-36]。运用扩张器在乳腺癌术后进行重建,对于患者而言,面临术后感染的风险也越大。不仅高血糖会导致感染,低血糖由于降低自身免疫和诱发促炎,和高血糖具有同样的风险[37]。 2.2.2 术中因素 淋巴结清扫:在乳腺癌根治术进行重建时,需要进行前哨和腋窝淋巴结清扫,而清扫淋巴结会增加感染的风险以及恶性乳腺疾病复发的可能[38]。淋巴结作为体内可以阻截和清除这些细菌或毒素等异物,阻止病变蔓延和扩散的防御屏障,清扫后可能会影响感染的抵抗作用。清扫腋窝淋巴结所造成的感染风险远大于前哨淋巴结[39-40],腋窝淋巴结清扫术后剩余的乳房软组织和皮肤的淋巴引流减少可能使患者易于伤口愈合不良和发展感染[40],以及去除这些淋巴结后腋窝中浆液增多致使需要引流再度增加感染概率[41]。 扩张器和植入物表面粗糙程度:扩张器和植入物作为异体组织,在植入体内后会激活免疫反应形成胶原纤维包膜,引起包膜挛缩。在20世纪80年代末期出现的纹理表面,旨在促进组织向内生长并限制假体的运动,从而避免错位,并破坏与传统光滑表面扩张器出现的周围包膜挛缩相关的胶原纤维化,但目前关于使用纹理表面的扩张器与植入物减少包膜挛缩发生率的争议仍然存在。 纹理表面与周围软组织的轻松黏附也可能导致周围空间的缩小,有利于限制积液和血清肿的形成,相比之下,光滑扩张器因为没有纹理来固定周围软组织,因此会存在一个更大、更持久的假体周围空间,这会导致可能的引流量增加和血清肿[42],但临床上通常会重点关注血清肿的发生,避免病情进一步发展。就感染方面而言,有证据表明纹理表面的扩张器或植入物感染风险更大,KHAVANI等[43]通过分析1 119例假体乳房再造后,发现粗糙表面的假体可能导致更高的感染发生风险,FAIRCHILD等[44]在进行大量重建手术后,发现表面光滑的扩张器所导致的感染率和外植率较粗糙表面均有明显降低。由于细菌附着生长的能力跟扩张器及植入物的比表面积(面积与体积之比)呈线性相关;同时研究还证实感染导致生物膜的累积与表面积存在相关性[45-46],粗糙表面在结构上的特性决定了其具有更大的比表面积,细菌定植和感染概率均有增加。亲水表面的物质可以减少细菌的黏附,而扩张器或植入物表面高度疏水,随着粗糙程度的增加,表面纹理的润湿性逐渐降低,促进巨噬细胞表达更高水平的促炎因子,加重了炎症反应[47-48],长期存在的炎症还可能会导致乳腺癌的复发[49]。通过对使用不同表面植入物的病例分析中发现,在乳腺癌术后重建患者中,使用纹理植入物的无病生存率显著低于光滑表面组,且与肿瘤分期和雌激素受体的情况无关[50]。 使用脱细胞真皮基质:脱细胞真皮基质的引入彻底改变了基于植入物的重建,它利用部分肌肉覆盖的优势来改善乳房重建并提供下外侧组织支持[51],作为一种将异体或异种真皮通过胰酶消化等方法去除表皮细胞成分后的真皮基质,包含了正常皮肤胶原纤维束和完整基底膜结构,但使用脱细胞真皮基质可能会增加感染的风险,也许与它们是一种非血管化材料有关,并且可能会出现较高的血清肿发生率,影响术区血供,最终可能导致扩张器的丢失[52-53]。KIM等[54]在7年间通过对57个病例进行感染方面的单因素分析,17.5%的患者发生了严重的感染并发症;LUAN等[55]在108例乳房重建术后随访中发现8.3%的病例出现了严重感染。在实际手术操作中,使用脱细胞真皮基质操作不当造成局部褶皱可能是导致细菌定植或感染的重要原因。 对侧预防性乳房切除术(后重建):由于疾病意识的提高、乳腺癌筛查工作、基因检测等原因的影响,预防性乳房切除术的比例逐步上升[56-58],尽管在没有基因突变的情况下对侧乳腺癌的发病概率很低,同时大量数据也表明了对侧预防性乳房切除术并不能提供更多益处[59] ,但从心理上讲,许多患者因为担心患上新的原发性乳腺癌而倾向于接受对侧预防性乳房切除术[60-62]。在对侧预防性乳房切除术中使用软组织扩张器进行重建是目前的主流方式,而双侧乳房切除术后的并发症发生率高于单侧[63-64]。OZTURK等[65]通过分析62例患者的病历资料,在双侧乳房切除术后重建中最常见的并发症是感染,治疗侧的术后感染率约为 12.8%,而预防侧约为 8.3%,NEALON等[66]的研究也证实了这种情况。在使用抗生素治疗后,所有预防侧的感染较治疗侧均能有效治愈。虽然对侧预防性乳房切除术能够从患者本身带来一定益处的同时,也带来了额外的感染风险,并且由于相对较短的随访时间,对随访期外的感染情况评估可能存在不足[65]。因此建议患者在做出对侧预防性乳房切除术的决定时,应跟医生仔细考虑双侧手术的额外风险。目前不同表面的扩张器和植入物均有优缺点[42,46,67-71],见表2。 "

2.2.3 术后因素 恶性乳腺疾病:存在乳腺浸润性癌的患者手术部位术后感染多于良性病变[34],并且绝大部分乳腺癌患者伴有淋巴结转移,需在术中进行淋巴结清扫,这与前面术中因素所描述的淋巴结清扫带来的感染风险增大相吻合,因此乳腺癌患者进行重建后需着重关注假体情况,防止感染的发生。 引流:有研究发现术后引流管的使用与增加感染风险有显著相关性[72],引流时间延长也会导致同样问题[34]。在长时间引流情况下,感染风险与引流方式无关,在乳腺癌淋巴结清扫术后,为防止腋窝积液和浆液增多,需长时间放置引流管,适当延长引流时间有利于清除血肿,降低感染风险,但长时间的引流可能出现细菌定植[73],超过21 d的引流有很大概率发生感染[74-75],严格控制引流时间以及判断拆除引流,对于控制扩张器术后感染有一定的临床意义。OLLECH等[76]通过分析110例患者的174例术后再造引流数据,将其分为单引流和双引流两组,结果证实单引流对于减低扩张器感染存在显著趋势。 放射治疗:乳房切除术后放射治疗现在已作为具有病理危险因素的浸润性乳腺癌女性乳房切除术后的标准治疗,随着乳腺切除术后重建的数量增多,发现放射治疗会使得乳房重建的并发症风险增高[77]。基于扩张器的重建中,放射治疗的介入会导致感染等并发症出现的趋势增加[78]。有研究在分别对不同的患者群体进行比较分析后发现,接受放射治疗是导致晚期感染的重要独立因素之一,相对于未进行放射治疗的患者,感染和移除的比率增加了近5倍,还影响了感染后的修复植入物的可能性[32],并且吸烟和糖尿病被认为是增强辐射影响的危险因素,显示出不同的统计显著性[79]。目前认为放射治疗可能会造成包括微血管损伤,成纤维细胞功能障碍,胶原蛋白沉积减少和紊乱,血管生成减少以及伤口拉伸强度降低,从而增加感染的风险[40]。虽然辐射是导致感染的风险因素,但在出现感染后,放射治疗并不妨碍成功保留植入物。即便接受过放射治疗的患者只要充分了解相关风险,仍然可以基于植入物进行重建[80]。 阀门位置:使用皮肤软组织扩张器进行重建时,需注意阀门放置部位,内置阀门与外置阀门在临床运用各有优缺点[81],在普通扩张中,外置阀门具有操作简单,注水时无疼痛,减轻患者压力等优点[82],更受患者青睐。但与内置阀门相比,外置阀门存在更高感染率[83],而且由于阀门外置,或因某些护理操作不当,使得导管感染的风险增加。 可能的感染原因:在临床上有患者可能由于其他途径出现感染,例如伤口裂开导致的愈合延迟[84]、扩张区皮肤溃烂以及扩张后期局部毛囊炎所导致的邻近部位感染等,并且部分患者由于术后出现血肿或血清肿,压迫周围组织,影响血运循环以及改变局部组织内环境,都会增加感染风险。有文献报道,居住在农村的患者由于当地缺少相应的医疗条件以及自身对卫生保健知识了解不够,加之出院延续护理的发展缓慢,导致未能进行常规消毒从而增加了感染的发生[85]。 乳腺癌术后需要进行重建的患者在选择重建方式时要保持谨慎态度,由于多种风险因素会导致感染的发生,因此评估患者自身情况和治疗方案上需要综合考虑。对于所有患者而言,年龄、吸烟和肥胖不是限制重建的主要原因,而糖尿病的患者也可以在控制血糖水平的前提下择期手术。由于乳腺癌是恶性肿瘤,是否有淋巴结转移是决定后续治疗的关键,未发现淋巴结转移的患者,可以暂缓放射治疗,以避免放射带来的各种并发症。而需要放射治疗的患者而言,优先选择扩张器进行重建可以避免放射或辐射造成的损伤。另外在扩张器和植入物的选择上,对于高感染风险的患者来说,光滑表面较纹理表面的植入物在减少感染方面存在优势。 作者将目前在乳房重建中使用扩张器或植入物并发感染的临床风险因素作一归纳,见表3,图4。 "

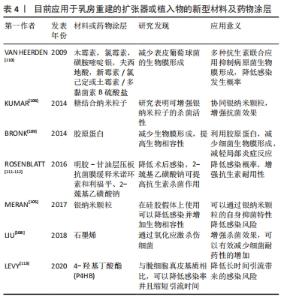
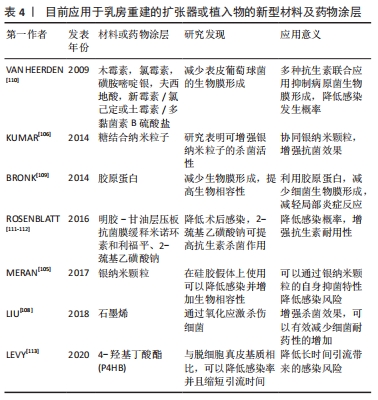
2.3 基于植入物在乳房重建中并发感染的对策 对于组织扩张器感染的定义,目前还未有明确的标准进行区分,虽然疾病预防与控制中心对外科手术部位感染的定义是明确的,但大多数医生并没有遵循它,这可能是因为指南没有准确描述基于植入物的乳房重建解剖结构,并且它们的使用没有发现术后感染的真实发生率[14,16],此外该指南也没有考虑到整形外科领域特有的因素,例如受损组织的更大表面积和软组织中假体的植入[86]。在临床,医生倾向于用临床检查提示需要抗生素进行治疗,或引流物培养呈阳性,又或因疑似感染再次手术进行评判。 2.3.1 感染的治疗方式 引起感染的细菌可能来源于患者自身,也有可能是人为污染造成的[87]。抗生素是对抗细菌感染的首选药物。窄谱抗生素由于抗菌谱窄早已停止使用,目前在临床上使用经验性广谱抗生素进行治疗,使用原则是适当的覆盖多种革兰阴性和革兰阳性(包括MRSA)细菌,尤其是使用脱细胞真皮基质进行重建的患者。此外还需根据当地细菌感染的监测水平选择敏感的抗生素。由于在临床治疗分离的感染菌株中,金黄色葡萄球菌、表皮葡萄球菌和铜绿假单胞菌所占比例最大,针对选择覆盖上述细菌的抗生素意义较大,如果有培养物,可以相应地调整治疗。此外,对于表皮葡萄球菌的感染,早期能否有效治疗至关重要,表皮葡萄球菌是一种毒性特别强的病原体,还会产生可以防止抗生素渗透的生物膜。WEICHMAN等[88]的研究显示表皮葡萄球菌对历史上使用率最高的头孢唑啉有约70% 的耐药性,而左氧氟沙星在治疗表皮葡萄球菌感染方面表现出更高的敏感性。因此对于轻度感染,首先采用口服抗生素治疗,应优先考虑使用氟喹诺酮类药物,包括左氧氟沙星或环丙沙星。如果患者不宜口服治疗,则除了亚胺培南或庆大霉素外,还应使用万古霉素[88],并减少扩张器容积,恢复局部血流供应,促进感染恢复。在48 h内,患者若感染症状没有改善或者加重,出现广泛红肿伴发热及疼痛,或可能存在肿胀,则认为为中度感染,需要对感染部位进行细菌培养及药敏监测,后续针对性选择合适抗生素通过静脉注射进行治疗[89],例如万古霉素或达托霉素与哌拉西林-他唑巴坦或亚胺培南/碳青霉烯类药物的组合[90],必要时可以进行冲洗引流,用抗生素持续进行冲洗,直到症状减退。 尽管有抗生素治疗但仍持续肿胀,出现脓性引流伴或不伴蜂窝织炎、侵袭性或非典型微生物或全身感染的症状,提示患者可能出现重度感染[91],针对此类患者需要及时行清创术,取出扩张器并消毒清理,彻底清除囊腔脓性分泌物及肉芽等。重新植入扩张器,并放置引流管配合滴注甲硝唑引流,静脉滴注敏感抗生素,待扩张皮瓣感染征象消失,引流液变清亮透明后停止滴注,将引流管改为负压吸引,待无引流液后拔出,感染控制后再继续按计划注水[92]。若仍然出现反复感染则停止扩张,取出扩张器,待感染完全被控制后再行扩张术。此外,NOWIKIEWICZ等[93]治疗乳房重建后铜绿假单胞菌的慢性感染中,使用了高压氧结合抗生素,得到了很好的疗效。 2.3.2 感染的预防措施 在临床上,患者围术期常预防性使用抗生素降低感染风险,目前认为在乳房重建中预防性使用抗生素可以降低术后感染的发生率[94]。通常将头孢唑啉、庆大霉素、杆菌肽抗生素溶液用于在手术前清洗乳房植入物,同时可以最大限度地减少包膜挛缩的发生率。术后预防最常见的是头孢氨苄,其次是克林霉素和阿莫西林/舒巴坦[89]。MCCULLOUGH等[95]的分析发现部分地区分离的细菌对第一代头孢菌素的耐药率高达20%-54%。持续使用此类抗生素,会导致耐药性更强的细菌感染,因此这类抗生素也不太适合围手术期使用。WEICHMAN等[88]也发现虽然磺胺甲恶唑相比头孢类抗生素能减少感染,但只建议作为预防药物,而不作为一线治疗药物。目前对于乳房重建术后是否需要延长抗生素的使用时间尚有争议,没有明确证据表明可以降低术后手术部位感染的发生率[96]。DRURY等[97]分析了1 036例患者使用抗生素的情况后发现,术后24 h抗生素治疗的患者与接受抗生素治疗超过 24 h患者的外科手术部位感染发生率差异无显著性意义,同样PHILLIPS等[98]也发现预防性抗生素的使用时间长短与外科手术部位感染发生率无明显关系,仅用24 h抗生素预防相对于长时间使用组在外科手术部位感染上发现时间早且程度较轻。虽然研究表明长时间使用抗生素对于感染的预防没有明显意义,但事实上,大多数接受非自体乳房重建的患者接受抗生素治疗的时间超过 24 h,因为经扩张器或假体的细菌播散可能会导致感染或生物膜的产生,护理成本增加、重建失败、辅助治疗的治疗时间延迟以及患者满意度下降。因此有学者建议将抗生素的使用时间至少延长至48 h,而且鉴于抗生素使用48 h的感染率较低,因此需要更大的队列人群来确定术后48 h后使用抗生素的最佳时间[99-100]。 另一方面,疾病预防与控制中心发布的外科手术部位感染预防指南强调了患者准备、无菌操作和手术过程中对细节关注的重要性,需要医生在实际操作中严格遵守相关规定。有报道称在手术时使用聚维酮碘灌洗手术残腔能有效预防围术期感染,将扩张器类假体用抗生素溶液充分浸泡后也能有效降低假体乳房的感染,同时可减少假体乳房表面生物挛缩膜挛缩的发生[5,101]。 2.4 新型材料及方法在乳房重建中的应用 抗生素能够有效对抗感染,但由于滥用导致细菌耐药不断增加,目前发现一种可以编码新德里金属-β-内酰胺酶1的超级细菌,其对碳青霉烯类抗生素也有耐药性[102],开发新的抗菌治疗对于控制因手术和手术后并发症而引起的医院感染变得至关重要[103],并且由于使用扩张器和植入物本身存在手术和手术后污染的问题。在这种情况下,免疫反应越强,无血管纤维化层越厚,全身抗菌治疗的效果就越低[104]。 纳米粒子是一种粒径在1-100 nm的微小材料,可以抵抗细菌黏附。银纳米颗粒作为公认的抗微生物制剂,有学者在体外证明了其在硅胶假体上与成纤维细胞有良好的生物相容性以及抗真菌特性[105]。目前还研究了与糖蛋白相关的银纳米颗粒[106],糖残基的存在增强了杀生物活性,有助于纳米粒子渗透到细胞膜中,成纤维细胞的增殖也没有受到干扰。石墨烯是研究热门的一种新型材料,具有高比表面积、高导热性和导电性、卓越的催化性能,也存在抗菌特性的潜在特质[107],硅胶上的氧化石墨烯涂层通过氧化应激诱导显示出抗菌活性,对金黄色葡萄球菌有杀伤作用[108]。胶原蛋白作为炎症反应中可以包裹外来物质的物质,有学者提出可以将其用于植入物表面避免生物膜形成和提高生物相容性[109],胶原涂层可促进细胞黏附和增加活力。因此,能够减少污染的植入物新材料有望提高这些重建手术成功率。 在植入物上使用药物进行涂层也是目前研究较多的方向。VAN HEERDEN等[110]已在体外证明,在硅片上用含有木霉素、氯霉素、磺胺嘧啶银、夫西地酸、新霉素/氯己定或土霉素/多黏菌素B硫酸盐的药膏可防止表皮葡萄球菌的生物膜形成。ROSENBLATT等[111-112]开发了一种明胶-甘油层压板抗菌膜,覆盖在组织扩张器上,可以局部释放抗生素米诺环素和利福平,用于降低术后感染的发生,其后续还在该基础上添加2-巯基乙磺酸钠(MeSNA),发现了MeSNA可通过抑制抗菌膜的蛋白水解吸收并协同增强抗生素对常见微生物病原体的效力,增强抗生素的耐用性。另外使用脱细胞真皮基质与感染率的升高以及重建失败有关,但目前仍然较多使用。LEVY等[113]发现聚4-羟基丁酸酯作为一种生物合成网状物,可以编织成可吸收材料用于重建,且相较于脱细胞真皮基质总体感染率更低,引流时间也显著缩短。而另一种材料,钛涂层聚丙烯网在2008年起在欧洲被批准用于乳房手术后,也被证实对比脱细胞真皮基质有着较低感染率等特点,具有广泛应用的临床前景[114-115]。 近年来,在乳房重建中使用自体真皮移植物作为材料应用逐渐广泛。作为脱细胞真皮基质的替代品,自体真皮移植可以从整个身体的许多供体部位获得作为天然自体组织,它们具有更高的生物相容性以及与脱细胞真皮基质相同的美学效果[116-117],更重要的是使用自体真皮移植物可以显著降低并发症的发生率,降低感染的风险[116,118]。而且最近JAGSI等[77]和NELSON等[119]发现在利用自体组织进行的乳房再造在放射治疗后的感染较少见,证实了自体组织的使用可以降低放射治疗后感染的发生率。 目前随着材料科学的进步,选择具有抗菌和防微生物附着特性的医用材料成为治疗细菌感染的重点,见表4。 "
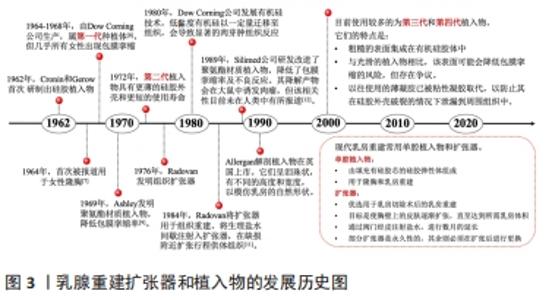
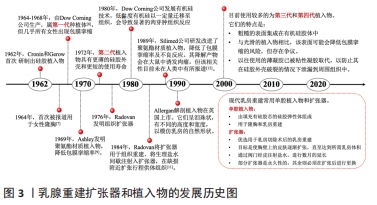
| [1] FAHAD ULLAH M. Breast cancer: current perspectives on the disease status. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1152:51-64. [2] HOMSY A, RÜEGG E, MONTANDON D, et al. Breast reconstruction: a century of controversies and progress. Ann Plast Surg. 2018;80(4):457-463. [3] ILONZO N, TSANG A, TSANTES S, et al. Breast reconstruction after mastectomy: a ten-year analysis of trends and immediate postoperative outcomes. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland). 2017;32:7-12. [4] TER LOUW RP, NAHABEDIAN MY. Prepectoral breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140(5S):51S-59S. [5] DASSOULAS KR, WANG J, THUMAN J, et al. Reducing infection rates in implant-based breast reconstruction: impact of an evidence-based protocol. Ann Plast Surg. 2018;80(5):493-499. [6] MANDERS EK, OAKS TE, AU VK, et al. Soft-tissue expansion in the lower extremities. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1988;81(2):208-219. [7] CRONIN TD. Augmentation mammaplasty: a new” natural feel” prosthesis. Transact, III Internat Congr Plast Surg. 1964. [8] YOUNG VL, WATSON ME. Breast implant research:where we have been, where we are, where we need to go. Clin Plast Surg. 2001;28(3):451-483. [9] ASHLEY FL. A new type of breast prosthesis. Preliminary report. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1970;45(5):421-424. [10] RADOVAN C. Adjacent flap development using expandable silastic implant; proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons, Boston, Mass, F.1976. [11] RADOVAN C. Tissue expansion in soft-tissue reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984;74(4):482-492. [12] HANDEL N, GUTIERREZ J. Long-term safety and efficacy of polyurethane foam-covered breast implants. Aesthet Surg J. 2006;26(3):265-274. [13] OLSEN MA, NICKEL KB, FOX IK. Surveillance and prevention of surgical site infections in breast oncologic surgery with immediate reconstruction. Curr Treat Options Infect Dis. 2017;9(2):155-172. [14] KRAENZLIN FS, SAUNDERS H, ALIU O, et al. Classification of breast tissue expander infections:Back to the basics. J Surg Oncol. 2019;120(2):142-147. [15] KLEIN GM, PHILLIPS BT, DAGUM AB, et al. Infectious Loss of Tissue Expanders in Breast Reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2017;78(2):149-152. [16] AZOUZ V, MIRHAIDARI S, WAGNER DS. Defining infection in breast reconstruction: a literature review. Ann Plast Surg. 2018;80(5):587-591. [17] SZYMANKIEWICZ M, NOWIKIEWICZ T, BIEDKA M. Significance of infections in implant loss after breast reconstruction in the course of breast cancer treatment. Pol J Microbiol. 2019;68(3):343-351. [18] SHARARA SL, SAUNDERS HM, FABRE V, et al. Infection surveillance and prevention strategies to detect and prevent postaccess breast tissue expander infections. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2019;40(11):1275-1277. [19] ADLER N, ELIA J, BILLIG A, et al. Complications of nonbreast tissue expansion: 9 years experience with 44 adult patients and 119 pediatric patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2015;50(9):1513-1516. [20] DONG C, ZHU M, HUANG L, et al. Risk factors for tissue expander infection in scar reconstruction:a retrospective cohort study of 2374 consecutive cases. Burns Trauma. 2020;8:tkaa037. [21] YOON J, CHUNG JH, HWANG NH, et al. Bacterial profile of suction drains and the relationship thereof to surgical-site infections in prosthetic breast reconstruction. Arch Plast Surg. 2018;45(6):542-549. [22] FRANCHELLI S, PESCE M, BALDELLI I, et al. Analysis of clinical management of infected breast implants and of factors associated to successful breast pocket salvage in infections occurring after breast reconstruction. Int J Infect Dis. 2018;71:67-72. [23] ANTONY AK, MCCARTHY CM, CORDEIRO PG, et al. Acellular human dermis implantation in 153 immediate two-stage tissue expander breast reconstructions: determining the incidence and significant predictors of complications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125(6):1606-1614. [24] ROUBAUD MS, CAREY JN, VARTANIAN E, et al. Breast reconstruction in the high-risk population: current review of the literature and practice guidelines. Gland Surg. 2021;10(1):479-486. [25] LEYNGOLD MM, STUTMAN RL, KHIABANI KT, et al. Contributing variables to post mastectomy tissue expander infection. Breast J. 2012;18(4):351-356. [26] HUANG X, QU X, LI Q. Risk factors for complications of tissue expansion: a 20-year systematic review and meta-analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011; 128(3):787-797. [27] BLOK YL, VAN LIEROP E, PLAT VD, et al. Implant loss and associated risk factors following implant-based breast reconstructions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021;9(7):e3708-e3708. [28] SMOLLE C, TUCA A, WURZER P, et al. Complications in tissue expansion: a logistic regression analysis for risk factors. Burns. 2017;43(6):1195-1202. [29] THORARINSSON A, FRÖJD V, KÖLBY L, et al. Patient determinants as independent risk factors for postoperative complications of breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2017;6(4):355-367. [30] HANWRIGHT PJ, DAVILA AA, HIRSCH EM, et al. The differential effect of BMI on prosthetic versus autogenous breast reconstruction: a multivariate analysis of 12,986 patients. The Breast. 2013;22(5):938-945. [31] NGUYEN KT, HANWRIGHT PJ, SMETONA JT, et al. Body mass index as a continuous predictor of outcomes after expander-implant breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2014;73(1):19-24. [32] SINHA I, PUSIC AL, WILKINS EG, et al. Late surgical-site infection in immediate implant-based breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017; 139(1):20-28. [33] GABRIEL A, SIGALOVE S, SIGALOVE NM, et al. Effect of body mass index on outcomes after prepectoral breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(3):550-558. [34] BANUELOS J, SABBAGH MD, ROH SG, et al. Infections following immediate implant-based breast reconstruction: a case-control study over 11 years. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(6):1270-1277. [35] RIFKIN WJ, KANTAR RS, CAMMARATA MJ, et al. Impact of diabetes on 30-day complications in mastectomy and implant-based breast reconstruction. J Surg Res. 2019;235:148-159. [36] HART A, FUNDERBURK CD, CHU CK, et al. The impact of diabetes mellitus on wound healing in breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2017;78(3):260-263. [37] LAW TY, MOELLER E, HUBBARD ZS, et al. Preoperative hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia are related to postoperative infection rates in implant-based breast reconstruction. J Surg Res. 2018;232:437-441. [38] MURTHY BL, THOMSON CS, DODWELL D, et al. Postoperative wound complications and systemic recurrence in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2007; 97(9):1211-1217. [39] ARMSTRONG RW, BERKOWITZ RL, BOLDING F. Infection following breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 1989;23(4):284-288. [40] WANG F, PELED AW, CHIN R, et al. The impact of radiation therapy, lymph node dissection, and hormonal therapy on outcomes of tissue expander-implant exchange in prosthetic breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;137(1):1-9. [41] THOMSON DR, SADIDEEN H, FURNISS D. Wound drainage after axillary dissection for carcinoma of the breast. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013; (10):CD006823. [42] CHIU WK, FRACOL M, FELD LN, et al. Judging an expander by its cover: a propensity-matched analysis of the impact of tissue expander surface texture on first-stage breast reconstruction outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;147(1):1e-6e. [43] KHAVANIN N, CLEMENS MW, PUSIC AL, et al. Shaped versus round implants in breast reconstruction: a multi-institutional comparison of surgical and patient-reported outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(5):1063-1070. [44] FAIRCHILD B, ELLSWORTH W, SELBER JC, et al. Safety and efficacy of smooth surface tissue expander breast reconstruction. Aesthet Surg J. 2020;40(1): 53-62. [45] JONES P, MEMPIN M, HU H, et al. The functional influence of breast implant outer shell morphology on bacterial attachment and growth. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;142(4):837-849. [46] JAMES GA, BOEGLI L, HANCOCK J, et al. Bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation on textured breast implant shell materials. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2019;43(2):490-497. [47] CAPPELLANO G, PLONER C, LOBENWEIN S, et al. Immunophenotypic characterization of human T cells after in vitro exposure to different silicone breast implant surfaces. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0192108. [48] BARR S, HILL E W, BAYAT A. Functional biocompatibility testing of silicone breast implants and a novel classification system based on surface roughness. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;75:75-81. [49] TAKESHITA T, YAN L, ASAOKA M, et al. Late recurrence of breast cancer is associated with pro-cancerous immune microenvironment in the primary tumor. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):16942. [50] LEE KT, KIM S, JEON BJ, et al. Association of the implant surface texture used in reconstruction with breast cancer recurrence. JAMA Surg. 2020; 155(12):1132-1140. [51] SALZBERG CA. Nonexpansive immediate breast reconstruction using human acellular tissue matrix graft (AlloDerm). Ann Plast Surg. 2006;57(1):1-5. [52] HALLBERG H, RAFNSDOTTIR S, SELVAGGI G, et al. Benefits and risks with acellular dermal matrix (ADM) and mesh support in immediate breast reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2018;52(3):130-147. [53] IVEY JS, ABDOLLAHI H, HERRERA FA, et al. Total muscle coverage versus alloderm human dermal matrix for implant-based breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;143(1):1-6. [54] KIM SY, BANG SI. Impact of acellular dermal matrix (ADM) use under mastectomy flap necrosis on perioperative outcomes of prosthetic breast reconstruction. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2017;41(2):275-281. [55] LUAN A, PATEL AA, MARTIN SA, et al. Single-Unit technique for the use of acellular dermal matrix in immediate expander-based breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2021;74(5):981-986. [56] MARMOR RA, DAI W, JIANG X, et al. Increase in contralateral prophylactic mastectomy conversation online unrelated to decision-making. J Surg Res. 2017;218:253-260. [57] VENETIS MK, MACGEORGE EL, BAPTISTE DF, et al. Social network, surgeon, and media influence on the decision to undergo contralateral prophylactic mastectomy. Am J Clin Oncol. 2018;41(6):519-525. [58] MONTICCIOLO DL, NEWELL MS, HENDRICK RE, et al. Breast cancer screening for average-risk women: recommendations from the ACR commission on breast imaging. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017;14(9):1137-1143. [59] ECK DL, PERDIKIS G, RAWAL B, et al. Incremental risk associated with contralateral prophylactic mastectomy and the effect on adjuvant therapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(10):3297-3303. [60] SANDO IC, BILLIG JI, AMBANI SW, et al. An evaluation of the choice for contralateral prophylactic mastectomy and patient concerns about recurrence in a reconstructed cohort. Ann Plast Surg. 2018;80(4):333-338. [61] ABBOTT A, RUETH N, PAPPAS-VARCO S, et al. Perceptions of contralateral breast cancer:an overestimation of risk. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(11):3129. [62] MOMOH AO, COHEN WA, KIDWELL KM, et al. Tradeoffs associated with contralateral prophylactic mastectomy in women choosing breast reconstruction: results of a prospective multicenter cohort. Ann Surg. 2017; 266(1):158-164. [63] KWOK AC, GOODWIN IA, YING J, et al. National trends and complication rates after bilateral mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction from 2005 to 2012. Am J Surg. 2015;210(3):512-516. [64] SILVA AK, LAPIN B, YAO KA, et al. The effect of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy on perioperative complications in women undergoing immediate breast reconstruction: a NSQIP analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015; 22(11):3474-3480. [65] OZTURK CN, OZTURK C, SOUCISE A, et al. Bilateral immediate two-stage breast reconstruction in patients with unilateral breast cancer: outcomes analysis and risk assessment. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2021;74(3): 480-485. [66] NEALON KP, SOBTI N, GADD M, et al. Assessing the additional surgical risk of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy and immediate breast implant reconstruction. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020;179(2):255-265. [67] BUONOMO OC, MORANDO L, MATERAZZO M, et al. Comparison of round smooth and shaped micro-textured implants in terms of quality of life and aesthetic outcomes in women undergoing breast reconstruction: a single-centre prospective study. Updates Surg. 2020;72(2):537-546. [68] NAHABEDIAN MY. Shaped versus round implants for breast reconstruction: indications and outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2014;2(3):e116. [69] O’SHAUGHNESSY K. Evolution and update on current devices for prosthetic breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2015;4(2):97-110. [70] MONTEMURRO P, PAPAS A, HEDÉN P. Is rotation a concern with anatomical breast implants? A statistical analysis of factors predisposing to rotation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(6):1367-1378. [71] ADAMS JR WP, CULBERTSON EJ, DEVA AK, et al. Macrotextured breast implants with defined steps to minimize bacterial contamination around the device:experience in 42,000 implants. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140(3): 427-431. [72] BOUSTANY AN, ELMARAGHI S, AGOCHUKWU N, et al. A breast prosthesis infection update:two-year incidence, risk factors and management at single institution. Indian J Plast Surg. 2018;51(1):7-14. [73] LEE KT, HONG SH, JEON BJ, et al. Predictors for prolonged drainage following tissue expander-based breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(1):9e-17e. [74] CHEN CF, LIN SF, HUNG CF, et al. Risk of infection is associated more with drain duration than daily drainage volume in prosthesis-based breast reconstruction: a cohort study. Medicine. 2016;95(49):e5605. [75] LISA A, BELGIOVINE C, MAIONE L, et al. Study of inflammatory and infection markers in periprosthetic fluid:correlation with blood analysis in retrospective and prospective studies. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6650846. [76] OLLECH CJ, BLOCK LM, AFIFI AM, et al. Effect of drain placement on infection, seroma, and return to operating room in expander-based breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2017;79(6):536-540. [77] JAGSI R, JIANG J, MOMOH AO, et al. Complications after mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction for breast cancer: a claims-based analysis. Ann Surg. 2016;263(2):219-227. [78] LEE KT, MUN GH. Optimal sequencing of postmastectomy radiotherapy and two stages of prosthetic reconstruction: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24(5):1262-1268. [79] CHUBA PJ, STEFANI WA, DUL C, et al. Radiation and depression associated with complications of tissue expander reconstruction. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017;164(3):641-647. [80] OZTURK CN, OZTURK C, SOUCISE A, et al. Expander/implant removal after breast reconstruction: analysis of risk factors and timeline. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2018;42(1):64-72. [81] ABDALI H, HADILOU M. Finding of a clinical trial on symptoms and patients satisfaction under surgery with tissue expander with external port. J Res Med Sci. 2015;20(1):37-39. [82] KESKIN M, KELLY CP, YAVUZER R, et al. External filling ports in tissue expansion: confirming their safety and convenience. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(5):1543-1551. [83] 张旭东,赵启明,夏东胜,等 注射壶内置和外置危险因素的分析[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2009,20(8):478-480. [84] SONG JH, KIM YS, JUNG BK, et al. Salvage of infected breast implants. Arch Plast Surg. 2017;44(6):516-522. [85] 付菊芳,王丹丹,于方方,等.皮肤软组织扩张器置入术感染的病例对照研究[J].中国感染控制杂志,2015,14(5):317-320. [86] PIPER ML, ROUSSEL LO, KOLTZ PF, et al. Characterizing infections in prosthetic breast reconstruction: a validity assessment of national health databases. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2017;70(10):1345-1353. [87] HANNA KR, TILT A, HOLLAND M, et al. Reducing infectious complications in implant based breast reconstruction: impact of early expansion and prolonged drain use. Ann Plast Surg. 2016;76 Suppl 4:S312-5. [88] WEICHMAN KE, LEVINE SM, WILSON SC, et al. Antibiotic selection for the treatment of infectious complications of implant-based breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2013;71(2):140-143. [89] OZTURK C, OZTURK CN, PLATEK M, et al. Management of expander- and implant-associated infections in breast reconstruction. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2020;44(6):2075-2082. [90] VIOLA GM, BAUMANN DP, MOHAN K, et al. Improving antimicrobial regimens for the treatment of breast tissue expander-related infections. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2016;4(5):e704. [91] CHUN JK, SCHULMAN MR. The infected breast prosthesis after mastectomy reconstruction:successful salvage of nine implants in eight consecutive patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120(3):581-589. [92] 常宏,周毕峰,崔鑫,等.整形病区扩张器置入部位感染病原菌分析与感染的临床治疗[J].中华整形外科杂志,2016,32(3):191-195. [93] NOWIKIEWICZ T, SZYMANKIEWICZ M, ZEGARSKA B, et al. Clinical outcomes of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treatment of postoperative chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa wound infection following implant reconstruction of the breast. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2020;37(6):1009-1011. [94] RANGANATHAN K, SEARS ED, ZHONG L, et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis after immediate breast reconstruction: the reality of its efficacy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;141(4):865-877. [95] MCCULLOUGH MC, CHU CK, DUGGAL CS, et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis and resistance in surgical site infection after immediate tissue expander reconstruction of the breast. Ann Plast Surg. 2016;77(5):501-505. [96] WANG F, CHIN R, PIPER M, et al. Do prolonged prophylactic antibiotics reduce the incidence of surgical-site infections in immediate prosthetic breast reconstruction? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138(6):1141-1149. [97] DRURY KE, LANIER ST, KHAVANIN N, et al. Impact of postoperative antibiotic prophylaxis duration on surgical site infections in autologous breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2016;76(2):174-179. [98] PHILLIPS BT, FOURMAN MS, BISHAWI M, et al. Are prophylactic postoperative antibiotics necessary for immediate breast reconstruction? Results of a prospective randomized clinical trial. J Am Coll Surg. 2016; 222(6):1116-1124. [99] 曲亚平,栾杰.假体乳房再造术的感染与抗生素应用策略[J].中华整形外科杂志,2020,36(10):1156-1159. [100] AVASHIA YJ, MOHAN R, BERHANE C, et al. Postoperative antibiotic prophylaxis for implant-based breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131(3):453-461. [101] 陈海军,司丕蕾,贾琳娇,等.乳房重建术后假体乳房感染的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2018,12(10):589-592. [102] VENTOLA CL. The antibiotic resistance crisis: part 1: causes and threats. P&T. 2015;40(4):277-283. [103] STEWART PS, BJARNSHOLT T. Risk factors for chronic biofilm-related infection associated with implanted medical devices. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(8):1034-1038. [104] WITHEREL CE, ABEBAYEHU D, BARKER TH, et al. Macrophage and fibroblast interactions in biomaterial-mediated fibrosis. Adv Health Mater. 2019;8(4): e1801451. [105] MERAN Z, BESINIS A, DE PERALTA T, et al. Antifungal properties and biocompatibility of silver nanoparticle coatings on silicone maxillofacial prostheses in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(3): 1038-1051. [106] KUMAR CG, SUJITHA P. Green synthesis of Kocuran-functionalized silver glyconanoparticles for use as antibiofilm coatings on silicone urethral catheters. Nanotechnology. 2014;25(32):325101. [107] KUMAR P, HUO P, ZHANG R, et al. Antibacterial properties of graphene-based nanomaterials. Nanomaterials. 2019;9(5):737. [108] LIU Y, WEN J, GAO Y, et al. Antibacterial graphene oxide coatings on polymer substrate. Appl Surf Sci. 2018;436:624-630. [109] BRONK JK, RUSSELL BH, RIVERA JJ, et al. A multifunctional streptococcal collagen-mimetic protein coating prevents bacterial adhesion and promotes osteoid formation on titanium. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(7):3354-3362. [110] VAN HEERDEN J, TURNER M, HOFFMANN D, et al. Antimicrobial coating agents: can biofilm formation on a breast implant be prevented? J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009;62(5):610-617. [111] ROSENBLATT J, VIOLA GM, REITZEL RA, et al. Novel in situ liquefying antimicrobial wrap for preventing tissue expander infections following breast reconstructive surgeries. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016; 104(2):369-374. [112] ROSENBLATT J, REITZEL RA, VIOLA GM, et al. Sodium mercaptoethane sulfonate reduces collagenolytic degradation and synergistically enhances antimicrobial durability in an antibiotic-loaded biopolymer film for prevention of surgical-site infections. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:3149536. [113] LEVY AS, BERNSTEIN JL, XIA JJ, et al. Poly-4-hydroxybutyric acid mesh compares favorably with acellular dermal matrix in tissue expander-based breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2020;85(S1 Suppl 1):S2-S7. [114] CASELLA D, BERNINI M, BENCINI L, et al. TiLoop® Bra mesh used for immediate breast reconstruction: comparison of retropectoral and subcutaneous implant placement in a prospective single-institution series. Eur J Plast Surg. 2014;37(11):599-604. [115] GENTILE P, BERNINI M, ORZALESI L, et al. Titanium-coated polypropylene mesh as innovative bioactive material in conservatives mastectomies and pre-pectoral breast reconstruction. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4640-4653. [116] DAVIS C, BOYD C, MATEO DE ACOSTA ANDINO DA, et al. Dermal autografts in breast reconstruction:a review of past and current trends. Ann Plast Surg. 2020;84(5):618-622. [117] LYNCH MP, CHUNG MT, RINKER BD. A comparison of dermal autograft and acellular dermal matrix in tissue expander breast reconstruction: long-term aesthetic outcomes and capsular contracture. Ann Plast Surg. 2015;74:S214-S217. [118] NORTH WD, KUBAJAK CS, MARTIN B, et al. Dermal autograft using donor breast as alternative to acellular dermal matrices in tissue expander breast reconstruction: a comparative review. Ann Plast Surg. 2017;78(6S): S282-S285. [119] NELSON JA, DISA JJ. Breast reconstruction and radiation therapy: an update. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140(5S):60S-68S. |
| [1] | Wu Jing, Yao Yingce, Yang Xiaowei, Xue Boshi, Zhao Jianbin, Yang Chen, Luan Tianfeng, Zhou Zhipeng. Intervention of muscle strength training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lower limb function and biomechanical changes in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [2] | Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin, Wang Yang, Wang Xiaojuan, Lyu Peng, Chen Long, Shi Zhen, Xie Wei, Zhu Yiliang, Li Xugui. Risk factors for cage retropulsion following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1394-1398. |
| [3] | Yang Cekai, Cai Zhuoyan, Chen Ming, Liu Hao, Weng Rui, Cui Jianchao, Zhang Shuncong, Yao Zhensong. Relationship between degeneration of paraspinal muscle and refractures in postmenopausal women treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1414-1419. |
| [4] | Han Bing, Liu Hongbin, Wang Hehong, Zhao Hanqing, Zhao Riguang, Sun Yiyan, Zhang Yu. Correlation between lower limb alignment and risk factors of patellofemoral pain syndrome in young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1211-1216. |
| [5] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [6] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| [7] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [8] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [9] | Li Wenlan, Wang Wenyuan, Ren Wenxiu, Zhang Yupei, Yang Xiaoyan, Wang Zhigang, Xia Jizhu. Preparation of a near-infrared photoresponsive biomimetic nanoprobe and its application in photothermal detection and treatment of breast cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 669-675. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Meng Qingfeng, Chang Zhengqi. Mechanism of negative pressure wound therapy in the auxiliary treatment of bone and soft tissue infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 621-626. |
| [11] | Wang Haotian, Wu Mao, Yang Junfeng, Shao Yang, Li Shaoshuo, Yin Heng, Yu Hao, Wang Guopeng, Tang Zhi, Zhou Chengwei, Wang Jianwei. Postoperative pulmonary infection in elderly patients with hip fracture: construction of a nomogram model for influencing factors and risk prediction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5785-5792. |
| [12] | Pan Shihong, Liu Ruiduan. Mitophagy and intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5872-5876. |
| [13] | Liu Dongyuan, Guan Haishan, Shi Haoran, Liu Xiaoliang, Zhou Haosheng. Risk factors for adjacent vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5884-5891. |
| [14] | Geng Qidi, Jiang Yongdong, Wu Yufeng. Albumin/globulin ratio in diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: a system evaluation and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5892-5898. |
| [15] | Chang Ying, Xia Yuan, Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Xiong Wenjuan, Zhao Xianghu. Effectiveness of different specific exercise therapies in treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5899-5904. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||