Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (36): 5892-5898.doi: 10.12307/2024.673
Previous Articles Next Articles
Albumin/globulin ratio in diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: a system evaluation and meta-analysis
Geng Qidi, Jiang Yongdong, Wu Yufeng
- Zhongshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Zhongshan 524800, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-09-21Accepted:2023-11-06Online:2024-12-28Published:2024-02-28 -
Contact:Wu Yufeng, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Zhongshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Zhongshan 524800, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Geng Qidi, Master candidate, Physician, Zhongshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Zhongshan 524800, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program, No. 2021YFC2401300
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Geng Qidi, Jiang Yongdong, Wu Yufeng. Albumin/globulin ratio in diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: a system evaluation and meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5892-5898.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
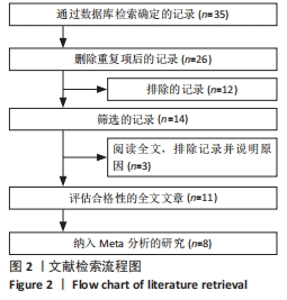
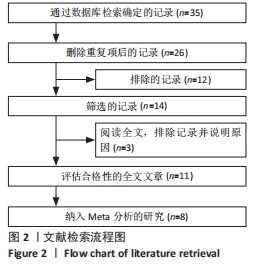
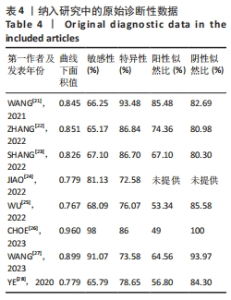
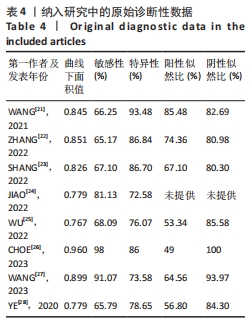
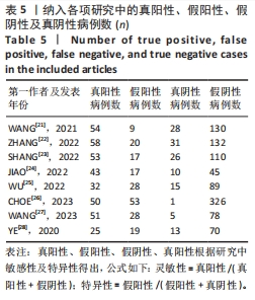
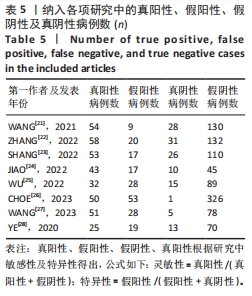
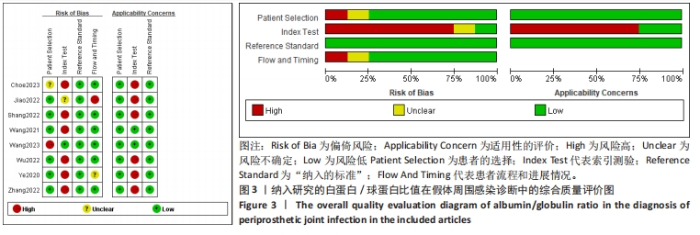
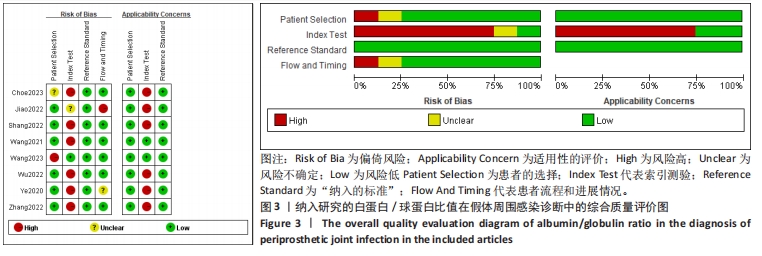
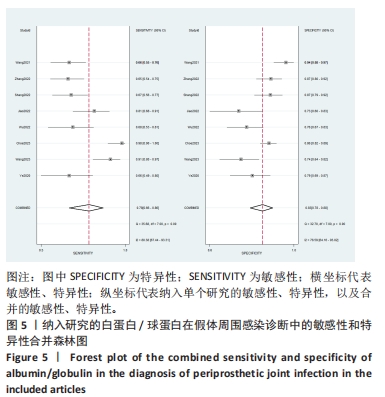
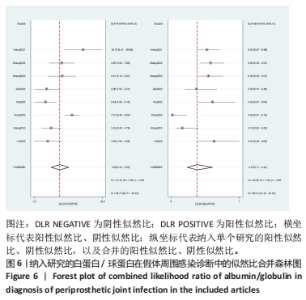
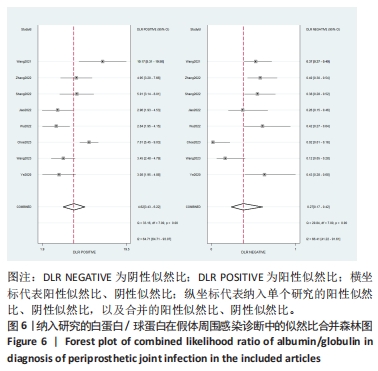
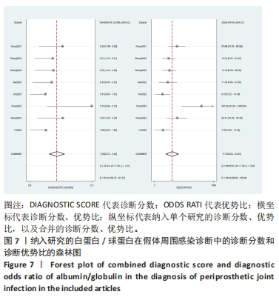
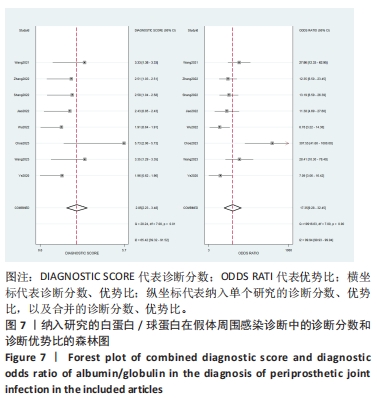
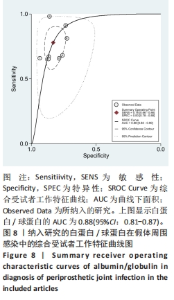
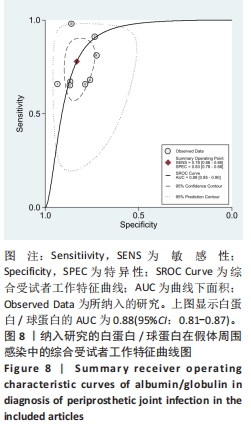
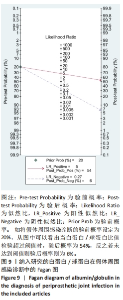
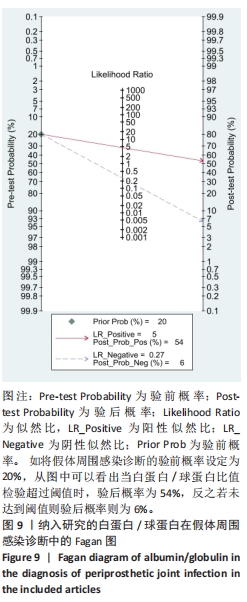
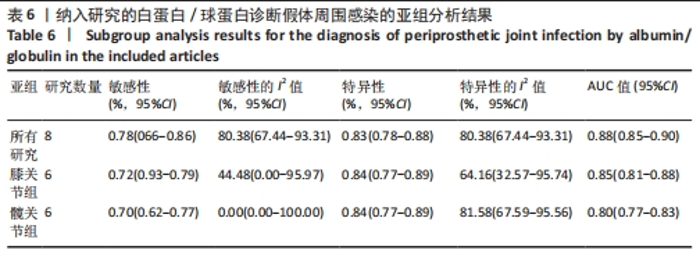
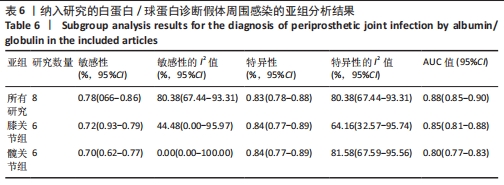
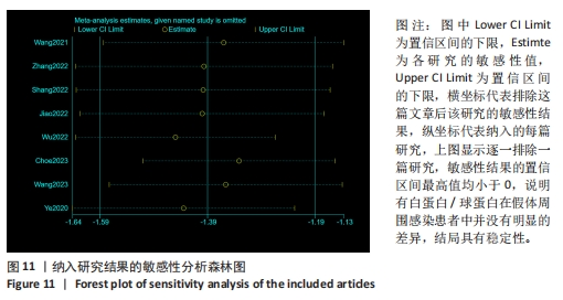
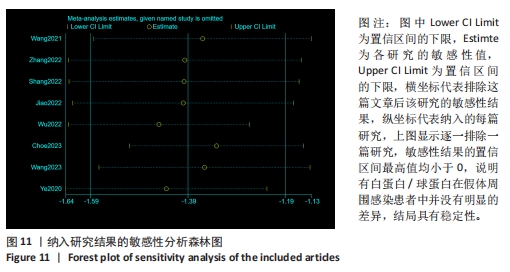
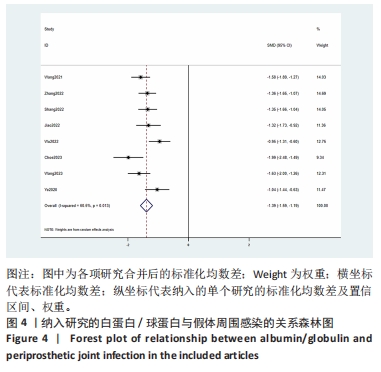
2.3 诊断价值评估结果 总体而言,在8项研究中,对495例假体周围感染患者与786例无菌性松动患者进行对比研究,发现与无菌性松动组相比,假体周围感染患者的白蛋白/球蛋白比值水平有显著降低(SMD=-1.39,95%CI:-1.59至-1.19,P < 0.001),见图4。合并诊断的敏感度和特异度分别为0.78(95%CI:0.66-0.86)和0.83(95%CI:0.78-0.88);但是不同研究间存在明显的异质性,合并敏感性和特异性的I2值分别为80.38%(95%CI:67.44-93.31)和78.59%(95%CI:64.16-93.02),见图5。合并后的阳性似然比、阴性似然比分别为4.63(95%CI:3.43-6.22),0.27(95%CI:0.17-0.42),见图6。合并后的诊断分数和诊断优势比分别为2.85 (95%CI:2.23-3.48)和17.35(95%CI:9.29-32.45),见图7。综合受试者工作特征曲线下面积为0.88(95%CI:0.85-0.90),见图8。有研究报道,假体周围感染在关节置换后翻修的原因中约占据了20%,所以文章可以将假体周围感染诊断的验前概率设置为20%,从而得出Fagan图,见图9,从图中可以看出白蛋白/球蛋白比值检验超过阈值时,验后概率为54%,反之若未达到阈值则验后概率则为6%。"
| [1] SIMON MJK, BEYERSDORFF J, STRAHL A, et al. Diagnostic value of open incisional biopsies in suspected, difficult-to-diagnose periprosthetic hip joint infection prior to revision surgery. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(3): 1663-1670. [2] FESTA E, ASCIONE T, BERNASCONI A, et al. Diagnostic performance of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, monocyte to lymphocyte ratio, platelet to lymphocyte ratio, and platelet to mean platelet volume ratio in periprosthetic hip and knee infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022; 12(9):2033. [3] ALAMANDA VK, SPRINGER BD. Perioperative and modifiable risk factors for periprosthetic joint infections (PJI) and recommended guidelines. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018;11(3):325-331. [4] HOLM CE, SOERENSEN MS, YILMAZ M, et al. Evaluation of tumor-prostheses over time: complications, functional outcome, and comparative statistical analysis after resection and reconstruction in orthopedic oncologic conditions in the lower extremities. SAGE Open Med. 2022;10:20503121221094190. [5] PANNU TS, VILLA JM, ENGH C 3rd, et al. Plasma d-dimer does not anticipate the fate of reimplantation in two-stage exchange arthroplasty for periprosthetic joint infection: a preliminary investigation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021;479(7):1458-1468. [6] JACOB B, MAKAREWICZ O, HARTUNG A, et al. In vitro additive effects of dalbavancin and rifampicin against biofilm of Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):23425. [7] LI C, OJEDA THIES C, XU C, et al. Is combining serum interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein a reliable diagnostic tool in periprosthetic joint infections? J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):450. [8] BULLOCK AF, GREENLEY SL, MCKENZIE GAG, et al. Relationship between markers of malnutrition and clinical outcomes in older adults with cancer: systematic review, narrative synthesis and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020;74(11):1519-1535. [9] CAPKIN S, GULER S, OZMANEVRA R. C-reactive protein to albumin ratio may predict mortality for elderly population who undergo hemiarthroplasty due to hip fracture. J Invest Surg. 2021;34(11):1272-1277. [10] KLIM S M, AMERSTORFER F, GLEHR G, et al. Combined serum biomarker analysis shows no benefit in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. Int Orthop. 2020;44(12):2515-2520. [11] WANG YT, KUO LT, LAI CH, et al. Low pretreatment albumin-to-globulin ratios predict poor survival outcomes in patients with head and neck cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer. 2023; 14(2):281-289. [12] GOODROSE-FLORES C, BONN S, KLASSON C, et al. Appetite in palliative cancer patients and its association with albumin, CRP and quality of life in men and women-cross-sectional data from the palliative D-study. Life (Basel). 2022;12(5):671. [13] LAI KJ, HSIEH YP, CHIU PF, et al. Association of albumin and globulin with mortality risk in incident peritoneal dialysis patients. Nutrients. 2022;14(14):2850. [14] CHEN Z, SONG C, YAO Z, et al. Associations between albumin, globulin, albumin to globulin ratio and muscle mass in adults: results from the national health and nutrition examination survey 2011-2014. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22(1):383. [15] CHO Y, PARK SB, YOON JY, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio can predict overall survival in patients with stage II to III colorectal cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(11): e33279. [16] YANG D, SHEN J, HUANG H, et al. Elevated albumin to globulin ratio on day 7 is associated with improved function outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients with intravenous thrombolysis. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15: 2695-2705. [17] LIBERATI A, ALTMAN DG, TETZLAFF J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700. [18] WHITING PF, RUTJES AW, WESTWOOD ME, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(8):529-536. [19] PARVIZI J, ZMISTOWSKI B, BERBARI EF, et al. New definition for periprosthetic joint infection: from the Workgroup of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(11):2992-2994. [20] PARVIZI J, TAN TL, GOSWAMI K, et al. The 2018 definition of periprosthetic hip and knee infection: an evidence-based and validated criteria. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(5):1309-1314.e2. [21] WANG H, ZHOU H, JIANG R, et al. Globulin, the albumin-to-globulin ratio, and fibrinogen perform well in the diagnosis of Periprosthetic joint infection. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):583. [22] ZHANG H, XIE S, LI Y, et al. The potential performance of serum albumin to globulin ratio, albumin and globulin in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection and prediction of reinfection following reimplantation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):730. [23] SHANG G, FEI Z, XU H, et al. Globulin and albumin to globulin ratio precisely diagnose periprosthetic joint infection and determine the timing of second-stage reimplantation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):12. [24] JIAO JB, HUANG JC, CHEN X, et al. Albumin to globulin ratio, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, and globulin levels do not outperform ESR or CRP when diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):404. [25] WU H, PAN L, MENG Z, et al. C-reactive protein (CRP)/albumin-to-globulin ratio (AGR) is a valuable test for diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection: a single-center retrospective study. J Orthop Traumatol. 2022;23(1):36. [26] CHOE H, KOBAYASHI N, ABE K, et al. Evaluation of serum albumin and globulin in combination with c-reactive protein improves serum diagnostic accuracy for low-grade periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38(3):555-561. [27] WANG R, SHI G, ZHANG H, et al. Globulin and albumin/globulin ratios as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of acute and chronic peri-prosthetic joint infections: a retrospective study. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2023;24(1):58-65. [28] YE Y, CHEN W, GU M, et al. Serum globulin and albumin to globulin ratio as potential diagnostic biomarkers for periprosthetic joint infection: a retrospective review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):459. [29] WANG Y, LI C, WANG W, et al. Serum albumin to globulin ratio is associated with the presence and severity of inflammatory bowel disease. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:1907-1920. [30] 王仁伟.球蛋白、白蛋白/球蛋白比率在诊断急慢性假体周围感染中的临床应用[D].太原:山西医科大学,2022. [31] MIRSAEIDI M, OMAR HR, SWEISS N. Hypoalbuminemia is related to inflammation rather than malnutrition in sarcoidosis. Eur J Intern Med. 2018;53:e14-e16. [32] VINCENT JL, DUBOIS MJ, NAVICKIS RJ, et al. Hypoalbuminemia in acute illness: is there a rationale for intervention? A meta-analysis of cohort studies and controlled trials. Ann Surg. 2003;237(3):319-334. [33] WANG Z, MAO H, XU G. Fibrinogen, albumin-to-globulin ratio, and fibrinogen to albumin-to-globulin ratio may be potential diagnostic biomarkers for infected tibial nonunion. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;121:110542. [34] CHEN Y, CHEN Y, ZHAO L, et al. Albumin/globulin ratio as Yin-Yang in rheumatoid arthritis and its correlation to inflamm-aging cytokines. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:5501-5511. [35] WANG Y, LI S, HU X, et al. The prognostic value of serum albumin-globulin ratio in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:3545-3554. [36] LI K, FU W, BO Y, et al. Effect of albumin-globulin score and albumin to globulin ratio on survival in patients with heart failure: a retrospective cohort study in China. BMJ Open. 2018;8(7):e022960. [37] DENG Y, PANG Q, MIAO RC, et al. Prognostic significance of pretreatment albumin/globulin ratio in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:5317-5328. [38] DENG B, ZHOU B, ZHANG S, et al. Clinical features and factors associated with severity and fatality among patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome Bunyavirus infection in Northeast China. PLoS One. 2013; 8(11):e80802. [39] ZHANG J, WANG T, FANG Y, et al. Clinical significance of serum albumin/globulin ratio in patients with pyogenic liver abscess. Front Surg. 2021;8:677799. [40] CARLI AV, ABDELBARY H, AHMADZAI N, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of serum, synovial, and tissue testing for chronic periprosthetic joint infection after hip and knee replacements: a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(7):635-649. |
| [1] | Guo Sutong, Feng Dehong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Liu Yi, Qian Zhengying, Li Mingyang. Construction and finite element analysis of normal and osteoporotic hip models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [2] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [3] | Li Chaojie, Gulati•Maitirouzi, Aierxiding•Abulaiti, Zheng Hui, Tu Hudi. Finite element analysis of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction at different flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1359-1364. |
| [4] | Wu Jing, Yao Yingce, Yang Xiaowei, Xue Boshi, Zhao Jianbin, Yang Chen, Luan Tianfeng, Zhou Zhipeng. Intervention of muscle strength training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lower limb function and biomechanical changes in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [5] | Min Meipeng, Wu Jin, URBA RAFI, Zhang Wenjie, Gao Jia, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Fan Lei. Role and significance of artificial intelligence preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1372-1377. |
| [6] | Shan Jiaxin, Zhang Yilong, Wu Hongtao, Zhang Jiayuan, Li Anan, Liu Wengang, Xu Xuemeng, Zhao Chuanxi. Changes in muscle strength and pain in patients receiving Jianpi Yiqi Huoxue Formula after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1378-1382. |
| [7] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [8] | Li Xiaoqiang, Chen Wei, Li Mingyue, Shan Tianchi, Shen Wen. Value of preoperative quantitative ultrasound analysis of quadriceps femoris in predicting chronic post-surgical pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1388-1393. |
| [9] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [10] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [11] | Zhong Jun, Wang Wen. Network meta-analysis of different anatomical repair strategies to improve chronic lateral ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1470-1476. |
| [12] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [13] | Han Bing, Liu Hongbin, Wang Hehong, Zhao Hanqing, Zhao Riguang, Sun Yiyan, Zhang Yu. Correlation between lower limb alignment and risk factors of patellofemoral pain syndrome in young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1211-1216. |
| [14] | Zuo Xinwei, Liu Gang, Bai Huizhong, Xu Lin, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Mu Xiaohong. Relationship between lumbar spine development and hip development in children with spastic cerebral palsy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1247-1252. |
| [15] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||