Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (36): 5872-5876.doi: 10.12307/2024.672
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mitophagy and intervertebral disc degeneration
Pan Shihong1, Liu Ruiduan2
- 1Department of Spinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical College, Guilin 541001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Spinal Surgery, Seventh Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Foshan 528244, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-08-29Accepted:2023-11-10Online:2024-12-28Published:2024-02-28 -
Contact:Liu Ruiduan, MD, Chief physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, Seventh Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Foshan 528244, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Pan Shihong, Master candidate, Department of Spinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical College, Guilin 541001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82260442 (to LRD); Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2022JJA140036 (to LRD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pan Shihong, Liu Ruiduan. Mitophagy and intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5872-5876.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
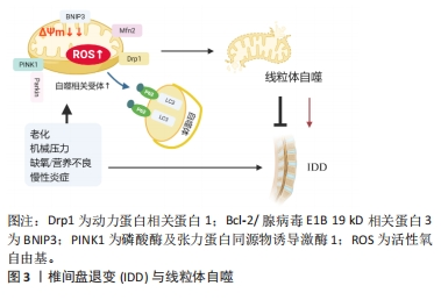
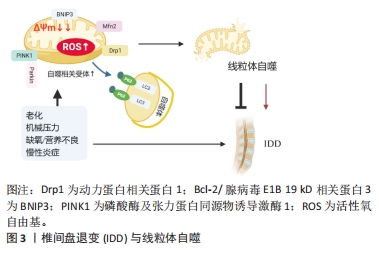
2.1 线粒体结构和功能 线粒体是细胞内的一种重要细胞器,有2层膜结构,外膜将线粒体和细胞质分开,内膜包裹着被称为基质的部分。线粒体是细胞能量的主要来源,线粒体功能主要有助于调节细胞钙水平、增殖、凋亡、生物合成途径,以及最重要的细胞质量控制。因此维持一个健康和功能正常的线粒体池是至关重要的。线粒体功能障碍是细胞代谢异常的重要原因,参与多种骨病的发生和发展,包括但不限于骨关节病、骨肉瘤、骨质疏松和椎间盘退变[5]。线粒体自噬作为线粒体受损或功能失调的选择性自噬,与线粒体质量控制和稳态密切相关[5],这表明调节线粒体自噬水平可能是治疗椎间盘退变的一种新策略。 2.2 线粒体自噬 线粒体自噬(Mitophagy)是自噬机制对线粒体的选择性识别和降解,被证明是线粒体质量控制的主要机制之一[6]。线粒体自噬是对功能障碍线粒体的选择性自噬清除,在细胞对各种应激源的反应中发挥着至关重要的作用,如生物能量应激、氧化应激和蛋白毒性应激[6],有助于维持细胞内稳态并抑制内在凋亡途径的启动[7]。线粒体自噬流量的受损会导致功能失调的线粒体和与各种疾病相关的活性氧自由基积累。线粒体自噬与椎间盘退变性疾病的发生发展也有密切关联,并且其在椎间盘退变性疾病的进程中发挥双重作用:一方面,线粒体自噬的适当激活有助于维持椎间盘细胞的稳态,在功能上保护髓核细胞免受线粒体途径诱导的凋亡[8],同时也可以通过去除功能失调的线粒体来抑制软骨细胞凋亡并减少活性氧自由基的产生[9-10];另一方面,异常的线粒体自噬会导致线粒体功能障碍和细胞死亡,最终促进椎间盘退变的进展[11]。 2.3 椎间盘退变与线粒体自噬 椎间盘退变是导致残疾的重大原因,极大地增加了社会负担。目前对于椎间盘退变的发病机制尚不完全明了,但有相关证据表明炎症浸润、细胞外基质的降解、髓核细胞的过度衰老以及异常凋亡在椎间盘退变的进展中有重要作用。线粒体自噬的启动通常是由线粒体膜电位的异常、缺氧环境以及过量产生的活性氧自由基引起的,过度或不适当的机械负荷、老化、慢性炎症等被认为是椎间盘退变发展的重要因素,同时这些因素参与线粒体自噬的激活[12-13]。现有证据表明持续存在的机械负荷可能直接影响椎间盘细胞中细胞外基质成分的合成,并由此直接导致髓核细胞的衰老以及凋亡[14]。有研究构建了过度压缩诱导细胞衰老的大鼠髓核细胞模型,结果表明过度机械压缩通过磷酸酶及张力蛋白同源物诱导激酶1(PTEN Induced putative kinase 1,PINK1)/Parkin通路激活线粒体自噬,促进髓核细胞的衰老[15]。压缩破坏了线粒体分裂/融合稳态,导致髓核细胞中线粒体分裂增加,同时线粒体-溶酶体融合和溶酶体降解能力受损导致线粒体自噬流阻断,而核因子红细胞 2 相关因子 2(nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2,Nrf2)抗氧化途径未被充分激活,从而造成受损线粒体的累积以及持续氧化损伤,促进椎间盘退变进展[16]。高强度的机械压缩通过氧化应激和活性氧自由基途径加速髓核细胞的早衰[17]。而氧化应激可诱导线粒体自噬,并通过氧化应激线粒体损伤释放活性氧自由基的恶性循环加剧细胞衰老,导致线粒体进一步损伤。 慢性炎症可能导致线粒体损伤,从而导致细胞内活性氧自由基急剧升高[18]。肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白3(A20)通过激活线粒体自噬抑制NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(nod-like receptor,pyrin domain containing 3,NLRP3)炎症小体激活,从而抑制髓核细胞的凋亡[19]。髓核细胞的炎症应激在椎间盘退变的发病机制中起着重要作用。有研究表明白细胞介素1β可以诱导焦亡和NLRP3炎症激活,同时导致髓核细胞线粒体氧化应激损伤和功能障碍[20]。此时上调沉默信息调节因子1 (silent information regulator 1,SIRT1)通过激活髓核细胞线粒体自噬缓解白细胞介素1β诱导的NLRP3炎性小体激活以及炎症因子长期刺激导致活性氧的产生,以保持线粒体的质量和清除受损的线粒体维持椎间盘髓核细胞的稳定[20],提示可能将相关炎症因子及其靶向蛋白作为治疗研究的潜在前景。 健康的椎间盘组织是哺乳动物中最大的无血管组织,缺氧以及营养缺乏是其主要特征。髓核细胞高表达缺氧诱导因子1α(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1α)主转录因子,通过上调糖酵解使细胞适应缺氧。缺氧会导致线粒体的改变,包括氧化磷酸化以及细胞色素C氧化酶活性的减少、增加活性氧自由基的产生,由于上述损伤,无疑会诱导增加线粒体自噬的产生[21]。缺氧通过增加线粒体断裂、升高动力蛋白相关蛋白 1和Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B 19 kD相关蛋白3(BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kD interacting protein 3,BNIP3)水平以及BNIP3线粒体易位,诱导髓核细胞的线粒体自噬[22]。同时在营养缺乏的条件下,抑制转录因子FOXO3的表达,可以抑制髓核的线粒体自噬,从而维持髓核细胞中的细胞外基质组成[23]。 综上,强机械压力、老化、缺氧、慢性炎症等在诱发椎间盘退变的过程中,线粒体自噬是线粒体质量控制的关键过程,发挥重要的调节作用。基础水平的线粒体自噬通过选择性消除过量的或受损的异常线粒体来保护细胞免受各种刺激。然而,过度的应激可能导致线粒体过度去除,从而加剧氧化应激诱导的损伤,加剧椎间盘退变进展(图3)。进一步了解椎间盘退变中线粒体自噬发生相关的机制,有助于了解线粒体自噬在椎间盘退变过程中复杂的生物学功能,并为椎间盘退变的治疗策略提供新思路。"
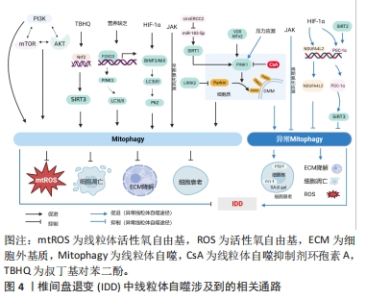
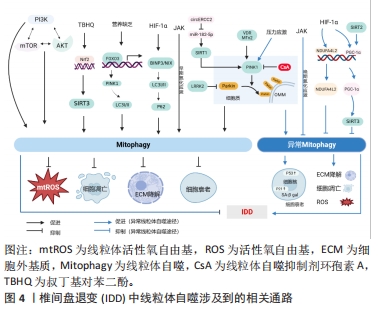
2.4 椎间盘退变中线粒体自噬相关通路 2.4.1 经典PINK1/Parkin通路诱导线粒体自噬 PINK1介导的线粒体自噬是一种被广泛研究的、经典的线粒体自噬途径。PINK1是一种蛋白激酶,在线粒体外膜中高表达。在该途径中,PINK1将Parkin从细胞质募集到线粒体外膜上,在PINK1磷酸化以及Parkin泛素化后,激活线粒体自噬受体如P62,P62与自噬蛋白LC3相互作用后形成线粒体自噬体(Mitophagosome),其与溶酶体融合后导致线粒体被降解[24-25]。LAN等[26]报道,Parkin激活后通过促进线粒体自噬进一步抑制氧化应激诱导的大鼠髓核细胞凋亡以及线粒体功能障碍。PINK1/Parkin靶向去极化的线粒体会降解功能失调的线粒体,并阻止它们向外周移动[21]。这表明PINK1/Parkin途径可能是椎间盘退变潜在治疗靶点。 SIRT1是依赖于烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸的组蛋白脱乙酰酶家族成员之一,参与如组蛋白脱乙酰化、蛋白质酰化和脱乙酰化等各种细胞生理过程,以及各种抗氧化和氧化应激的过程,如DNA损伤修复、代谢、线粒体功能等[27-28]。有研究证明SIRT1在神经退行性疾病中是PINK1/Parkin依赖的线粒体自噬的上游调控分子[29]。在椎间盘退变中,SIRT1通过调节线粒体自噬标记蛋白如PINK1、Parkin、LC3Ⅰ/Ⅱ以及P62的表达促进线粒体自噬,改善白细胞介素1β诱导的线粒体功能障碍和减少线粒体活性氧积累,进而抑制髓核细胞中的NLRP3炎性小体激活,发挥保护作用[20]。同期XIE等[30]研究发现,环状RNA ERCC2(circERCC2)直接通过靶向调控miR-182-5p/SIRT1信号轴,激活线粒体自噬,从而抑制叔丁基氢过氧化物诱导的髓核细胞凋亡、细胞外基质降解,从而抑制椎间盘退变进展。线粒体中SIRT1高表达时,全长PINK1(66 kD)被修饰为裂解产物(55 kD),裂解后的PINK1与募集的Parkin蛋白与LC3Ⅱ结合,然后启动线粒体自噬过程以清除靶向线粒体[31]。研究者进一步发现,敲低富含亮氨酸的重复激酶2可以促进Parkin募集,同时激活Parkin介导的线粒体自噬通路,抑制氧化应激诱导的髓核细胞的线粒体依赖性凋亡,抑制椎间盘退变的发展[32]。大多数研究支持Parkin介导的线粒体自噬对椎间盘退变缓解的积极作用,而少数研究显示Parkin介导的细胞自噬对椎间盘退变缓解有消极作用,这表明精确调节线粒体自噬的程度可能对椎间盘退变的治疗至关重要。 PINK1协同磷酸化Parkin,将其转化为活性磷酸泛素依赖性E3连接酶,以消除基质金属蛋白酶引起的受损线粒体的损失[33],其机制是Parkin易位到有缺陷的线粒体,募集p62/SQSTM1,随后自噬体吞噬受损的线粒体以及发生溶酶体降解[34]。Parkin信号传导在线粒体自噬激活中发挥关键作用,调节相关线粒体外膜蛋白的泛素化并促进功能失调的线粒体降解[26],这表明Parkin是椎间盘退变治疗的一个有前途的靶点。Parkin介导的线粒体自噬联合Nrf2介导的抗氧化系统阻止了氧化应激诱导的椎间终板软骨细胞凋亡,并有利于终板软骨细胞的存活[35]。 2.4.2 非依赖PINK1/Parkin途径诱导线粒体自噬 线粒体自噬除依赖PINK1/Parkin途径激活外,也可以通过其他各种途径发生,包括HIF-1α、BNIP3/NIX、JAK/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(Akt)/mTOR通路激活。非依赖PINK1/Parrkint通路的线粒体自噬主要依赖于包含LIR(LC3相互作用区)基序的受体蛋白,这些受体蛋白通过其LIR基序直接作用于LC3,不经历泛素化过程,从而实现线粒体自噬[36]。BNIP3/NIX、含 FUN14域蛋白 1(FUN14domain containing 1,FUNDC1) 是常见的包含LIR基序的受体蛋白[37-38],主要在缺氧条件下调节线粒体自噬。 HIF-1α是在髓核中稳定表达的主转录因子,通过糖酵解的上调帮助髓核细胞适应缺氧环境,对维持髓核细胞在缺氧条件下的稳态以及生存至关重要[39]。MADHU等[22]研究表明缺氧环境通过HIF-1α上调BNIP3/NIX的表达,并通过控制BNIP3向线粒体的易位触发线粒体自噬维持髓核细胞的稳态。同时,BNIP3/NIX可以与生精相关蛋白(SPATA18)相互作用去除氧化物[40],并与钙黏蛋白6相互作用,调节DNM1L(Dynamin 1 like)/动力蛋白相关蛋白 1介导的分裂从而维持线粒体稳态[41]。缺氧情况下,另一线粒体受体蛋白FUNDC1与DNM1L和OPA1相互作用,FUNDC1的去磷酸化刺激FUNDC1-OPA1复合物的分离,从而增加FUNDC1与DNM1L的关联,促进线粒体分裂和促进线粒体自噬[42]。XU等[43]的研究结果表明,氧化应激诱导的线粒体自噬激活以及髓核细胞凋亡受HIF-1α/ NDUFA4L2信号调节,后续的实验证明,NDUFA4L2的上调通过抑制过度的线粒体自噬来改善髓核细胞的凋亡,最终缓解椎间盘退变。上述研究表明,HIF-1α介导的线粒体自噬在椎间盘退变中可能是有益的,也可能是有害的。需要进一步的研究来揭示HIF-1α介导的线粒体自噬在椎间盘退变中的调节作用,从而合理调节HIF-1α的表达,使其在椎间盘退变发育的不同阶段发挥更有益的作用。受体蛋白在介导线粒体直接自噬中发挥主要作用,但除上述的受体外,近期研究表明某些脂质也参与LC3的直接作用中,比如心磷脂和神经酰胺。心磷脂是一种通常位于线粒体内膜的磷脂,能够外化外膜并作为线粒体自噬受体,有助于清除神经元细胞中受损的线粒体[44]。神经酰胺也已被发现是一种可能的受体,用于将LC3B-II自溶体锚定在线粒体膜上,从而诱导致命的线粒体自噬[45]。 炎症信号或氧化应激可以激活JNK/MAPK通路[46],WANG等[47]报道了骨髓间充质干细胞中的非经典JNK依赖性线粒体自噬激活,研究发现,有限时间(< 1 h)内的氧化应激诱导主要以JNK依赖的方式激活线粒体自噬,应用线粒体自噬抑制剂(环孢素A)和JNK抑制剂(SP600125)在抑制线粒体自噬的同时,都增加了细胞凋亡和分解代谢活性。SIRT家族中SIRT2、SIRT3在髓核细胞的线粒体抗氧化应激的生理过程中发挥重要作用[48]。现有的研究表明SIRT2通过作用于过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α来抑制线粒体自噬,以抑制氧化应激诱导的纤维环细胞凋亡[49]。同时,也有部分研究报道了SIRT4和SIRT5参与线粒体相关活动的调节[48],由此可以推测SIRTs家族中可能有多种介质参与线粒体自噬的调节,期待将来有更进一步的研究(图4)。"
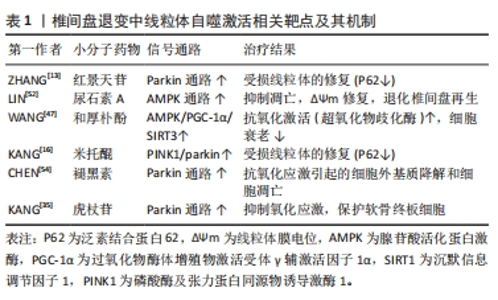
2.5 线粒体自噬相关的靶向治疗策略 线粒体自噬通过各种途径参与了椎间盘退变的发生发展过程,靶向线粒体自噬相关的通路可能是治疗椎间盘退变的有效方法。从中药红景天中提取的红景天苷通过激活PINK1介导的线粒体自噬改善髓核细胞的线粒体功能障碍以及抑制细胞凋亡[50]。 同时有研究表明透明质酸治疗可以通过增强补体1q结合蛋白来诱导线粒体自噬,补体1q结合蛋白可以对抗氧化应激引起的活性氧自由基过度产生、线粒体损伤、细胞凋亡、衰老和细胞外基质降解;透明质酸可以通过线粒体自噬激活来改善机械应激引起的细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解[51]。除此之外,也有研究发现尿石素A可以通过腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶通路激活促进线粒体自噬来抑制叔丁基氢过氧化物诱导的髓核细胞凋亡,口服尿石素A改善了大鼠模型中穿刺诱导的椎间盘退变进展[52],这些结果突出了尿石素A在预防和治疗椎间盘退变方面的潜力。线粒体未折叠蛋白反应和线粒体自噬调节机制的紊乱可能是椎间盘退变的一个危险因素,线粒体未折叠蛋白反应主要通过Sestrin 2信号通路诱导线粒体自噬,减少髓核细胞细胞的凋亡,改善髓核细胞细胞的代谢,从而缓解椎间盘退变;线粒体未折叠蛋白反应激动剂烟酰胺核糖有可能成为治疗椎间盘退变的药物[53]。线粒体醌是线粒体靶向抗氧化剂,其通过促进PINK1/Parkin介导的线粒体自噬以及恢复线粒体自噬流量,从而改善线粒体功能障碍和氧化还原异常,达到预防和治疗椎间盘退变的目的[16]。褪黑素治疗椎间盘退变的机制在于其诱导Parkin介导的髓核细胞线粒体自噬,以清除受损的线粒体并减少活性氧自由基和凋亡因子的释放,从而抑制氧化应激诱导的髓核细胞凋亡和细胞外基质变性[54]。同时有研究发现和厚朴酚(Honokiol)上调Drp-1和线粒体融合蛋白2,并以SIRT3依赖的方式,通过上调BNIP3和LC3-Ⅱ与LC3-Ⅰ的比例增加线粒体自噬,改善椎间盘退变的进展[48]。抗霉素A也可以通过激活线粒体自噬抑制骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡[47]。虎杖苷可以上调Parkin和Nrf2从而减少线粒体活性氧自由基的产生,改善线粒体功能障碍从而保护软骨终板细胞,同时动物实验也证明虎杖苷抑制椎间盘退变的进展[35]。 红景天苷、透明质酸、尿石素A、线粒体醌、褪黑素、和厚朴酚以及虎杖苷这些药物通过调控线粒体自噬延缓椎间盘退变的进展,在动物实验以及细胞层面取得了积极的研究结果(表1)。因此,这些药物后续的临床转化也非常值得关注。经过对临床试验注册的网站(https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/;https://www.chictr.org.cn/index.html )进行查询发现,除和厚朴酚尚未进入临床转化,其他小分子药物均进入临床试验中,但是目前更多的是这些药物在其他病种中的研究,尚没有与椎间盘退变应用相关的研究。其中褪黑素涉及到与骨相关疾病的研究,如褪黑素预防(NCT01152580)和治疗骨质疏松症(NCT01690000、NCT01870115),以及近期发布的研究探索褪黑素治疗膝骨关节炎(NCT06012175),褪黑素联合腰内侧支阻滞手术治疗下背痛患者(NCT02415309)。尽管这些小分子药物应用于椎间盘退变中还停留于临床前阶段,但是它们具有巨大的临床转化的前景,尤其是褪黑素,期待后续更多临床研究探索它们对椎间盘退变的治疗效果。"
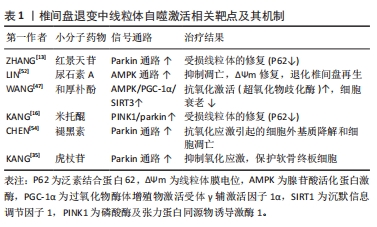
| [1] GRUNHAGEN T, WILDE G, SOUKANE DM, et al. Nutrient supply and intervertebral disc metabolism. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:30-35. [2] MCELROY GS, CHANDEL NS. Mitochondria control acute and chronic responses to hypoxia. Exp Cell Res. 2017;356(2):217-222. [3] GÖRLACH A, BERTRAM K, HUDECOVA S, et al. Calcium and ROS: A mutual interplay. Redox Biol. 2015;6:260-271. [4] YANG S, ZHANG F, MA J, et al. Intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: The antiapoptotic effect of oestrogen. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100978. [5] ZENG Z, ZHOU X, WANG Y, et al. Mitophagy-A New Target of Bone Disease. Biomolecules. 2022;12(10):1420. [6] WU H, WEI H, SEHGAL SA, et al. Mitophagy receptors sense stress signals and couple mitochondrial dynamic machinery for mitochondrial quality control. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;100:199-209. [7] ASHRAFI G, SCHWARZ TL. The pathways of mitophagy for quality control and clearance of mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20(1):31-42. [8] HIROTA Y, AOKI Y, KANKI T. [Mitophagy: selective degradation of mitochondria by autophagy]. Seikagaku. 2011;83(2):126-130. [9] ANSARI MY, KHAN NM, AHMAD I, et al. Parkin clearance of dysfunctional mitochondria regulates ROS levels and increases survival of human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(8):1087-1097. [10] TANG Q, ZHENG G, FENG Z, et al. Trehalose ameliorates oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress via selective autophagy stimulation and autophagic flux restoration in osteoarthritis development. Cell Death Dis. 2017; 8(10):e3081. [11] NASTO LA, ROBINSON AR, NGO K, et al. Mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a causal role in aging-related intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(7):1150-1157. [12] GULLBRAND SE, PETERSON J, AHLBORN J, et al. ISSLS Prize Winner: Dynamic Loading-Induced Convective Transport Enhances Intervertebral Disc Nutrition. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(15):1158-1164. [13] ZHANG Z, XU T, CHEN J, et al. Parkin-mediated mitophagy as a potential therapeutic target for intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9(10):980. [14] LE MAITRE CL, FREEMONT AJ, HOYLAND JA. Expression of cartilage-derived morphogenetic protein in human intervertebral discs and its effect on matrix synthesis in degenerate human nucleus pulposus cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11(5):R137. [15] HUANG D, PENG Y, LI Z, et al. Compression-induced senescence of nucleus pulposus cells by promoting mitophagy activation via the PINK1/PARKIN pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(10):5850-5864. [16] KANG L, LIU S, LI J, et al. The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant MitoQ protects against intervertebral disc degeneration by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and redox imbalance. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(3):e12779. [17] LI P, HOU G, ZHANG R, et al. High-magnitude compression accelerates the premature senescence of nucleus pulposus cells via the p38 MAPK-ROS pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):209. [18] YOO SM, JUNG YK. A Molecular Approach to Mitophagy and Mitochondrial Dynamics. Mol Cells. 2018;41(1):18-26. [19] ZHOU R, YAZDI AS, MENU P, et al. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature. 2011;469(7329):221-225. [20] MA Z, TANG P, DONG W, et al. SIRT1 alleviates IL-1β induced nucleus pulposus cells pyroptosis via mitophagy in intervertebral disc degeneration. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;107:108671. [21] WU H, CHEN Q. Hypoxia activation of mitophagy and its role in disease pathogenesis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015;22(12):1032-1046. [22] MADHU V, BONESKI PK, SILAGI E, et al. Hypoxic Regulation of Mitochondrial Metabolism and Mitophagy in Nucleus Pulposus Cells Is Dependent on HIF-1α-BNIP3 Axis. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(8):1504-1524. [23] WANG Y, YANG Y, ZUO R, et al. FOXO3 protects nucleus pulposus cells against apoptosis under nutrient deficiency via autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;524(3):756-763. [24] HEO JW, NO MH, PARK DH, et al. Effects of exercise on obesity-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017; 21(6):567-577. [25] SABERI M, ZHANG X, MOBASHERI A. Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction with small molecules in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Geroscience. 2021;43(2):517-537. [26] LAN T, ZHENG YC, LI ND, et al. CRISPR/dCas9-Mediated Parkin Inhibition Impairs Mitophagy and Aggravates Apoptosis of Rat Nucleus Pulposus Cells Under Oxidative Stress. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:674632. [27] HU X, ZHENG W. Chemical Probes in Sirtuin Research. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018;154:1-24. [28] JĘŚKO H, WENCEL P, STROSZNAJDER RP, et al. Sirtuins and Their Roles in Brain Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(3):876-890. [29] ZHAO N, XIA J, XU B. Physical exercise may exert its therapeutic influence on Alzheimer’s disease through the reversal of mitochondrial dysfunction via SIRT1-FOXO1/3-PINK1-Parkin-mediated mitophagy. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;10(1):1-3. [30] XIE L, HUANG W, FANG Z, et al. CircERCC2 ameliorated intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating mitophagy and apoptosis through miR-182-5p/SIRT1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(10):751. [31] EIYAMA A, OKAMOTO K. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in mammalian cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015;33:95-101. [32] LIN J, ZHENG X, ZHANG Z, et al. Inhibition of LRRK2 restores parkin-mediated mitophagy and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(4): 579-591. [33] MAO X, FU P, WANG L, et al. Mitochondria: Potential Targets for Osteoarthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:581402. [34] NGUYEN TN, PADMAN BS, LAZAROU M. Deciphering the Molecular Signals of PINK1/Parkin Mitophagy. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26(10):733-744. [35] KANG L, LIU S, LI J, et al. Parkin and Nrf2 prevent oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in intervertebral endplate chondrocytes via inducing mitophagy and anti-oxidant defenses. Life Sci. 2020;243:117244. [36] LAMARK T, SVENNING S, JOHANSEN T. Regulation of selective autophagy: the p62/SQSTM1 paradigm. Essays Biochem. 2017;61(6):609-624. [37] BUNKER EN, LE GUERROUÉ F, WANG C, et al. Nix interacts with WIPI2 to induce mitophagy. Embo J. 2023:e113491. [38] KUANG Y, MA K, ZHOU C, et al. Structural basis for the phosphorylation of FUNDC1 LIR as a molecular switch of mitophagy. Autophagy. 2016;12(12):2363-2373. [39] NOGUéS X, MARTINEZ-LAGUNA D. Update on osteoporosis treatment. Med Clin (Barc). 2018;150(12):479-486. [40] NAKAMURA Y, KITAMURA N, SHINOGI D, et al. BNIP3 and NIX mediate Mieap-induced accumulation of lysosomal proteins within mitochondria. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30767. [41] GUGNONI M, SANCISI V, GANDOLFI G, et al. Cadherin-6 promotes EMT and cancer metastasis by restraining autophagy. Oncogene. 2017;36(5):667-677. [42] CHEN M, CHEN Z, WANG Y, et al. Mitophagy receptor FUNDC1 regulates mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy. Autophagy. 2016;12(4):689-702. [43] XU WN, ZHENG HL, YANG RZ, et al. Mitochondrial NDUFA4L2 attenuates the apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells induced by oxidative stress via the inhibition of mitophagy. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(11):1-16. [44] CHU CT, JI J, DAGDA RK, et al. Cardiolipin externalization to the outer mitochondrial membrane acts as an elimination signal for mitophagy in neuronal cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(10):1197-1205. [45] SENTELLE RD, SENKAL CE, JIANG W, et al. Ceramide targets autophagosomes to mitochondria and induces lethal mitophagy. Nat Chem Biol. 2012;8(10):831-838. [46] LI Z, WANG J, DENG X, et al. Compression stress induces nucleus pulposus cell autophagy by inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and activation of the JNK pathway. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(3):337-349. [47] WANG J, NISAR M, HUANG C, et al. Small molecule natural compound agonist of SIRT3 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(11):1-14. [48] FAN P, YU XY, XIE XH, et al. Mitophagy is a protective response against oxidative damage in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2019;229:36-45. [49] PAGLIARINI V, WIRAWAN E, ROMAGNOLI A, et al. Proteolysis of Ambra1 during apoptosis has a role in the inhibition of the autophagic pro-survival response. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(9):1495-1504. [50] ZHANG Z, XU T, CHEN J, et al. Correction: Parkin-mediated mitophagy as a potential therapeutic target for intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(10):915. [51] ZHANG F, WANG S, GAO M, et al. Hyaluronic acid ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via promoting mitophagy activation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022; 10:1057429. [52] LIN J, ZHUGE J, ZHENG X, et al. Urolithin A-induced mitophagy suppresses apoptosis and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration via the AMPK signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;150:109-119. [53] XU WN, LIU C, ZHENG HL, et al. Sesn2 Serves as a Regulator between Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response and Mitophagy in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(2):571-592. [54] CHEN Y, WU Y, SHI H, et al. Melatonin ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via the potential mechanisms of mitophagy induction and apoptosis inhibition. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(3):2136-2148. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [3] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [4] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [5] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [6] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [7] | Mu Bingtao, Yu Jingwen, Liu Chunyun, Guo Minfang, Meng Tao, Yang Pengwei, Wei Wenyue, Song Lijuan, Yu Jiezhong, Ma Cungen. Immunomodulatory effect of astragaloside IV on T cells of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1057-1062. |
| [8] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [9] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [10] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [11] | Xie Yanli, Wei Siang, Zhang Guodong. Effects of treadmill exercise on metabolism and chronic neuroinflammation in type 1 diabetes mice of different sexes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5577-5583. |
| [12] | Lan Yao, Chen Liuyang, Song Wenhui. Key biomarkers for the diagnosis of intervertebral disc degeneration associated with oxidative stress: identification based on bioinformatics and machine learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5591-5597. |
| [13] | Zhou Guanjin, Li Yanan, Li Tao. Neferine inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced chondrocyte apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5624-5629. |
| [14] | Yang Jingyan, Ma She, Huang Renjun, Wang Chaoyi, Zhao Yuyang, Yu Dong. Causal relationship between trunk and lower limb fat mass and intervertebral disc degeneration based on a Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5688-5694. |
| [15] | Guo Lei, Qi Yansong, Niu Xiaobo. Regulatory role of transforming growth factor beta subfamily in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5695-5701. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||