Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (35): 5591-5597.doi: 10.12307/2024.828
Previous Articles Next Articles
Key biomarkers for the diagnosis of intervertebral disc degeneration associated with oxidative stress: identification based on bioinformatics and machine learning
Lan Yao, Chen Liuyang, Song Wenhui
- Department of Orthopaedic Spinal Surgery, The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-08Accepted:2024-01-16Online:2024-12-18Published:2024-03-15 -
Contact:Song Wenhui, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopaedic Spinal Surgery, The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Lan Yao, Master candidate, Department of Orthopaedic Spinal Surgery, The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lan Yao, Chen Liuyang, Song Wenhui. Key biomarkers for the diagnosis of intervertebral disc degeneration associated with oxidative stress: identification based on bioinformatics and machine learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5591-5597.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
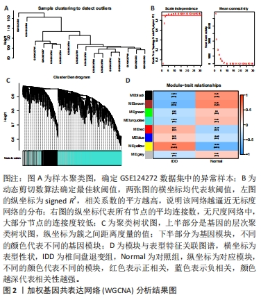
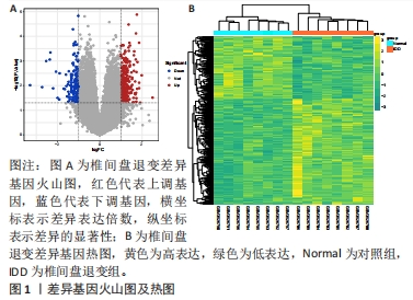
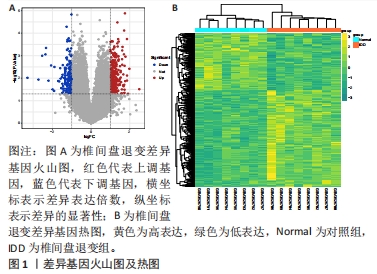
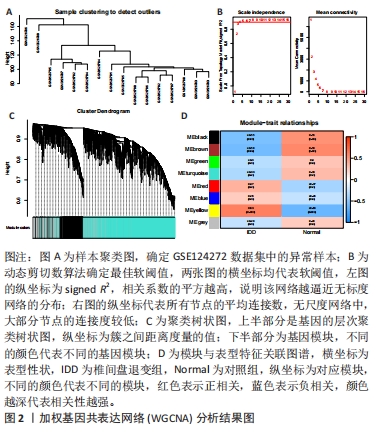
2.2 WGCNA分析结果 在生物系统中,特定的功能调节常是由一个或多个基因共同参与的,这些基因在某些方面具有一定的相似性表达,因此通过基因共表达分析可以确定参加某些特定功能的基因集。运用“WGCNA”包对已注释GSE124272数据集进行分析。在样本聚类中没有发现明显异常值,见图2A,基于无标度拓扑拟合指数曲线选取软阈值为4,见图2B,构建了分层聚类树状图,见图2C,最终共鉴定出8个模块,见图2D,其中黄色模块基因集正相关最高(r=0.63,P=0.009,2 445个),而棕色基因集负相关最高(r=-0.58,P=0.02,2 642个)。选取了上述两个模块作为与椎间盘退变显著相关的关键模块,共包含5 087个基因。"
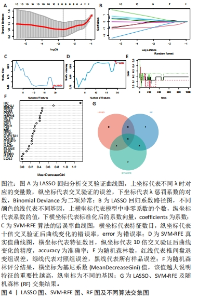
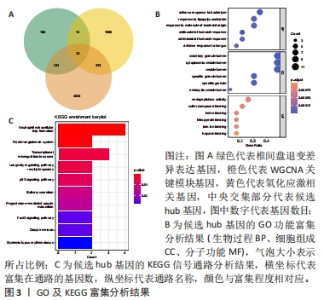
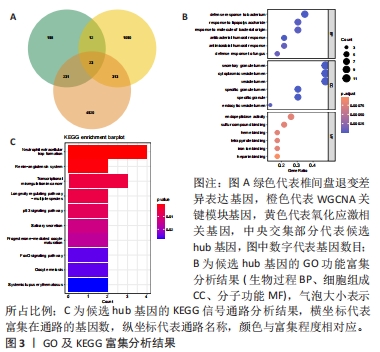
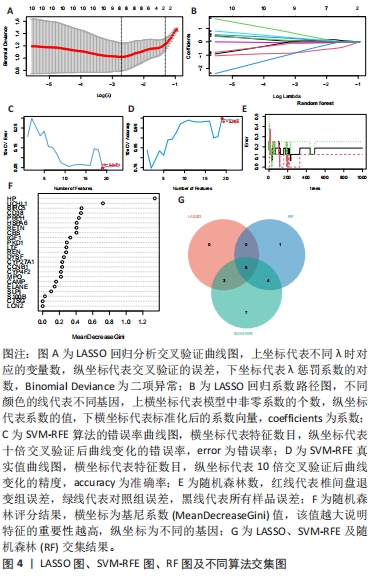
2.4 机器学习分析结果 运用LASSO回归分析算法,最终筛选出包括HSPA6,UCHL1,HP,PKD1,ELANE,S100B,PRPH和REN在内的8个特征基因,见图4A,B;通过SVM-RFE算法结果表明,当特征数为19时,包含23个关键基因的分类器误差最小,因此最终选取了19个特征基因,包括HSPA6,PKD1,PRPH,REN,UCHL1,IGF1,CD38,CYP27A1,HP,ELANE,BIRC5,CCNB1,CAMP,LTF,S100B,SLPI,MPO,DYSF,RETN,CBS,CTSG,CYP4F2和LCN2,见图4C,D;运用随机森林分析,通过基尼系数(MeanDecreaseGini)的降低来衡量特征基因的分类重要性,最终确定了10个最显著基因作为特征基因,包括HP,UCHL1,BIRC5,CD38,PRPH,HSPA6,RETN,CBS,IGF1和PKD1,见图4E,F。将这3种算法选取的特征基因取交集共鉴定出5个最佳特征基因,分别为HSPA6,PKD1,HP,UCHL1和PRPH,见图4G。"
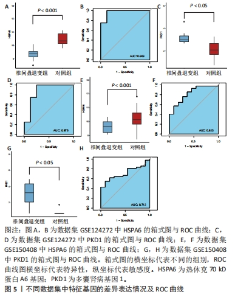
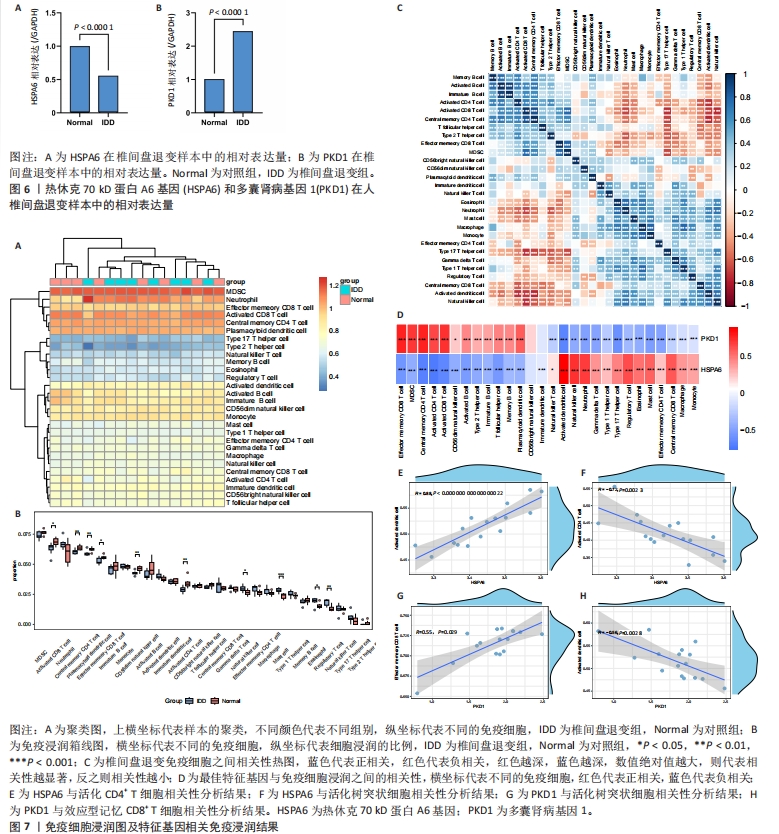
2.5 qPCR实验验证差异基因的表达 qPCR检测结果显示,HSPA6的表达在椎间盘退变组中显著低于对照组(P < 0.000 1),见图6A,PKD1的表达显著高于对照组(P < 0.000 1),见图6B。 2.6 免疫浸润分析结果 基于ssGSEA算法获得GSE124272椎间盘退变样本免疫细胞表达,其中自然杀伤细胞、肥大细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞和调节性T细胞显著高于对照组,见图7A,B。免疫浸润细胞间的相关性分析显示未成熟B细胞和活化B细胞是正相关性最强的一对(r=0.91,P < 0.001),中央型记忆CD4+ T细胞和活化树突状细胞是负相关性最强的一对(r=-0.75,P < 0.001),见图7C。与此同时,HSPA6及PKD1与多种免疫细胞呈显著性相关,见图7D,其中HSPA6与活化树突状细胞正相关最为显著(r=0.88,P < 0.001),与活化CD4+ T细胞负相关最为显著(r=-0.72,P < 0.01),见图7E,F;PKD1与效应型记忆CD8+ T细胞(r=0.55,P=0.029)正相关最为显著,而与活化树突状细胞(r=-0.56,P=0.028)负相关最为显著,见图7G,H。提示免疫细胞可能与差异基因协同作用,影响着椎间盘的稳定性。"
| [1] MOHD II, TEOH SL, MOHD NN, et al. Discogenic low back pain: anatomy, pathophysiology and treatments of intervertebral disc degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):208-224. [2] DIWAN AD, MELROSE J. Intervertebral disc degeneration and how it leads to low back pain. JOR Spine. 2023;6(1):e1231. [3] 史文生.MRI对下腰痛者椎间盘退变的评价价值[J].影像研究与医学应用,2023,7(21):57-59. [4] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZÁLEZ-GAY MÁ, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022; 18(1):47-60. [5] ROH EJ, DARAI A, KYUNG JW, et al. Genetic therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1579-1593. [6] CHENG F, YANG H, CHENG Y, et al. The role of oxidative stress in intervertebral disc cellular senescence. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13(6):1038171. [7] ZHAO Y, XIANG Q, LIN J, et al. Oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration: new insights from bioinformatic strategies. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2239770. [8] 周明瀚,张慧,郑先波,等.不同氧浓度下髓核细胞中PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α信号通路表达对延缓椎间盘退变的意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(28):4491-4497. [9] HUANG X, LIU S, WU L, et al. High Throughput single cell RNA sequencing, bioinformatics analysis and applications. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1068: 33-43. [10] WANG T, ZHENG X, LI R, et al. Integrated bioinformatic analysis reveals YWHAB as a novel diagnostic biomarker for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):6449-6462. [11] SU Y, TIAN X, GAO R, et al. Colon cancer diagnosis and staging classification based on machine learning and bioinformatics analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2022;145:105409. [12] BARSHIR R, FISHILEVICH S, INY-STEIN T, et al. GeneCaRNA: a comprehensive gene-centric database of human non-coding RNAs in the GeneCards suite. J Mol Biol. 2021;433(11):166913. [13] RITCHIE ME, PHIPSON B, WU D, et al. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43(7):e47. [14] 徐文飞,明春玉,段戡,等.WGCNA和机器学习识别骨关节炎铁死亡特征基因及实验验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(30):4909-4914. [15] LI Y, LU S, LAN M, et al. A prognostic nomogram integrating novel biomarkers identified by machine learning for cervical squamous cell carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):223. [16] LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559. [17] SUN Q, BAI L, ZHU S, et al. Analysis of lymphoma-related genes with gene ontology and kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes enrichment. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:8503511. [18] HU X, NI S, ZHAO K, et al. Bioinformatics-led discovery of osteoarthritis biomarkers and inflammatory infiltrates. Front Immunol. 2022;13:871008. [19] DHAWAN R, MOHANTY AK, KUMAR M, et al. Data from salivary gland proteome analysis of female Aedes aegypti Linn. Data Brief. 2017;13: 274-277. [20] YU G, WANG LG, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012;16(5):284-287. [21] LI Z, SILLANPÄÄ MJ. Overview of LASSO-related penalized regression methods for quantitative trait mapping and genomic selection. Theor Appl Genet. 2012;125(3):419-435. [22] CHEN J, QI F, LI G, et al. Identification of the hub genes involved in stem cell treatment for intervertebral disc degeneration: a conjoint analysis of single-cell and machine learning. Stem Cells Int. 2023;2023:7055264. [23] SANZ H, VALIM C, VEGAS E, et al. SVM-RFE: selection and visualization of the most relevant features through non-linear kernels. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018;19(1):432. [24] HUANG X, ZENG J, ZHOU L, et al. A new strategy for analyzing time-series data using dynamic networks: identifying prospective biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32448. [25] ELLIS K, KERR J, GODBOLE S, et al. A random forest classifier for the prediction of energy expenditure and type of physical activity from wrist and hip accelerometers. Physiol Meas. 2014;35(11):2191-2203. [26] GUO W, MU K, LI WS, et al. Identification of mitochondria-related key gene and association with immune cells infiltration in intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Genet. 2023;14:1135767. [27] WU B, HUANG X, ZHANG M, et al. Significance of immune-related genes in the diagnosis and classification of intervertebral disc degeneration. J Immunol Res. 2022;2022:2616260. [28] CHEN H, BOUTROS PC. VennDiagram: a package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:35. [29] ROBIN X, TURCK N, HAINARD A, et al. pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:77. [30] LIVAK KJ, SCHMITTGEN TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408. [31] HÄNZELMANN S, CASTELO R, GUINNEY J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14:7. [32] RUAN D, HE Q, DING Y, et al. Intervertebral disc transplantation in the treatment of degenerative spine disease: a preliminary study. Lancet. 2007;369(9566):993-999. [33] YU L, HAO Y, PENG C, et al. Effect of Ginsenoside Rg1 on the intervertebral disc degeneration rats and the degenerative pulposus cells and its mechanism. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;123:109738. [34] XIN J, WANG Y, ZHENG Z, et al. Treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(7):1271-1280. [35] WANG J, XIA D, LIN Y, et al. Oxidative stress-induced circKIF18A downregulation impairs MCM7-mediated anti-senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(3):285-297. [36] WEN P, ZHENG B, ZHANG B, et al. The role of ageing and oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:1052878. [37] WANG Y, CHENG H, WANG T, et al. Oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration:Molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis and treatment. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(9):e13448. [38] VO N, NIEDERNHOFER LJ, NASTO LA, et al. An overview of underlying causes and animal models for the study of age-related degenerative disorders of the spine and synovial joints. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(6):831-837. [39] CAO G, YANG S, CAO J, et al. The role of oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2166817. [40] VICTORELLI S, PASSOS JF. Reactive oxygen species detection in senescent cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1896:21-29. [41] TANG G, WANG Z, CHEN J, et al. Latent infection of low-virulence anaerobic bacteria in degenerated lumbar intervertebral discs. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):445. [42] ASTUR N, MACIEL B, DOI AM, et al. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) to determine microbiome of herniated intervertebral disc. Spine J. 2022; 22(3):389-398. [43] LI W, LAI K, CHOPRA N, et al. Gut-disc axis: a cause of intervertebral disc degeneration and low back pain? Eur Spine J. 2022;31(4):917-925. [44] LI W, DING Z, ZHANG H, et al. The roles of blood lipid-metabolism genes in immune infiltration could promote the development of IDD. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:844395. [45] SUN K, SUN X, SUN J, et al. Tissue renin-angiotensin system (tRAS) induce intervertebral disc degeneration by activating oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:3225439. [46] LI Z, WYSTRACH L, BERNSTEIN A, et al. The tissue-renin-angiotensin-system of the human intervertebral disc. Eur Cell Mater. 2020;40:115-132. [47] GUO Y, GUO K, HU T, et al. Correlation between serum angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) levels and intervertebral disc degeneration. Peptides. 2022;157:170867. [48] DEANE C, BROWN IR. Knockdown of heat shock proteins HSPA6 (Hsp70B’) and HSPA1A (Hsp70-1) sensitizes differentiated human neuronal cells to cellular stress. Neurochem Res. 2018;43(2):340-350. [49] SHEN S, WEI C, FU J. RNA-sequencing reveals heat shock 70-kDa protein 6 (HSPA6) as a novel thymoquinone-upregulated gene that inhibits growth, migration, and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Front Oncol. 2021;11:667995. [50] ZHANG HJ, LIAO HY, BAI DY, et al. MAPK /ERK signaling pathway: a potential target for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;143:112170. [51] CAO S, LIU H, FAN J, et al. An oxidative stress-related gene pair (CCNB1/PKD1), competitive endogenous RNAs, and immune-infiltration patterns potentially regulate intervertebral disc degeneration development. Front Immunol. 2021;12:765382. [52] QU Z, QUAN Z, ZHANG Q, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of differential lncRNA and gene expression in patients with intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(2):1504-1512. [53] LIU D, WANG CJ, JUDGE DP, et al. A Pkd1-Fbn1 genetic interaction implicates TGF-β signaling in the pathogenesis of vascular complications in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25(1):81-91. [54] CHEN S, LEI L, LI Z, et al. Grem1 accelerates nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting TGF-β-mediated Smad2/3 phosphorylation. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(4):518-530. [55] CHEN S, LIU S, MA K, et al. TGF-β signaling in intervertebral disc health and disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019, 27(8):1109-1117. [56] WU T, LI X, JIA X, et al. Krüppel like factor 10 prevents intervertebral disc degeneration via TGF-β signaling pathway both in vitro and in vivo. J Orthop Translat. 2021;29:19-29. [57] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(1):44-56. [58] LI J, YU C, NI S, et al. Identification of core genes and screening of potential targets in intervertebral disc degeneration using integrated bioinformatics analysis. Front Genet. 2022;13:864100. [59] LAN T, HU Z, GUO W, et al. Development of a novel inflammatory-associated gene signature and immune infiltration patterns in intervertebral disc degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2481071. [60] PENG B, HAO J, HOU S, et al. Possible pathogenesis of painful intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(5):560-566. [61] KEPLER CK, MARKOVA DZ, DIBRA F, et al. Expression and relationship of proinflammatory chemokine RANTES/CCL5 and cytokine IL-1β in painful human intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(11):873-880. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | He Xinyu, Zhou Honghai, Jiang Hong, Ma Zhijia, Su Shaoting, Lin Zehong, Tian Junming, Chen Longhao, Liu Baijie. Changes in lumbosacral sagittal plane parameters of L5/S1 disc herniation reabsorption [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1330-1335. |
| [3] | Shan Jiaxin, Zhang Yilong, Wu Hongtao, Zhang Jiayuan, Li Anan, Liu Wengang, Xu Xuemeng, Zhao Chuanxi. Changes in muscle strength and pain in patients receiving Jianpi Yiqi Huoxue Formula after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1378-1382. |
| [4] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [5] | Shen Jiangyong, He Xi, Tang Yuting, Wang Jianjun, Liu Jinyi, Chen Yuanyuan, Wang Xinyi, Liu Tong, Sun Haoyuan. RAS-selective lethal small molecule 3 inhibits the fibrosis of pathological scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1168-1173. |
| [6] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [7] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [8] | Tan Nengxian, Wu Wenzheng, Zheng Churong, Luo Lieliang, Gu Peng, Ouyang Chongzhi, Zheng Xiaohui. Finite element analysis of different fixation methods of partially threaded cannulated screws for treating vertical femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 873-878. |
| [9] | Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Li Hongzhi, Zhou Jinming, Guan Shengyi, Yu He. Open reduction and internal fixation via the para-Achilles tendon approach for the treatment of posterior malleolus sandwich fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 934-938. |
| [10] | Zhou Xiaowen, Fu Zuchang, Huang Fei, Ai Jianguo, Zhao Feng. Bone defect blocked by bone cement segmental filling in single-plane tibial bone transport [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 736-740. |
| [11] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Zhang Chi, Zhang Yisheng, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei, Tang Fubo, Mai Wei, Zhou Jinyan. Analysis of serum differential proteomics in patients with acute cervical spondylotic radiculopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 535-541. |
| [12] | Jiang Meijiao, Zhang Junxia, Shao Yangyang, Lu Fangfang, Yin Guofu, Yang Fang. Sensitivity factor analysis of asymmetric gait quality evaluation model based on random forest algorithm [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5805-5810. |
| [13] | Linghu Xitao, Gui Jiaqi, Liang Zhuozhi, Wa Qingde, Huang Shuai. Bioinformatics analysis of m6A-associated genes in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5811-5816. |
| [14] | Ge Jin, Huang Dong, Yan Jinlian, Xu Zhengquan, Wang Yehua. Relationship between low back pain and spinal-pelvic sagittal parameter changes in patients with hip-spine syndrome after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5823-5827. |
| [15] | Zhao Yan, Wu Fan, Li Hong, Wan Shengyu, He Jin, Zhu Binren, Jiang Congbing. Prolonging use of tranexamic acid is helpful to reduce perioperative hidden blood loss in senile patients with intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5858-5864. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||