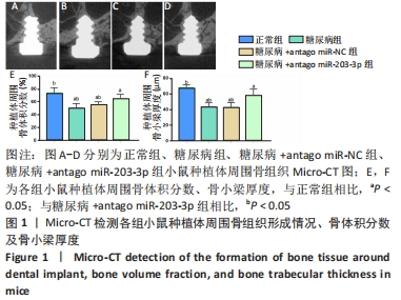
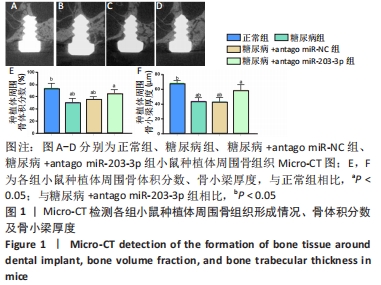
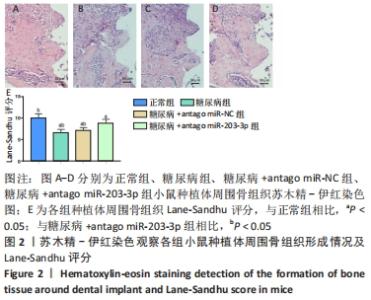
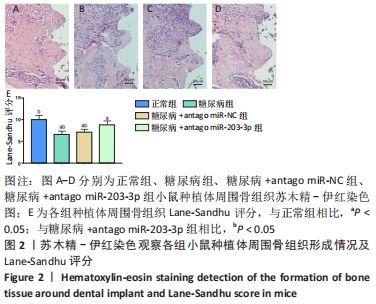
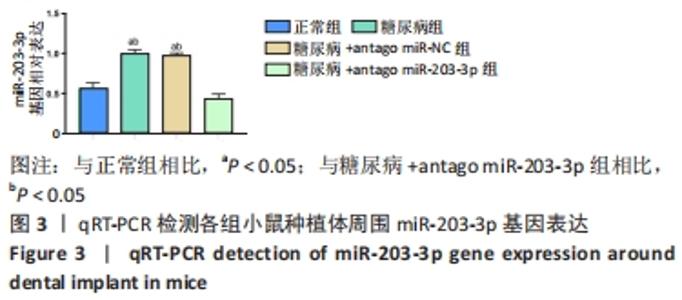
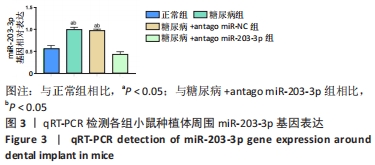
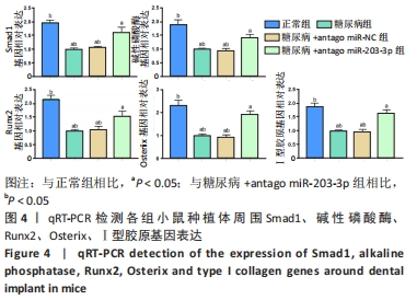
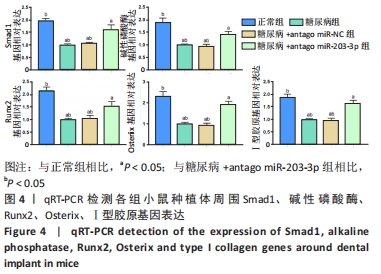
[1] 赵鹏飞,王琪.伴糖尿病患者种植骨缺损的病因及治疗的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2019,46(2):244-248.
[2] 聂莹,张志宏.糖尿病对种植体周围骨组织的影响[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2010,37(4):451-453.
[3] HU XF, WANG L, XIANG G, et al. Angiogenesis impairment by the NADPH oxidase-triggered oxidative stress at the bone-implant interface: Critical mechanisms and therapeutic targets for implant failure under hyperglycemic conditions in diabetes. Acta Biomater. 2018;73:470-487.
[4] DELIC D, EISELE C, SCHMID R, et al. Characterization of Micro-RNA Changes during the Progression of Type 2 Diabetes in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(5):665.
[5] 陈昶舟,赵海潮,付西峰,等.miR-203-3p在肝癌细胞中的表达及其对细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响[J].现代肿瘤医学,2021,29(18):3133-3138.
[6] TAIPALEENMÄKI H, BROWNE G, AKECH J, et al. Targeting of Runx2 by miR-135 and miR-203 Impairs Progression of Breast Cancer and Metastatic Bone Disease. Cancer Res. 2015;75(7):1433-1444.
[7] TANG Y, ZHENG L, ZHOU J, et al. miR‑203‑3p participates in the suppression of diabetes‑associated osteogenesis in the jaw bone through targeting Smad1. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(3):1595-1607.
[8] GARCÍA-HERNÁNDEZ A, ARZATE H, GIL-CHAVARRÍA I, et al. High glucose concentrations alter the biomineralization process in human osteoblastic cells. Bone. 2012;50(1):276-288.
[9] LAMBERTUCCI AC, LAMBERTUCCI RH, HIRABARA SM, et al. Glutamine supplementation stimulates protein-synthetic and inhibits protein-degradative signaling pathways in skeletal muscle of diabetic rats. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50390.
[10] LI H, WANG Y, ZHANG D, et al. Glycemic fluctuation exacerbates inflammation and bone loss and alters microbiota profile around implants in diabetic mice with experimental peri-implantitis. Int J Implant Dent. 2021;7(1):79.
[11] 唐诗倩,陆士娟,马添翼,等.miRNA-1对慢性充血性心力衰竭小鼠左心室心肌Cx43蛋白表达的影响[J].沈阳药科大学学报,2021,38(7):706-713.
[12] DE LUCA M, AIUTI A, COSSU G, et al. Advances in stem cell research and therapeutic development. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(7):801-811.
[13] DE OLIVEIRA PGFP, BONFANTE EA, BERGAMO ETP, et al. Obesity/Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes Mellitus on Peri-implantitis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020;31(8):596-610.
[14] 王惠,李风兰.Ⅱ型糖尿病与牙种植体骨结合相关生物标记物的研究进展[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2020,21(6):376-381.
[15] LIU J, XU Y, SHU B, et al. Quantification of the differential expression levels of microRNA-203 in different degrees of diabetic foot. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(10):13416-13420.
[16] CAI Z, LI K, YANG K, et al. Suppression of miR-203-3p inhibits lipopolysaccharide induced human intervertebral disc inflammation and degeneration through upregulating estrogen receptor α. Gene Ther. 2020; 27(9):417-426.
[17] TU B, LIU S, YU B, et al. miR-203 inhibits the traumatic heterotopic ossification by targeting Runx2. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(10):e2436.
[18] 唐宇英. miR-203-3p对糖尿病颌骨成骨的调控作用及分子机制研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2018.
[19] 李丽莉. BMP-Smad信号通路的调节及其在成骨分化中的作用[D].济南:山东大学,2013.
[20] 孙雨晴.基于BMP2/Smad1/Runx2/Osterix通路探讨健骨颗粒氯仿萃取部位对体外成骨细胞分化的影响[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2018.
[21] WANG T, XU Z. miR-27 promotes osteoblast differentiation by modulating Wnt signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;402(2):186-189.
[22] 杨艳兰,徐普,张文柏,等.NPP/C-HA/rhBMP-2复合支架修复兔股骨缺损的实验研究[J].上海口腔医学,2021,30(4):344-349.
[23] 罗诒财,李昊.增强芳香烃受体表达对糖尿病模型大鼠牙槽骨缺损区愈合及炎症反应的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2166-2171.
[24] KONSTANTONIS D, PAPADOPOULOU A, MAKOU M, et al. The role of cellular senescence on the cyclic stretching-mediated activation of MAPK and ALP expression and activity in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Exp Gerontol. 2014;57:175-180.
[25] KOMORI T. Regulation of Proliferation, Differentiation and Functions of Osteoblasts by Runx2. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1694.
[26] CELIL AB, CAMPBELL PG. BMP-2 and insulin-like growth factor-I mediate Osterix (Osx) expression in human mesenchymal stem cells via the MAPK and protein kinase D signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(36): 31353-31359.
[27] KOCIJAN R. Osteogenesis imperfecta: from bench to bedside. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2015;165(13-14):263.
|