Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (27): 4314-4319.doi: 10.12307/2022.861
Previous Articles Next Articles
Aligned poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/type I collagen fibers promote tendon-bone healing after anterior cruciate ligament rupture
Hu Qiuyu1, Yang Long2, Yang Yong2, Song Shenchao1
- 1School of Public Health, Key Laboratory of Environmental Pollution Monitoring and Disease Control, Ministry of Education, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-03Accepted:2021-04-10Online:2022-09-28Published:2022-03-10 -
Contact:Song Shenchao, Professor, School of Public Health, Key Laboratory of Environmental Pollution Monitoring and Disease Control, Ministry of Education, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Hu Qiuyu, Master candidate, School of Public Health, Key Laboratory of Environmental Pollution Monitoring and Disease Control, Ministry of Education, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China Yang Long, Doctoral candidate, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China Hu Qiuyu and Yang Long contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81802175, (to YL); a grant from Department of Science and Technology of Guizhou Province, No. [2020]1Y312, (to YL); the First-Class Discipline Construction Project in Guizhou Province - Public Health and Preventive Medicine, No. 2017[85] (to SSC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Qiuyu, Yang Long, Yang Yong, Song Shenchao. Aligned poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/type I collagen fibers promote tendon-bone healing after anterior cruciate ligament rupture[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4314-4319.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
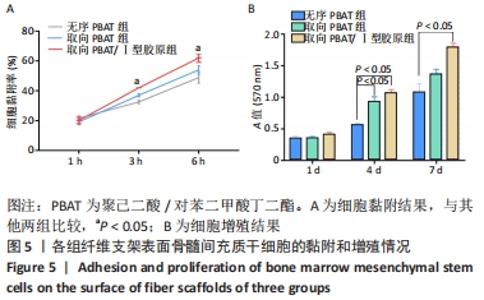
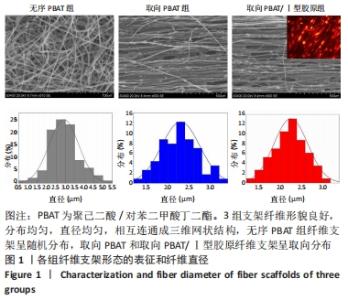
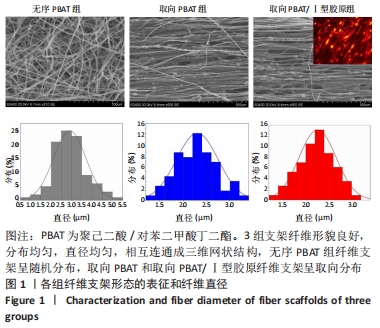
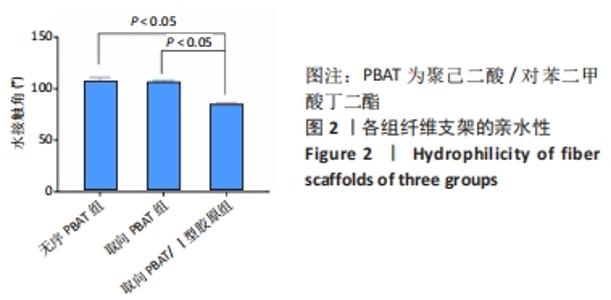
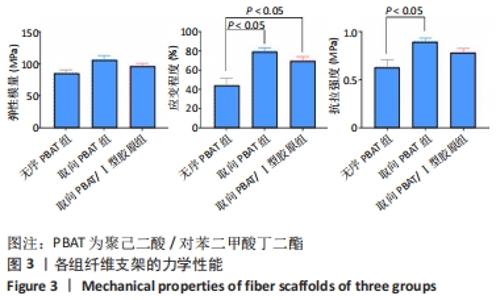
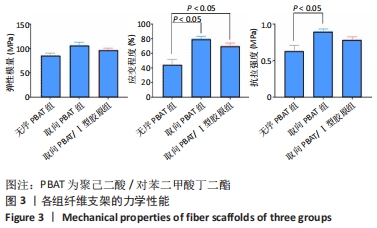
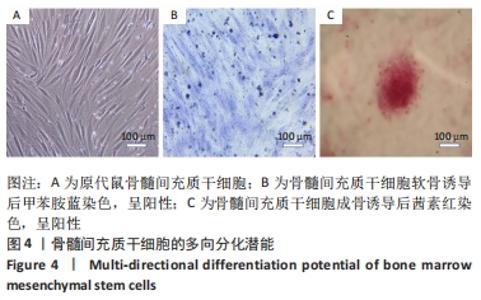
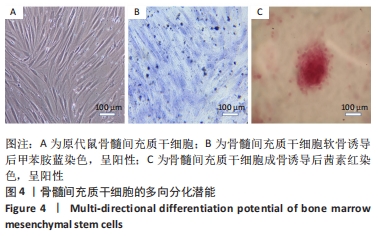
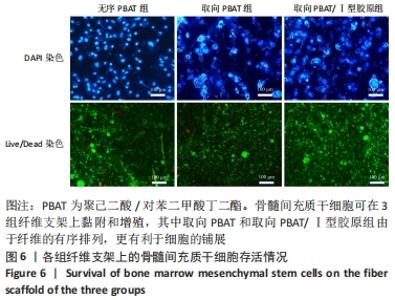
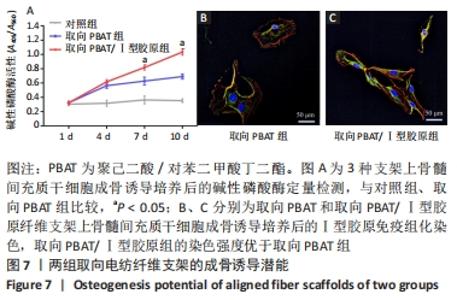
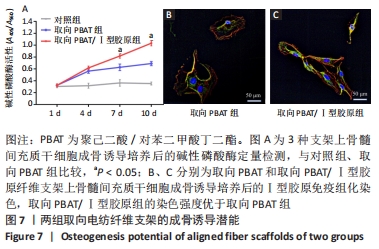
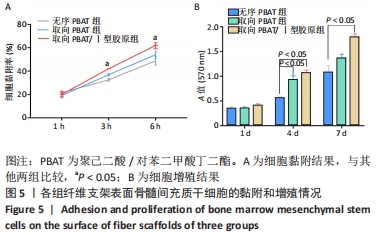
2.5 静电纺丝支架细胞黏附实验结果 共培养1,3,6 h后,细胞可在3组纤维支架上黏附生长,并随时间延长细胞数量逐渐增加,取向PBAT/Ⅰ型胶原组的细胞黏附数量多于无序 PBAT组、取向PBAT组(P < 0.05),见图5A。 2.6 静电纺丝支架细胞增殖实验结果 骨髓间充质干细胞在3组支架上均可持续增殖,第4天时,两组取向纤维支架的细胞数量高于无序纤维组(P < 0.05),两组取向纤维支架之间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);第7天时,取向PBAT/Ⅰ型胶原组的细胞量高于无序PBAT组(P < 0.05),取向PBAT/Ⅰ型胶原组与取向PBAT组、取向PBAT与无序PBAT组细胞数量比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),3组支架均未见明显细胞毒性,见图5B。"
| [1] RODRÍGUEZ-SANZ J, PÉREZ-BELLMUNT A, LÓPEZ-DE-CELIS C, et al. Thermal and non-thermal effects of capacitive-resistive electric transfer application on different structures of the knee: a cadaveric study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):22290. [2] CHEN G, WANG S. Comparison of single-bundle versus double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction after a minimum of 3-year follow-up: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:14604-14614. [3] HUANG J, CHEN F, JIAN G, et al. Effect of culture complex of BMSCs and sodium hydroxide-and GRGDSPC-treated PET on the reconstruction of injured anterior cruciate ligament in a rabbit model. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:6902. [4] GOSHIMA K, KITAOKA K, NAKASE J, et al. Familial predisposition to anterior cruciate ligament injury. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2014;1: 62-66. [5] 柴双,吕松岑.前交叉韧带重建术后促进腱-骨愈合因素的研究进展[J].医学综述,2017,23(4):718-723. [6] BELL RD, SHULTZ SJ, WIDEMAN L, et al. Collagen gene variants previously associated with anterior cruciate ligament injury risk are also associated with joint laxity. Sports Health. 2012;4:312-318. [7] LIU H, YANG L, ZHANG E, et al. Biomimetic tendon extracellular matrix composite gradient scaffold enhances ligament-to-bone junction reconstruction. Acta Biomater. 2017;56:129-140. [8] INGAVLE GC, LEACH JK. Advancements in electrospinning of polymeric nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(4): 277-293. [9] 朱乐全,卢剑华,冉俊岭,等.骨形态发生蛋白2基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞复合纤维蛋白胶促进前交叉韧带重建后的腱-骨愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(1):30-34. [10] ULERY BD, NAIR LS, LAURENCIN CT. Biomedical Applications of Biodegradable Polymers. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys. 2011;49(12):832-864. [11] MALIKMAMMADOV E, TANIR TE, KIZILTAY A, et al. PCL and PCL-based materials in biomedical applications. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(7-9):863-893. [12] 李豪,徐勇,夏会堂,等.基于静电纺丝人脐带华通胶构建组织工程软骨的实验研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2019,15(6):393-397. [13] 吴晨星,王卉,张克勤.静电纺丝技术构建的丝素蛋白基纤维材料在组织工程领域中的应用[J].现代丝绸科学与技术,2020,35(4):27-30+35. [14] 陈娇,舒莉萍,李轩泽,等.聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物负载人骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(26):4109-4114. [15] 李宜炯,王欣,李瑞琦,等.基于碳纳米管的三维多孔骨组织工程支架材料研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2020,37(12):2266-2269. [16] 高龙,张赵文斌,常江.生物玻璃/聚乳酸多孔微球的制备及其作为细胞载体的研究[J].无机材料学报,2020,35(10):1163-1168. [17] BHARADWAZ A, JAYASURIYA AC. Recent trends in the application of widely used natural and synthetic polymer nanocomposites in bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;110:110698. [18] 王健,周栩.第三代超声辅助吸脂获取的h ADSCs构建组织工程软骨的实验研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2020,16(2):91-96. [19] 冯子嫣,樊逸菲,郭玖思,等.组织工程半月板支架材料的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(8):1019-1028. [20] FUKUSHIMA K, WU MH, BOCCHINI S, et al. PBAT based nanocomposites for medical and industrial applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2012;32(6):1331-1351. [21] WANG X, CUI L, FAN S, et al. Biodegradable Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Antibacterial Nanocomposites Reinforced with MgO Nanoparticles. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(4):507. [22] ELIAS CMV, MAIA FILHO ALM, SILVA LRD, et al. In Vivo Evaluation of the Genotoxic Effects of Poly (Butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/ Polypyrrole with Nanohydroxyapatite Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Materials (Basel). 2019; 12(8):1330. [23] 刘鋆,杨龙,王伟宇,等.聚3-羟基丁酸酯4-羟基丁酸酯/聚乙二醇/氧化石墨烯组织工程支架的制备和性能评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(22):3466-3472. [24] BIANCHI E, RUGGERI M, ROSSI S, et al. Innovative Strategies in Tendon Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(1):89. [25] COSTA-PINTO AR, SALGADO AJ, CORRELO VM, et al. Adhesion, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of a mouse mesenchymal stem cell line (BMC9) seeded on novel melt-based chitosan/polyester 3D porous scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part A. 2008;14:1049-1057. [26] FUKUSHIMA K, RASYIDA A, YANG MC. Characterization, degradation and biocompatibility of PBAT based nanocomposites. Appl Clay Sci. 2013;80-81:291-298. [27] JAO WC, LIN CH, HSIEH JY, et al. Effect of immobilization of polysaccharides on the biocompatibility of poly(butyleneadipate-coterephthalate) films. Polym Adv Technol. 2010;21:543-553. [28] NAR M, STAUFENBERG G, YANG B, et al. Osteoconductive bio-based meshes based on Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co -hydroxyvalerate) and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends. Mater Sci Eng C. 2014;38:315-324. [29] WANG A, GAN Y, YU H, et al. Improvement of the cytocompatibility of electrospun poly[(R)-3- hydroxybutyrate-co-(R)- 3-hydroxyvalerate] mats by Ecoflex. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100:1505-1511. [30] SANTANA-MELO GF, RODRIGUES BVM, DA SILVA E, et al. Electrospun ultrathin PBAT/nHAp fibers influenced the in vitro and in vivo osteogenesis and improved the mechanical properties of neoformed bone. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;155:544-552. [31] YIN Z, CHEN X, CHEN JL, et al. The regulation of tendon stem cell differentiation by the alignment of nanofibers. Biomaterials. 2010;31(8):2163-2175. [32] CHEN B, WANG B, ZHANG WJ, et al. In vivo tendon engineering with skeletal muscle derived cells in a mouse model. Biomaterials. 2012;33(26):6086-6097. [33] WAN Y, CHEN W, YANG J, et al. Biodegradable poly(L-lactide)-poly(ethylene glycol) multiblock copolymer: synthesis and evaluation of cell affinity. Biomaterials. 2003;24(13):2195-2203. [34] JUNCOSA-MELVIN N, BOIVIN GP, GOOCH C, et al. The effect of autologous mesenchymal stem cells on the biomechanics and histology of gel-collagen sponge constructs used for rabbit patellar tendon repair. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(2):369-379. [35] AN K, LIU H, GUO S, et al. Preparation of fish gelatin and fish gelatin/poly(L-lactide) nanofibers by electrospinning. Int J Biol Macromol. 2010;47(3):380-388. [36] RIESTER O, BORGOLTE M, CSUK R, et al . Challenges in Bone Tissue Regeneration: Stem Cell Therapy, Biofunctionality and Antimicrobial Properties of Novel Materials and Its Evolution. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):192. [37] LEE JM, VERES SP. Advanced glycation end-product cross-linking inhibits biomechanical plasticity and characteristic failure morphology of native tendon. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(4):832-841. [38] PANZAVOLTA S, GIOFFRE M, FOCARETE ML, e tal. Electrospun gelatin nanofibers: optimization of genipin cross-linking to preserve fiber morphology after exposure to water. Acta biomater. 2011;7(4):1702-1709. [39] SENSINI A, MASSAFRA G, GOTTI C, et al. Tissue Engineering for the Insertions of Tendons and Ligaments: An Overview of Electrospun Biomaterials and Structures. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:645544. [40] BASHUR CA, SHAFFER RD, DAHLGREN LA, et al. 2009. Effect of fiber diameter and alignment of electrospun polyurethane meshes on mesenchymal progenitor cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15:2435-2445. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [5] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [6] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [7] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [8] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [9] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [11] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [12] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [13] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [14] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [15] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||